What Other Drugs Will Affect Hepatitis A And B Vaccine
Before receiving this vaccine, tell the doctor about all other vaccines you have recently received.
Also tell the doctor if you have recently received drugs or treatments that can weaken the immune system, including:
-
steroid medicine
-
medicine to treat psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, or other autoimmune disorders or
-
medicines to treat or prevent organ transplant rejection.
If you are using any of these medications, you may not be able to receive the vaccine, or may need to wait until the other treatments are finished.
This list is not complete. Other drugs may affect hepatitis A and B vaccine, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal products. Not all possible drug interactions are listed here.
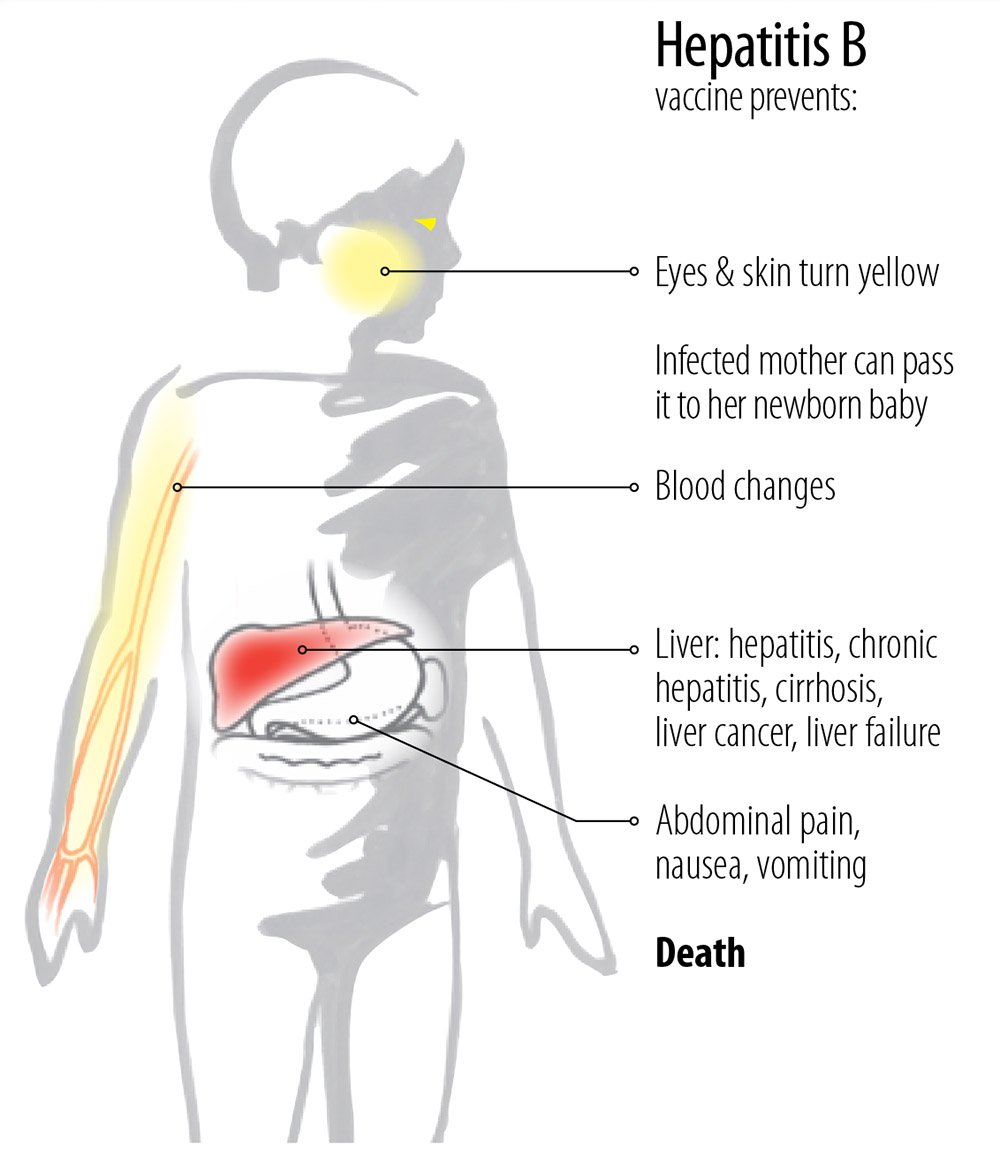
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis A And B
Not all infected adults will experience symptoms. That means you could contract hepatitis A or B, and spread the viruses to others, without realizing it.
Symptoms of hepatitis A may include*:
Fever
Jaundice
Loss of appetite
Dark urine
Fatigue
* TWINRIX is not indicated to treat the symptoms of, or reduce serious consequences associated with hepatitis A and B.
Possible consequences of hepatitis A.*Hepatitis A infection can have mild to severe consequences on infected individuals that can last from a few weeks to several months.
Chronic hepatitis and carrier states are not linked with hepatitis A infection.
However, relapsing hepatitis, a condition where a person gets worse again after a period of improvement, can last up to a year in 15% of cases.
While most infected people recover, the older you are, the more severe hepatitis A can be.
Approximately 25% of infected adults are hospitalized.
The overall case fatality rate, which is the proportion of deaths among the number of hepatitis A cases, is approximately 0.5%, but can reach 2.6% in adults over 60 years of age.
* TWINRIX is not indicated to treat the symptoms of, or reduce serious consequences associated with hepatitis A and B.
Symptoms of hepatitis B may include*:
Fatigue
Jaundice
Loss of appetite
Dark urine
Clay-coloured stool
* TWINRIX is not indicated to treat the symptoms of, or reduce serious consequences associated with hepatitis A and B.
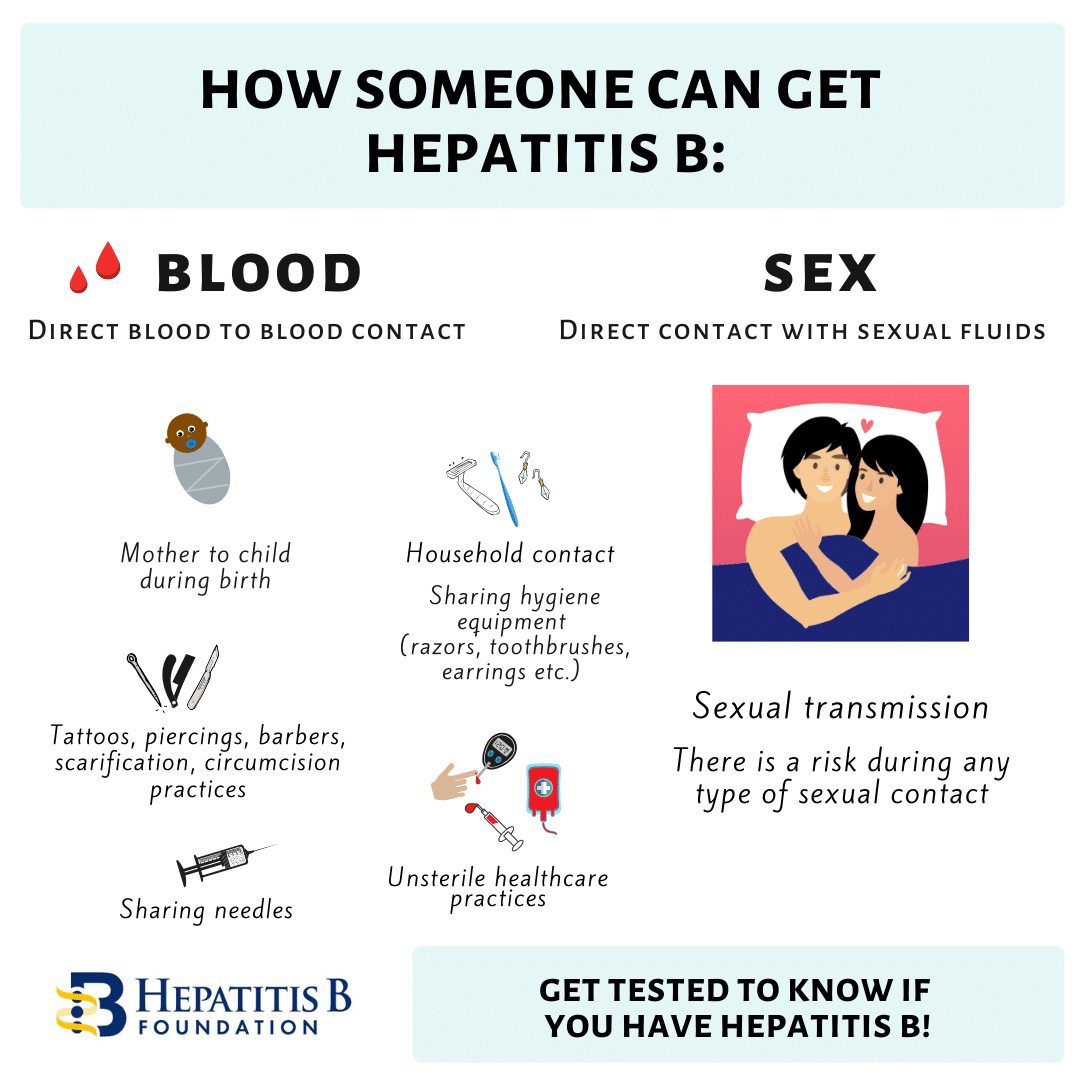
How Can I Contract Hepatitis B
You can contract hepatitis B by coming into contact with the bodily fluids of an infected person.
Resort activities that may put you at risk for hepatitis B include:
Getting a manicure, pedicure, tattoo, piercing, or acupuncture with improperly sterilized tools
Having sexual contact with an infected partner
Giving first aid to, or receiving it from, an infected person
Receiving a medical or dental procedure with contaminated equipment
Sharing personal grooming items with an infected person
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis A Vaccine Cost Walgreens
How Is Hepatitis B Prevented
Testing & Vaccination
- The hepatitis B vaccine offers excellent protection against HBV. The vaccine is safe and highly effective. Vaccination consists of 3 doses of vaccine over the course of 6 months. Protection lasts for 20 years to life.
- The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that all children should receive hepatitis B vaccine starting at birth. .
- The CDC recommends hepatitis B vaccine for persons traveling to countries where HBV is common .
- If you have one or more risk factors for hepatitis B infection, you should get a simple HBV blood test. The blood test will determine whether you are:
- immune to hepatitis B or
- susceptible to hepatitis B and need vaccination or
- infected with hepatitis B and need further evaluation by a physician
Perinatal Hepatitis
- California law requires testing of all pregnant women for hepatitis B infection
- If the mother is HBV-infected, she will pass the infection to the baby during the birth process, unless the baby gets immunized within hours of birth
- Giving the infant HBIG and HBV vaccine right away will reliably prevent infection of the infant
- Other family members should best tested for hepatitis B too, and given vaccine if they are not already infected or immune
Healthy Habits
After Exposure to Hepatitis B
How Much Does A Hepatitis B Titer Test Cost
The cost of a hepatitis B test varies based on where you get the test. Prices range from roughly $24 to $110.
Your insurance may cover some or all of the cost. Under the Affordable Care Act, all new health plans must cover preventative services including hepatitis B vaccination and testing without a deductible or copay.
Also Check: What Form Of Hepatitis Is Sexually Transmitted
Why Should I Vaccinate My Newborn Child If I Know That I Am Not Infected With Hepatitis B Virus
Before the hepatitis B vaccine, every year in the United States about 18,000 children were infected with hepatitis B virus by the time they were 10 years old. This statistic is especially important because people are much more likely to develop liver cancer or cirrhosis if they are infected early in life, rather than later in life .
About 9,000 of the 18,000 children infected in the first 10 years of life caught the virus from their mother during birth. However, many young children didn’t catch the disease from their mother. They caught it from either another family member or someone else who came in contact with the child. Because hepatitis B can be transmitted by relatively casual contact with items contaminated with the blood of an infected person, and because many people who are infected with hepatitis B virus don’t know that they have it, it is virtually impossible to be “careful enough” to avoid this infection.
For these reasons, all young children are recommended to receive the hepatitis B vaccine. The best time to receive the first dose is right after birth. This will ensure that the child will be protected as early as possible from catching hepatitis B from people who dont know that they are infected with the virus.
Listen to Dr. Offit explain why newborns get the hepatitis B vaccine by watching this short video, part of the series Talking About Vaccines with Dr. Paul Offit.
Emerging Hepatitis B Virus Infection In Vaccinated Populations: A Rising Concern
1Department of Internal Medicine, National Taiwan University Hospital, Taipei 10002, Taiwan
2Graduate Institute of Clinical Medicine, National Taiwan University College of Medicine, Taipei 10002, Taiwan
3Hepatitis Research Center, National Taiwan University Hospital, Taipei 10002, Taiwan
Don’t Miss: New Treatment For Hepatitis B
I Have Hep B Do I Need Extra Protection Against Covid
No. You can protect yourself against COVIDin the same ways as everyone else. We all need be careful to stop the spread of COVID, for our own health and for the health of our communities.
You should take extra care to protect yourself from COVID if you: have an additional health condition are over 70 are over 50 and Aboriginal have a weakened immune system.
Follow Government advice on keeping safe and stopping the spread of COVID E> > >
Who Should Not Receive The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Talk to your healthcare provider before getting the hepatitis B vaccine if:
- You have had a severe allergic reaction to the hepatitis B vaccine or any of its ingredients in the past.
- You have had an allergic reaction to yeast in the past.
- You are moderately or severely ill.
- You are currently taking immunosuppressive medications.
In addition, pregnant people should not receive the Heplisav-B or PreHevbrio vaccines until more safety information is available.
Also Check: Hepatitis B 100 Cure 2017
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a highly contagious liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus . The infection can range in severity from mild to acute. It may last just a few weeks or become a serious, chronic, and potentially fatal health condition.
The best way to prevent this infection is to get the hepatitis B vaccine. Heres what you need to know.
Hepatitis A And Hepatitis B Vaccine Dosing Information
Usual Adult Dose for Hepatitis B Prophylaxis:
Primary immunization: 1 mL IM in the deltoid area at 0, 1 and 6 months.Alternatively, a 4 dose schedule given on days 0, 7, and 21 to 30 followed by a booster at month 12 may be used.
Usual Adult Dose for Hepatitis A Prophylaxis:
Primary immunization: 1 mL IM in the deltoid area at 0, 1 and 6 months.Alternatively, a 4 dose schedule given on days 0, 7, and 21 to 30 followed by a booster at month 12 may be used.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Antibody Non Reactive Meaning
Poor Responders And Failure Of Hbv Vaccination
Although the current vaccines are highly effective, there are still some populations with suboptimal immunogenic responses, such as preterm infants, the elderly, smokers, obese individuals, and those with chronic liver or renal diseases, diabetes mellitus or human immunodeficiency virus infection.14 For newborns, HBV vaccination should be given within 24 h of delivery with or without hepatitis B immune globulin otherwise, the protective efficacy will be lower.15 It is known that the hepatitis B vaccine has a lower immunogenicity in preterm infants than in infants born at term, especially those with gestational ages < 34 weeks16 or birth weights < 1800 g.17 For preterm infants of HBsAg-negative mothers, deferring the first vaccination dose by 1 month is recommended to improve the vaccine’s immunogenicity and efficacy.18
Some newborns fail to complete their vaccination courses, and approximately 10% of children born to HBeAg-positive mothers with high viral loads become persistently infected with HBV owing to HBIG or vaccination failure.19 These newborn HBV carriers, along with the existing adult chronic HBV carriers, are still at risk of developing HBV-related complications, such as cirrhosis and HCC, in the following 30 years.
Hbv Infections In Previously Vaccinated Subjects: An Unusual Clinical Course
To better understand the HBV infections that occur in HBV-vaccinated subjects, it is important to follow prospectively individuals who might be exposed to HBV.24 A large-scale longitudinal survey of 18 779 subjects showed that vaccination in infancy provides adequate long-term protection for up to 20 years. Despite occasional exposure to HBV , the risk of persistent HBV infection did not increase with age, before adulthood.8
This diagram shows the dynamic change in the serum anti-HBs antibody titre, HBV DNA and ALT levels during acute HBV infection in an HBV vaccinee. If the infection occurs in a subject with a protective level of anti-HBs antibody, then viraemia would be detected only transiently, and anti-HBc seroconversion would result. If the infection occurs in a subject with an anti-HBs antibody titre below the protective level, then higher HBV viraemia would be detected and would sometimes be followed by an elevation of aminotransferase levels. The anti-HBs antibody titre immediately rises above the protective level this increase is the so-called anamnestic effect of anti-HBs antibody. The dotted line indicates the protective level of anti-HBs antibody in the upper panel and the normal level of ALT in the lower panel.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Ways You Can Get Hepatitis C
Who Should Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
The CDC recommends it for all babies, who should get their first dose as newborns.
Other people who need it include:
- People younger than age 19 who haven’t been vaccinated
- Anyone who has a sex partner with hepatitis B
- People who are sexually active but arenât in a long-term relationship in which both partners are monogamous
- Anyone being evaluated or treated for an STD
- Men who have sex with men
- People who share needles used to inject drugs
- Anyone who lives with someone who has hep B
- Anyone whose job routinely puts them at risk for coming in contact with blood or blood-contaminated body fluids
- People with end-stage kidney disease
- People who live and work in facilities for people who are developmentally disabled
- Travelers to regions with moderate to high rates of hepatitis B
- People with chronic liver disease
- People with HIV infections
You should not get the vaccine if you had a severe allergic reaction to an earlier dose or are allergic to yeast, because yeast is used to make the vaccine.
Should I Get The Hep B Vaccine And Will This Protect Me Against Covid
The hep B vaccine will ONLY protect you from the hep B virus it will not provide any protection from COVID.
We definitely recommend getting the hep B vaccine to protect yourself from hep B, however now might not be the best time for it. The decision is yours.
AN IMPORTANT NOTE: if you are at risk of hep B for instance if you live with, or have sex with, someone who might have hep B, or are a healthcare worker we recommend you do get vaccinated against hep B as soon as possible.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B In Blood Test
Transmission Symptoms And Treatment
How is HBV transmitted?
HBV is transmitted through activities that involve percutaneous or mucosal contact with infectious blood or body fluids , including
- sex with a partner who has HBV infection
- injection drug use that involves sharing needles, syringes, or drug-preparation equipment
- birth to a person who has HBV infection
- contact with blood from or open sores on a person who has HBV infection
- exposures to needle sticks or sharp instruments and
- sharing certain items with a person who has HBV infection that can break the skin or mucous membranes , potentially resulting in exposure to blood.
How long does HBV survive outside the body?
HBV can survive outside the body and remains infectious for at least 7 days .
What should be used to clean environmental surfaces potentially contaminated with HBV?
Any blood spills should be disinfected using a 1:10 dilution of one part household bleach to 9 parts water. Gloves should be worn when cleaning up any blood spills.
Who is at risk for HBV infection?
The following populations are at increased risk for becoming infected with HBV:
- Infants born to people with HBV infection
- Sex partners of people with HBV infection
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject drugs
- Household contacts or sexual partners of known people with chronic HBV infection
- Health care and public safety workers at risk for occupational exposure to blood or blood-contaminated body fluids
- Patients on hemodialysis
Who should be screened for HBV?
How Can I Prevent Hepatitis B
The best way to prevent hepatitis B infection is to get vaccinated. All newborns, children through age 18, and adults who are at risk of hepatitis B infection should get the vaccine. Adults at risk of hepatitis B infection who should be vaccinated include:
- Household contacts and sex partners of people with hepatitis B
- People with multiple sex partners or sexually transmitted infections
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject drugs
- People in high risk settings or programs
- People on hemodialysis
- People with chronic liver disease or with HIV infection
- People with hemophilia and others who receive certain blood products
- People with diabetes mellitus between the ages of 19 to 59 years
- Health care and public safety workers who may have contact with blood/body fluids
- Travelers to certain countries where there are high rates of hepatitis B
Don’t Miss: Get Tested For Hepatitis C
Do The Benefits Of The Hepatitis B Vaccine Outweigh Its Risks
Every year in the United States about 2,000 people die following an overwhelming hepatitis B virus infection. In addition, every year about 22,000 people are infected with hepatitis B. Some of them will remain chronically infected, putting them at high risk of the long-term consequences of hepatitis B virus infection: cirrhosis and liver cancer. In fact, with the exception of influenza and COVID-19 viruses, hepatitis B virus causes more severe disease and death in the United States than any other vaccine-preventable disease. On the other hand, the hepatitis B vaccine is an extremely rare cause of a severe allergic reaction called anaphylaxis. To date, no one has died from this reaction, but it is theoretically possible that this could occur.
Because hepatitis B virus is a common cause of severe disease and death in the United States, and because the hepatitis B vaccine does not cause permanent damage or death, the benefits of the hepatitis B vaccine clearly outweigh its risks.
Vaccines For Hepatitis A & B
You may have a family member who has viral hepatitis. Or perhaps you recently saw a news brief about a celebrity who contracted hepatitis A or B. Whatever the reason, you want information about a viral illness that you may not have thought much about. What is viral hepatitis? Are you at risk for it? Do you need viral hepatitis vaccines?
Read Also: Hepatitis B Antigens And Antibodies
What Do The Results Mean
A hepatitis B blood panel consists of three tests that can be done with just one blood sample:
- Hepatitis B surface antigen . A positive test indicates that youre infected with hepatitis B and that you can spread it to other people. Further tests are needed to see if you have an acute or chronic infection.
- Hepatitis B core antibody . A positive result can indicate a past or current hepatitis B infection, but doesnt mean youre immune. A positive result needs to be interpreted by a doctor by examining the results of the other two tests.
- Hepatitis B surface antibody . A positive test indicates that youre protected from hepatitis B either through previous infection or vaccination .
The combination of these tests can indicate your hepatitis B status and whether you need to be vaccinated. Your test will give a negative or positive result for each category depending on whether your results are above or below the cutoff value.
Most peoples test results fall into the following categories. But its possible to have a result that doesnt fall into one of these groups. If youre reading your results yourself, be careful not to confuse HBsAb with HBcAb.
| HBsAG |
is associated with hepatitis B immunity after vaccination. But research has found that anti-HBs decline over time.
A found that more than 95 percent of people had anti-HBs levels greater than 10IU/L two years after vaccination. But this rate decreased to 70 percent after eight years.