Hbv Dna Hbv Genotype And Hbv Drug Resistance Assays
Specimen: Serum or plasma
Container: Red-top tube, yellow-top tube , gel-barrier tube, plasma preparation tube, or lavender tube
Collection method: Routine venipuncture
The specimen should be transfused to separate plasma/serum from cells within 6 hours and kept frozen when testing cannot be done promptly.
The tests use PCR amplification, DNA probe hybridization, and sequencing method.
We Implement Proven Measures To Keep Your Data Safe
At HealthMatters, were committed to maintaining the security and confidentiality of your personal information. Weve put industry-leading security standards in place to help protect against the loss, misuse, or alteration of the information under our control. We use procedural, physical, and electronic security methods designed to prevent unauthorized people from getting access to this information. Our internal code of conduct adds additional privacy protection. All data is backed up multiple times a day and encrypted using SSL certificates. See our Privacy Policy for more details.
Popular search
Hepatitis B Immune Globulin
Hepatitis B immune globulin is prepared from plasma containing high concentrations of anti-HBs and provides short-term protection from infection. Before hepatitis B vaccines were available, HBIG was the only product available for post-exposure prophylaxis. Currently, HBIG, administered in conjunction with hepatitis B vaccine, is recommended for: infants born to HBsAg-positive mothers unvaccinated sexual contacts of a person known or at high risk to be HBsAg-positive and unvaccinated persons with a percutaneous exposure to someone who is known or at high risk to be HBsAg positive. HBIG administration alone is the primary means of protection after exposure to HBV in known nonresponders to hepatitis B vaccination.92
When used for post-exposure prophylaxis, HBIG should be given as soon as possible after exposure, ideally within 12 hours after birth for infants born to HBsAg-positive mothers or within 24 hours after other exposures. Limited data suggest that the efficacy of HBIG is reduced if administered more than 7 days after a percutaneous exposure or 14 days after a sexual exposure.92
J. Peter R. Pelletier MD, FCAP, FASCP, Faisal Mukhtar MBBS, MD, FCAP, FASCP, in, 2020
Also Check: Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis
Negative But Other Hepatitis Tests Are Positive
Your HBsAb test may be negative even when other hepatitis B tests are positive, showing active or chronic infection. Further testing is necessary, especially for the hepatitis B surface antigen , which shows that the virus itself is circulating in your bloodstream and that you have an active or chronic infection.
Reactivation Risk In Anti
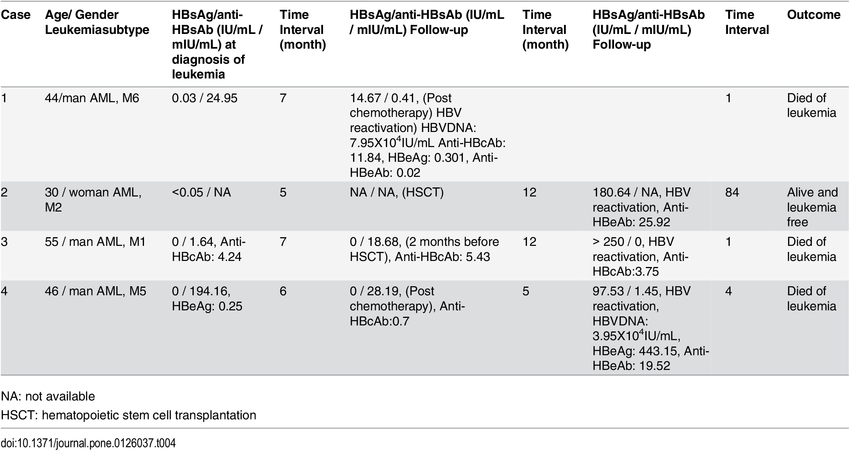
Table 1 American Gastroenterological Association classification of reactivation risk in HBsAg/anti-HBc patients Full size table
The risk of HBV reactivation can be assessed based on positivity for HBV serum biomarkers and the type, duration, combination of agents, and dosing of immunosuppressive or chemotherapeutic agents . HBV reactivation risk can be as high as 4070% in anti-HBc-only, patients who are undergoing chemotherapy with B cell depleting antibodies like rituximab .
Noting that reactivation after immunosuppressive therapy is associated with significant morbidity and mortality, the AGA recommends antiviral prophylaxis for patients classified as at either moderate or high risk for reactivation for low-risk patients, there is no prophylaxis recommendation monitoring is per provider preference but seemingly sufficient . Entecavir and tenofovir prodrugs should be used as first-line prophylaxis or therapy due to their stronger antiviral potency and high threshold for resistance.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis B Caused By
Don’t Miss: Can Alcohol Cause Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B Surface Ab Reactive
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â its anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â its anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Read Also: What Is Hepatic Function Panel
Antibody Responses During Hepatitis B Viral Infection
-
Affiliation Department of Mathematics, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, Virginia, United States of America
-
Affiliation Theoretical Division, Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, New Mexico, United States of America
-
Affiliation Theoretical Division, Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, New Mexico, United States of America
Also Check: Where Do I Get Hepatitis A Vaccine
The Treatment Programs Role In The Screening Process
Medical staff members at substance abuse treatment programs might assume the primary role for screening individuals for and explaining the screening process and test results. Opioid treatment programs with medical staff members should screen for and C at intake and periodically as indicated. In programs without onsite medical staff, clients may be referred elsewhere for screening with minimal involvement of the substance abuse treatment program.
Regardless of the type of program, counselors should have a basic understanding of the importance of screening, the screening process, and the meaning of the results. Counselors can encourage clients referred for screening to follow through and complete the screening and evaluation process . Clients might feel anxious about being diagnosed with hepatitis, and they might delay or avoid getting screened.
Provides Information To Assist In Interpretation Of The Test Results
A positive result indicates recovery from acute or chronic hepatitis B virus infection or acquired immunity from HBV vaccination. This assay does not differentiate between a vaccine-induced immune response and an immune response induced by infection with HBV. A positive total antihepatitis B core result would indicate that the hepatitis B surface antibody response is due to past HBV infection.
Per assay manufacturer’s instructions for use, positive results, defined as anti-HBs levels of 12.0 mIU/mL or greater, indicate adequate immunity to hepatitis B from past hepatitis B or HBV vaccination. However, per current CDC guidance, individuals with anti-HBs levels greater than 10 mIU/mL after completing an HBV vaccination series are considered protected from hepatitis B.
Negative results, defined as anti-HBs levels of less than 5.0 mIU/mL, indicate a lack of recovery from acute or chronic hepatitis B or inadequate immune response to HBV vaccination. The US Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices does not recommend more than 2 HBV vaccine series in nonresponders.
Indeterminate results, defined as anti-HBs levels in the range from 5 to 11.9 mIU/mL, indicate inability to determine if anti-HBs is present at levels consistent with recovery or immunity. Repeat testing is recommended in 1 to 3 months.
Recommended Reading: Royal Canin Hepatic Wet Food
Whats The Prognosis For Hepatitis B
Your doctor will know youâve recovered when you no longer have symptoms and blood tests show:
- Your liver is working normally.
- You have hepatitis B surface antibody.
But some people donât get rid of the infection. If you have it for more than 6 months, youâre whatâs called a carrier, even if you donât have symptoms. This means you can give the disease to someone else through:
- Unprotected sex
Read Also: How Much Does Hepatitis C Medicine Cost
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Serum
Diagnosis of acute, recent, or chronic hepatitis B infection
Determination of chronic hepatitis B infection status
This test is not offered as a screening or confirmatory test for blood donor specimens.
This test, by itself , is not useful during the “window period” of acute hepatitis B virus infection . Testing for acute HBV infection should also include hepatitis B core IgM antibody .
Also Check: How Can Hepatitis B Be Transmitted
What Is The Purpose Of A Hepatitis B Test
Hepatitis B test is performed to detect, classify, and treat hepatitis B virus infection.
Hepatitis B blood tests involve the measurement of several HBV-specific antigens and antibodies. In addition, HBV blood tests also include liver enzymes and liver function tests to assess and monitor the condition of the liver and provide appropriate treatment.
The HBV specific tests include the following:
- HBsAg: HBsAg is an antigen found on the surface of hepatitis B virus. HBsAg may be detected in the blood any time after 1 week post-exposure to HB virus, but usually appears after 4 weeks.
- Anti-HBs: Anti-HBs are antibodies produced by the bodys immune system to fight HBsAg. Anti-HBs from a prior infection or vaccination provides immunity against further infection.
- Hepatitis B core antigen : HBcAg is an antigen found in the core layer which covers the hepatitis B viral DNA.
- Hepatitis B core antibody : Anti-HBc is the antibody that fights HBcAg. Anti-HBc is the first detectable antibody after HBV infection. There are two kinds of Anti-HBc:
- Immunoglobulin M hepatitis B core antibody : IgM anti-HBc indicates acute or reactivated recent infection within the previous 6 months.
- Immunoglobulin G hepatitis B core antibody : IgG anti-HBc may indicate previous or chronic infection. Once present, IgG anti-HBc persists for a lifetime.
What Do Hepatitis B Test Results Mean
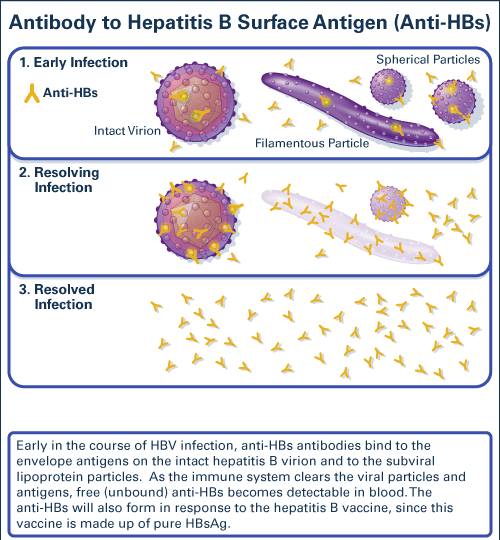
Hepatitis B test results help determine if HBV infection is negative or positive, and if positive, whether the infection is acute or chronic, or if recovery is complete. A combination of results are considered to identify and classify HBV infection status.
The following are some interpretations of hepatitis B test results:
Table: Hepatitis B test results and interpretations
| Test |
|---|
Read Also: How Do You Catch Hepatitis B And C
What Is A Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Test
Hepatitis B surface antibody test is part of a panel of blood tests to diagnose HBV infection. Hepatitis B surface antibody test determines the presence and quantity of anti-HBs in the blood serum, which can indicate protection from HBV infection.
Hepatitis B disease affects the liver and commonly spreads through body fluids such as blood, semen, and vaginal secretions.
Does Hepatitis B Show Up In Routine Blood Tests
Routine blood tests do not detect hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatitis B tests are specifically done if blood tests show abnormal liver function results, or if a person experiences symptoms or falls into the high-risk category for HBV infection.
A panel of HBV-specific blood tests are required to detect HBV infection.
Also Check: How Contagious Is Hepatitis C Sexually
What Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
When you are exposed to hepatitis B, your body mounts an immune reaction against it as an invader. This happens whether you are exposed due to blood or sexual contact or if you are vaccinated with the hepatitis B vaccine.
The hepatitis B virus has proteins on its surface that cause your immune system to produce antibodies. With the vaccine, the sample contains the protein only and not the virus itself.
The first response your body will make when exposed to hepatitis B is to manufacture hepatitis B IgM antibodies. These early antibodies are produced to fight against several parts of the virus including its core. These antibodies are seen in the initial response, but they eventually fade away.
Your immune system then begins to produce IgG antibodies. It continues to produce these antibodies for the rest of your life. In this way, your immune system is always ready to attack hepatitis B virus when it is exposed to it.
Hepatitis B Vaccine And Surface Antibody Titer Faqs
PLEASE NOTE: This is program specific some programs require 3 Hepatitis B vaccines AND a positive Hepatitis B Surface Antibody titer while others will accept 3 vaccines OR a titer. Please read the information in your CastleBranch account carefully so that you know exactly what you need to meet your programs requirements. If you have any questions, please email and a team member will respond.
Recommended Reading: What Does Hepatitis B Mean
Hepatitis B Blood Tests
The Hepatitis B Panel of Blood Tests
Only one sample of blood is needed for a hepatitis B blood test, but the Hepatitis B Panel includes three parts. All three test results are needed to fully understand whether a person is infected or not. Below is an explanation of the 3-part Hepatitis B Panel of blood test results.
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen
The Hepatitis B vaccine is the best way to prevent infection. Vaccination is highly recommended. It takes three vaccines to complete series. Following groups should receive hepatitis B vaccine: all infants, at time of birth any children and adolescents who are vaccinated at birth, adults being treated for sexually transmitted infection, people living in institutional settings, people whose work brings them into contact with blood HIV – positive individuals, men who have sex with men people with multiple sexual partners injection drug users family members of those with hepatitis B individuals with chronic diseases people traveling to areas with high rates of hepatitis B in other words, just about everyone should receive hepatitis B vaccine. It is a relatively inexpensive and very safe vaccine. There are also other ways to reduce your risk of HBV infection. You should always ask sexual partners to get test for hepatitis B. Use a condom or dental dam when having anal, vaginal, or oral sex. Avoid drug use. If youre traveling internationally, check to see if your destination has a high incidence of hepatitis B and make sure you are fully vaccinated prior to travel.
* Please keep in mind that all text is machine-generated, we do not bear any responsibility, and you should always get advice from professionals before taking any actions.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get Hepatitis A And B
How Common Is Hepatitis B
The number of people who get this disease is down, the CDC says. Rates have dropped from an average of 200,000 per year in the 1980s to around 20,000 in 2016. People between the ages of 20 and 49 are most likely to get it.
About 90% of infants and 25-50% of children between the ages of 1-5 will become chronically infected. In adults, approximately 95% will recover completely and will not go on to have a chronic infection.
As many as 1.2 million people in the U.S. are carriers of the virus.
Transmission Of Hepatitis B
The hepatitis B virus is transmitted through blood and sexual fluids. This can most commonly occur in the following ways:
Direct contact with infected blood
Unprotected sex
Use of illegal or street drugs
Needles and other medical/dental equipments or procedures that are contaminated or not sterile
From an infected woman to her newborn during pregnancy and childbirth
Body piercing, tattooing, acupuncture and even nail salons are other potential routes of infection unless sterile needles and equipment are used. In addition, sharing sharp instruments such as razors, toothbrushes, nail clippers, earrings and body jewelry can be a source of infection.
Hepatitis B is NOT transmitted casually. It cannot be spread through toilet seats, doorknobs, sneezing, coughing, hugging or eating meals with someone who is infected with hepatitis B.
You May Like: What Does Hepatitis B Do
Also Check: Is Hepatitis C And Hiv The Same
Is Hepatitis B Contagious
Hepatitis B is highly contagious. It spreads through contact with infected blood and certain other bodily fluids. Although the virus can be found in saliva, its not spread through sharing utensils or kissing. It also doesnt spread through sneezing, coughing, or breastfeeding. Symptoms of hepatitis B may not appear for 3 months after exposure and can last for 212 weeks. However, you are still contagious, even
To screen for hepatitis B, your doctor will perform a series of blood tests.
What Does A Reactive Result To A Hepatitis B Test Mean
The meaning of a reactive result for a hepatitis B test depends on the type of test performed, according to the Hepatitis B Foundation. The three most common blood tests detect the presence of hepatitis B surface antigens, hepatitis B surface antibodies or hepatitis B core antibodies.
In the hepatitis B surface antigen test, a reactive or positive result means that a person is currently infected with the hepatitis B virus, explains the Hepatitis B Foundation. Reactive results from the hepatitis B surface antibody test means that people are now immune to the virus because they have been infected in the past and their immune systems produced antibodies to fight the infection. For the hepatitis B core antibody test, a reactive or positive result can mean either that a person is currently infected with hepatitis B virus or have been some time in the test. A reactive result for this test can also be a false positive, meaning that the person has never been infected with the virus.
Also Check: How To Test For Hepatitis
Hepatitis B Virus Antigens And Antibodies
The Structure of Hepatitis B Virus
The hepatitis B virus is a small DNA virus with unusual features similar to retroviruses, which is a prototype virus of the Hepadnaviridae family. HBV causes acute and chronic hepatitis in humans. The hepatitis B virus consists of an outer lipid envelope and an icosahedral nucleocapsid core composed of protein. The virus is one of the smallest enveloped animal viruses with a virion diameter of 42 nm, and also named Dane particles. Dane particles contains both envelope and core.
The outer envelope contains embedded proteins which are involved in viral binding of susceptible cells. There are three types of proteins: small hepatitis surface proteins, middle hepatitis surface proteins and large hepatitis surface proteins, they are totally composed of hepatitis B surface proteins. The nucleocapsid encloses the viral DNA and a DNA polymerase that has reverse transcriptase activity.
There are three types of Hepatitis B Virus particles in infectious serum by electron microscopy, Dane particles, filamentous particles and spherical particles. Except for Dane particles , there also exist pleomorphic forms, as filamentous particles and spherical particles .
Hepatitis B Virus Antigens
The X gene codes for HBxAg. The product of the X gene is hepatitis B x antigen . It may be involved in carcinogenesis.
Hepatitis B Virus Antibodies
Also Check: Hepatitis C Viral Rna Genotype Lipa