Treatment Programs And Support
Doctors may recommend alcohol treatment programs for people who find it difficult to cut out alcohol. Programs are available both in and out of hospital settings, depending on the severity of the dependence.
These programs can help people reduce and eventually stop consuming alcohol. Examples of these programs include:
Diagnosis Of Alcoholic Hepatitis
Your doctor will conduct a physical examination and ask about your history of alcohol consumption. It is important to be honest in describing your drinking habits. Your doctor might ask to interview family members about your drinking.
To test for liver disease, your doctor might recommend:
- Liver function tests
- An ultrasound, CT or MRI scan of the liver
- A liver biopsy, if other tests and imaging dont provide a clear diagnosis or if you are at risk of other causes of hepatitis
Sexual Differences In Incidence
Women are more susceptible than men to the adverse effects of alcohol. Women develop alcoholic hepatitis after a shorter period and smaller amounts of alcohol abuse than men, and alcoholic hepatitis progresses more rapidly in women than in men.
The estimated minimum daily ethanol intake required for the development of cirrhosis is 40 g for men and 20 g for women older than 15-20 years. Furthermore, for patients who continue to drink after a diagnosis of alcoholic liver disease, the 5-year survival rate is approximately 30% for women compared with 70% for men.
To date, no single factor can account for this increased female susceptibility to alcoholic liver damage. Lower gastric mucosal alcohol dehydrogenase content in women has been suggested to possibly lead to less first-pass clearance of alcohol in the stomach. A higher prevalence of autoantibodies has been found in the sera of alcoholic females compared with alcoholic males, but their clinical significance is questionable. Perhaps hormonal influences on the metabolism of alcohol or the higher prevalence of immunologic abnormalities is responsible for the differences described in the prevalence of alcoholic liver damage between men and women.
Don’t Miss: How Often Hepatitis B Vaccine
Risk Factors For Alcoholic Hepatitis
The major risk factor for alcoholic hepatitis is the amount of alcohol you consume. The amount of alcohol intake that puts a person at risk of alcoholic hepatitis isnt known. But most people with the condition have a history of drinking more than 3.4 ounces equivalent to seven glasses of wine, seven beers or seven shots of spirits daily for at least 20 years.
Other risk factors include:
- Your sex. Women seem to have a higher risk of developing alcoholic hepatitis possibly because of differences in the way alcohol is processed in women.
- Obesity. Heavy drinkers who are overweight might be likelier to develop alcoholic hepatitis and to progress from that condition to cirrhosis.
- Genetic factors. Studies suggest there may be a genetic component in alcohol-induced liver disease although its difficult to separate genetic and environmental factors.
- Race and ethnicity. Although its difficult o separate genetic and environmental factors, African-Americans and Hispanics might be at higher risk of alcoholic hepatitis.
- Binge drinking. Consuming five or more drinks at one time might increase your risk of alcoholic hepatitis.
Racial And Age Differences In Incidence
Although no genetic predilection is noted for any particular race, alcoholism and alcoholic liver disease are more common in minority groups, particularly among Native Americans. Likewise, since the 1960s, death rates of alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis have consistently been far greater for the nonwhite population than the white population. The nonwhite male rate of alcoholic hepatitis is 1.7 times the white male rate, 1.9 times the nonwhite female rate, and almost 4 times the white female rate.
Alcoholic hepatitis can develop at any age. However, its prevalence parallels the prevalence of ethanol abuse in the population, with a peak incidence in individuals aged 20-60 years.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Affects What Organs
What Is A Kidney Disease
When the kidneys fail to perform optimally, it marks the onset of kidney disease. Kidney dysfunction can be slow and progressive, leading to chronic kidney disease or sudden and fast, as in acute kidney disease. Under both circumstances, the kidneys fail to filter out excess water and waste from the blood. As the toxic waste is not excreted and circulates within the body, it poses serious health complications and is potentially life-threatening.
Role Of The Immune System
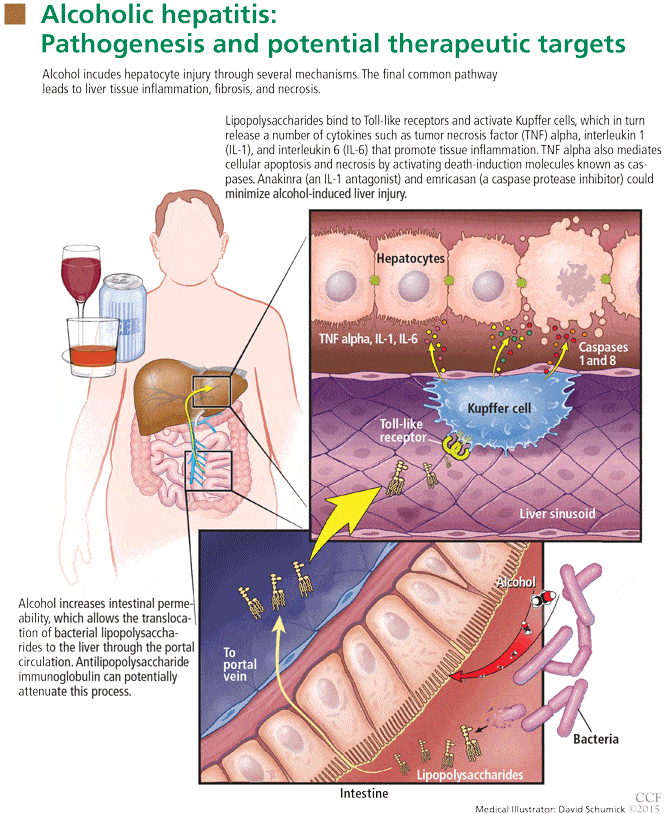
Active alcoholic hepatitis often persists for months after cessation of drinking. In fact, its severity may worsen during the first few weeks of abstinence. This observation suggests that an immunologic mechanism may be responsible for perpetuation of the injury. The levels of serum immunoglobulins, especially the immunoglobulin A class, are increased in persons with alcoholic hepatitis. Antibodies directed against acetaldehyde-modified cytoskeletal proteins can be demonstrated in some individuals. Autoantibodies, including antinuclear and antisingle-stranded or antidouble-stranded DNA antibodies, have also been detected in some patients with alcoholic liver disease.
B and T lymphocytes are noted in the portal and periportal areas, and natural killer lymphocytes are noted around hyalin-containing hepatocytes. Patients have decreased peripheral lymphocyte counts with an associated increase in the ratio of helper cells to suppressor cells, signifying that lymphocytes are involved in a cell-mediated inflammatory process. Lymphocyte activation upon exposure to liver extracts has been demonstrated in patients with alcoholic hepatitis. Immunosuppressive therapy with glucocorticoids appears to improve survival and accelerate recovery in patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Or C Which Is Worse
Prevention Of Alcoholic Hepatitis
You might reduce your risk of alcoholic hepatitis if you:
- Drink alcohol in moderation, if at all. For healthy adults, moderate drinking means up to one drink a day for women and up to two drinks a day for men.
- The only certain way to prevent alcoholic hepatitis is to avoid all alcohol.
- Protect yourself from hepatitis C. Hepatitis C is an infectious liver disease caused by a virus. Untreated, it can lead to cirrhosis. If you have hepatitis C and drink alcohol, youre far more likely to develop cirrhosis than is someone who doesnt drink. Alcohol consumption may exacerbate injury caused by other pathogenic factors, including hepatitis viruses. Approximately 20% of patients presenting with alcoholic hepatitis have concomitant hepatitis C virus infection 3). Extensive epidemiologic studies suggest that the risk of cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C infection is greatly exacerbated by heavy alcohol ingestion. Possible mechanisms include the impairment of immune-mediated viral killing or enhanced virus gene expression due to the interaction of alcohol and hepatitis C virus.
- Check before mixing medications and alcohol. Ask your doctor if its safe to drink alcohol when taking your prescription medications. Read the warning labels on over-the-counter medications. Dont drink alcohol when taking medications that warn of complications when combined with alcohol especially pain relievers such as acetaminophen .
Causes Of Acute Kidney Disease
- Impaired blood supply to the kidneys
- Direct injury to the kidneys
- Urine backing up in the kidneys
These situations emerge when:
- You suffer a traumatic injury with acute blood loss
- You suffer from chronic dehydration, which leads to break down of muscle tissue
- You suffer from a severe infection
- There is an enlarged prostate or kidney, a stone that obstructs urine flow.
- You are addicted to a certain category of drugs that directly damage the kidneys.
- You had complications during pregnancy such as eclampsia and preeclampsia
- You suffer from autoimmune diseases
- You suffer from chronic heart disease or liver infection
Also Check: What Are Some Signs Of Hepatitis C
Role Of Concomitant Viral Disease
Alcohol consumption may exacerbate liver injury caused by other pathogenic factors, including hepatitis viruses. Approximately 20% of patients presenting with alcoholic hepatitis have concomitant hepatitis C virus infection. Extensive epidemiologic studies suggest that the risk of cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C infection is greatly exacerbated by heavy alcohol ingestion. Possible mechanisms include the impairment of immune-mediated viral killing or enhanced virus gene expression due to the interaction of alcohol and hepatitis C virus.
Features Due To Underlying Cirrhosis
Concomitant cirrhosis is present in about 50%-60% cases with AH. Hence, these patients may have features of cirrhosis such as spider angiomas, palmar erythema, ascites and variceal bleeding. Other commonly noted features are Dupuytrens contracture, gynecomastia and loss of pubic or axillary hair, parotid gland enlargement and testicular atrophy in males and amenorrhea with infertility in females. Although these are seen more commonly with alcoholic cirrhosis, these are not specific or sensitive for diagnosis of alcohol related cirrhosis.
You May Like: Can You Have Hepatitis B And Not Know It
How Is It Diagnosed
- Medical history. Your doctor may ask about your medical past to see if thereâs reason to believe you may have alcohol-related liver problems.
- Questionnaire. Theyâll ask you questions to determine if your drinking has become a problem.
- Blood tests. These will check your liver enzymes. Abnormally high levels are a sign of liver damage.
- Liver biopsy. Your doctor may request one in addition to blood tests.
How Long Does It Take To Recover From Alcohol
People who quit drinking alcohol after diagnosis show great improvement after six to 12 months. Milder cases often resolve completely. More severe cases can continue to show gradual improvement over the following years. Some livers may bear permanent scarring, but as long as you stay abstinent from alcohol, there wont be ongoing damage.
Also Check: New Drugs For Hepatitis B
Is Alcoholic Hepatitis Reversible
Alcoholic hepatitis is sometimes reversible. If the condition isnt severe, individuals can recover from liver damage caused by alcohol abuse. It is clear that the condition will continue to worsen if a person continues to drink. Drinking alcohol also increases the risk of developing cirrhosis, a liver condition that can be deadly.
Medical conditions that commonly occur alongside alcoholic hepatitis, such as infections, pneumonia, tuberculosis, internal bleeding, diabetes, pancreatitis and cancer, may be irreversible.
Alcohol addiction is a common contributor to alcoholic hepatitis. Alcoholics, the common term for people with alcoholism, usually have to receive treatment for alcoholism to increase the likelihood of successfully reversing alcoholic hepatitis.
How Much Do You Have To Drink To Get Alcohol
Theres no single formula that leads to alcohol-induced hepatitis in everybody. But statistically, youre more at risk if you drink heavily on a regular basis for an extended period of time. Heavy drinking means different things for men and women . For people assigned male, its about four standard drinks a day or more than 14 drinks per week. For people assigned female, its about three drinks per day or more than 7 drinks per week.
Heavy drinking can also look like occasional binge drinking more than five drinks in a night for men and people AMAB or four for women and people AFAB. Binge drinking at least five times a month is considered heavy. If you keep up this pace for as little as six months, your risk of developing alcohol-induced hepatitis rises significantly. Most people have been drinking for five years or more, with periods of abstinence.
Is alcohol-induced hepatitis contagious?
No. Alcohol-induced hepatitis isnt viral, as other types of hepatitis are. You cant pass the disease on to others in the same way that you might pass on a virus. However, chronic heavy drinking can be viral in the social sense. When friends or family binge drink together, they reinforce in each other the behavior that can lead to alcohol-induced hepatitis.
You May Like: How Is Hepatitis C Transmitted Cdc
Addressing Aud Of Individuals With Alcoholic Hepatitis
Many people who develop alcohol-related liver disease struggle with whats known as an alcohol use disorder . Furthermore, in addition to varying states of progressive liver disease, people with AUD are likely to have developed significant physiological dependence to alcohol and are at risk of experiencing unpleasant and potentially risky alcohol withdrawal symptoms when stopping use.8 The knowledge of an impending withdrawal syndrome can make it that much more difficult for a person to take the steps necessary to begin recovery.
Acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms vary in severity from mild to physically dangerous and may be experienced as soon as 8 hours after the last time alcohol is consumed.8 Given the likelihood of marked physical dependence, people who have with longstanding, compulsive, or otherwise problematic patterns of drinking behavior should not quit drinking cold turkey without medical supervision.
The acute alcohol withdrawal syndrome may include symptoms such as headache, anxiety, insomnia, confusion, tremors, hyperthermia, diaphoresis , and racing pulse.8,9 As symptoms progress in severity, individuals may begin to experience agitation, visual and/or auditory hallucinations, or seizures.8,9
Following successful detox and withdrawal management, an inpatient or outpatient rehabilitation program may be recommended to allow further work toward recovery and relapse prevention.
How Do Doctors Diagnose Alcoholic Hepatitis
Diagnosis of alcoholic hepatitis will begin with an assessment of your medical history. Your doctor will ask about your overall health and your history of alcohol use. They may also perform a physical exam to check for an enlarged liver.
An ultrasound can help doctors determine if the bile duct system is blocked or if there are signs of other underlying liver diseases. In some cases, a liver biopsy might also be necessary to rule out other conditions.
Doctors can also use blood tests to confirm a diagnosis. The levels of a liver enzyme called aspartate aminotransferase are often higher in people with alcoholic hepatitis. Another blood marker called carbohydrate-deficient transferrin can also indicate chronic alcohol intake.
Don’t Miss: Can I Donate Organs If I Had Hepatitis A
Cirrhosis Of The Liver
Cirrhosis happens when scar tissue permanently replaces the healthy tissue of your liver. Scar tissue affects the normal function of your liver and can eventually cause it to fail.
If you develop cirrhosis as a result of heavy alcohol use, alcoholic hepatitis can get worse. Cirrhosis can also raise your risk of liver cancer.
What Are The Symptoms Of Alcoholic Hepatitis
Alcoholic hepatitis can cause a wide variety of symptoms. Most people with the condition experience a loss of appetite and malnutrition, leading to weight loss. People with severe alcoholic hepatitis may also experience jaundice, a condition where the skin, mucous membranes, and whites of the eyes turn yellow.
Additional symptoms include:
If you have any of these symptoms, contact your doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
Don’t Miss: Signs Of Hepatitis B Infection
Medications To Reduce Liver Inflammation
If you have severe alcoholic hepatitis, your doctor might recommend:
- Corticosteroids. These medications have shown some short-term benefit in increasing survival of certain people with severe alcoholic hepatitis. However, corticosteroids have serious side effects and generally arent prescribed if you have failing kidneys, gastrointestinal bleeding or an infection.
- Pentoxifylline. Your doctor might recommend this anti-inflammatory medication if you have severe alcoholic hepatitis and cant take corticosteroids. The overall benefit of pentoxifylline for alcoholic hepatitis isnt clear. Studies indicate that pentoxifylline might not be effective for people with mild alcoholic hepatitis or for people who havent responded to steroid treatment.
Causes Of Alcoholic Hepatitis

Alcoholic hepatitis develops when the alcohol that you drink damages your liver. Just how alcohol damages the liver and why it does so only in some heavy drinkers isnt clear.
It is known that:
- The bodys process for breaking down alcohol produces highly toxic chemicals
- These chemicals trigger inflammation that destroys liver cells
- Over time, scars replace healthy liver tissue, interfering with liver function
- This irreversible scarring is the final stage of alcoholic liver disease
Other factors that can contribute to alcoholic hepatitis include:
- Other types of hepatitis. If you have hepatitis C and also drink even moderately youre more likely to develop cirrhosis than if you dont drink.
- Malnutrition. Many people who drink heavily are malnourished, because they eat poorly or because alcohol and its byproducts prevent the body from properly absorbing nutrients. Lack of nutrients contributes to liver cell damage.
Also Check: Is There A Home Test For Hepatitis C
What Causes Alcoholic Hepatitis
When alcohol gets processed in the liver, it produces highly toxic chemicals. These chemicals can injure the liver cells. This injury can lead to inflammation and, eventually, alcoholic hepatitis.
Although heavy alcohol use can lead to alcoholic hepatitis, experts arent entirely sure why the condition develops in some people but not in others.
Alcoholic hepatitis develops in a minority of people who heavily use alcohol no more than 35 percent, according to the American Liver Foundation. It can also develop in people who use alcohol only moderately.
Because alcoholic hepatitis doesnt occur in all people who heavily use alcohol, other factors may influence the development of this condition.
Risk factors include:
- having genetic factors that affect how the body processes alcohol
- living with liver infections or other liver disorders, such as hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and hemochromatosis
- abdominal CT scan
- ultrasound of the liver
Your doctor may order a liver biopsy to confirm a diagnosis of alcoholic hepatitis. A liver biopsy requires your doctor to remove a tissue sample from the liver. Its an invasive procedure with certain inherent risks, but biopsy results can show the severity and type of liver condition.
Hypermetabolic State Of The Hepatocyte
Hepatic injury in alcoholic hepatitis is most prominent in the perivenular area of the hepatic lobule. This zone is known to be sensitive to hypoxic damage. Ethanol induces a hypermetabolic state in the hepatocytes, partially because ethanol metabolism via MEOS does not result in energy capture via formation of ATP. Rather, this pathway leads to the loss of energy in the form of heat. In some studies, antithyroid drugs, such as propylthiouracil , that reduce the basal metabolic rate of the liver have shown to be beneficial in the treatment of alcoholic hepatitis.
Don’t Miss: Can A Hepatitis B Carrier Get Vaccinated
What Are The Treatments For Alcoholic Hepatitis
The main treatment for alcoholic hepatitis is drinking cessation. While this will improve many symptoms, it will not reverse cirrhosis.
Once you stop using alcohol, a doctor may recommend supplemental treatments, such as:
- Corticosteroids: These medications may help reduce liver inflammation and speed up liver cell regeneration. Doctors typically only administer corticosteroids when alcoholic hepatitis is severe.
- Vitamin and nutrient supplements: These supplements treat malnutrition and improve a persons overall health. If alcoholic hepatitis is severe, a doctor may use a feeding tube to pass nutrient-rich liquids directly into a persons digestive system.
- Liver transplant: This is when a doctor replaces a damaged liver with a healthy one from a donor. Doctors usually only perform this procedure when the liver is severely damaged.
You may also benefit from talk therapy, which focuses on helping you control negative thoughts and overcome alcohol addiction. There are many types of talk therapy, including psychotherapy, cognitive behavioral therapy, and dialectical behavioral therapy.
If you feel you need help to quit, you can join a support group for alcohol addiction and recovery. The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism provides resources for those who want to quit drinking.