Causes And Risk Factors
HCV causes hepatitis C. People contract the virus through blood-to-blood contact with contaminated blood. For transmission to occur, blood containing HCV must enter the body of a person without HCV.
A speck of blood, invisible to the naked eye, can carry hundreds of hepatitis C virus particles, and the virus is not easy to kill.
The report the following risk factors for developing hepatitis C:
- using or having used injectable drugs, which is currently the most common route in the U.S.
- receiving transfusions or organ transplants before 1992, which is before blood screening became available
- having exposure to a needle stick, which is most common in people who work in healthcare
- being born to a mother who has hepatitis C
The CDC offer advice on cleaning syringes if it is not possible to use clean and sterile ones. Although bleach can kill the HCV in syringes, it may not have the same effect on other equipment. Boiling, burning and using alcohol, peroxide, or other common cleaning fluids to wash equipment can reduce the amount of HCV but might not stop a person from contracting the infection.
It is extremely dangerous to inject bleach, disinfectant, or other cleaning products, so people should make sure they rinse the syringe thoroughly. A person should only ever use bleach to clean equipment if new, sterile syringes and equipment are not available.
People who are at risk due to these factors can have screening to rule out HCV.
- peginterferon alfa-2a
The Discovery Of Hepatitis C Virus Was A Landmark In Public Health
For those of us who grew up in the hepatology field when non-A non-B hepatitis was a common topic of discussion in the clinic and the laboratory, the award of the Nobel prize for the discovery of HCV in 2020 marked a fitting end to a long saga. This is the second Nobel prize awarded to investigators in viral hepatitis recognizing the major advances in this field of clinical and laboratory research . Initially viral hepatitis was regarded as an epidemic disease which was a major problem in congregated settings such as residential schools and military establishments. It became a major issue in time of war when epidemics reduced the effectiveness of armies in the field. Much important early research was funded by the military. Only later did it become apparent that chronic viral hepatitis could lead to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma . Many millions of people were infected making it one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality in some parts of the world. In the early 2000s it was estimated that chronic viral hepatitis was responsible for over one million deaths annually. The development of vaccines for hepatitis B and effective anti-viral therapy for hepatitis B and C have been dramatically effective and offer the prospect of banishing these diseases to the sidelines of human history.
Pearls And Other Issues
Hepatitis D has been long associated with HBV infections and cannot exert pathological influence without the presence of HBV infection. Two forms of infection exist coinfection and superinfection . Superinfection tends to be more severe than coinfection. Due to the preexisting hepatitis B infection, anti-HBcAg IgM is undetectable in superinfection states but can be noted in coinfection.
Also Check: Where Do You Get Hepatitis B
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Vaccine Schedule For Adults
What About Sex And Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C can be spread through sexual intercourse, but the risk is considered to be low. It is extremely rare among monogamous couples, meaning couples who only have sex with one another. The risk increases if you:
- Have multiple sex partners
- Have a sexually transmitted disease
- Are infected with HIV
There is no evidence that Hepatitis C is spread by oral sex.
To reduce the chance of getting or giving Hepatitis C through sexual contact, follow these guidelines:
- Use latex condoms every time you have sex, particularly if you have:
- More than one partner
- Rough sex that might make one of you bleed
- Sex during your or your partners menstrual period
- Sex when you or your partner has an open sore on either of your genitals
Hepatitis C: How Does It Spread
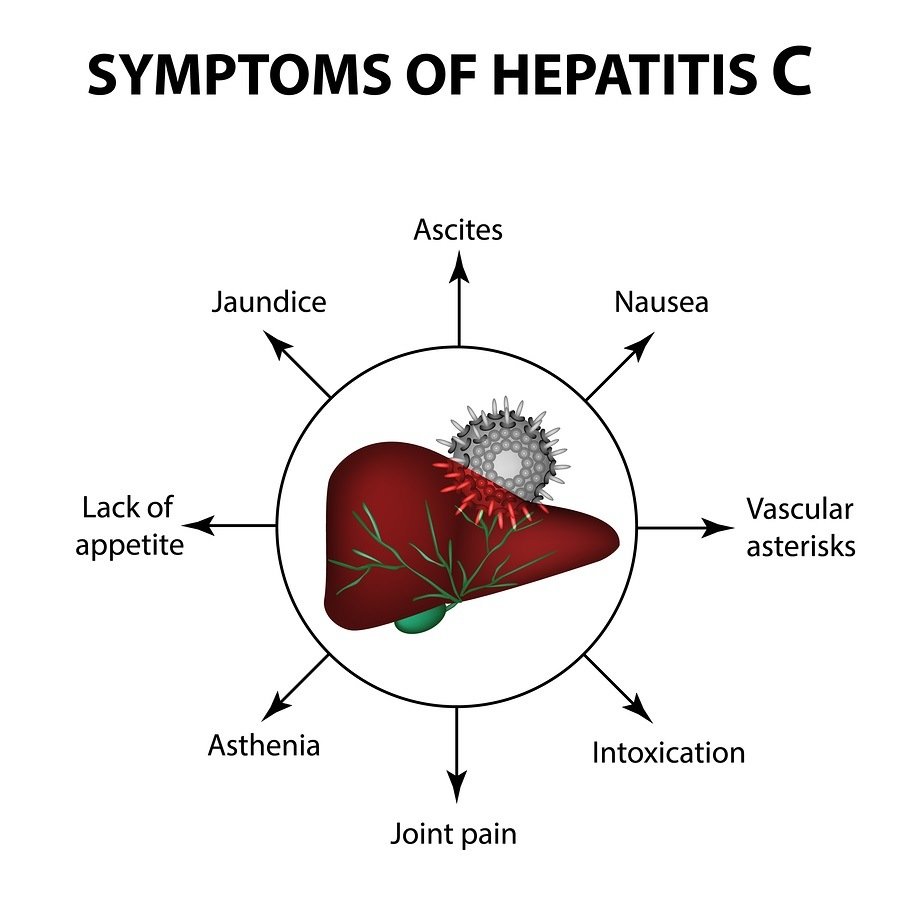
It spreads through infected blood. In the U.S., sharing needles or other items used to inject drugs is the most common cause of infection. Getting a tattoo or body piercing with an infected needle is another means of exposure. A mother may pass the virus to their child at birth. In rare cases, unprotected sex spreads hepatitis C, but the risk appears small. Having multiple sex partners, HIV, or rough sex seems to raise risk for spreading hepatitis C.
Read Also: How Long Can You Live With Hepatitis C Without Treatment
Read Also: Can Hepatitis Cause Itchy Skin
What The Cdc Recommends
Were you born between 1945 and 1965? If so, then youre a member of the Hepatitis C generation. The CDC recently recommended that all people born between during this time have a 1-time screening test for Hepatitis C. We now have new drugs that can treat and cure Hepatitis C so you should go get tested today.
The life you save may be your own! Please contact your local healthcare provider.
Skin Signs Of Liver Damage
Hepatitis C causes chronic inflammation of the liver, which over time causes progressive scarring known as fibrosis. Cirrhosis occurs when the scarring is severe enough to interfere with the function of the liver.
In rare cases, ongoing liver damage can cause cells to change at the genetic level, leading the hepatocellular carcinoma .
Read Also: Hepatitis C Symptoms In Child
Acute Vs Chronic Hepatitis B
A hepatitis B infection can result in either an acute infection or a chronic infection. When a person is first infected with the hepatitis B virus, it is called an acute infection . Most healthy adults that are infected do not have any symptoms and are able to get rid of the virus without any problems. Some adults are unable to get rid of the virus after six months and they are diagnosed as having a chronic infection. A simple blood test can diagnose an acute or chronic hepatitis B infection.
The risk of developing a chronic hepatitis B infection is directly related to the age at which a person is first exposed to the hepatitis B virus. The younger a person is when they are first infected, the greater the risk of developing a chronic hepatitis B infection:
- More than 90% of infants that are infected will develop a chronic hepatitis B infection
- Up to 50% of young children between 1 and 5 years who are infected will develop a chronic hepatitis B infection
- 5-10% of healthy adults 19 years and older who are infected will develop a chronic hepatitis B infection
The recommendation for hepatitis B vaccination of babies and children is so important because they are at the greatest risk of developing a chronic infection if they are not protected against the hepatitis B virus as soon as possible.
Medical Help For Treatment
Now that you know what the early warning signs of hepatitis C are, look back at your own health history. If you have been exposed, or have had a period where you had symptoms of hep C, call your doctor. Remember, according to the CDC, 8 out of 10 people with hep C will not experience symptoms. By getting a simple blood test, you can start treatment with the latest medications. Within weeks, you can be hep C free and your body can start healing.
Recommended Reading: Can You Transmit Hepatitis Sexually
Rashes Associated With Chronic Hcv
Many skin conditions are associated with chronic hepatitis C, some common and others uncommon. They include pruritus , a common condition affecting up to 40% of those with chronic HCV infection.
Four skin conditions directly linked to HCV can cause rashes during the chronic stage of infection:
- Lichen planus: This is an inflammatory condition caused by an abnormal immune response that affects the skin and mucous membranes. Symptoms include flat, purplish, itchy bumps on the skin, swollen gums, and painful erosive patches on the tongue.
- Mixed cryoglobulinemia: This is an inflammatory condition caused by an abnormal immune response that affects blood vessels. Symptoms include a raised, purplish skin rash , typically on the lower legs. Itchiness is also common.
- Porphyria cutanea tarda: This is a rare condition that causespainful lesions on sun-exposed areas of skin. Hyperpigmentation , hypopigmentation , and waxy, hardened skin plaques can also occur.
- Necrolytic acral erythema: This is another rare condition that starts with an outbreak of blistering rash that soon evolves into darkened areas of hardened, cracked skin. The feet are most commonly affected.
These skin conditions can occur for reasons other than hepatitis C. Even so, HCV testing is recommended due to their strong association with HCV.
Prurigo nodularis, a chronic itchy skin condition with a symmetrical rash, is also more common in people with hepatitis C.
Rashes From Hcv Treatment
Hepatitis C is treated with a class of drugs called direct-acting antiviral . While DAAs can cure the vast majority of HCV infections, they can also cause side effects, including fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting.
Skin-related side effects can also occur during treatment, after treatment, or both, typically causing:
Read Also: Hepatitis C Virus Is Spread Through The Contact Of
Hepatitis C Early Warning Signs You Definitely Should Know
Because of its relatively late discovery, people born before the 70s and 80s are especially at risk because they were never tested for Hepatitis C. This is why they account for the majority of cases in the US, and are far more likely of being infected when compared to other age groups. For these reasons, its incredibly important to know how to identify the symptoms of this disease. The earlier Hepatitis C is detected, the sooner a proper diagnoses and treatment can begin.
As far as medical conditions go, Hepatitis C is a very modern one. Following research in the 70s, it was officially confirmed as a virus and published about in 1989. What was quickly apparent was that it was very dangerous because of how hard it is to diagnose early.
Can Hepatitis Be Treated
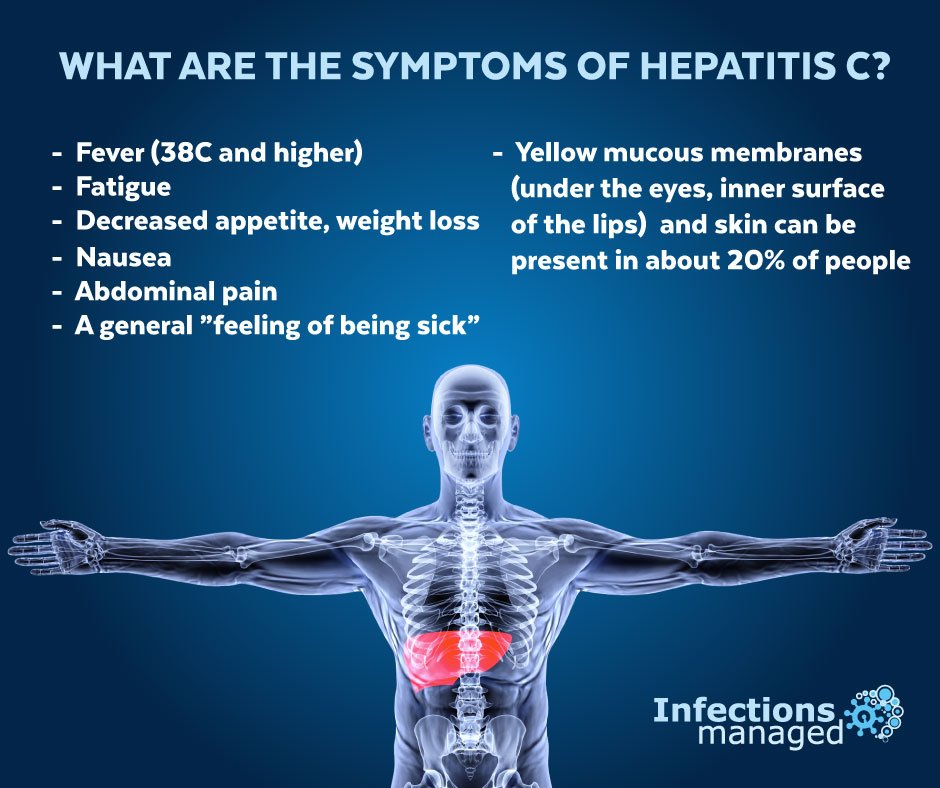
Today, hepatitis management is applicable through different medications and the blood product intravenous immunoglobulin for temporary immunity. However, specific antiviral effects like a nucleotide polymerase inhibitor work in slowing down the virus. Although there are famous names like Ledipasvir with sofosbuvir and Pegylated interferon and ribavirin, some of these medications arent prescribed anymore. However, modern medical technology is changing chronic liver diseases using oral tablets taken every day for at least two to six months.
Ask your pharmacist or your current liver doctor to know if certain drugs arent verified with FDA or harmful to your health status.
Dont Miss: Hepatitis C Symptoms In Females
Read Also: What Happens When You Get Hepatitis C
Deterrence And Patient Education
Patient education remains one of the most important components in preventative measures regarding HBV infection.
Education should be provided to expecting parents about the importance of vaccination and to clarify erroneous beliefs about vaccinations.Patient education should also include counseling about the avoidance of risky behaviors that predispose an individual to be infected, including promiscuous sexual activity or intravenous drug abuse. They should also be advised not to share items such as shaving razors, toothbrushes, or hair combs due to possible transmission via mucosal contact or through microtrauma to protective barriers.
Who Should Get Tested For Hepatitis C
alk to your doctor about getting tested for Hepatitis C if you:
- Are a current or former drug user who used needles to inject, even if you only did this one time or did it many years ago
- Have a sex partner who has chronic Hepatitis C or have had many sex partners
- Had your blood filtered by a machine for a long period of time because your kidneys werent working
- Received a blood transfusion or organ transplant from a donor before July 1992
- Received a blood clotting factor to treat a bleeding disorder before 1987
- Are a healthcare worker and were exposed to blood through a needle stick or had other contact with blood or bodily fluids
- Have evidence of liver disease, such as abnormal liver tests
- Were born between 1945 and 1965. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends a one-time screening for all baby boomers.
Learn more, use the Centers for Disease Controls Hepatitis Risk Assessment tool.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Hepatitis C Antibody Test
How Is Hepatitis C Treated
There is no vaccine for hepatitis C. The aim of treatment for hepatitis C is to eradicate the virus from the blood completely, and to protect the liver from developing cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Several medications are available to treat hepatitis C. The hepatitis C virus has six different types or strains . The type and length of treatment may vary. Some hepatitis strains do not respond to antiviral medications as well as others. Some medications may not be suitable for all patients with hepatitis C, because of the side effects or the patients other medical conditions.
These are the medications approved for treatment of hepatitis C infection:
- Sofosbuvir : Tablet taken once a day. Used in combination with other antiviral drugs.
- Ledipasvir/sofosbuvir : Pill taken once a day for 12 to 24 weeks, depending on how serious the disease is.
- Simeprevir : Capsule taken once a day with other medications called peginterferon alfa and ribavirin
Also Check: Hepatitis C Vs Hepatitis B
Contaminated Needles And Infected Blood
You can get hepatitis C from sharing contaminated needles, syringes and other injecting equipment during recreational drug use. Banknotes and straws used for snorting may also pass the virus on.
Being exposed to unsterilised tattoo and body piercing equipment can also pass hepatitis C on. Occasionally, you can get it from sharing a towel, razor blades or a toothbrush if there is infected blood on them.
Hepatitis C infection is also passed on in healthcare settings, from needle stick injuries or from medical and dental equipment that has not been properly sterilised. In countries where blood products are not routinely screened, you can also get hepatitis C by receiving a transfusion of unscreened blood and blood products.
You can prevent hepatitis C by:
- never sharing needles and syringes or other items that may be contaminated with infected blood
- only having tattoos, body piercings or acupuncture in a professional setting, where new, sterile needles are used
- following the standard infection control precautions, if youre working in a healthcare setting.
You May Like: How To Read Hepatitis B Test Results
Hepatitis Affects The Whole Body
Having liver disease opens a gate through the body where the inflammation starts affecting the bloodstream. Hepatitis can have comorbidities with organs like the kidney, heart, lungs, skin, and bones.
Frequently, patients with hepatitis also forget its effect on periodontal diseases. So, teeth and gum problems like broken teeth are also common. Furthermore, there are more extensive connections of hepatitis skin rash that most patients dont recognize.
Rare and chronic diseases caused by agents that involve the skin are more than internal causes. Several types of hepatitis can be silent for many years. As people age and reach the senior stage, there are more visible signs of liver inflammation and diseases.
Also Check: Can You Get Hepatitis C
Reactive Or Positive Hepatitis C Antibody Test
- A reactive or positive antibody test means that Hepatitis C antibodies were found in the blood and a person has been infected with the Hepatitis C virus at some point in time.
- Once people have been infected, they will always have antibodies in their blood. This is true even if they have cleared the Hepatitis C virus.
- A reactive antibody test does not necessarily mean that you have Hepatitis C. A person will need an additional, follow-up test.
Persons for Whom HCV Testing Is Recommended
- Adults born from 1945 through 1965 should be tested once
- Ever injected drugs, including those who injected once or a few times many years ago
- Have certain medical conditions, including persons:
- who received clotting factor concentrates produced before 1987
- who were ever on long-term hemodialysis
- with persistently abnormal alanine aminotransferase levels
- who have HIV infection
Read Also: What Is The Best Medication For Hepatitis B
How Can I Prevent Hepatitis C
Since there is no vaccine for hepatitis C, the best way to prevent hepatitis C infection is to avoid contact with the blood of infected people. This includes:
- If you shoot drugs, never share works with anyone. This includes all drug injection equipment that can get blood on or in it . Sterile syringes can be purchased over the counter in most pharmacies in Massachusetts by anyone 18 years of age or older. Find out about drug treatment programs that can help you stop using drugs.
- Only get tattoos or body piercings at places using sterile equipment and supplies.
- Never share razors, toothbrushes, or nail clippers
Treatment For Hepatitis C
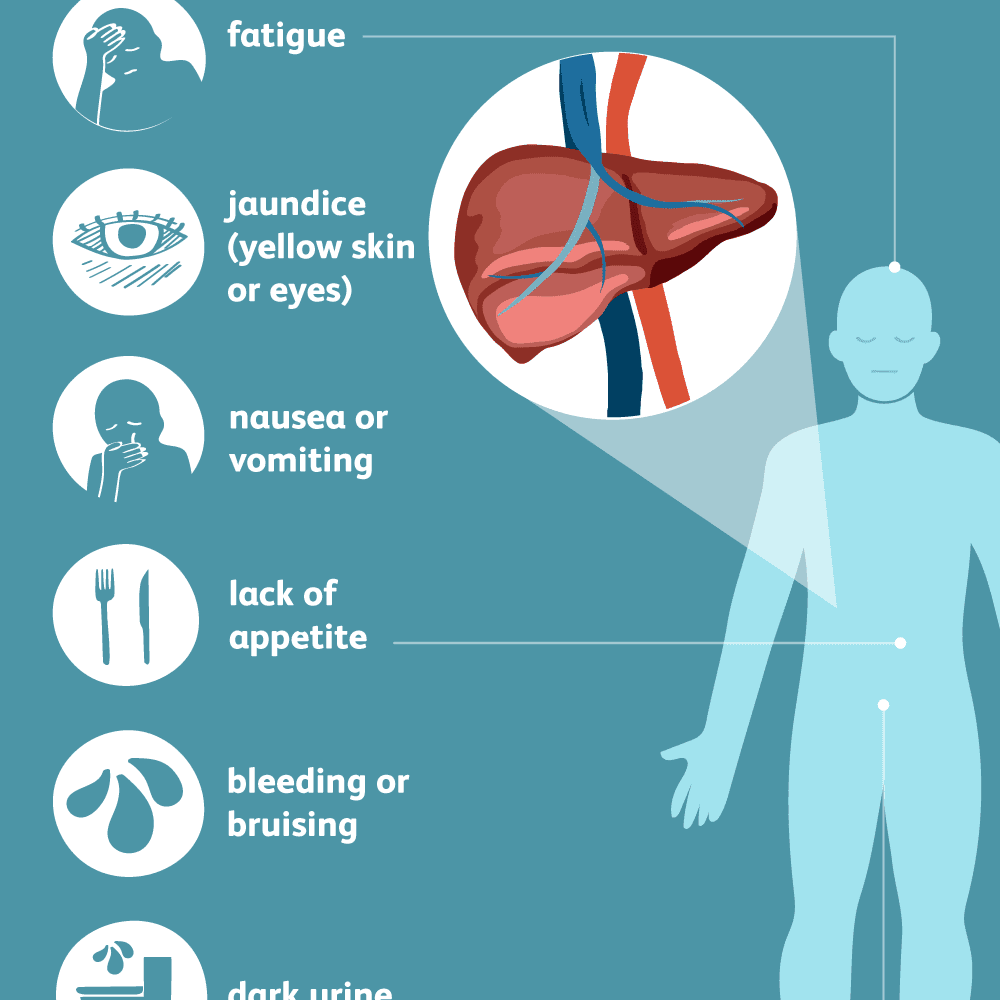
The goal of treatment is to clear the virus from the body. If you have acute hepatitis C, you probably wont have symptoms, and the virus will clear on its own without treatment. In the case of chronic hepatitis, your doctor may treat the virus with antiviral medication for 12 to 24 weeks.
Until 2011, there were only two drugs available to treat hepatitis C: pegylated interferon and ribavirin . These drugs were often used in combination with each other.
The drugs currently used to treat hepatitis C include:
You May Like: Booster For Hepatitis B Vaccine