An Interesting Case Of Isolated False
He S. Yang
1Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, New York Presbyterian Hospital, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY, USA
2Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, New York Presbyterian Hospital, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY, USA
Abstract
1. Introduction
Here, we report a case of a female patient with persistent isolated HBsAg positivity with a lack of symptoms, other serological markers, risk factors, or vaccination to explain the positivity, highly suggestive of a false-positive result requiring thorough investigation to evaluate potential interferences.
2. Case Report
Upon further review of the patients history, no recognized, self-reported risk factors for viral hepatitis including unprotected sex, blood transfusions, tattoos, or intravenous drug abuse were reported. Furthermore, the patient denied personal or family history of liver disease or jaundice. Physical examination did not reveal stigmata of liver disease. Considering the patients low risk for blood-borne infections, it was suspected that the HBsAg and HIV screening results might be false positives due to an unknown interference with the analytical assays.
The patient was retested 3 months after her Mohs surgery. The HBsAg and HIV screening tests remained positive. This study has been approved by the institutional review board of Weill Cornell Medicine.
3. Discussion
Data Availability
Conflicts of Interest
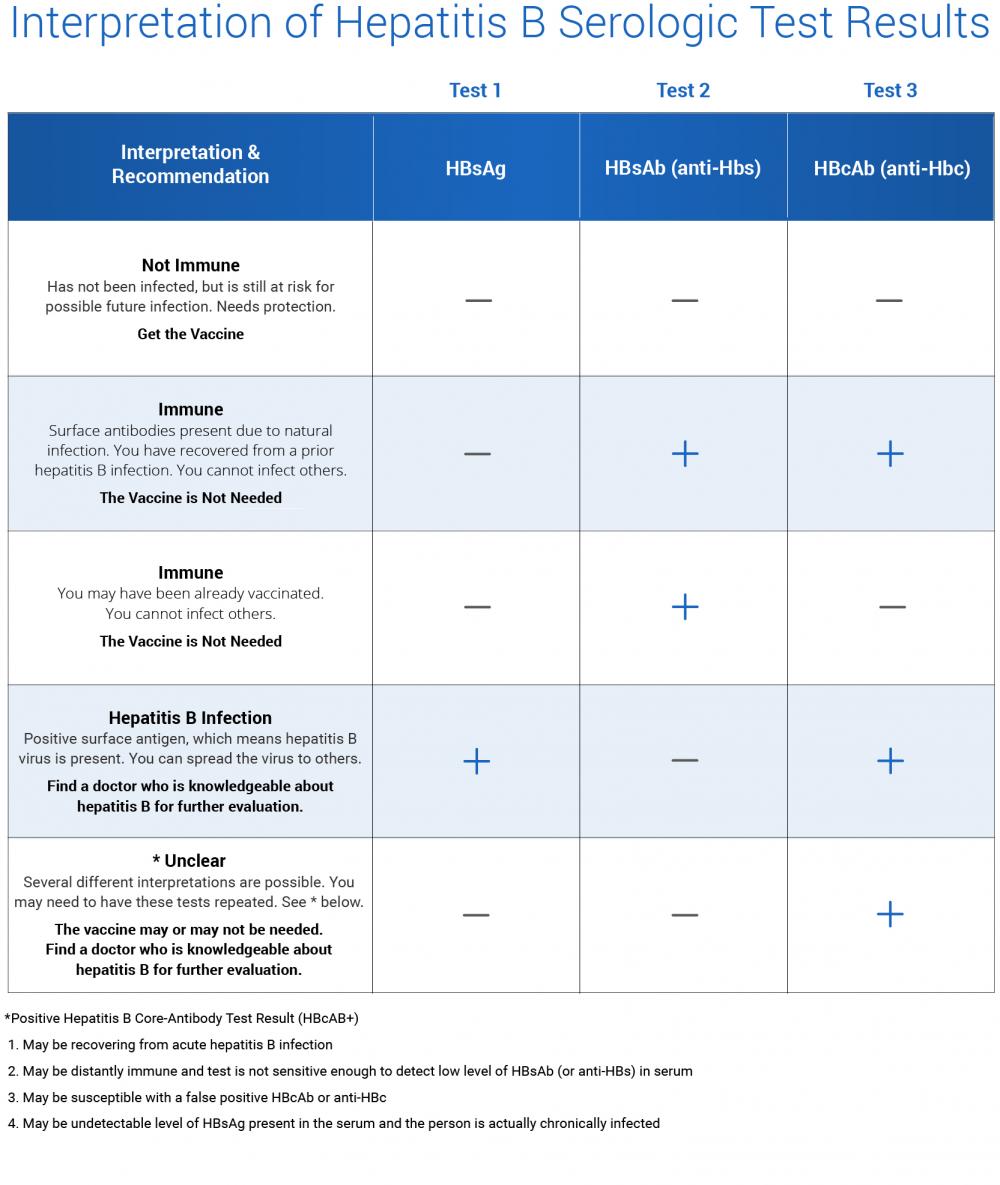
Questions For Your Doctor About Test Results
Patients may find it helpful to ask questions about their hepatitis B test results. Questions that may be helpful include:
- What was my test result?
- Do I have an acute or chronic hepatitis B infection?
- Does the test result suggest that I have immunity for hepatitis B?
- Would I benefit from hepatitis B vaccination?
- Do I need any follow-up tests based on my hepatitis B test results?
What Is The Difference Between The Hepatitis B Surface Antigen And The Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
The basic blood test for hepatitis B consists of three screening tests: a hepatitis B surface antigen test, which determines whether a person currently has the infection a hepatitis B core antibody test, which determines whether a person has ever been infected and a hepatitis B surface antibody test, which determines
Read Also: Antiviral Medication For Hepatitis C
Is Hepatitis B Contagious
Hepatitis B is highly contagious. It spreads through contact with infected blood and certain other bodily fluids. Although the virus can be found in saliva, its not spread through sharing utensils or kissing. It also doesnt spread through sneezing, coughing, or breastfeeding. Symptoms of hepatitis B may not appear for 3 months after exposure and can last for 212 weeks. However, you are still contagious, even
To screen for hepatitis B, your doctor will perform a series of blood tests.
Can Hbsag And Hbsab Be Positive
Both in vitro simulation and in vivo animal models demonstrated that HBsAg antigen and HBsAb of the same serotypes could not coexist, but HBsAg antigen and HBsAb of different serotype could coexist. HBsAg/HBsAb double positive hepatitis B virus infection could be due to infection of viruses of different serotypes.
Also Check: What Is The Cure For Hepatitis C
Read Also: Can You Donate Plasma If You Have Hepatitis B
What Does A Reactive Result To A Hepatitis B Test Mean
The meaning of a reactive result for a hepatitis B test depends on the type of test performed, according to the Hepatitis B Foundation. The three most common blood tests detect the presence of hepatitis B surface antigens, hepatitis B surface antibodies or hepatitis B core antibodies.
In the hepatitis B surface antigen test, a reactive or positive result means that a person is currently infected with the hepatitis B virus, explains the Hepatitis B Foundation. Reactive results from the hepatitis B surface antibody test means that people are now immune to the virus because they have been infected in the past and their immune systems produced antibodies to fight the infection. For the hepatitis B core antibody test, a reactive or positive result can mean either that a person is currently infected with hepatitis B virus or have been some time in the test. A reactive result for this test can also be a false positive, meaning that the person has never been infected with the virus.
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test
A hepatitis B surface antigen test shows if youre contagious. A positive result means you have hepatitis B and can spread the virus. A negative result means you dont currently have hepatitis B. This test doesnt distinguish between chronic and acute infection. This test is used together with other hepatitis B tests to determine the .
Read Also: How Would You Know If You Have Hepatitis C
What Abnormal Results Mean
There are different tests for hepatitis A and hepatitis B. A positive test is considered abnormal.
A positive test may mean:
- You currently have a hepatitis infection. This may be a new infection , or it may be an infection that you have had for a long time .
- You had a hepatitis infection in the past, but you no longer have the infection and cant spread it to others.
Hepatitis A test results:
- IgM anti-hepatitis A virus antibodies, you have had a recent infection with hepatitis A
- Total antibodies to hepatitis A, you have a previous or past infection, or immunity to hepatitis A
Hepatitis B test results:
- Hepatitis B surface antigen : you have an active hepatitis B infection, either recent or chronic
- Antibody to hepatitis B core antigen , you have a recent or past hepatitis B infection
- Antibody to HBsAg : you have a past hepatitis B infection or you have received the hepatitis B vaccine and are unlikely to become infected
- Hepatitis B type e antigen : you have a chronic hepatitis B infection and you are more likely to spread the infection to others through sexual contact or by sharing needles
Antibodies to hepatitis C can most often be detected 4 to 10 weeks after you get the infection. Other types of tests may be done to decide on treatment and monitor the hepatitis C infection.
Also Check: Can You Spread Hepatitis C
Question 7 Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Antibody Always Acquired After A Completed Vaccination Protocol
No. After three intramuscular doses of vaccine, > 90% of healthy adults and > 95% of those < 19 years of age develop immunity .1 However, there is an age-specific decline in development of immunity. After age 40 years, about 90% of people become immune, but by age 60 years, only 75% of people become immune.1 Larger vaccine doses or an increased number of doses are required to induce immunity in many hemodialysis patients and in other immunocompromised people.1
References
Recommended Reading: How Can You Get Hepatitis C
Identifying Patterns Of Risky Behavior
Screening is an opportunity to draw attention to the clients behaviors that put him or her at risk for contracting :
- Ask for the clients perception of his or her risk for having contracted : How likely do you think it is that the test will be positive?
- Listen for and identify behaviors that put the client at risk for contracting , B, and C and HIV, especially unprotected sex and sharing injection drug paraphernalia.
- Assess the clients alcohol consumption.
Preparing Clients For Screening
Once clients are comfortable talking about viral , they might be more willing to undergo screening. However, clients might be anxious about the test itself a reassurance that testing is a simple procedure can help allay these concerns. Many substance use treatment facilities do not offer screening, and clients might need to be referred elsewhere. The following strategies can enhance the discussion of the hepatitis screening process and hepatitis prevention:
Read Also: Can Hepatitis C Spread Through Saliva
Read Also: Hepatitis C Antibody Test Results
What Is A Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Titer
The hepatitis B surface antibody test , looks for antibodies that your immune system makes in response to the surface protein of the hepatitis B virus. The hepatitis B surface antibody is also referred to as anti-HBs and should not be confused with HBsAg, which stands for hepatitis B surface antigen.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis C Genotype 1a
Educating Clients About Viral Hepatitis
Clients may believe they know about viral , but their understanding of the disease may not be accurate. It is easy to confuse the three main types of viral , B, and C. Clients may have formed impressions based on limited or incorrect information. Counselors should briefly describe hepatitis A, B, and C, including their prevalence, , and relationship to drug use, as well as to other infections, such as HIV and sexually transmitted diseases. Specific strategies for speaking with clients include:
- Speak clearly and keep the message simple, focused, and brief.
- Use language, examples, and concepts that the client understands.
- Use appropriate visual aids.
- Frame numerical statements in terms that are easy to visualize. Say 5 out of 100 people rather than 5 percent of the population say more than half instead of the majority.
- Repeat the information at different times in different ways. The average client retains only approximately one-third of what he or she is told. Summarize essential points.
- Pay attention to a clients response to the information. For example, if a client stiffens his or her posture, consider saying, I notice that this topic seems to make you uncomfortable. It does for a lot of people. Please tell me what youre feeling right now. Id really like to help you with this.
- Use the opportunity to describe the potential detrimental effects of alcohol and other substance use on the liver of a person who is infected with HCV.
Don’t Miss: What Is Acute Hepatic Porphyria
Does Hepatitis B Show Up In Routine Blood Tests
Routine blood tests do not detect hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatitis B tests are specifically done if blood tests show abnormal liver function results, or if a person experiences symptoms or falls into the high-risk category for HBV infection.
A panel of HBV-specific blood tests are required to detect HBV infection.
Also Check: How Much Is Hepatitis A Vaccine
Membranous Nephropathy And Hepatitis B
Children with HBV-related MN show positivity of HbsAg and usually hepatitis B surface antibody is not detected. The hepatitis B early antigen can be detected in serum of 90% of patients.27 Hypocomplementemia is observed at the onset of disease , but titers of C3, C4 return to normal in the later part of disease.27 Circulatory immune complexes are detected in 80% of patients. Serum levels of transaminases may be raised on presentation.20,24 Liver biopsy shows evidence of chronic persistent hepatitis mainly in children, but chronic active hepatitis is seen in adults.
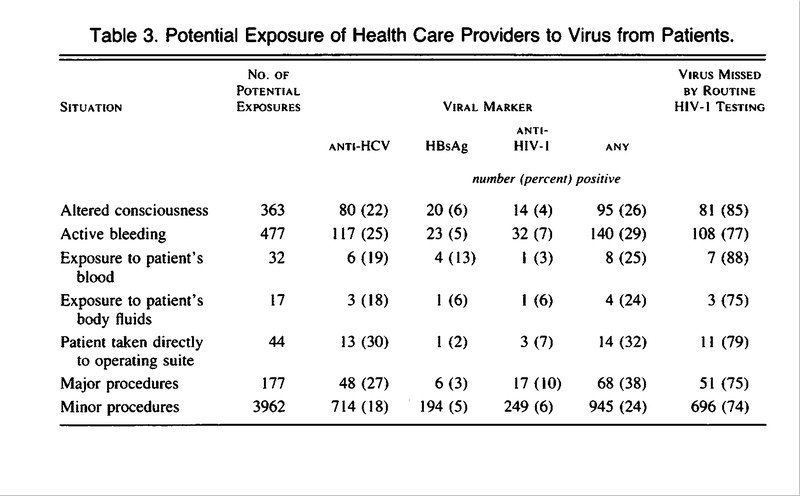
David O. Freedman, … Elaine C. Jong, in, 2008
Read Also: Who Should Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen
Health Streets Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test checks for a current infection of the hepatitis B virus. If the test is positive, then the person can be contagious to others.
Online registration is simple. You choose the lab location based on ZIP code during registration. An authorization barcode is instantly emailed to you and texted directly to the phone of the person being tested. A map of the clinic location will accompany the barcode. The registrant can then walk into the testing facility and show the barcode along with photo ID. Results are fast and stored securely online. Individuals and employers can register online or call to order tests.
Recommended Reading: Hepatic Porphyrias Diagnosis And Management
Hepatitis B Blood Tests
The Hepatitis B Panel of Blood Tests
Only one sample of blood is needed for a hepatitis B blood test, but the Hepatitis B Panel includes three parts. All three test results are needed to fully understand whether a person is infected or not. Below is an explanation of the 3-part Hepatitis B Panel of blood test results.
Read Also: How Long Can You Live With Hepatitis
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Positive
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Options
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen
Quick Links:
bolt
What Is the Difference Between a Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test and a Hepatitis B Antibody Test?
The hepatitis B surface antigen test can detect current hepatitis B infection, while the hepatitis B antibody test checks for the antibodies that are presumed to provide immunity to hepatitis B.
expand_less
When Should Someone Get a Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test?
If someone is suspected to have hepatitis B, this test is intended to identify a chronic or current infection.
expand_less
What Does a Positive Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test Mean?
A positive test means the person is currently infected or has a chronic infection of hepatitis B. This means that the person has the hepatitis B virus in their blood and can be contagious.
expand_less
About Our Other Services
For industries that require specific occupational health testing, such as healthcare, construction, and manufacturing, Health Street offers quick and easy scheduling. Simply enter your ZIP code and choose the location nearest to you or the person being tested. When the registration process has been completed, we will email you the registration barcode to and a map to the facility.
Why Choose Health Street
Also Check: Can Hepatitis A Be Transmitted Sexually
Measures Of Immune Response And Duration Of Immunity/protection
In high-risk individuals who have had titers checked after primary HB immunization, a small percentage of apparently healthy recipients do not mount a detectable response to the vaccine. This failure to respond is related to factors such as age , male gender, smoking, obesity, HIV infection, or chronic disease. Persons > 40 years of age have an immune response < 90%, whereas only 65%75% of persons > 65 years of age develop protective anti-HBs antibody levels.29 For persons with these risk factors and who are at high risk of HB exposure, a postvaccination serology 16 months after the last dose should be done. Patients without detectable anti-HBs titers after primary series should begin a standard three-dose series and have serology 1 month after each dose for up to three doses until they seroconvert, or may wait until the three additional doses are administered before being tested. A similar approach can be taken for health care providers who have received a complete HB series but have undetectable anti-HBsAg titers.
Kyong-Mi Chang, in, 2012
Read Also: Hepatitis C Is Caused By
Comparison Of The Positive Rates Between Baseline Anti
Compared with baseline anti-HBs group, the positive rates of anti-HBs were higher in baseline anti-HBs group at 1 year after receiving the booster vaccine. The positive rates of anti-HBs in baseline anti-HBs group were slightly higher than anti-HBs group at 4 years after receiving the booster vaccine. The statistical results are shown in Table 4.
Negative But Other Hepatitis Tests Are Positive
Your HBsAb test may be negative even when other hepatitis B tests are positive, showing active or chronic infection. Further testing is necessary, especially for the hepatitis B surface antigen , which shows that the virus itself is circulating in your bloodstream and that you have an active or chronic infection.
Also Check:
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis C Screening
What Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
When you are exposed to HBV, your body mounts an immune defense to specifically target and neutralize the invader. Unlike innate immunity which mounts a generalized defense against all invaders, this type of immunity is disease-specific.
This immune response occurs whether you are exposed to HBV through blood or sexual contact, or if you are vaccinated with the hepatitis B vaccine.
The virus has proteins on its surface, called antigens, that serve as unique identification tags. When HBV enters the body, the immune system “encodes” antibodies specific to these antigens so that it can recognize and attack the virus should it appear again.
There are two types of antibodies produced in response to the virus:
- Immunoglobulin M is the antibody that mounts the initial attack but eventually fades away.
- Immunoglobulin G is the antibody that provides long-lasting immune protection against HBV. The immunity can last for many years, but it gradually wanes over time.
The Positive Rates Of Anti
A total of 24751 subjects were anti-HBs negative before the hepatitis B booster vaccination. After receiving the hepatitis B vaccine, the positive conversion rates of anti-HBs were 74.62% at 1 year after receiving booster vaccine, and 67.66% at 4 years. There was statistically significant difference in the positive conversion rates of anti-HBs at 1 and 4 years after vaccination. The negative conversion rates of anti-HBs within 14 years after vaccination were 20.07% , the positive conversion rates of anti-HBs within 14 years were 13.11% , and the positive maintenance rates of anti-HBs within 14 years were 54.55% .
Visualizing the positive rate of anti-HBs in baseline anti-HBs group
Based on gender based on age based on family history of HBV.
Also Check: How Do You Prevent Hepatitis C