Can Bleach Or Cleaner Kill Hepatitis A
Disinfectant that contains bleach can kill the hepatitis A virus on hard non-porous surfaces like toilet seats. However, freezing does not kill HAV.
If you cook food that is contaminated for one minute at cooking temperatures higher than 185ºF , it will kill HAV. However, food can be contaminated after cooking, so it is very important to wash your hands well with soap and water.
Is Hepatitis B Shortening Your Life
In women, chronic HBV infection increases the relative risk of mortality to 1.16 , compared to non-carriers, which is consistent with previous research findings. This translates to a decrease in life expectancy from 82.0 years in non-carriers to 80.1 years in carriers (Figure
What is the difference between acute and chronic hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B During Pregnancy
If a woman with HBV becomes pregnant, they may transmit the virus to their baby. Women should inform the doctor who delivers their baby that they have HBV.
The infant should receive an HBV vaccine and HBIG with 1224 hours of birth. This significantly reduces the risk that they will develop HBV.
The HBV vaccine is safe to receive while pregnant.
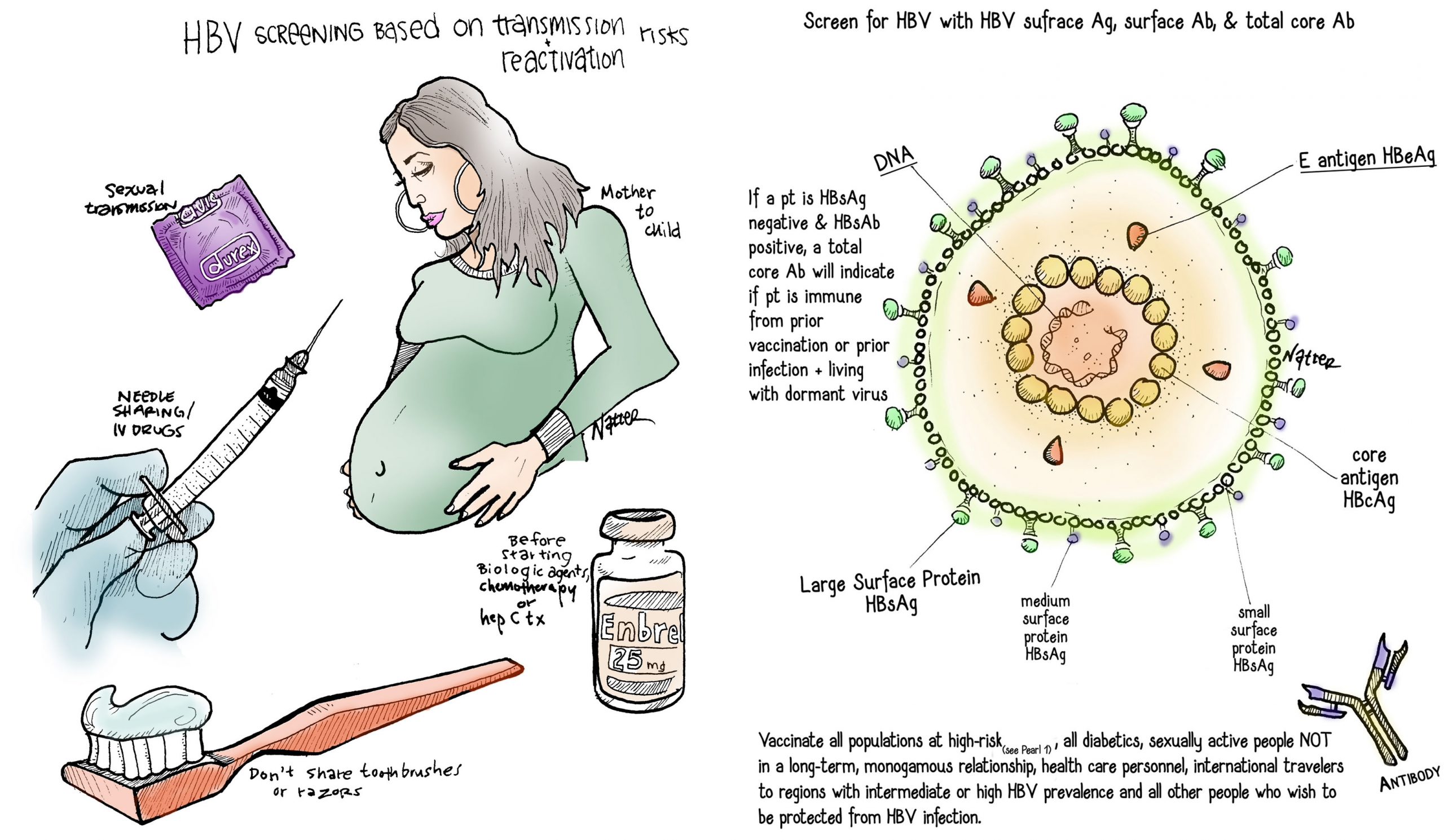
People with a high risk of HBV include:
- the infants of mothers with HBV
- the sexual partners of people with HBV
- people who engage in sexual intercourse without contraception and those who have multiple sexual partners
- men who have sex with men
- people who inject illicit drugs
- those who share a household with a person who has a chronic HBV infection
- healthcare and public safety workers who are at risk of occupational exposure to blood or contaminated bodily fluids
- people receiving hemodialysis, which is a type of kidney treatment
- people taking medications that suppress the immune system, such as chemotherapy for cancer
People can prevent HBV infection by:
- wearing appropriate protective equipment when working in healthcare settings or dealing with medical emergencies
- not sharing needles
- following safe sexual practices
- cleaning any blood spills or dried blood with gloved hands using a 1:10 dilution of one part household bleach to 10 parts water
A vaccine against HBV has been available since 1982.
People who should receive this vaccine include:
Donât Miss: How Does Hepatitis Spread From Person To Person
Don’t Miss: Does The Hpv Vaccine Protect Against Hepatitis B
What Is Acute Fulminant Hepatitis
Rarely, individuals with acute infections with HAV and HBV develop severe inflammation, and the liver fails . These patients are extremely ill with the symptoms of acute hepatitis already described and the additional problems of confusion or coma , as well as bruising or bleeding . In fact, up to 80% of people with acute fulminant hepatitis can die within days to weeks therefore, it is fortunate that acute fulminant hepatitis is rare. For example, less than 0.5% of adults with acute infection with HBV will develop acute fulminant hepatitis. This is even less common with HCV alone, although it becomes more frequent when both HBV and HCV are present together.
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test
A hepatitis B surface antigen test shows if you have an active infection. A positive result means you have hepatitis B and can transmit the virus to others. A negative result means you dont currently have hepatitis B.
This test doesnt distinguish between chronic and acute infection. This test is used together with other hepatitis B tests to determine the state of a hepatitis B infection.
Read Also: The Spread Of Hiv And Hepatitis In The Healthcare Setting
Autoimmune Hepatitis Causes And Risk Factors
Doctors aren’t sure exactly what causes your immune system to turn against your liver. Your genes may have something to do with it, since AIH can run in families.
But genes aren’t the whole story. Something you come into contact with may trigger your genes to set autoimmune hepatitis in motion. This could include:
- Medicines such as statins and hydralazine or antibiotics like nitrofurantoin and minocycline
- Infections such as viral hepatitis, herpes, Epstein-Barr, and measles
Children At Risk Of New Unexplained Acute Hepatitis Outbreak Un Health Agency
The world is currently facing a new outbreak of unexplained acute hepatitis infections affecting children, the World Health Organization warned on Thursday, World Hepatitis Day.
The current uptick focuses attention on the thousands of acute viral hepatitis infections that occur every year among children, adolescents, and adults.
Today is #WorldHepatitisDay, a day to raise awareness of viral hepatitis, which leads to severe disease and liver cancer. We are facing a new outbreak of acute hepatitis infections affecting children. Learn more about s plan on our website:
UN Bonn
Recommended Reading: Purina Pro Plan Hp Hepatic
Parenteral Routes: Transmission Of Hepatitis B Hepatitis D And Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B, C, and D viruses are all transmitted by what is known as the parenteral route. Parenteral simply means that these viruses can be introduced by all routes except through the intestinal tract, which leaves the door wide open in terms of possible exposure. Let’s look at the possible transmission routes for each of these types of hepatitis virus more closely.
How Can You Prevent Hepatitis A
There is a vaccine, made from an inactivateddeadvirus to prevent hepatitis A. If you are not sure you have had the vaccine, you can ask your doctor to test you to see if you have been vaccinated.
You can also practice good hand washing hygiene. Make sure you use soap and warm water to wash your hands for at least 15 to 30 seconds after you use the toilet, change diapers, and before and after touching food.
If you are traveling in another country, especially a developing country, drink only bottled water and use only bottled water to brush your teeth, wash your produce, and freeze for ice cubes.
You May Like: How Does Hepatitis A Spread
Who Should Be Vaccinated
Children
- All children aged 1223 months
- All children and adolescents 218 years of age who have not previously received hepatitis A vaccine
People at increased risk for hepatitis A
- International travelers
- Men who have sex with men
- People who use or inject drugs
- People with occupational risk for exposure
- People who anticipate close personal contact with an international adoptee
- People experiencing homelessness
People at increased risk for severe disease from hepatitis A infection
- People with chronic liver disease, including hepatitis B and hepatitis C
- People with HIV
Other people recommended for vaccination
- Pregnant women at risk for hepatitis A or risk for severe outcome from hepatitis A infection
Any person who requests vaccination
There is no vaccine available for hepatitis C.
What Is Hepatitis E
Hepatitis E, also called enteric hepatitis , is similar to hepatitis A, and more prevalent in Asia and Africa. It is also transmitted through the fecal-oral route. It is generally not fatal, though it is more serious in women during pregnancy and can cause fetal complications. Most patients with hepatitis E recover completely.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Rash On Hands
If I Have Hepatitis How Can I Avoid Giving It To Someone Else
For hepatitis A, one of the best things you can do is wash your hands a lot. That will keep the virus out of food and drinks.
If you have hepatitis B and C, you need to find ways to keep others from making contact with your blood. Follow these tips:
- Cover your cuts or blisters.
- Carefully throw away used bandages, tissues, tampons, and sanitary napkins.
- Don’t share your razor, nail clippers, or toothbrush.
- If your blood gets on objects, clean them with household bleach and water.
- Don’t breastfeed if your nipples are cracked or bleeding.
- Don’t donate blood, organs, or sperm.
- If you inject drugs, don’t share needles or other equipment.
Show Sources
Cases Reported In Canada

As of July 27, 2022, there are 22 cases of acute severe hepatitis in children in Canada meeting the national case definition. Two cases previously reported no longer meet the national case definition. Their information is no longer included in the investigation. Case data are preliminary and may change as more information becomes available.
The breakdown by province is as follows:
- Alberta
- Ontario
- Quebec
The children, who are between < 1 and 13 years old, became sick between November 3, 2021 and June 29, 2022. All children were hospitalized. Two children have required a liver transplant. No deaths have been reported. Some children may live in one jurisdiction and receive treatment in another jurisdiction. These children are being counted in the province where they live.
It is important to note that the definition being used to include cases in the national investigation is very broad. This means that any children with acute severe hepatitis where a cause is not certain are being included in initial investigations. Some of these children may have a diagnosis for their liver condition, but they are being included to explore possible factors that may have triggered the condition. PHAC is reporting information to the World Health Organization. Additional information for cases is being reviewed, and the investigation into the possible causes is ongoing.
Read Also: Natural Cure For Hepatitis A
What Causes Hcv
Hepatitis C virus is a liver infection you can catch when the blood of an infected person enters your bloodstream. You can get HCV by:
- sharing drug injection equipment such as needles or syringes
- being born to a mother with HCV
- having an accidental needle stick
- sharing personal items contaminated with HCV+ blood like nail clippers, razors or toothbrushes
- receive a tattoo or body piercing using unsterile equipment
- receiving hemodialysis
- receiving a blood transfusion or organ transplant before 1992 or received clotting factor concentrates before 1987
- having unprotected sex with an infected person, especially for men who have sex with men
- an exposure from a healthcare worker, although this is uncommon
Hepatitis C is not spread through food or water. You also don’t get it from sharing food utensils, breastfeeding your baby, kissing, hugging, holding hands, coughing or sneezing.
Related: Medications Used to Treat Hepatitis C
Who Is At Risk
Anyone who has not been vaccinated or previously infected can get infected with the hepatitis A virus. In areas where the virus is widespread , most hepatitis A infections occur during early childhood. Risk factors include:
- poor sanitation
- living in a household with an infected person
- being a sexual partner of someone with acute hepatitis A infection
- use of recreational drugs
- travelling to areas of high endemicity without being immunized.
Read Also: What Is A Hepatic Diet For Dogs
How Does A Person Get Hepatitis
A person can get hepatitis A through the following sources:
- Food or water contaminated with the fecal matter of an infected person
- Sexual contact
A person can get hepatitis B in many ways, which include:
- Having sexual contact with an infected person
- Sharing needles
- Being in direct contact with an infected persons blood
- Transferred from mother to the fetus
- Getting an infected needle prick
- Being in contact with an infected persons body fluid
A person can get hepatitis C through:
- Sharing infected needles
- Being in direct contact with an infected persons blood
- Getting an infected needle prick
- Having sexual contact with an infected person
Hepatitis D can be spread through:
- Transferred from mother to the fetus
- Being in contact with the infected fluid or blood
- A person can get hepatitis D only if they are infected previously with hepatitis B.
Hepatitis E mainly infects people who eat or drink food or water contaminated with the virus. Under-cooked foods can also spread hepatitis E. It is more dangerous in pregnant women.
Chronic Hepatitis B Infection
People who test positive for the hepatitis B virus for more than six months are diagnosed as having a chronic infection. This means their immune system was not able to get rid of the hepatitis B virus and it still remains in their blood and liver.
The risk of developing a chronic hepatitis B infection is also directly related to the age at which one first becomes exposed to the hepatitis B virus:
- 90% of infected newborns and babies will develop a chronic hepatitis B infection
- Up to 50% of infected children will develop a chronic hepatitis B infection
- 5-10% of infected adults will develop a chronic hepatitis B infection
Learning that you have a chronic hepatitis B infection can be very upsetting. Because most people do not have symptoms and can be diagnosed decades after their initial exposure to the hepatitis B virus, it can be a shock and a surprise to be diagnosed with a chronic hepatitis B infection. The good news is that most people with chronic hepatitis B should expect to live a long and healthy life.
There are effective drug therapies that can control and even stop the hepatitis B virus from further damaging a liver. There are also promising new drugs in the research pipeline that could provide a cure in the very near future. Although the risk of developing a serious liver disease or liver cancer is higher for those living with chronic hepatitis B than those who are not infected, there are still many simple things a person can do to help reduce their risks.
Read Also: Can You Catch Hepatitis C From Your Own Blood
When It Is Serious
Although it is not common, acute hepatitis can become serious, especially if it is not detected right away or if it is left untreated. If the hepatitis worsens, it can limit liver and biliary duct function. This can increase your risk for bleeding, interfere with protein production, and compromise your immune system.
Some people may also experience acute liver failure after being diagnosed with acute hepatitis. Liver failure should be caught early so that medical interventions can be initiated promptly.
Hiv And Hbv Coinfection
About 2% of people with HIV in the United States are coinfected with HBV both infections have similar routes of transmission. People with HIV are at greater risk for complications and death from HBV infection. All people with HIV are recommended to be tested for HBV, and if susceptible, are further recommended to receive the hepatitis B vaccination or, if chronically infected, evaluated for treatment to prevent liver disease and liver cancer. For more information about HIV and HBV coinfection, visit HIV.govâs pages about hepatitis B and HIV coinfection.
Read Also: New Meds For Hepatitis C
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis E Causes And Treatment
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis A
If you have not had the vaccine, and your infection has been confirmed by a blood sample, your healthcare provider might give you the hepatitis A vaccine or immune globulin . This only works if the medicine is given within two weeks of you being exposed to HAV.
If you were exposed and are unable to get the vaccine or the immune globulin, you are likely to recover without treatment. However, your healthcare provider will probably recommend that you follow the following self-care recommendations:
- Get plenty of rest.
- Eat a healthy diet.
- Avoid alcohol.
- Review any type of medicineprescription and over-the-counterthat you take with your healthcare provider. Even things like supplements or vitamins could cause damage to your liver.
Screening For Liver Cancer
If people have chronic hepatitis B, screening for liver cancer is done every 6 months. The following are done:
-
Ultrasonography
-
Sometimes blood tests to measure the level of alpha-fetoprotein
The level of alpha-fetoproteinâa protein normally produced by immature liver cells in fetusesâusually increases when liver cancer is present.
You May Like: How Bad Is Hepatitis B
How Do You Know If Hepatitis B Is Acute Or Chronic
Most healthy adults who are infected have no symptoms and are able to clear the virus without any problems. Some adults are unable to clear the virus after six months and are diagnosed with a chronic infection. A simple blood test can diagnose an acute or chronic infection with the hepatitis B virus.
Is hepatitis B considered chronic?
Hepatitis B is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis B virus. Some people with hepatitis B are only sick for a few weeks , but for others the disease progresses to a serious and permanent disease called chronic hepatitis B.
Deterrence And Patient Education
Vaccinations for both hepatitis A virus and hepatitis B virus have been available since the 1990s and have significantly decreased the incidence of these infections. Hepatitis A virus gets transferred by fecal-oral contamination, and improved food handling, water purification, and improved hygiene will reduce the risk of spreading infection. The risk of contracting hepatitis B and hepatitis C infection can be decreased by avoiding IV drug use and safe sex practices.
Accidently toxic ingestion of acetaminophen by children can be reduced with safe storage practices out of reach from children and utilizing packaging that utilize childproof safety precautions. Also, in adults, unintentional toxic ingestion can be reduced with education about the many non-prescription products which contain acetaminophen.
For stable minimally symptomatic patients, if an etiology for acute hepatitis is not determined initially, then they need follow-up to monitor for the normalization of the liver tests or further evaluation if the abnormal test results continue.
You May Like: Can Hepatic Steatosis Be Reversed
Treatment Of Acute Viral Hepatitis
-
Supportive care
For most people with acute viral hepatitis, special treatment is not necessary. However, people with severe acute hepatitis may require hospitalization so that symptoms can be treated. If doctors suspect that fulminant hepatitis is developing, the person is hospitalized so that mental status can be monitored, liver tests can be done, and doctors can determine whether liver transplantation is needed.
After the first several days, appetite usually returns and people do not need to stay in bed. Severe restrictions of diet or activity are unnecessary, and vitamin supplements are not required. Most people can safely return to work after the jaundice clears, even if their liver test results are not quite normal.
People with hepatitis should not drink alcohol until they have fully recovered.
The infected liver may not process drugs normally. So a doctor may need to stop a drug or reduce the dosage of a drug that could accumulate to harmful levels in the body . Thus, people with hepatitis should tell their doctor all the drugs they are taking , so that the dosage of the drug can be adjusted if necessary.
If itching occurs, cholestyramine, taken by mouth, is often effective.