What Are The Recommended Schedules For Hepatitis B Vaccination
- The vaccination schedule most often used for children and adults is 3 intramuscular injections, the second and third doses administered 1 and 6 months, respectively, after the first dose.
Alternate schedules have been approved for certain vaccines and/or populations.
Recommended Immunization Schedule for Children and Adolescents Aged 18 Years or Younger, UNITED STATES, 2017
Hepatitis B vaccine :
- Monovalent Hepatitis B vaccine should be administered within 24h of birth for medically stable infants weighing 2,000 grams born to hepatitis B surface antigen -negative mothers. The recommendations for vaccination of infants < 2,000 grams remain unchanged.
- Preterm infants weighing < 2,000 g born to HBsAg-negative mothers should receive the first dose of vaccine 1 month after birth or at hospital discharge.
Who Is Most Affected
In the United States, rates of new HBV infections are highest among adults aged 40-49 years, reflecting low hepatitis B vaccination coverage among adults at risk. The most common risk factor among people with new HBV infections is injecting drugs, related to the opioid crisis.
The highest rates of chronic hepatitis B infection in the United States occur among foreign-born individuals, especially people born in Asia, the Pacific Islands, and Africa. Approximately 70% of cases in the United States are among people who were born outside of the United States. CDC developed this map of the geographic distribution of hepatitis B around the world – PDF. Other groups who have higher rates of chronic HBV infection include people who inject drugs and men who have sex with men.
How Likely Is Hepatitis B Virus Infection To Become Chronic
The risk for chronic infection varies according to the age at infection and is greatest among young children. Approximately 90% of infants and 25%50% of children aged 15 years will remain chronically infected with hepatitis B virus . By contrast, approximately 95% of adults recover completely from hepatitis B virus infection and do not become chronically infected.
You May Like: Best Medicine For Hepatitis B
Medically Reviewed By Dr Gerardo Sison Pharmd
Gerardo Sison, Pharm.D., is a registered pharmacist who has worked in clinical and retail settings providing drug education for healthcare professionals and patients alike. He graduated Cum Laude from the University of Florida where he earned a Doctorate of Pharmacy . He piloted a longitudinal clinical research program and completed his clinical internship at St. Josephs Hospital in Tampa, Florida. Read More > >
Should Persons Be Tested For Immunity To Hepatitis B Before Being Vaccinated
Routine prevaccination testing for immunity has not been recommended because it has not generally been found to be cost-effective. However, in adult populations that have an expected high prevalence of hepatitis B virus infection , conducting prevaccination serologic testing for susceptibility prior to or at the same time of the initial vaccine dose might be considered to be cost saving, by reducing the cost of the complete the vaccination series.
Prevaccination testing for susceptibility is recommended for foreign-born persons born in Africa, Asia, the Pacific Islands, and other regions with high endemicity of hepatitis B virus infection unvaccinated household, sexual, and needle-sharing contacts of HBsAg-positive persons and for HIV-infected persons. Serologic testing should not be a barrier to vaccination. The first vaccine dose should be administered immediately after collection of the blood sample for serologic testing. Vaccination of persons who are immune to hepatitis B virus infection because of current or previous infection or vaccination is not harmful and does not increase the risk for adverse events.
Also Check: How Long Does A Person Live With Hepatitis C
Emerging Hbv Curative Therapies
There are numerous new HBV drugs in the pipeline. There are two main therapeutic strategies in the approach to HBV cure: direct-acting antivirals targeting various stages of the HBV life cycle and immunomodulators that aim to improve host immune response . Here, we focus on novel agents in phase 2/3 trials with published data on human subjects, as these agents are further down the pipeline and have the potential to reach clinical care sooner .
FIG. 4
Who Is At Risk
Anyone who has not been vaccinated or previously infected can get infected with the hepatitis A virus. In areas where the virus is widespread , most hepatitis A infections occur during early childhood. Risk factors include:
- poor sanitation
- living in a household with an infected person
- being a sexual partner of someone with acute hepatitis A infection
- use of recreational drugs
- travelling to areas of high endemicity without being immunized.
Don’t Miss: What Medicine Cures Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B Virus Diagnosis
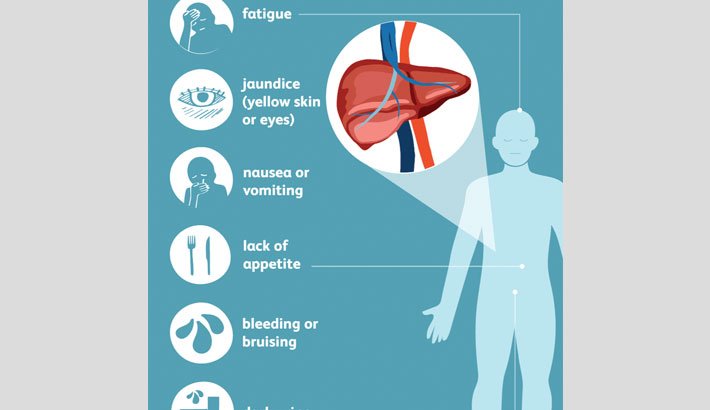
Your doctor will examine you and look for signs of liver damage, such as yellowing skin or belly pain. Tests that can help diagnose hepatitis B or its complications are:
- Blood tests and Hepatitis Serology. Blood tests can detect signs of the hepatitis B virus in your body and tell your doctor whether its acute or chronic. A simple blood test can also determine if youre immune to the condition.
- Liver ultrasound. A special ultrasound called transient elastography can show the amount of liver damage.
- Liver biopsy. Your doctor might remove a small sample of your liver for testing to check for liver damage. During this test, your doctor inserts a thin needle through your skin and into your liver and removes a tissue sample for laboratory analysis.
Laboratory diagnosis of hepatitis B infection focuses on the detection of the hepatitis B surface antigen .
- Acute hepatitis B virus infection is characterized by the presence of hepatitis B surface antigen and immunoglobulin M antibody to the core antigen, HBcAg . During the initial phase of infection, patients are also seropositive for hepatitis B e antigen . Hepatitis B e antigen is usually a marker of high levels of replication of the virus. The presence of HBeAg indicates that the blood and body fluids of the infected individual are highly infectious.
How long does it take for blood to test HBsAg-positive after exposure to Hepatitis B virus ?
The Hepatitis B Vaccine
The hepatitis B vaccine is one of the most effective ways to prevent hepatitis B. Its usually divided into three doses, which are given over the course of six months. In many countries, infants receive their first dose of the vaccine at birth.
The Centers for Disease Control recommends that all children under the age of 19 be vaccinated if they havent already received the vaccination. Adults can also get the hepatitis B vaccine, and its generally recommended if you have an increased risk of infection due to:
- traveling to or living in a region where hepatitis B is common
- being sexually active with more than one partner
- working in a medical setting
- using intravenous drugs
If youve been exposed to the hepatitis B virus and havent been vaccinated, try to see a doctor right away. They can administer the first dose of the vaccine, though youll need to follow up to receive the remaining doses over the next few months.
They can also prescribe a medication called
Recommended Reading: Natural Remedies For Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B E Antigen
HBeAg is a secreted product of the nucleocapsid gene of hepatitis B virus and is released from the infected liver cells into the blood that is found in serum during acute and chronic hepatitis B. Its presence indicates that the virus is replicating and the infected person has high levels of hepatitis B virus.
- A positive HBeAg indicates high levels of virus in the blood and a person is considered infectious.
- A negative HBeAg indicates very low to no virus in the blood and a person is usually considered less infectious sometimes this can indicate a person has a mutant hepatitis B virus .
HBeAg test detects how much virus is in the blood as a result of very active viral replication. A negative test result indicates the virus may not be actively reproducing in the liver. In general, a person is considered very infectious when the HBeAg test is positive, and less infectious when the test is negative. The loss of e-Antigen can occur naturally or as a result of drug treatment. Sometimes a negative HBeAg test result can indicate a mutant hepatitis B virus is present. So, the absence of e-Antigen does not always mean there is little or no active viral replication. The doctor can confirm with additional tests.
What Are The Hepatitis B Vaccines Licensed For Use In The United States
Two single-antigen vaccines and three combination vaccines are currently licensed in the United States.
Single-antigen hepatitis B vaccines
- RECOMBIVAX HB®
Combination vaccines
- PEDIARIX®: Combined hepatitis B, diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis , and inactivated poliovirus vaccine. Cannot be administered before age 6 weeks or after age 7 years.
- TWINRIX®: Combined Hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccine. Recommended for persons aged 18 years who are at increased risk for both Hepatitis A virus and HBV infections.
- COMVAX® : Combined hepatitis B-Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine. Cannot be administered before age 6 weeks or after age 71 months.
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis C Antibody Mean
Who Is More Likely To Get Hepatitis B
People are more likely to get hepatitis B if they are born to a mother who has hepatitis B . Hepatitis B virus can spread from mother to child during birth. For this reason, people are more likely to have hepatitis B if they 15):
- were born in a part of the world where 2 percent or more of the population has hepatitis B infection
- were born in the United States, didnt receive the hepatitis B vaccine as an infant, and have parents who were born in an area where 8 percent or more of the population had hepatitis B infection
People are also more likely to have hepatitis B if they:
- are infected with HIV, because hepatitis B and HIV spread in similar ways
- have lived with or had sex with someone who has hepatitis B
- have had more than one sex partner in the last 6 months or have a history of sexually transmitted disease
- are men who have sex with men
- are injection drug users
- work in a profession, such as health care, in which they have contact with blood, needles, or body fluids at work
- live or work in a care facility for people with developmental disabilities
- have diabetes
- have hepatitis C
- have lived in or travel often to parts of the world where hepatitis B is common External link
- have been on kidney dialysis
- live or work in a prison
- had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before the mid-1980s
In the United States, hepatitis B spreads among adults mainly through contact with infected blood through the skin, such as during injection drug use, and through sexual contact 16).
Concurrent Administration Of Vaccines
HA vaccine may be administered concomitantly with other vaccines or with Ig. Different injection sites and separate needles and syringes must be used for concurrent parenteral injections.
If concurrently providing HA-containing vaccine and Ig, separate anatomic injection sites should be used for each injection.
Passive immunization with human Ig preparations can interfere with the immune response to measles-mumps-rubella , measles-mumps-rubella-varicella and univalent varicella vaccines . These vaccines should be given at least 14 days prior to administration of a human Ig preparation, or delayed until the antibodies in the Ig preparation have degraded. Refer to Blood Products, Human Immunoglobulin and Timing of Immunization in Part 1 for additional information.
Refer to Timing of Vaccine Administration in Part 1 for additional information about concurrent administration of vaccines.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis A
How Long Does Protection From Hepatitis B Vaccine Last
Studies indicate that immunologic memory remains intact for at least 20 years among healthy vaccinated individuals who initiated hepatitis B vaccination > 6 months of age. The vaccine confers long-term protection against clinical illness and chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Cellular immunity appears to persist even though antibody levels might become low or decline below detectable levels.
Among vaccinated cohorts who initiated hepatitis B vaccination at birth, long-term follow-up studies are ongoing to determine the duration of vaccine-induced immunity.
Hepatitis C And Blood Spills
When cleaning and removing blood spills, use standard infection control precautions at all times:
- Cover any cuts or wounds with a waterproof dressing.
- Wear single-use gloves and use paper towel to mop up blood spills.
- Clean the area with warm water and detergent, then rinse and dry.
- Place used gloves and paper towels into a plastic bag, then seal and dispose of them in a rubbish bin.
- Wash your hands in warm, soapy water then dry them thoroughly.
- Put bloodstained tissues, sanitary towels or dressings in a plastic bag before throwing them away.
Recommended Reading: Can You Catch Hepatitis C From Spit
Causes Of Noninfectious Hepatitis
Although hepatitis is most commonly the result of an infection, other factors can cause the condition.
Alcohol and other toxins
Excess alcohol consumption can cause liver damage and inflammation. This may also be referred to as alcoholic hepatitis.
The alcohol directly injures the cells of your liver. Over time, it can cause permanent damage and lead to thickening or scarring of liver tissue and liver failure.
Other toxic causes of hepatitis include misuse of medications and exposure to toxins.
Autoimmune system response
In some cases, the immune system mistakes the liver as harmful and attacks it. This causes ongoing inflammation that can range from mild to severe, often hindering liver function. Itâs three times more common in women than in men.
How Is Hepatitis C Diagnosed
Specific or increased levels of liver enzymes in the blood raise the suspicion of a virus hepatitis. Since 1991, it has been possible to detect virus antibodies against the Hepatitis C virus in the blood of patients. Because the screening test is not 100% reliable, a positive test result must always be confirmed.
A negative result indicates the absence of Hepatitis C. With an acute infection it can sometimes take many weeks for the body to produce antibodies. Then it may be necessary to do a complex additional test for the RNA virus itself. This research can only take place in specialized laboratories.
If an active virus infection is detected, then it must be investigated how severe the inflammation is and to what extent damage to the liver has already occurred. Physical examination assesses the size of the liver and spleen and looks for signs of poor functioning of the liver, such as jaundice. This examination is supplemented by a sound photograph and blood test. If this is found that although there is Hepatitis C virus in the blood, there is no inflammatory activity in the liver and there is also no liver injury present, it will be decided to wait.
Here it will be assessed whether antiviral agents should be started. In this assessment, it will often be necessary to remove a piece of tissue from the liver in order to obtain more certainty about the nature and severity of the condition using a microscope.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis B And C
Prevention Is The Best Medicine
Even though hepatitis C rarely spreads within a household, if you or a family member have the disease, it’s wise to take precautions to prevent its spread especially if anyone in your home is immune compromised, or has cuts or open sores that increase the risk of infection.
In general, use these common sense preventive tips:
- Unless you are in a long-term, monogamous relationship, practice safe sex.
- Clean up spilled or dried blood with a bleach-based cleaning solution and wear rubber gloves.
- Do not share razors.
- Do not share toothbrushes. “Though hepatitis C is not transmitted through saliva, there might be blood on the toothbrush,” Reau says.
Note that hepatitis C is not transmitted by sharing eating utensils, hugging, kissing, coughing or sneezing.
Prevention Of Hepatitis B Virus Infection
The hepatitis B vaccine is typically given as three or four injections over six months. You cant get hepatitis B from the vaccine.
The hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for:
- Newborns
- Children and adolescents not vaccinated at birth
- Those who work or live in a center for people who are developmentally disabled
- People who live with someone who has hepatitis B
- Health care workers, emergency workers and other people who come into contact with blood
- Anyone who has a sexually transmitted infection, including HIV
- Men who have sex with men
- People who have multiple sexual partners
- Sexual partners of someone who has hepatitis B
- People who inject illegal drugs or share needles and syringes
- People with chronic liver disease
- People with end-stage kidney disease
- Travelers planning to go to an area of the world with a high hepatitis B infection rate
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Is It Curable
Hepatitis B Cure In Human Trials
Australian researchers have begun clinical trials of a combination drug therapy that has proven to be 100 percent effective as a hepatitis B cure in preclinical models. The therapy combines birinapant, an antiviral drug, and entecavir, an anticancer drug. The two drugs work together to eliminate the hepatitis B virus, or HBV, from the body.
Take Precautions To Avoid Hepatitis B Virus
Other ways to reduce your risk of Hepatitis B virus include:
- Know the Hepatitis B virus status of any sexual partner. Dont engage in unprotected sex unless youre absolutely certain your partner isnt infected with hepatitis B virus or any other sexually transmitted infection.
- Use a new latex or polyurethane condom every time you have sex if you dont know the health status of your partner. Remember that although condoms can reduce your risk of contracting hepatitis B virus, they dont eliminate the risk.
- Dont use illegal drugs. If you use illicit drugs, get help to stop. If you cant stop, use a sterile needle each time you inject illicit drugs. Never share needles.
- Be cautious about body piercing and tattooing. If you get a piercing or tattoo, look for a reputable shop. Ask about how the equipment is cleaned. Make sure the employees use sterile needles. If you cant get answers, look for another shop.
- Ask about the hepatitis B vaccine before you travel. If youre traveling to a region where hepatitis B is common, ask your doctor about the hepatitis B vaccine in advance. Its usually given in a series of three injections over a six-month period.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Home Test Kit