Hepatitis B Vaccination Schedule For Children And Infants
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that babies and children receive three 0.5 milliliter doses of either Engerix-B or Recombivax HB, starting just after birth.
The current recommended hepatitis B vaccine schedule for children and infants is as follows:
| Hepatitis B Vaccination Schedule for Infants and Children | |
|---|---|
| Hepatitis B Vaccine Dose | |
| 3 | 618 months old |
If your child is undergoing hemodialysis, your healthcare provider may recommend that they receive additional doses of the HBV vaccine.
Does The Hepatitis B Vaccine Have Side Effects
Some children will develop pain or soreness in the local area of the shot, and low-grade fever.
There is one extremely rare, but serious, side effect. About 1 out of every 600,000 doses of the hepatitis B vaccine will cause a severe allergic reaction, called anaphylaxis, with symptoms including swelling of the mouth, difficulty breathing, low blood pressure or shock. Anaphylaxis usually occurs within 15 minutes of receiving the vaccine. Although anaphylaxis can be treated, it is quite frightening. People should remain at the doctors office for about 15 minutes after getting the vaccine.
Although the hepatitis B vaccine is made in yeast cells, no one has ever been shown to be allergic to the yeast proteins contained in the hepatitis B vaccine .
Persons New To Canada
Health care providers who see persons newly arrived in Canada should review the immunization status and update immunization for these individuals, as necessary. In many countries outside of Canada, HB vaccine is in limited use.
All persons from a country that is endemic for HB should be assessed and vaccinated against HB if not immune and not infected. Individuals born in developing countries are more likely to be carriers of HB, necessitating vaccination of their sexual and household contacts based on review of their serologic test results. HB vaccine is recommended for all household contacts whose families have immigrated to Canada from areas in which there is a high prevalence of HB and who may be exposed to HB carriers through their extended families or when visiting their country of origin.
Children adopted from countries in which there is a high prevalence of HB infection should be screened for HBsAg and, if positive, household or close contacts in the adopting family should be immunized before adoption or as soon as possible thereafter. Adults going to pick-up children from these countries should be vaccinated before departure. Refer to Immunization of Persons New to Canada in Part 3 for additional information.
Don’t Miss: Pro Plan Hepatic Dog Food
What To Do If You Miss A Scheduled Dose
The recommended schedule for the HBV vaccine follows a three-dose pattern, with all doses complete within 6 months. The good news is that if you miss a dose, you dont need to start the series of shots all over.
If you missed getting the second dose 1 month after the first, make an appointment as soon as possible. If you miss the third dose, you should also try to get it as quickly as possible. Keep in mind that the second and third doses
How Do You Catch Hepatitis B Virus
Blood from a person infected with hepatitis B virus is heavily contaminated with the virus. As a result, contact with blood is the most likely way to catch hepatitis B. Even casual contact with the blood of someone who is infected can cause infection.
Healthcare workers are at high risk of catching the disease, as are intravenous drug users and newborns of mothers infected with the virus. Sexual contact can also expose people to infection. The virus is also present in low levels in saliva.
You May Like: What Kind Of Hepatitis Is Contagious
The Hepatitis B Vaccine And Immunosuppressants
If you are taking or about to start taking a medication that suppresses your immune response, let your healthcare provider know. Immunosuppressants may make certain vaccines less effective. Your healthcare provider may recommend that you get the hepatitis B vaccine at a particular time during your course of medication.
How Is The Hepatitis B Vaccine Made
People are protected against hepatitis B virus infection by making an immune response to a protein that sits on the surface of the virus. When hepatitis B virus grows in the liver, an excess amount of this surface protein is made. The hepatitis B vaccine is made by taking the part of the virus that makes surface protein and putting it into yeast cells. The yeast cells then produce many copies of the protein that are subsequently used to make the vaccine. When the surface protein is given to children in the vaccine, their immune systems make an immune response that provides protection against infection with the hepatitis B virus.
The first hepatitis B vaccine was made in the 1980s by taking blood from people infected with hepatitis B virus and separating or purifying the surface protein from the infectious virus. Because blood was used, there was a risk of contaminating the vaccine with other viruses that might be found in blood, such as HIV. Although contamination with HIV was a theoretical risk of the early, blood-derived hepatitis B vaccine, no one ever got HIV from the hepatitis B vaccine. That is because the blood used to make vaccine was submitted to a series of chemical treatments that inactivated any possible contaminating viruses. Today, there is no risk of contaminating the vaccine with other viruses because the surface protein is manufactured in the laboratory.
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatic Artery Infusion
Why Do You Need A Hepatitis B Shot
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that cant be transferred person-to-person unless you have contact with an infected persons bodily fluids. Annual infection rates of HBV are going down in the United States thanks to vaccines. So you might be wondering if you or your child needs a shot to protect against hepatitis B.
Emergency Hepatitis B Vaccination
If you have been exposed to the hepatitis B virus and have not been vaccinated before, you should get immediate medical advice, as you may benefit from having the hepatitis B vaccine.
In some situations, you may also need to have an injection of antibodies, called specific hepatitis B immunoglobulin , along with the hepatitis B vaccine.
HBIG should ideally be given within 48 hours, but you can still have it up to a week after exposure.
Don’t Miss: Is There A Cure For Hepatitis C Now
Dosage Forms & Strengths
Contraindicated
- belimumab
belimumab decreases effects of hepatitis b vaccine by immunosuppressive effects risk of infection. Contraindicated. Do not administer live vaccines 30 days before or concurrently with belimumab.
Serious – Use Alternative
Monitor Closely
Minor
-
chloroquine decreases effects of hepatitis b vaccine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ozanimod
ozanimod decreases effects of hepatitis b vaccine by immunosuppressive effects risk of infection. Minor/Significance Unknown. No clinical data are available on the efficacy and safety of vaccinations in patients taking ozanimod. Vaccinations may be less effective if coadministered with ozanimod.
Does Hepatitis B Go Away
In most cases, hepatitis B goes away on its own. You can relieve your symptoms at home by resting, eating healthy foods, drinking plenty of water, and avoiding alcohol and drugs. Also, find out from your doctor what medicines and herbal products to avoid, because some can make liver damage caused by hepatitis B worse.
Also Check: How Do You Know If You Have Hepatitis B
How Do Inactivated Viral Vaccines Work
Inactivated viralvaccines are sterile biologic products that provide immunity against viral infections. Inactivated viral vaccines work by stimulating the bodys immune system to produce antibodies against specific types of viruses, and protect a person from becoming infected when exposed to these viruses.
In the case of SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus that causes respiratory illness and has led to the COVID-19 pandemic, vaccines do not entirely prevent infection but protect vaccinated individuals from serious illness and hospitalization from the disease.
Inactivated viral vaccines contain particles of proteins or genetic material from viruses. Inactivated viral vaccines may also contain substances that preserve and stabilize the vaccine, and enhance immune response. Some viral vaccines are delivered in inactivated harmless viruses such as human adenovirus.
Inactivated viral vaccines may be made from:
- Surface proteins of the viruses enable the virus to hold on to a human cell, enter inside and replicate.
- Modified RNA particles from the virus can enter host cells and induce the production of viral antigen, which stimulates an immune response from the body.
- Recombined DNA material from multiple strains and subtypes of viruses, killed to eliminate disease-causing capability.
Currently, inactivated viral vaccines approved by the FDA protect against viral infectious diseases that include:
- Coronavirus disease , caused by SARS-Cov-2 virus
Adults
Babies And Children Can Develop Chronic Hbv

You may be wondering why the recommendations for the HBV vaccine start on the first day of life.
Adults who contract HBV will likely not experience long-term complications from hepatitis B. But the same is not the case for babies. As many as of babies who contract an HBV infection at birth from their mothers become chronically infected with HBV.
Children between the ages of 1 and 5 who get an HBV infection have a 25 percent of people who become chronically infected during childhood will develop liver cancer or cirrhosis. Thats why pediatricians want children to have immunity from HBV from the earliest possible age. Many babies and children exposed to HBV receive post-exposure prophylaxis, which decreases chance of infection.
If youre pregnant, youll most likely have a blood test to see if youre positive for hepatitis B. This allows doctors to find out if theres a chance that you could pass on the virus. These tests are highly sensitive and have a good accuracy rate, but they arent perfect. Additionally, a pregnant person may become infected between the time of the test and giving birth. The first dose of the vaccine given at birth lowers the risk of a newborn baby contracting hepatitis B.
Recommended Reading: How Long Can You Live With Hepatitis B
Screen For Contraindications And Precautions
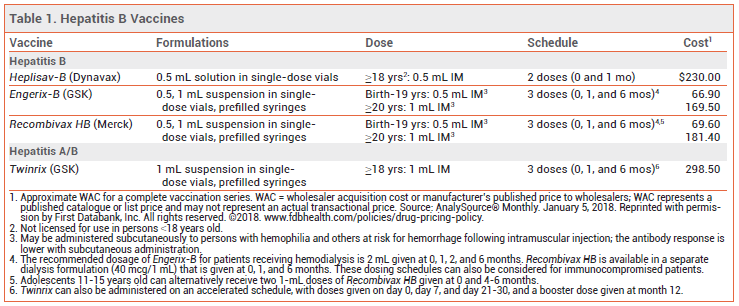
- Do not administer Heplisav-B to individuals with a history of severe allergic reaction after a previous dose of any hepatitis B vaccine or to any component of Heplisav-B, including yeast.
- Consult the package insert for precautions, warnings, and contraindications and Hepatitis B Vaccine Safety for additional information and possible side effects.
Is It Okay To Get An Extra Dose Of Hepatitis B Vaccine
Yes. Although extra doses of vaccine are not recommended, you can think of the extra dose as another chance for the immune system to see the hepatitis B virus. A vaccine is not the only time the immune system will see the virus or bacteria contained in it. People may be exposed to the virus or bacteria at school or the store or when visiting family or friends. An extra dose of vaccine is like one more exposure, except the difference is that the virus or bacteria in any vaccine has been made safe, so it wont make you ill.
Read Also: Hepatitis A And B Shot
Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule For Adults
Hepatitis B is a vaccine-preventable viral disease that involves inflammation of the liver.
The hepatitis B virus usually leads to a short-term infection known as acute hepatitis B. If their infection is left untreated, some people develop chronic hepatitis B. Chronic hepatitis B is a serious, permanent condition that can cause organ damage, cirrhosis , liver cancer, liver failure, and even death.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , all people should be vaccinated against hepatitis B starting at birth. Adults who are at risk of developing hepatitis B should also receive the vaccine, which is highly effective in preventing infection.
Read on to learn more about the hepatitis B vaccine for adults, including who should receive it, the details of the dosage schedule, side effects, and more.
Latest Infectious Disease News
The drug interactions listed above are not all of the possible interactions or adverse effects. For more information on drug interactions, visit the RxList Drug Interaction Checker.
It is important to always tell your doctor, pharmacist, or health care provider of all prescription and over-the-counter medications you use, as well as the dosage for each, and keep a list of the information. Check with your doctor or health care provider if you have any questions about the medication.
You May Like: Treatment For Hepatitis C Medications
Facts About Hepatitis B
- Two billion people, or one in three, have been infected with hepatitis B worldwide. Of these, almost 300 million live with chronic hepatitis B. This means about 1 of every 26 people throughout the world are living with a chronic hepatitis B infection.
- Each year about 900,000 people die from hepatitis B worldwide, and about 2,000 of these deaths occur in the United States.
- Hepatitis B is transmitted through blood and is 100 times more infectious than HIV. An estimated one billion infectious viruses are in one-fifth of a teaspoon of blood of an infected person, so exposure to even a very small amount, such as on a shared toothbrush, can cause infection.
- Hepatitis B is sometimes referred to as the silent epidemic because most people who are infected do not experience any symptoms.
- Liver cancer accounted for about 5% of cancer deaths in the U.S. during 2020.
- Almost half of liver cancers are caused by chronic infection with hepatitis B.
- The World Health Organization recommends the inclusion of hepatitis B vaccine in immunization programs of all countries in 2019, more than 8 of 10 infants born throughout the world received three doses of hepatitis B vaccine.
For Adults And Children
This vaccine schedule involves three doses within 2 months, followed by a booster dose at 1 year.
The initial accelerated doses provide immediate protection from HBV, and the booster dose helps provide long-term protection.
Below is the accelerated vaccination schedule approved for both adults and children:
| Vaccine series | |
|---|---|
| 2 months after the first dose | 1 year after the first dose |
Recommended Reading: How Many Hepatitis C Genotypes Are There
Interchangeability And Dosing Schedule
- 2-dose HepB vaccine series only applies when both doses consist of HepB-CpG, administered at least 4 weeks apart.
- Series consisting of a combination of 1 dose of HepB-CpG and a vaccine from a different manufacturer should do the following:
- Adhere to the 3-dose schedule minimum intervals of 4 weeks between dose 1 and 2, 8 weeks between dose 2 and 3, and 16 weeks between dose 1 and 3. However, if HepB-CpG is substituted for dose 2 of HepB-alum, a provider has the option of administering the next dose of HepB-CpG a minimum of 4 weeks from the previous dose for a complete series.
What Is Hepatitis B Virus
Hepatitis B virus attacks the liver. Hepatitis B virus infections are known as the “silent epidemic” because many infected people don’t experience symptoms until decades later when they develop hepatitis , cirrhosis , or cancer of the liver . Every year in the United States about 22,000 new hepatitis B infections occur and about 2,000 people die from their infections.
You May Like: Hepatitis C Viral Load Test
Hepatitis B Vaccine Side Effects
Most people only experience mild, short-term side effects from the hepatitis B vaccine. Common side effects include:
- Headache
- Fever
- Pain, redness, or swelling at the site of injection
Severe allergic reactions to the hepatitis B vaccine are very rare. If you have symptoms of an allergic reaction shortly after getting the HepB vaccinesuch as difficulty breathing, facial swelling, or hivesseek medical help immediately.
The hepatitis B vaccine is safe and effective for most people. However, there are certain people who should not get the HepB vaccine, including:
- People who are moderately or severely ill at the time of vaccination
- People who have had a severe allergic reaction to yeast
- People who have had a severe allergic reaction to a hepatitis B vaccine in the past
International Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedules
*Please note that the first dose should be given as soon as possible. Additional doses require minimum time intervals between doses in order for the vaccine to be effective.
The hepatitis B vaccine is an injection that is generally given in the arm and as a three-dose series. The World Health Organization recommends a 0, 1, and 6-month vaccine schedule, though schedules may vary based on a countrys national immunization program. Completing the hepatitis B vaccine series, preferably beginning at birth, will ensure protection against hepatitis B, hepatitis delta and lower the lifetime risk of liver cancer. Greater than 90% of babies and up to 50% of young children who are not vaccinated and are infected with hepatitis B will have lifelong infection, which makes the birth dose essential to their protection. Please note that the vaccine brand name, manufacturer and associated schedules for adults, children and infants may be unique to different countries, though there is a list of WHO prequalified vaccines.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Infants
The World Health Organization recommends all infants receive the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth and to complete the vaccine series with additional shots at 1 month and 6 months of age. Beginning the hepatitis B vaccine at birth will ensure protection against hepatitis B for life.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Children and Adults
4-Dose Combination Vaccine Series for Infants
Additional Resource Links:
Read Also: How Do You Prevent Hepatitis C