What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a contagious liver disease that ranges in severity from a mild illness lasting a few weeks to a serious, lifelong illness. It results from infection with the hepatitis B virus. Hepatitis B can be either “acute” or “chronic.”
Acute hepatitis B virus infectionis a short-term illness that occurs within the first 6 months after someone is exposed to HBV. Acute infection can – but usually does not – lead to chronic infection.
Chronic hepatitis B virus infectionis a long-term illness that occurs when the virus remains in a person’s body.
The younger a person is when infected with hepatitis B virus, the greater his or her chance of developing chronic hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B virus is contained in blood and body fluids. It is passed from person to person when blood, semen, or other body fluid infected with the virus enters the body of a person who is not infected. You cannot get hepatitis B by shaking hands or hugging someone. It is also not spread through food or water.
People can become infected with the virus during activities such as:
- Birth
- Sex with an infected partner
- Sharing needles, syringes, or other drug-injection equipment
- Sharing items such as razors or toothbrushes with an infected person
- Direct contact with the blood or open sores of an infected person
- Exposure to blood by sticks from needles or other sharp instruments
People can have hepatitis B infection and not know it. People can pass the virus to others and not know it.
What Does High/low Viral Load Mean
Viral load is the amount of virus present in the bloodstream. It is expressed as the amount of viral genetic material per milliliter of blood. The amount of virus does not predict how severe the liver disease is or will become. The level of the viral load does not tell us anything about the risk of liver damage or how sick someone is. In hepatitis C, it matters if virus is present or absent. Some treatment regimens can be shortened if the patient has a low viral load to start with, but most often, treatment regimens are the same for people with high hepatitis C viral loads or low viral loads.
The RNA test is essential for making the diagnosis of hepatitis C infection–having a positive RNA test is the definition of having infection. After the diagnosis is made, the RNA level does not need to be checked over and over unless it is checked during the time that the patient is undergoing treatment. During treatment, regular RNA tests are done to follow the dropping virus level until it reaches an undetectable state. But before treatment and after treatment, repeated RNA testing is not necessary.
What Foods Should I Avoid
Everyone should avoid eating a lot of fat, cholesterol, salt and processed sugar, even if their liver is healthy. In addition, those with HCV should limit or avoid alcohol. Drinking alcohol will speed up liver damage.
Eating properly can help decrease some of the symptoms of Hepatitis C, like feeling tired and sick. Drink lots of water for general health benefits. HCV is not a digestive disease diet will not affect the disease. Your provider may put you on a special diet if you have advanced liver disease.
Read Also: How Can I Tell If I Have Hepatitis C
Spread Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is spread through blood-to-blood contact when blood from a person with hepatitis C enters another persons bloodstream.
The most common way people become infected with hepatitis C in Australia is by sharing injecting equipment such as needles, syringes, spoons and tourniquets. It is possible to be infected with hepatitis C after only one risk event.
Hepatitis C may also be spread through:
- tattooing and body piercing with equipment that has not been properly cleaned, disinfected or sterilised such as backyard tattoos’. Registered parlours with appropriate infection control procedures are not a risk
- needlestick injuries in a healthcare setting
- receiving blood transfusions in Australia prior to 1990 before hepatitis C virus testing of blood donations was introduced
- medical procedures, blood transfusions or blood products and mass immunisation programs provided in a country other than Australia
- pregnancy or childbirth there is a 5% chance of a mother with chronic hepatitis C infection passing on the virus to her baby during pregnancy or childbirth.
Breastfeeding is safe, however if nipples are cracked or bleeding cease breastfeeding until they have healed.
Less likely possible routes of transmission of hepatitis C include:
Hepatitis C cannot be transmitted by:
- kissing
- sharing food, cups or cutlery
- shaking hands or day-to-day physical contact.
How Do You Get Hepatitis C

Hepatitis C spreads when blood or body fluids contaminated with the hepatitis C virus get into your bloodstream through contact with an infected person.
You can be exposed to the virus from:
- Sharing injection drugs and needles
- Having sex, especially if you have HIV, another STD, several partners, or have rough sex
- Being stuck by infected needles
- Birth — a mother can pass it to a child
- Sharing personal care items like toothbrushes, razor blades, and nail clippers
- Getting a tattoo or piercing with unclean equipment
You canât catch hepatitis C through:
- Breastfeeding
- Casual contact
- Have been on long-term kidney dialysis
- Have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
- Have HIV
- Were born to a mother with hepatitis C
Since July 1992, all blood and organ donations in the U.S. are tested for the hepatitis C virus. The CDC says it is now rare that someone getting blood products or an organ would get hepatitis C. That said, The CDC recommends that anyone over the age of 18 get tested for Hepatitis C. If you haven’t been screened, you should consider having it done.
Learn more about the risk factors for hepatitis C.
You May Like: How Is Hepatitis C Transferred From Person To Person
What Lifestyle Changes Should I Make To Help Keep My Liver Healthy
Besides treating your hepatitis C with prescribed medications, you should exercise, lose weight , reduce your consumption of alcohol, and refrain from using , says Nelson. You should also get the hepatitis A and B vaccines.
The American Liver Foundation recommends that people with hepatitis C limit salt in their diet and avoid foods that are high in iron, such as spinach and red meat. And theres good news for coffee lovers: A study published in August 2017 in the Journal of Hepatology found that drinking coffee or herbal tea may help protect the liver from scarring, so you can include a few cups of joe in your diet.
Acute Hcv Infection And Clearance
HCV virus is present in blood 2â14 days after initial exposure. Concentrations of alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase increase and HCV-specific antibodies are produced 20â150 days after exposure.â Primary infection with HCV is generally asymptomatic, although 15â30% of individuals develop symptomatic acute hepatitis illness within 5â12 weeks of exposure lasting 2â12 weeks., Symptomatic primary HCV infection is often mild, with non-specific symptoms such as lethargy and myalgia, but individuals can present with jaundice., In about 25% of patients, acute infection is followed by viral clearance, defined as undetectable concentrations of HCV RNA in blood. Most of these individuals clear infection by 6 months or 12 months .â However, spontaneous HCV clearance after 1 year has been reported., Most patients do not have viral clearance and viraemia persists after 6 months, leading to chronic infection and progression to cirrhosis in 5â10% of individuals within 20 years.
Host polymorphisms of proteins such as HLA class I and II, natural-killer-cell receptors, chemokines, interleukins, and of interferon-stimulated genes have been associated with control of HCV. However, the genetic associations identified have not been confirmed in independent cohorts, differ in diverse populations, and studies are limited by small sample size or varying definitions of HCV outcome moreover, little is known about their functional basis.
You May Like: How Do You Get Rid Of Hepatitis C
How Do Doctors Treat Hepatitis B
Doctors typically dont treat hepatitis B unless it becomes chronic. Doctors may treat chronic hepatitis B with antiviral medicines that attack the virus.
Not everyone with chronic hepatitis B needs treatment. If blood tests show that hepatitis B could be damaging a persons liver, a doctor may prescribe antiviral medicines to lower the chances of liver damage and complications.
Medicines that you take by mouth include
A medicine that doctors can give as a shot is peginterferon alfa-2a .
The length of treatment varies. Hepatitis B medicines may cause side effects. Talk with your doctor about the side effects of treatment. Tell your doctor before taking any other prescription or over-the-counter medicines.
For safety reasons, you also should talk with your doctor before using dietary supplements, such as vitamins, or any complementary or alternative medicines or medical practices.
Ive Never Used Iv Drugs Or Been Stuck With A Dirty Needle How Did I Get Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is usually spread through direct contact with the blood of a person who has the disease. It can also be transmitted by needles used for tattooing or body piercing. In rare cases, hepatitis C can be passed from a mother to her unborn baby. This virus can be transmitted through sex and sharing razors or toothbrushes. These occurrences are also rare. Many times, the cause of hepatitis C is never found.
Also Check: Hepatic Steatosis Treatment Step By Step
If I Have Hepatitis C Infection Does This Mean I Am Going To Have Other Health Problems
Hepatitis C can cause scarring of the liver leading to cirrhosis and liver cancer. Other conditions have also been linked to hepatitis C and are known as extra-hepatic manifestations of hepatitis C. They include diabetes mellitus, arthritis, hypothyroid, and aplastic anemia among other conditions. Talk to your provider for more information.
What Laboratory Tests Diagnose Hepatitis C
Laboratory blood tests will be done to evaluate the patient’s liver function and to look for hepatitis C antibodies . If these tests indicate that the person has hepatitis C, a hepatitis C “viral load” test will be done. This looks for genetic material from the hepatitis C virus and measures the quantity of hepatitis C virus that is circulating in the patient’s blood. This is helpful in determining if treatment is appropriate and to monitor the success of the treatment .
Individuals who had hepatitis C in the past and cleared the virus on their own will have a positive HCV antibody test, but there will be no hepatitis C virus genetic material in the blood. If a person is immunosuppressed due to an immunological condition, cancer chemotherapy, immunotherapy or HIV/AIDS, the test results may be different and need to be evaluated accordingly.
You May Like: How Do I Get Hepatitis
What Are The Side Effects Of Treatment
The direct acting antiviral regimens used to treat hepatitis C today are extremely well tolerated. You may experience mild side effects like headache or fatigue. For details on the side effects, review the handout specific to medication you take.
In rare instances, providers may recommend the addition of the medication ribavirin for more difficult cases of hepatitis C. Ribavirin may cause additional side effects such as fatigue, shortness of breath, cough, anemia, or rash. Patients who receive ribavirin may need more frequent monitoring for side effects as well as adjustment of the dose if side effects are experienced. For detailed information on ribavirin, patients should review the ribavirin handout.
All Adults Pregnant Women And People With Risk Factors Should Get Tested For Hepatitis C
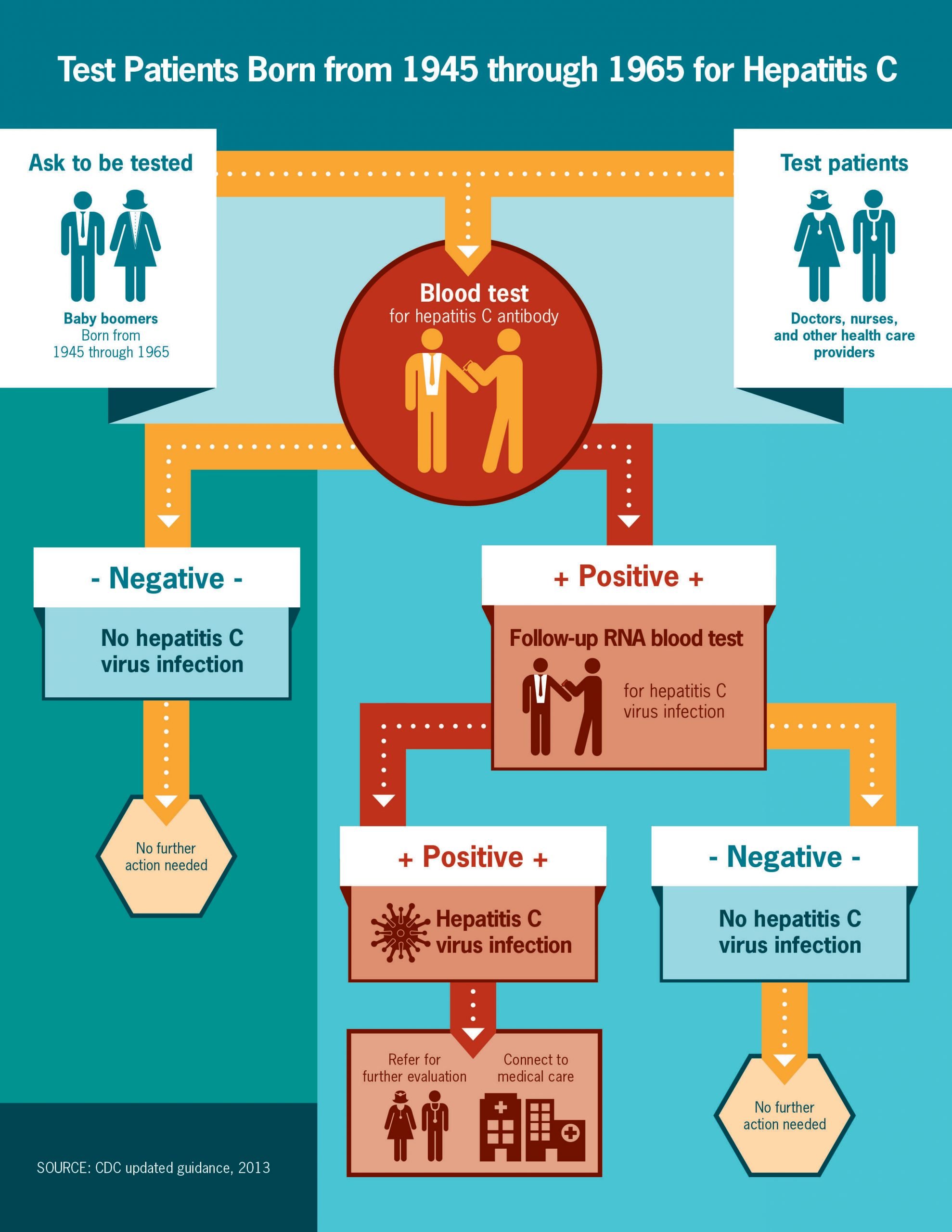
Most people who get infected with hepatitis C virus develop a chronic, or lifelong, infection. Left untreated, chronic hepatitis C can cause serious health problems, including liver damage, cirrhosis, liver cancer, and even death. People can live without symptoms or feeling sick, so testing is the only way to know if you have hepatitis C. Getting tested is important to find out if you are infected so you can get lifesaving treatment that can cure hepatitis C.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Vaccine For Babies
How Can I Tell If Someone Has Hepatitis C
Many people with hepatitis C don’t have any symptoms and are unaware they have the infection. They may develop symptoms later on as their liver becomes increasingly damaged. When symptoms do occur, they can be mistaken for another condition.
Symptoms can include:
- Flu-like symptoms, such as muscle aches and a high temperature
- Feeling tired all the time
- Loss of appetite
- Abdominal pain
- Feeling and being sick.
The only way to know for certain if these symptoms are caused by hepatitis C is to get tested.
Cost Of Hepatitis C Medicines
The newer direct-acting antiviral medicines for hepatitis C can be costly. Most government and private health insurance prescription drug plans provide some coverage for these medicines. Talk with your doctor about your health insurance coverage for hepatitis C medicines.
Drug companies, nonprofit organizations, and some states offer programs that can help pay for hepatitis C medicines. If you need help paying for medicines, talk with your doctor. Learn more about financial help for hepatitis C medicines.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Virus Ab 0.1
Hepatitis B In The United States
In the United States, about 862,000 people have chronic hepatitis B.6 Asian Americans and African Americans have higher rates of chronic hepatitis B than other U.S. racial and ethnic groups.10 Researchers estimate that about half of the people living with chronic hepatitis B in the United States are Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders.11 Chronic hepatitis B is also more common among people born in other countries than among those born in the United States.7
The hepatitis B vaccine has been available since the 1980s and, in 1991, doctors began recommending that children in the United States receive the hepatitis B vaccine. The annual rate of acute hepatitis B infections went down 88.5 percent between 1982 and 2015.12 In 2017, the annual number of hepatitis B infections rose in some states.13 Experts think the rise was related to increases in injection drug use. Injection drug use increases the risk of hepatitis B infection.
How Is It Treated
Hepatitis A is treated using supportive methods. These can include things like rest, fluids, and healthy foods. Medications can also help to ease some symptoms like fever, aches, and pains.
Theres a vaccine available to protect against infection with HAV. This is typically recommended for children as well as for people at an increased risk for contracting the virus.
Also, receiving a single dose of the hepatitis A vaccine may prevent you from becoming ill if youve been exposed to HAV. For it to be effective, the vaccine needs to be given of exposure.
Also Check: What Medication Cures Hepatitis C
Risk Factors For Liver Cancer: Youve Had Hepatitis C
Certain characteristics may put you at risk for liver cancer. Those with a history of the virus hepatitis C can develop related liver cancer 10 years after their diagnosis, Dr. Abou-Alfa says. The Center for Disease Control in the United States recommends anyone born between 1945 and 1965 get tested for the virus. Most Americans in that age group havent been screened, Dr. Brawley says. There is treatment that can cure hepatitis C and therefore prevent liver cancer.
In our country, the Canadian Liver Foundation has pushed for a similar screening strategy, but our current national approach focuses on testing higher-risk groups. Here are more facts about hepatitis in Canada.
How Can You Get Hepatitis C In Wales
As the virus may be transmitted by contact with blood from an infected person, certain people may be at a higher risk of acquiring hepatitis C.
These include:
- Injecting drug users who share needles
- Those coming into contact with blood products i.e. healthcare workers, prison officers
- Babies born to infected mothers
- People who received a blood transfusion before 1991 in the UK or in a country that does not screen its blood for the virus.
The virus is spread when the blood from an infected person gets into the bloodstream of another person or rarely from mother to baby, before or during birth.
Currently, the main way hepatitis C is spread in the UK is through drug use, by sharing contaminated equipment. Body piercing or tattooing using unsterilised equipment can spread the virus. Hepatitis C can be spread through sexual intercourse but this is very rare.
Recommended Reading: Ok Google What Is Hepatitis C
Stages Of Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus affects people in different ways and has several stages:
- Incubation period. This is the time between first exposure to the start of the disease. It can last anywhere from 14 to 80 days, but the average is 45
- Acute hepatitis C. This is a short-term illness that lasts for the first 6 months after the virus enters your body. After that, some people who have it will get rid of, or clear, the virus on their own.
- Chronic hepatitis C. For most people who get hepatitis C — up to 85% — the illness moves into a long-lasting stage . This is called a chronic hepatitis C infection and can lead to serious health problems like liver cancer or cirrhosis.
- Cirrhosis. This disease leads to inflammation that, over time, replaces your healthy liver cells with scar tissue. It usually takes about 20 to 30 years for this to happen, though it can be faster if you drink alcohol or have HIV.
- Liver cancer. Cirrhosis makes liver cancer more likely. Your doctor will make sure you get regular tests because there are usually no symptoms in the early stages.
Learn more about the stages and progression of hepatitis C.