How Is It Tested For And Diagnosed
After you discuss your symptoms with your doctor, they may order a blood test to check for the presence of a viral or bacterial infection. A blood test will reveal the presence of the hepatitis A virus.
Some people have only a few symptoms and no signs of jaundice. Without visible signs of jaundice, its hard to diagnose any form of hepatitis through a physical examination. When symptoms are minimal, hepatitis A can remain undiagnosed. Complications due to a lack of diagnosis are rare.
What Tests Should I Request To Confirm My Clinical Dx In Addition What Follow
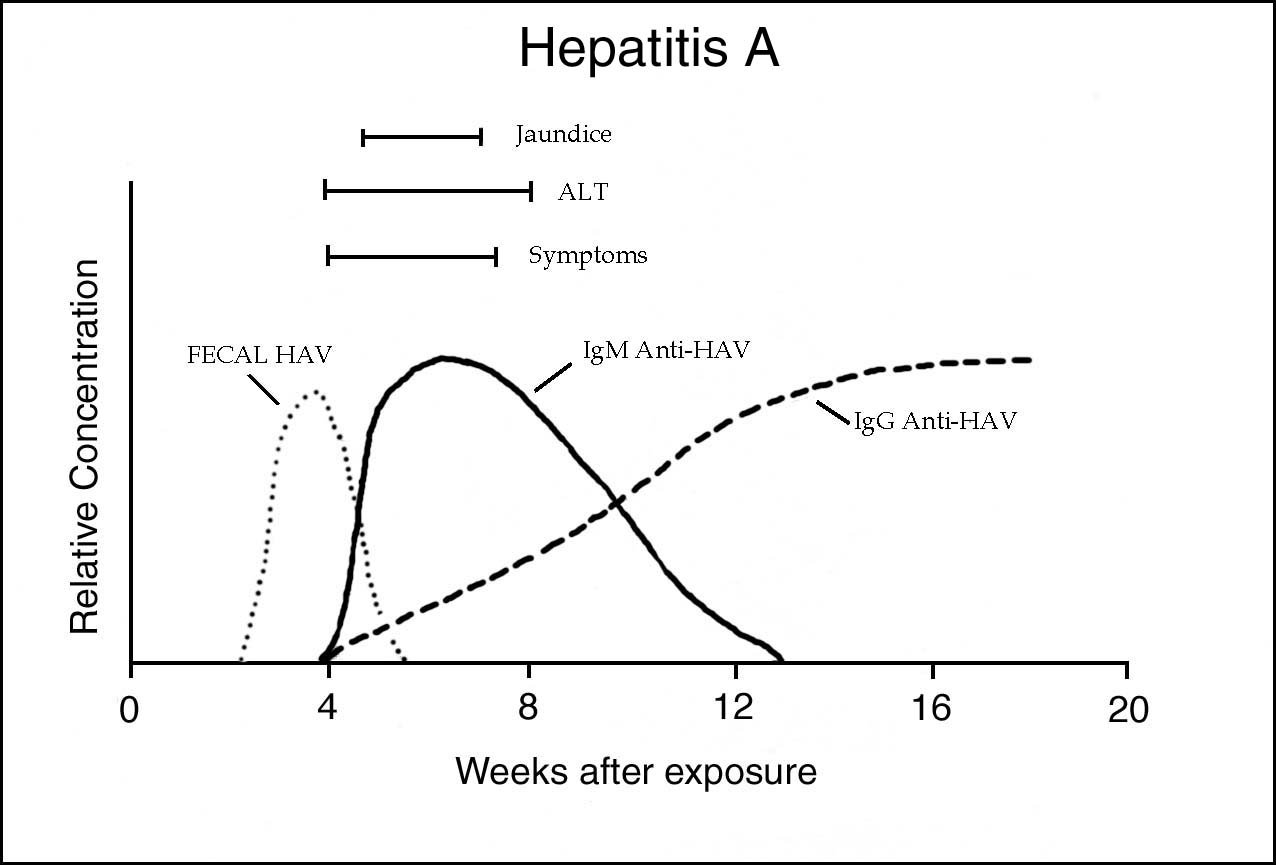
For diagnosis of hepatitis A, the test of choice is HAV IgM antibody. HAV IgM is usually present at the onset of symptoms and persists 4-6 months after resolution.
For assessment of HAV immune status due either to past infection or immunization, HAV total antibody is commonly used in lieu of a test for HAV IgG alone .
Table 1
Hepatitis A And International Travel
Who should receive protection against hepatitis A virus before travel?
All susceptible people traveling to or working in countries that have high or intermediate HAV endemicity are at increased risk for HAV infection. These travelers should be vaccinated or receive immune globulin before departure . For more information on international travel and hepatitis A, see CDCs travel page or ACIP updated recommendations on Prevention of Hepatitis A after Exposure to Hepatitis A Virus and in International Travelers.
How soon before international travel should the first dose of hepatitis A vaccine be given?
All unvaccinated people 12 months of age planning travel to an area with high or intermediate HAV endemicity should receive a single dose of vaccine as soon as travel is considered they should then complete the vaccine series with the appropriate dose and schedule. People traveling within 2 weeks should receive the initial dose of hepatitis A vaccine before departure and also simultaneously may be administered IG at a separate anatomic injection site for additional short-term protection . The hepatitis A vaccine series should be completed according to the routine schedule. Information on immune globulin dosing and additional information on hepatitis A vaccine and travel is available.
What should be done to protect international travelers < 6 months of age and other travelers unable to receive hepatitis A vaccine?
Also Check: Hepatitis B Surface Ab Immunity Qn
How Is Hepatitis A Treated
There is no formal treatment for hepatitis A. Because its a short-term viral infection that goes away on its own, treatment is typically focused on reducing your symptoms.
After a few weeks of rest, the symptoms of hepatitis A usually begin to improve. To ease your symptoms, you should:
- avoid alcohol
All Adults Pregnant Women And People With Risk Factors Should Get Tested For Hepatitis C
Most people who get infected with hepatitis C virus develop a chronic, or lifelong, infection. Left untreated, chronic hepatitis C can cause serious health problems, including liver damage, cirrhosis, liver cancer, and even death. People can live without symptoms or feeling sick, so testing is the only way to know if you have hepatitis C. Getting tested is important to find out if you are infected so you can get lifesaving treatment that can cure hepatitis C.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Signs Of Hepatitis
Read Also: Is Hepatitis B More Infectious Than Hiv
Who Is At Risk
Anyone who has not been vaccinated or previously infected can get infected with the hepatitis A virus. In areas where the virus is widespread , most hepatitis A infections occur during early childhood. Risk factors include:
- poor sanitation
- living in a household with an infected person
- being a sexual partner of someone with acute hepatitis A infection
- use of recreational drugs
- travelling to areas of high endemicity without being immunized.
How Is Hepatitis A Infection Prevented
Vaccination
- The hepatitis A vaccine offers excellent protection against HAV. The vaccine is safe and highly effective. Vaccination consists of 2 doses of vaccine spaced 6-12 months apart. Protection starts 1-2 weeks after the first dose of vaccine, and lasts for 20 years to life after 2 doses.
- The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that all children should receive hepatitis A vaccine starting at 1 year of age .
- The CDC recommends hepatitis A vaccine for all persons traveling to countries where HAV is common . For infants that will be traveling internationally, an early dose of Hepatitis A vaccine can be given at age 6-11 months.
Natural Immunity
- People who have hepatitis A infection become immune to HAV for the rest of their lives once they recover. They cannot get hepatitis A twice.
- The blood test for immunity to hepatitis A is called the Hepatitis A Total Antibody test. People who have had hepatitis A and those who have received hepatitis A vaccine show positive antibodies to hepatitis A on this test for the rest of their life.
Healthy Habits
- Good personal hygiene and proper sanitation help prevent the spread of the HAV virus. Always wash your hands with soap and water after using the bathroom, changing a diaper, and before preparing, serving, or eating food.
- Alcohol-based hand sanitizers do not kill the hepatitis A virus
After Exposure to HAV
You May Like: Medications Used To Treat Hepatitis C
How Long Does Hav Survive Outside The Body How Can The Virus Be Killed
HAV can live outside the body for months, depending on the environmental conditions. The virus is killed by heating to 185 degrees F for one minute. However, the virus can still be spread from cooked food if it is contaminated after cooking. Adequate chlorination of water, as recommended in the United States, kills HAV that enters the water supply.
What Do The Hepatitis A Test Results Mean
The test may indicate the following:
- Positive IgM results indicate that the antibody was found in your blood, meaning you may have an acute or recent HAV infection.
- Negative IgM results indicate the antibody was not found in your blood, meaning there is no active infection.
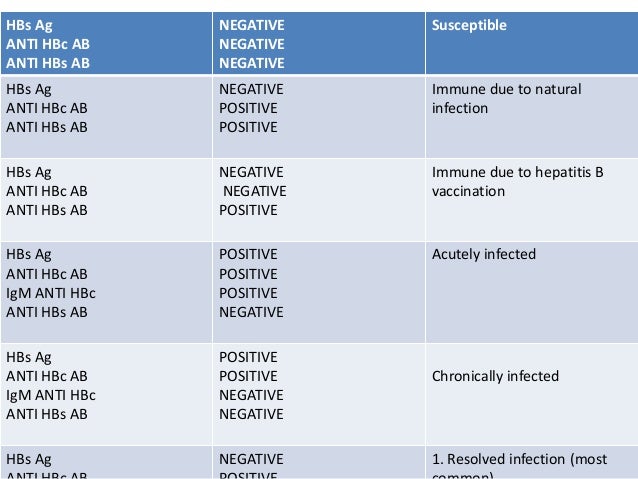
- Positive AB/IgG results indicate that the antibody was found in your blood, which means that you have been exposed to the virus in the past and have either developed immunity to HAV or have been vaccinated for it.
- Negative AB/IgG results indicate that the antibody was not found in your blood, meaning that you have not had a past HAV infection nor have been vaccinated or immunized to the virus.
Also Check: Hepatitis A Vaccine San Diego Free
Explanation Of Test Results:
If this test result is positive, it means your body was exposed to the hepatitis C virus and made antibodies . However, it does not tell you whether you are still infected with hepatitis C. If the antibody test result is positive, you should be tested for hepatitis C RNA , which determines whether you are chronically infected. The lab will perform this RNA test automatically if your hepatitis C antibody test is positive.
If the antibody test result is negative, it means you have not been infected with the hepatitis C virus, and further testing for hepatitis C usually is not needed.
Future Outlook And Conclusions
Studies have also been performed confirming the detection of specific proteins such as Her-2/neu and tumor markers such as CA-125, CA 153 are possible, but to date no diagnostic tests have been developed using saliva specimens. Viral diseases represent another target area for salivary diagnostics with a number of major disease antibodies and antigens all detectable in saliva. Oral fluid samples have already proved useful in the evaluation of immunization efficacy, particularly in the developing world, where immune response to measles, mumps, polio, tetanus, and rubella vaccines have been routinely carried out. More recently, a company from the United Kingdom, MicroImmune, has developed a saliva-based point-of-care device for the detection of measles-specific IgM antibodies. The group made up of scientists from the Public Health Laboratory in Colindale intend developing additional vaccine-specific rapid tests in the future.
S.A. Weinman, R. Taylor, in, 2014
Don’t Miss: How Do You Know You Have Hepatitis B
What Does It Mean If I Am Immune To Hepatitis A
Once your body has come into contact with the hepatitis A virus , you develop the IgG class of antibodies, providing you with immunity for the rest of your life. If you have these antibodies, it means that you are immune and can not get the hepatitis A infection again.
If your test results indicate that IgM antibodies were found, that means you have a current acute hepatitis A infection, and therefore were not previously made immune to the virus.
Hepatitis C And Health
How can health-care personnel avoid exposure to HCV?
Avoiding occupational exposure to blood is the primary way to prevent transmission of bloodborne illnesses among health-care personnel. To promote blood safety in the workplace, health-care personnel should consult infectious-disease control guidance from the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health and from CDC. Depending on the medical procedure involved, Standard Precautions may include the appropriate use of personal protective equipment .
What is the risk of acquiring hepatitis C after being accidentally exposed to HCV-contaminated blood or body fluids in the workplace?
Although sharps injuries have decreased in recent decades due to improved prevention measures, they continue to occur, placing health-care personnel at risk for several bloodborne pathogens like hepatitis C. A recent analysis of several studies revealed an overall 0.2% risk for infection among those exposed to HCV-antibody-positive blood through needlestick or sharps injuries . Updated guidelines for management and treatment of hepatitis Cexternal icon are available to provide guidance for health-care personnel who become infected via exposure to contaminated blood at the workplace.
Other than needlesticks, do other exposures place health-care personnel at risk for hepatitis C?
Should HCV-infected health-care personnel be restricted in their work?
Dont Miss: Is Hepatitis C An Autoimmune Disease
Read Also: Is Hepatitis C Contagious Sexually
How Do I Avoid Getting Sick
These tips will help protect you and your family from Hepatitis A:
- Wash your hands after using the washroom and changing diapers, and before preparing or eating food.
- When travelling, especially to developing countries:
- drink water from a safe supply
- avoid ice cubes in drinks
- eat only freshly cooked food
- avoid non-peelable raw fruit or vegetables
Also, these safe food practices will reduce your risk of contracting Hepatitis A and other foodborne illnesses.
What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis B Surface Antibody And Antigen
An antigen is a substance that induces antibody production. Hepatitis B surface antigen is a protein on the surface of hepatitis B virus.
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are produced by the bodys immune system in response to HBsAg. The presence of adequate hepatitis B surface antibodies in the blood indicates protection against hepatitis B virus infection.
Zerbor, iStock, Thinkstock
Testing positive for antibodies to the hepatitis C virus may be scary, but now you have information that can improve your health and well-being. This fact sheet will explore what testing positive means, and what you can do about it. Dont panic the knowledge you now have will help you make healthier decisions for you and your liver. Information is the key to living well with hepatitis C.
Also Check: What Happens If You Have Hepatitis B
Why It Is Done
Hepatitis virus testing is done to:
- Identify the type of hepatitis virus causing the infection.
- Screen people who have a higher chance of getting or spreading hepatitis A. This includes doctors, dentists, and nurses.
- Screen blood donors and donor organs. This is done to help prevent the spread of hepatitis A.
- Find out if a person has antibodies after getting a hepatitis A vaccination. Having antibodies means the vaccine worked.
- Find out if hepatitis A is the cause of abnormal liver function tests.
Can I Take The Test At Home
At-home hepatitis C tests are available that allow patients to collect a blood sample at home and mail it to a laboratory for testing. Test samples are collected through pricking a finger with a sharp object, called a lancet, thats included in the test kit.
At-home HCV testing is a form of hepatitis C antibody testing and does not test for hepatitis C RNA or the strains genotype. Testing for hepatitis C at home is not a substitute for testing performed by a health care professional, and positive test results may need to be confirmed by laboratory-based testing.
Recommended Reading: What Happens When You Have Hepatitis
Also Check: How Can Get Hepatitis B
What Is A Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Test
Hepatitis B surface antibody test is part of a panel of blood tests to diagnose HBV infection. Hepatitis B surface antibody test determines the presence and quantity of anti-HBs in the blood serum, which can indicate protection from HBV infection.
Hepatitis B disease affects the liver and commonly spreads through body fluids such as blood, semen, and vaginal secretions.
How Can I Avoid Getting Hepatitis A
There is a safe and effective vaccine that can protect you from getting hepatitis A. The vaccine is usually given in two doses six months apart. The vaccine will give you protection for up to 20 years. A combined vaccine for hepatitis A and hepatitis B is also available. Since up to 40% of the reported cases of hepatitis A occur in travellers, it is advisable to protect yourself with a hepatitis A vaccination six weeks before you leave.
Consider these additional safety precautions:
- Wash your hands frequently and thoroughly especially after using the washroom, before preparing food and before eating.
- Avoid raw or undercooked food.
- If you are travelling to countries with high rates of hepatitis A:
- Drink bottled or boiled water and use it for brushing your teeth.
- Drink bottled beverages without ice.
- Avoid uncooked food including salads.
- Avoid food from street vendors.
- Peel and wash fresh fruits and vegetables yourself.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Symptoms And Causes
False Positive Hepatitis C Antibody Test Results In Left Ventricular Assist Device Recipients: Increased Risk With Age And Transfusions
Grace Y. Minamoto1, Doreen Lee1, Adriana Colovai2, Dana Levy1, Ljiljana Vasovic3, Keith W. Roach4, Jonathan Shuter1, Daniel Goldstein5, David DAlessandro5, Ulrich P. Jorde6, Victoria A. Muggia1
1 Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Medicine, 2 Department of Pathology, Montefiore Medical Center and the Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, NY, USA 4Department of Medicine, Weill Medical College of Cornell University, New York, NY, USA Department of Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery, 6 Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine, Montefiore Medical Center and the Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, NY, USA
Correspondence to
Keywords: Hepatitis C left ventricular assist device allosensitization
Submitted Sep 30, 2016. Accepted for publication Dec 28, 2016.
doi: 10.21037/jtd.2017.01.10
Appropriate Uses Of The Hcv Rna Test
There are 4 major reasons that HCV RNA tests are used:
More rarely, HCV RNA is used when either very acute HCV infection is suspected or a false HCV Ab is suspected.
It would not be appropriate to repeatedly order HCV RNA viral load screening for a patient who is not on or was recently on HCV treatment, or to use the HCV viral load to determine the severity of the patients infection or the patients risk of developing significant liver disease.
Don’t Miss: Transplanting Hepatitis C Positive Kidneys
Role For Liver Transplant
Patients with HBV that develop acute liver failure, decompensated liver cirrhosis or HCC can potentially undergo liver transplantation as ultimate therapy. In the setting of posttransplant immunosuppression, the rate of HBV recurrence is high with survival rates < 50% after 2 years if no preventive measures are taken. Hence, based on donor and recipient serologies different strategies have been developed including the use of combination of HBV immunoglobulin during the anhepatic and postoperative phase when indicated, with indefinite use of high-genetic barrier nucleoside/nucleotide analogs demonstrating the lowest rates of HBV recurrence and post-transplant decompensation.
Ongoing Research And Future Directions
Current treatment options have changed the prognosis for HBV patients, but have been limited by its low cure rates. Hence, other targets in the viral life cycle have been evaluated to improve HBsAg seroconversion and potential cure. For example, inhibition of the HBV entry into the uninfected hepatocytes by blockage of the sodium taurocholate co-transporting peptide receptor in the HBV capsid has been studied with three drugs in different trial stages. Bulevirtide is a NTCP antagonist found to inhibit infection in mice injected with HBV in a phase 1 study it showed to be safe without occurrence of serious side effects in 36 healthy subjects at a max dose of 20 mg. Subsequently, a multicenter phase 2b randomized trial in 60 HBV/HDV patients receiving PEG-interferon, bulevirtide 2 mg or both with bulevirtide at 2 mg and 5 mg dosing for 48 wk showed a higher proportion of HBsAg decline or loss in patients with combination therapy. Other potential NTCP inhibitor are the cyclosporin derivatives such as SCY450 and SCY995, which have been found to inhibit hepatocyte HBV entry in vitro without affecting bile acid uptake, opening a new therapeutic window. Other experimental medications from the cyclophilin inhibitor family like alisporivir and CRV431, have shown reduction of HBV DNA and HBsAg in lab models possibly through a similar mechanism with promising results.
Also Check: Hepatitis A And B Shots