Who Should Not Get The Vaccine
Speak with your health care provider if you have had a life-threatening reaction to a previous dose of hepatitis B vaccine, or any component of the vaccine such as yeast, or to latex.
There is no need to delay getting immunized because of a cold or other mild illness. However, if you have concerns speak with your health care provider.
Important Information About Vaccine And Hepatitis B Immunoglobulin Shot Administration
Where available, the hepatitis B birth-dose and HBIG should be administered within 24 hours of birth in order to prevent the transmission of hepatitis B from mother to child. It is very important that the shots be given in opposite limbs, to ensure the highest effectiveness. Please see chart above for more information.
Which Adults Should Be Vaccinated Against Hepatitis B
According to CDC recommendations, adults in the following groups are recommended to receive hepatitis B vaccine:
General
- All people age 18 years and younger.
- Anyone 19 years and older who wants to be protected from hepatitis B.
People at risk for infection by sexual exposure
- Sex partners of people who are hepatitis B surface antigen -positive.
- Sexually active people who are not in long-term, mutually monogamous relationships.
- People seeking evaluation or treatment for a sexually transmitted disease.
- Men who have sex with men.
People at risk for infection by percutaneous or permucosal exposure to blood or body fluids
- Current or recent illegal injection drug users.
- Household contacts of people who are HBsAg-positive.
- Residents and staff of facilities for developmentally challenged people.
- Healthcare and public safety workers with reasonably anticipated risk for exposure to blood or blood-contaminated body fluids.
- People with end-stage renal disease, including predialysis, hemo-, peritoneal- and home-dialysis patients.
Others
- International travelers to regions with intermediate or high levels of endemic HBV infection.
- People with chronic liver disease.
- People with HIV infection.
- People with diabetes who are age 19 through 59 years. For those age 60 and older, clinicians should make a determination of need for
- vaccination based on their patients’ situation.
In a future issue, we will review the various hepatitis B serologic tests, who needs testing, and when they need it .
Recommended Reading: What Kind Of Disease Is Hepatitis C
Immunisation Against Hepatitis B For People At Risk
In Victoria free hepatitis B vaccine is provided for people who are at increased risk, including:
- Men who have sex with men.
- People living with HIV.
- People living with hepatitis C.
- Prisoners.
- People no longer in a custodial setting who commenced, but did not complete, a free vaccine course while in custody.
- Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people.
- People born in priority hepatitis B endemic countries who arrived in Australia in the last 10 years priority countries include China, Philippines, Malaysia, Vietnam, Afghanistan, Thailand, South Korea, Myanmar , Indonesia, Singapore, Hong Kong, Taiwan and Cambodia.
- Vulnerable citizens people who have experienced hardship that prevented them from accessing the vaccine earlier. Vulnerable citizens are vaccinated based on an individual assessment by an immunisation provider.
Immunisation is also recommended, but not free, for people who are at increased risk including:
If you think you have been exposed to hepatitis B, see a doctor immediately. Your doctor can give you treatment that, in some instances, can greatly reduce your risk of infection with hepatitis B.
Remember that being immunised against hepatitis B does not protect you against HIV, hepatitis C or other diseases spread by blood or bodily fluids. It is important that you take precautions to make sure you are not exposed to these diseases.
International Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedules
*Please note that the first dose should be given as soon as possible. Additional doses require minimum time intervals between doses in order for the vaccine to be effective.
The hepatitis B vaccine is an injection that is generally given in the arm and as a three-dose series. The World Health Organization recommends a 0, 1, and 6-month vaccine schedule, though schedules may vary based on a countrys national immunization program. Completing the hepatitis B vaccine series, preferably beginning at birth, will ensure protection against hepatitis B, hepatitis delta and lower the lifetime risk of liver cancer. Greater than 90% of babies and up to 50% of young children who are not vaccinated and are infected with hepatitis B will have lifelong infection, which makes the birth dose essential to their protection. Please note that the vaccine brand name, manufacturer and associated schedules for adults, children and infants may be unique to different countries, though there is a list of WHO prequalified vaccines.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Infants
The World Health Organization recommends all infants receive the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth and to complete the vaccine series with additional shots at 1 month and 6 months of age. Beginning the hepatitis B vaccine at birth will ensure protection against hepatitis B for life.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Children and Adults
4-Dose Combination Vaccine Series for Infants
Additional Resource Links:
Read Also: Hepatitis C Vaccine Schedule For Adults
Concurrent Administration Of Vaccines
HB-containing vaccines may be administered concomitantly with other vaccines or with HBIg. Different injection sites and separate needles and syringes must be used for concurrent parenteral injections.
Refer to Timing of Vaccine Administration in Part 1 for additional information about concurrent administration of vaccines.
Immunisation Against Hepatitis B For Children
Vaccination is the best protection against hepatitis B infection and is recommended for all infants and young children, adolescents and those in high-risk groups. Vaccination can be with a vaccine against hepatitis B alone or with a combination vaccine.
Protection against hepatitis B is available free of charge under the National Immunisation Program Schedule.
In Victoria, vaccination against hepatitis B is free for all babies and children including:
- Babies at birth vaccinate with hepatitis B vaccine as soon as possible after birth.
- Babies at 2, 4 and 6 months immunisation in the form of a diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, hepatitis B, polio and Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine .
- Premature babies at 12 months premature babies born under 32 weeks gestation or under 2,000g birth weight receive a single booster dose.
- Children up to and including 20 years of age.
Don’t Miss: Cost Of Hepatitis C Test
Why Do You Need A Hepatitis B Shot
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that cant be transferred person-to-person unless you have contact with an infected persons bodily fluids. Annual infection rates of HBV are going down in the United States thanks to vaccines. So you might be wondering if you or your child needs a shot to protect against hepatitis B.
For Adults At High Risk Of Exposure
Adults who have not received the hepatitis B vaccine series should be immunized when they have an increased risk of exposure. Job, travel, health condition, or lifestyle all may increase a person’s risk of contracting hepatitis B.
People who live or work where there is risk of exposure include:
- Health care and public safety workers who are likely to be exposed to blood or blood products.
- Clients and staff of institutions or residential settings with known or potential HBV carriers.
- People planning extended travel to China, Southeast Asia, Africa, and other areas where hepatitis B infection is high.
People who have health conditions that put them at high risk for exposure or a severe infection include:
- People who have a severe kidney disease that requires them to have their blood filtered through a machine .
- People who have chronic liver disease.
- People who have hemophilia and other conditions in which they need to have blood products on an ongoing basis.
- People who had a stem cell transplant.
People whose lifestyle puts them at high risk for exposure include:
- People who inject illegal drugs.
- Men who have sex with men.
- People who have had more than one sex partner in the past 6 months or who have a history of sexually transmitted infection.
- Household contacts and sex partners of hepatitis B carriers.
- Prison inmates.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Vaccine Cost Without Insurance
Why Should My Baby Get The Hepatitis B Shot
- Protects your child from against hepatitis B, a potentially serious disease.
- Protects other people from the disease because children with hepatitis B usually dont have symptoms, but they may pass the disease to others without anyone knowing they were infected.
- Prevents your child from developing liver disease and cancer from hepatitis B.
- Keeps your child from missing school or child care and you from missing work.
What Is Hepatitis B
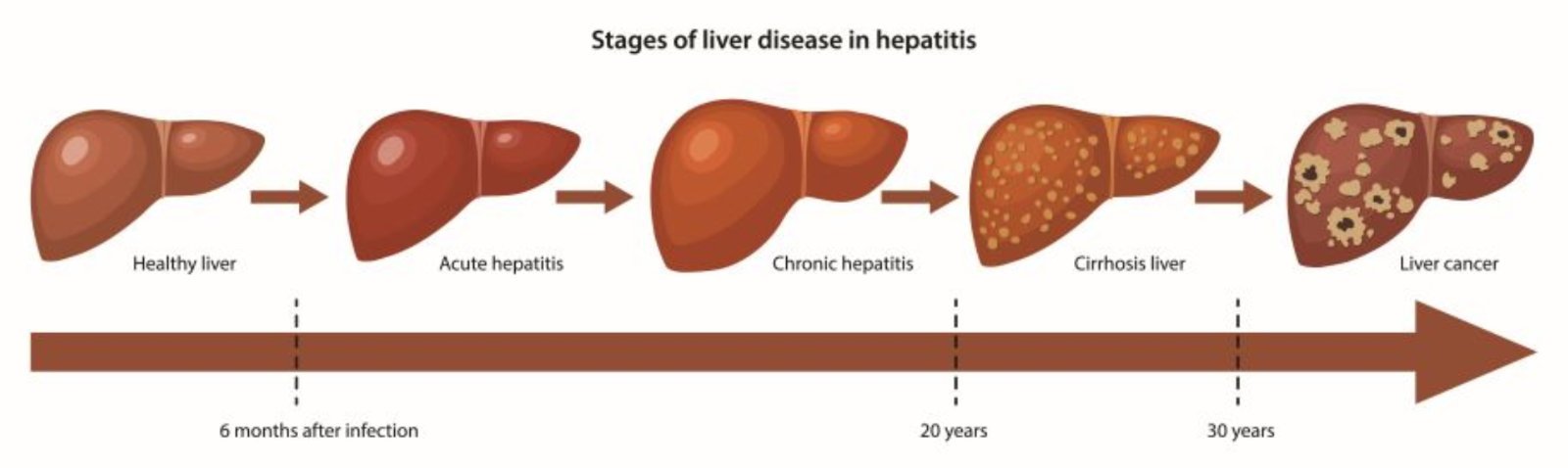
Hepatitis B is a contagious liver disease caused by the hepatitis B virus. When a person is first infected with the virus, he or she can develop an acute infection. Acute hepatitis B refers to the first 6 months after someone is infected with the hepatitis B virus. This infection can range from a very mild illness with few or no symptoms to a serious condition requiring hospitalization. Some people are able to fight the infection and clear the virus.
For others, the infection remains and is chronic, or lifelong. Chronic hepatitis B refers to the infection when it remains active instead of getting better after 6 months. Over time, the infection can cause serious health problems, and even liver cancer.
Read Also: Can Hepatitis C Be Cured Without Treatment
For Adults And Children
This vaccine schedule involves three doses within 2 months, followed by a booster dose at 1 year.
The initial accelerated doses provide immediate protection from HBV, and the booster dose helps provide long-term protection.
Below is the accelerated vaccination schedule approved for both adults and children:
| Vaccine series | |
|---|---|
| 2 months after the first dose | 1 year after the first dose |
Routine Administration Schedule For Hepatitis B Vaccine In Adults
- The dosing schedule is 0, 1 to 2 months, and 4 to 6 months.
- There is some flexibility in the schedule, but be sure to keep in mind the minimum intervals between doses:
- At least four weeks between doses #1 and #2
- At least eight weeks between doses #2 and #3
- At least 16 weeks between doses #1 and #3
- If your patient falls behind on the hepatitis B vaccination schedule , continue vaccinating from where your patient left off. The series does NOT need to be restarted.
Also Check: Daa Drugs For Hepatitis C
How And When Do Doctors Give Vaccines
For the hepatitis A vaccine:
You should get two doses, given as shots, 6 months apart for complete protection. The virus in the vaccine is killed .
Children should get the first dose between 12 and 23 months of age. Children older than age 2 can get the first dose at their next doctorâs visit.
If you need the vaccine because of upcoming travel, get it at least 1 month before you go.
For the hepatitis B vaccine:
For long-lasting immunity, you need three to four doses, depending on which type of vaccine is used. You get them as shots.
Children should get their first dose at birth and complete the series by age 6 months. Usually, the baby would get a second dose at 1 month old and the third dose at 6 months.
Babies born to women who have hepatitis B need a shot of hep B antibodies, as well as their first hep B vaccine shot, when theyâre born. They will also need follow-up blood tests to make sure theyâre OK.
Catch-up vaccinations are recommended for children and teens who were never vaccinated or who did not get all three shots.
If you’re an adult who wants to be vaccinated, you should talk about it with your doctor or pharmacist. If you are considering both vaccines, ask your doctor about vaccines that combine hep A and B.
Show Sources
Persons With Chronic Diseases
Refer to Immunization of Persons with Chronic Diseases in Part 3 for additional general information about vaccination of people with chronic diseases.
Chronic renal disease and patients on dialysis
People with chronic renal disease may respond sub-optimally to HB vaccine and experience more rapid decline of anti-HBs titres, and are therefore recommended immunization with a higher vaccine dose. Individuals undergoing chronic dialysis are also at increased risk for HB infection. In people with chronic renal disease anti-HBs titre should be evaluated annually and booster doses using a higher vaccine dose should be given as necessary.
Neurologic disorders
People with conditions such as autism spectrum disorders or demyelinating disorders should receive all routinely recommended immunizations, including HB-containing vaccine.
Chronic liver disease
HB immunization is recommended for non-immune persons with chronic liver disease, including those infected with hepatitis C, because they are at risk of more severe disease if infection occurs. Vaccination should be completed early in the course of the disease, as the immune response to vaccine is suboptimal in advanced liver disease. Post-immunization serologic testing may be used to confirm vaccine response.
Non-malignant hematologic disorders
Persons with bleeding disorders and other people receiving repeated infusions of blood or blood products are considered to be at higher risk of contracting HB and should be offered HB vaccine.
You May Like: How Do You Know If You Have Hepatitis A
Do The Benefits Of The Hepatitis B Vaccine Outweigh Its Risks
Every year in the United States about 2,000 people die following an overwhelming hepatitis B virus infection. In addition, every year about 22,000 people are infected with hepatitis B. Some of them will remain chronically infected, putting them at high risk of the long-term consequences of hepatitis B virus infection: cirrhosis and liver cancer. In fact, with the exception of influenza and COVID-19 viruses, hepatitis B virus causes more severe disease and death in the United States than any other vaccine-preventable disease. On the other hand, the hepatitis B vaccine is an extremely rare cause of a severe allergic reaction called anaphylaxis. To date, no one has died from this reaction, but it is theoretically possible that this could occur.
Because hepatitis B virus is a common cause of severe disease and death in the United States, and because the hepatitis B vaccine does not cause permanent damage or death, the benefits of the hepatitis B vaccine clearly outweigh its risks.
Who Should Get The Hbv Vaccine
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that all children and adults up to age 59 should receive the hepatitis B vaccine.
Infants should get their first hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth and complete their doses by age 6 to 18 months.
All unvaccinated children and adults through age 59 should receive the vaccine. Also, unvaccinated adults over the age 60 who are at risk of hepatitis B should get the vaccine.
Adults over age 60 who are not at risk of hepatitis B may also choose to get the shot.
Several types of the HBV vaccine are also safe to administer to pregnant women.
- people who have had more than one sex partner in the last 6 months
- men who have sex with men
- people seeking treatment for a sexually transmitted infection
- people whose partners or household members have hepatitis B
- people who inject drugs
- people who live or work in care facilities
- people who are on dialysis
- travelers to countries where hepatitis B is common
- people with chronic liver disease, HIV, or hepatitis C
- people who are in jail or prison
People who have diabetes should talk with a healthcare professional about their risk for contracting hepatitis B.
You May Like: Hepatitis B How Long Does It Last
Hepatitis B Vaccination Booster Dose After 18 Years Maintains Long
Primary vaccination against hepatitis B virus at birth may not provide adequate lifelong antibody levels, but a booster vaccine at age 18 years reinforces antibody levels for at least 4 more years, according to a study published in Infectious Diseases.
Vaccination against HBV is recommended in the first year of life to prevent infection, and studies demonstrate that this provides protection for 90% of the population for 30 years. Data on response to booster doses and long-term protection are lacking therefore, researchers sought to understand the protection duration of the HBV vaccine and the effect of additional doses on the level of protection against infection.
The researchers conducted a retrospective analysis of data from January 2013 to December 2016 of healthcare students in Israel. Participants were aged 19 to 25 years. Immunization history was obtained from medical records, including data for receipt of birth-dose HBV vaccine and booster at age 18 years. This booster is common in Israel, as many teenagers undergo emergency medical technician training that requires HBV vaccination regardless of previous immunization. Baseline antibody titer levels were measured at first clinic visit. A participant was considered protected against HBV if their anti-HBs titer was > 10 MIU/mL any participant with titers below this level received a booster dose of the HBV vaccine.
Reference
Babies And Children Can Develop Chronic Hbv
You may be wondering why the recommendations for the HBV vaccine start on the first day of life.
Adults who contract HBV will likely not experience long-term complications from hepatitis B. But the same is not the case for babies. As many as of babies who contract an HBV infection at birth from their mothers become chronically infected with HBV.
Children between the ages of 1 and 5 who get an HBV infection have a 25 percent of people who become chronically infected during childhood will develop liver cancer or cirrhosis. Thats why pediatricians want children to have immunity from HBV from the earliest possible age. Many babies and children exposed to HBV receive post-exposure prophylaxis, which decreases chance of infection.
If youre pregnant, youll most likely have a blood test to see if youre positive for hepatitis B. This allows doctors to find out if theres a chance that you could pass on the virus. These tests are highly sensitive and have a good accuracy rate, but they arent perfect. Additionally, a pregnant person may become infected between the time of the test and giving birth. The first dose of the vaccine given at birth lowers the risk of a newborn baby contracting hepatitis B.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Vs Hepatitis C