When To Contact A Doctor
A person should contact a doctor if they think that they may have had exposure to hepatitis B. The doctor can run a blood test to look for the presence of the infection and determine the next steps.
People who are concerned about contracting the virus may want to ask a doctor about getting the hepatitis B vaccine. This will protect them from future infections.
People who are living with a known case of chronic hepatitis B should visit a doctor regularly for screenings and blood tests to monitor the virus.
Is There A Cure For Chronic Hepatitis B
Currently, there is no complete cure for hepatitis B. But when managed properly, those living with the virus can expect to live a normal life. Maintaining a healthy diet and avoiding alcoholic beverages and tobacco products are crucial components in managing the disease.
You should also visit a doctor familiar with hepatitis B at least annuallythough twice a year might be best to monitor your liver through blood tests and medical imaging. As with most diseases, detecting it early leads to a better outcome. If youre exposed to the virus, you should get an antibody injection within 12 hours of exposure.
Could I Give It To Other People
Yes. As long as you carry the virus, you can infect others. You may pass it on to your sex partner, to those who live in close contact with you, and to those who share your needles for injecting drugs. All of these contacts should be examined by a doctor. If they are not yet infected, they should be vaccinated.
Pregnant women who are carriers may pass hepatitis B on to their babies around the time of birth. Most infected infants become carriers. A pregnant woman should have a test for hepatitis B at her first visit to a doctor. If she is a carrier, the infant can be vaccinated at birth to protect against infection.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Contact Hepatitis
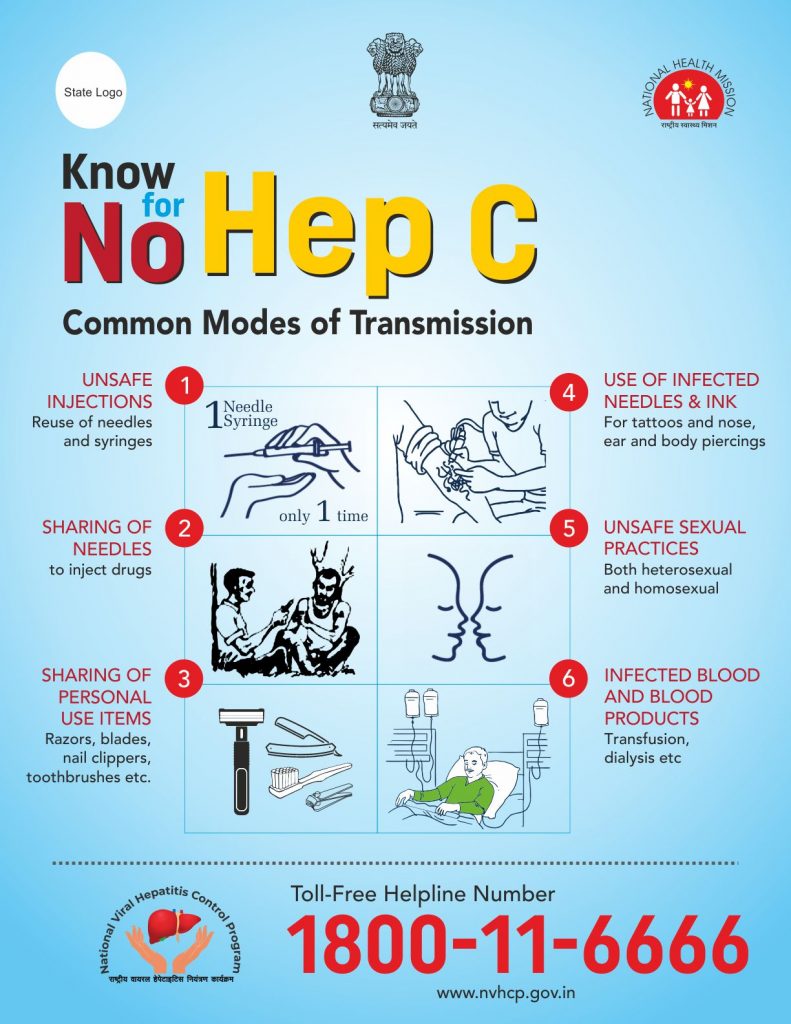
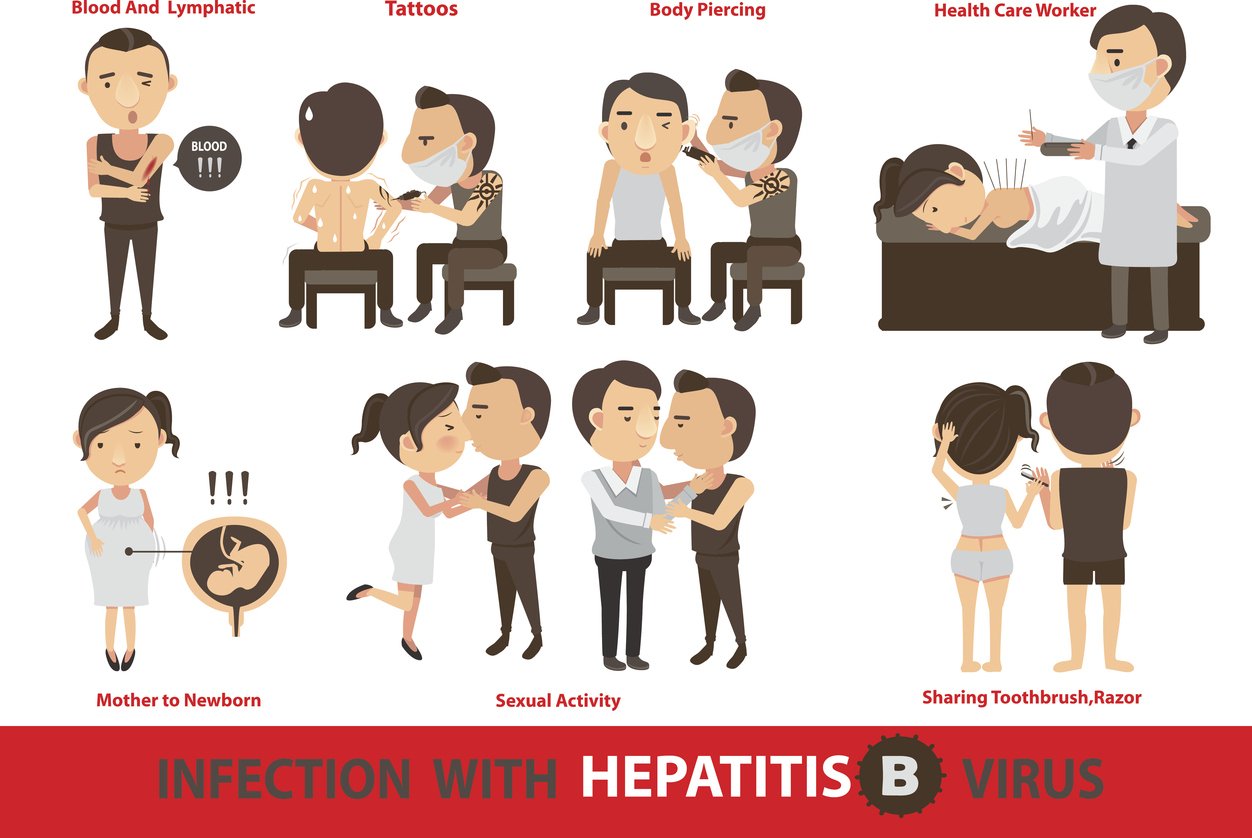
How Hbv Is Spread
It is possible for the hepatitis B virus to be spread through the bodily fluids of an infected person, which is to say that the virus can be transmitted through the blood, sweat, tears, saliva, semen, vaginal secretions, menstrual blood, and breast milk of an infected person. That said, having hepatitis B does not necessarily mean that you are infectious only some people with HBV are actually contagious.
Opportunities for exposure can include sharing a syringe or getting tattoos or body piercings with infected tools. But it also means that it is possible to be exposed during childbirth as well as sexual contact and intercourse. In fact, nearly two-thirds of acute cases of hepatitis B in the United States are caused by sexual exposure.
Though HBV can be spread through blood, there is generally very little risk of contracting the virus through blood transfusions as most countries began screening for it by 1975.
Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
Some people who are infected with the hepatitis B virus have mild, flu-like symptoms and some do not become sick at all. Children who are infected are less likely to have an illness or get sick after getting hepatitis B than adults.
In more severe cases, hepatitis B can cause:
- Loss of appetite.
- Pain in the joints.
- Jaundice .
Normally, these health problems disappear in a few weeks, but even when the person feels much better, they may still be infectious.
Most adults who become infected with the hepatitis B virus recover completely and do not become infected again. A few people become very ill in the time just after infection and need to go to hospital some may even die.
Also Check: Current Treatment For Hepatitis C
What Are The Types Of Hepatitis B
There are two types of hepatitis B infection: acute and chronic.
Acute
An acute infection happens at the beginning, when you first get infected with hepatitis B. Many people are able to clear it from their bodies and recover. In fact, this is true of about 4 in 5 adults who are infected.
Chronic
If you are not able to clear the infection within six months or longer, you have chronic hepatitis B. It is chronic hepatitis B that leads to inflammation and the serious, and possibly fatal, illnesses of cirrhosis of the liver and liver cancer. Treatment can slow disease progress, reduce the chance of liver cancer and increase your chances of surviving.
What Should You Know About Pregnancy And Hepatitis B
A pregnant woman who has hepatitis B can pass the infection to her baby at delivery. This is true for both vaginal and cesarean deliveries.
You should ask your healthcare provider to test you for hepatitis B when you find out you are pregnant. However, while it is important for you and your healthcare provider to know if you do have hepatitis B, the condition should not affect the way that your pregnancy progresses.
If you do test positive, your provider may suggest that you contact another healthcare provider, a liver doctor, who is skilled in managing people with hepatitis B infections. You may have a high viral load and may need treatment during the last 3 months of your pregnancy. A viral load is the term for how much of the infection you have inside of you.
You can prevent your infant from getting hepatitis B infection by making sure that your baby gets the hepatitis B vaccine in the hours after they are born along with the hepatitis B immunoglobulin. These two shots are given in two different locations on the baby. They are the first shots needed.
Depending on the type of vaccine used, two or three more doses must be given, usually when the baby is 1 month old and then 6 months old, with the last by the time the baby is 1 year old. It is critical that all newborns get the hepatitis B vaccination, but even more important if you have hepatitis B yourself.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Vaccine Booster For Healthcare Workers
How Hcv Is Spread
The hepatitis C virus is transmitted primarily through blood to blood contact, meaning that a person can become infected with the virus should the blood of a person who carries the virus be introduced into another person’s bloodstream.
Therefore, as with hepatitis B, blood transfusions , tattooing and body piercing, occupational exposure, medical procedures, and intravenous drug use can all lead to possible exposure to the virus. Unlike hepatitis B, however, sexual contact and childbirth have both been shown to be an inefficient route of exposure to HCV.
The hepatitis G virus is thought to be transmitted in a similar way to HCV.
How Is Hepatitis B Treated
Your healthcare provider will treat you based on what type of hepatitis B you have, acute or chronic.
Acute hepatitis B infections
If you develop an acute form of the condition, you probably wont need medical treatment. Instead, your doctor will likely suggest that you get plenty of rest, drink lots of fluids and maintain a healthy diet to support your body as it fights off the infection.
Chronic hepatitis B infections
If you have chronic hepatitis B, you might be a candidate for drug therapy. Usually, drug therapy is used only if you have active liver disease. There are seven drugs that are approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat hepatitis B. Two are injectable forms of interferon, while the five other antivirals are tablets.
You will need to take these medications every day. They help by slowing the viruss ability to multiply in your system. This helps reduce swelling and liver damage. Youll need to be regularly monitored for early signs of liver damage and liver cancer. Your healthcare provider will want to see you once or twice a year.
Also Check: What Is The Meaning Of Hepatitis
What Is My Risk
Your risk depends of several factors: destination, length of stay, what you do when you are travelling and whether you have direct contact with blood or other body fluids. In certain destinations, your risk may be higher, as some areas have higher numbers of people with chronic hepatitis B in the general population.
The risk increases with certain activities, such as unprotected sex, sharing needles, tattooing and acupuncture.
Aid and health care workers and anyone who receives medical or dental care with unsterilized or contaminated equipment in a country where hepatitis B occurs are also at greater risk.
What Tests Are There For Hepatitis B
All of the tests used to diagnose hepatitis B are blood tests. Some indicate different stages of the illness or immunity. The following list shows the different tests available, and what a positive result indicates for each of them.
- Hepatitis B surface antigen – Shows the person has hepatitis B. It can be detected during acute and chronic infection.
- Hepatitis B surface antibody – Shows the person has developed immunity to hepatitis B. It can be detected in people who have recovered from acute hepatitis B or been vaccinated against it.
- Hepatitis B e antigen – Shows the hepatitis B virus is multiplying, and that it can be more easily passed on.
- Hepatitis B e antibody – Shows the persons immune system has responded to hepatitis B and in some circumstances, the virus is not actively replicating.
- Hepatitis B core antibody – Shows a person has had hepatitis B, either past or present infection. If someone has immunity through vaccination he or she will not test positive.
- Hepatitis B virus DNA – Measures the amount of hepatitis B virus in the bloodstream and indicates how actively the virus is multiplying.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis A And B Symptoms
Good Nutrition And Rest
- All family members should eat a well-balanced diet that includes foods shown in the graphic MyPlate . You can find more information about balanced nutrition on the website ChooseMyPlate.gov .
- All family members should get at least 8 hours of sleep each night.
- Young children who are ill should rest during the day when possible.
How To Help Stop The Spread Of Hepatitis B
There are several things you can do to help stop the spread of this disease. Please follow these instructions until your doctor tells you the child with hepatitis is completely well:
- Good hand washing by all family members must be done. Hands should be washed using soap and warm water before meals, after using the bathroom and before preparing or serving food.
- Wash your hands after caring for your child. You may have come in contact with the hepatitis B virus from such things as changing diapers, cleaning up vomit, or exposure to blood.
- Wear disposable gloves when handling blood . Wash your hands after removing the gloves.
- Hepatitis B can be spread by sexual activity. Not having sex is the best way to keep Hepatitis B from being spread sexually. If an infected person has sex, a condom should be used every time. Condoms should be used until the doctor says there is no longer any risk of spreading the disease.
- All family members who are not infected should get Hepatitis B vaccines .
Recommended Reading: Is There A Home Test For Hepatitis C
What Laboratory Tests Are Available For Hepatitis B
Tests are available to detect the types of antigens used to identify the hepatitis B virus. The tests determine if the virus is present in the body tissue or blood. The amount of each type of antigen present indicates how advanced the disease is and how infective the individual has become.
Other tests are available to detect the body’s reaction to the viral infection or the body’s reaction to vaccination against the virus. These tests work by measuring the number of antibodies present in the blood.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
As hepatitis B infection is highly transmissible via accidental needlesticks, healthcare providers involved in taking care of a patient with HBV should exercise caution and practice proper preventative measures such as vaccination. Patient education should also include counseling about HBV transmission. The interprofessional team’s role is crucial in ensuring the best patient outcomes.
The vaccination rate is low in many developing countries, and the majority of patients are undiagnosed. Educational programs and improved awareness among the general public and healthcare providers are necessary to improve the identification of the patients, reduce transmission of the disease, and reduce the complications of hepatitis B infection.
Don’t Miss: Antiviral Drugs For Hepatitis A
Why It’s Important To Get Tested
Because hepatitis C is a highly infectious virus, the CDC recommends that adults 18 years or older get tested for hepatitis C at least once in their lifetime. This is also true for pregnant people during each pregnancy.
To test whether you have a hepatitis C infection, your healthcare provider will perform a hepatitis C antibody test to determine whether you have antibodies that were created in response to the infection.
If your test is positive, your healthcare provider will also perform a hepatitis C RNA test, which accurately determines whether you have a current infection.
Once it is determined you have an HCV infection, your healthcare provider will recommend the best course of treatment. For most people, treatment with antiviral drugs will be started. There are effective treatments that can cure HCV and prevent liver damage.
Enteric Routes: Transmission Of Hepatitis A And Hepatitis E
The Hepatitis A and hepatitis E viruses are both transmitted by enteric, that is digestive or by fecal, routes. This is also known as the fecal-oral route. To be exposed to these viruses, you must ingest fecal matter that is infected with the virus. While there are several ways in which this fecal-oral route can be established, poor hygiene and poor sanitary conditions in some countries lead to higher rates of infection of these viruses.
As a result, some areas of the world, like India, Bangladesh, and Central and South America, are particularly prone to the hepatitis E virus. About one-third of people in the United States have been exposed to the hepatitis A virus.
It is believed that the hepatitis F virus may also be spread by enteric routes.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Transmission Through Kissing
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infection of your liver. Itâs caused by a virus. There is a vaccine that protects against it. For some people, hepatitis B is mild and lasts a short time. These âacuteâ cases donât always need treatment. But it can become chronic. If that happens, it can cause scarring of the organ, liver failure, and cancer, and it even can be life-threatening.
Itâs spread when people come in contact with the blood, open sores, or body fluids of someone who has the hepatitis B virus.
It’s serious, but if you get the disease as an adult, it shouldnât last a long time. Your body fights it off within a few months, and youâre immune for the rest of your life. That means you can’t get it again. But if you get it at birth, itâ unlikely to go away.
âHepatitisâ means inflammation of the liver. There are other types of hepatitis. Those caused by viruses also include hepatitis A and hepatitis C.
Groups At High Risk Of Hep B Transmission
Hep B can only be passed on through blood-to-blood contact, unprotected sex or during birth so you might be at risk of having hep B if you:
- have moved to Australia from a country where hep C is widespread
- were born to a mother who was hep B positive during her pregnancy
- live or have lived with someone with hep B
- have or have had a sexual partner who has hep B
- have ever injected drugs or steroids
- are in prison or have ever been in prison
- have had blood transfusions, blood products or organ transplant in Australia before February 1990
- are of Aboriginal ancestry
- have had unsterile cosmetic or medical procedures.
- have had unsterile tattooing or piercing
- have ever taken part in unsterile traditional practices such as traditional tattooing, circumcision, initiation rituals involving blood, and scarification
- do not meet the above profiles but have abnormal liver function tests or experience hep B symptoms
Read Also: Can You Catch Hepatitis C From Having Sex
Can People With Hep C Be Blood Donors
You are ruled out as a blood donor if you have had hepatitis C, even if you have no symptoms. All blood donations in the U.S. are tested for hepatitis C antibodies, which will indicate whether the person has had HCV in the past. This is essential to prevent the transmission of HCV to the blood recipients.
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test
A hepatitis B surface antigen test shows if you have an active infection. A positive result means you have hepatitis B and can transmit the virus to others. A negative result means you dont currently have hepatitis B.
This test doesnt distinguish between chronic and acute infection. This test is used together with other hepatitis B tests to determine the state of a hepatitis B infection.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Screening 1945 To 1965
Etiology And Mechanisms Of Hbv Infection
Etiology
Hepatitis B virus
HBV is classified in the family Hepadnaviridae. It is a very small, partially double-stranded DNA virus. Humans are known to be the only natural host. HBV reaches the liver through the systemic circulation and can only replicate in hepatocytes . Since HBV is a hepatotropic virus, injury to the liver results from the immune-mediated destruction of infected hepatocytes .
The infectious HB virion has a diameter of 42-47 nm and is a double-shelled particle in serum. Its concentration can be as high as 108 virions per mL . The infectious HB virion consists of an outer lipoprotein coat containing hepatitis B surface antigen . HBsAg surrounds an inner nucleocapsid composed of hepatitis B core antigen that encapsidates the HBV genome and DNA polymerase .
Genome structure and proteins
FIGURE 1: Structure and organization of the HBV genome . The four protein-coding regions are shown by semicircular arrows. They include the precore and core gene the polymerase gene the X gene and the envelope genes pre-S1, pre-S2, and S . The positions of the direct repeats are indicated. Genome positions may change, depending on the HBV genotype . Abbreviations: HBV, hepatitis B virus P gene, the polymerase gene C gene, the core gene S gene, the surface gene.
Natural history of HBV infection
The natural history of chronic HBV infection can be separated into five stages, which are not necessarily sequential . These stages are summarized in Table 1 .