Interventions That Activate The Innate Immune Response
6.1.1. Toll-Like Receptor Agonists
Toll-like receptors constitute the first line of defense against invading microorganisms, in that they sense pathogen-associated molecular patterns leading to the production of cytokines through signal transduction pathways. TLR-7 and TLR-8 agonists are involved in endogenous IFN production, induction of IFN-stimulated genes , and activation of other signaling cascades such as the JAK/STAT pathway. The TLR-7 agonist GS-9620, when first tested in the human hepatocyte cell line HepaRG and primary hepatocytes infected with HBV, showed a durable suppression of HBV replication through induction of Type I IFN but no reduction in cccDNA levels . Similar results were obtained in the woodchuck and chimpanzee animal models , but when used in patients with HBV who were at the time suppressed with NA treatment, there was no significant effect on HBsAg levels . Combination treatment with another TLR-7 agonist and a capsid assembly modulator RO7049389 produced a significant reduction in HBV DNA and HBsAg levels in a mouse infected with a recombinant adeno-associated virus . In Chinese healthy human volunteers, single and multiple ascending doses resulted in IFN-a-induced cytokine production and induction of ISGs . Its efficacy in combination with other antivirals remains to be determined .
Whats The Prognosis For Hepatitis B
Your doctor will know youâve recovered when you no longer have symptoms and blood tests show:
- Your liver is working normally.
- You have hepatitis B surface antibody.
But some people don’t get rid of the infection. If you have it for more than 6 months, youâre whatâs called a carrier, even if you donât have symptoms. This means you can give the disease to someone else through:
- Unprotected sex
- Contact with your blood or an open sore
- Sharing needles or syringes
Doctors donât know why, but the disease does go away in a small number of carriers. For others, it becomes whatâs known as chronic. That means you have an ongoing liver infection. It can lead to cirrhosis, or hardening of the organ. It scars over and stops working. Some people also get liver cancer.
If youâre a carrier or are infected with hepatitis B, donât donate blood, plasma, body organs, tissue, or sperm. Tell anyone you could infect — whether itâs a sex partner, your doctor, or your dentist — that you have it.
Show Sources
CDC: âHepatitis B Questions and Answers for Health Professionals,â âHepatitis B Questions and Answers for the Public.â
Mayo Clinic: âHepatitis B.â
UpToDate: âHepatitis B virus: Screening and diagnosis.â
CDC.
HealthyPeople.gov: âHepatitis B in Pregnant Women: Screening.â
Annals of Internal Medicine: âScreening for Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Nonpregnant Adolescents and Adults: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement.â
What New Treatments Are On The Horizon For Hepatitis B/d Coinfected Patients
Although there are highly effective treatments available to manage hepatitis B, there are few available treatments for hepatitis D, and none are U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved. Hepatitis D is the most severe form of viral hepatitis, and coinfection can accelerate liver damage and cause cirrhosis or liver cancer in as little as 5 years for some patients. Currently there is no approved drug for acute or chronic hepatitis B/D coinfection, but in trials pegylated interferon alpha has shown to be somewhat effective. By stimulating the bodys immune system, around 25-30% of patients are able to suppress their hepatitis D viral load with weekly injections over 48 weeks. Emerging research is showing higher rates of effectiveness with prolonged interferon treatment beyond one year, but it can be difficult for patients to continue due to the physical and mental toll of interferon on the body. Antiviral medications that are proven effective against hepatitis B are sometimes prescribed along with interferon therapy for patients with a high hepatitis B viral load, but these have no effect on hepatitis D. It is urgent that more treatment options be developed for the millions of hepatitis B/D patients that are eagerly awaiting them.
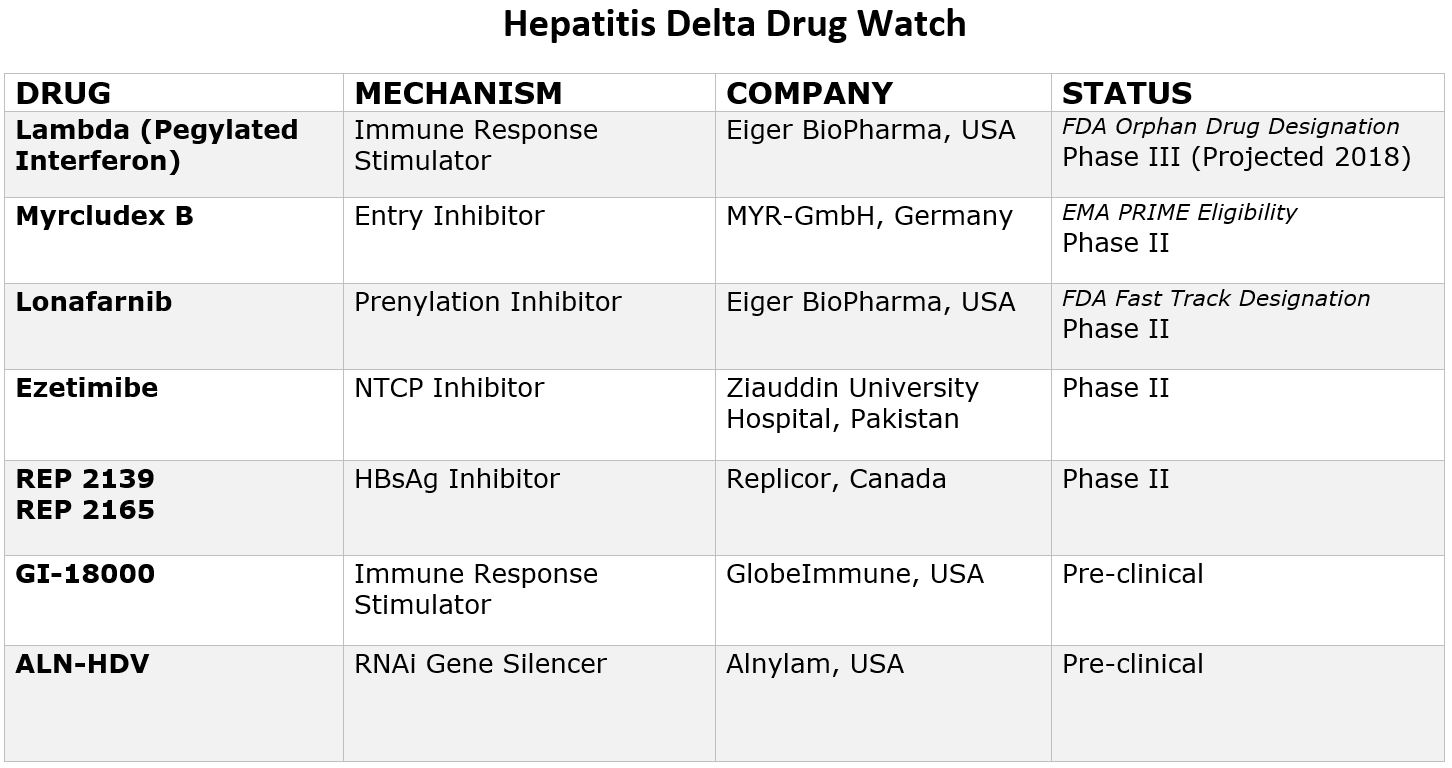
Pegylated Interferon Lambda
Myrcludex B
Ezetimibe
Lonafarnib
Rep 2139
GI-18000
ALN-HDV
Click here for more information about the phases of the clinical trial process.
You May Like: Where Can I Get Hepatitis B Vaccine For Free
Nucleocapsid Assembly Inhibitors And Core Inhibitors
The HBV core protein plays a central role in the viral replication cycle starting with uncoating and release of rcDNA, delivery to the nuclear pore basket, nucleocapsid formation and packaging of pgRNA, and finally interaction with HBsAg during the end stages of morphogenesis. There is indirect evidence that the protein binds to cellular promoters and regulates gene expression . In this respect it constitutes another attractive antiviral target.
The following two classes of core protein allosteric modulators have been discovered: the heteroaryldihydropyrimidines and the phenylpropenamides , sulfamoylbenzamides, and several other chemotypes .
HAP derivatives, misdirect core protein dimers to assemble aberrant non-capsid polymers, leading to the degradation of the core protein . GLS4 is a representative compound of the HAP family.
Type II CpAMs were found to accelerate formation of capsid assembly, possibly at an inappropriate time and place, thereby preventing pgRNA encapsidation and, instead, inducing the assembly of empty capsids .
In vitro, GLS4 inhibited virus accumulation in the supernatant of hepatic cell lines. This was tested in vivo in nude mice inoculated with HepAD38 cells, which then grew out as tumors, resulting in viremia. Treatment of mice with GLS4 and BAY 41-4109 caused a strong and sustained drop in HBV DNA to about the same extents both during and after treatment .
Who Can I Talk With During Treatment
Since hepatitis C treatment plans last several weeks, you should regularly attend medical appointments. Your doctor may have a list of local groups where you can find emotional support.
There may also be other resources like community nurses and walk-in clinics. With this information, youll know where to go for help between appointments.
Another option is to explore the online hepatitis C community, where people share their experiences with hepatitis C.
For example, the Inspire hepatitis C group allows people to connect, share stories, discuss treatment, and more.
Read Also: Interferon Treatment For Hepatitis C
Who Should Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
All newborn babies should get vaccinated. You should also get the shot if you:
- Come in contact with infected blood or body fluids of friends or family members
- Use needles to take recreational drugs
- Have sex with more than one person
- Are a health care worker
- Work in a day-care center, school, or jail
Gene Editing Strategies: Cccdna Formation Inhibitors
Silencing or depleting the cccDNA pool in infected hepatocytes is the goal in new approaches to treatment. Targeted mutagenesis has attracted considerable interest in recent years. This was achieved through the use of sequence-specific RNA-guided nucleases and proteins as a means to cure HBV infection by permanently disabling cccDNA . The RGN family includes zinc finger nucleases , transcription activator-like effector nucleases , and clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats with CRISPR-associated systems , all showing antiviral efficacy.
The cccDNA is a stable non-integrated minichromosome wrapped in transcriptionally active and inactive chromatin . Designer nucleases can cleave at pretargeted sequences in the HBV genome to result in predefined mutagenesis. Although mutated cccDNA can be transcribed, the resulting mutated viral proteins is not able to engage in viral replication. Hence, HBV cccDNA is an optimal target for nuclease gene editing, due to its episomal minichromosome configuration and sequence stability. More specifically, the efficacy of CRISPR/Cas9 for cleavage and inactivation of the cccDNA, as well as inhibition of hepatocarcinogenesis, has been reported .
Also Check: Can You Get Rid Of Hepatitis C For Good
Program And Video Timestamps:
0:01:34 Orange Shirt Day Introduction by Dr. Carla Coffin on Orange Shirt Day
Session I: Update on the Global Response to HBV
0:03:17 Welcoming Remarks by Dr. Timothy Block 0:06:30 HBV Science 101 by Dr. Thomas Tu0:15:30 The Road to HBV Cure New Findings by Dr. John Tavis 0:26:45 Towards HBV Elimination by Dr. Chari Cohen 0:36:19 Q& A Session moderated by Dr. Jordan Feld
Session II: The Challenge of Hepatitis B in Canada Community Forum 0:49:12 The HBV Epidemic in Canada by Dr. Carla Coffin 1:01:36 Community Forum Stories from Lived Experiences
Factors That Influence Ifn Response
HBV has been called a stealth virus since it does not induce a significant IFN response in the liver. Besides, sustained off-treatment response to exogenous IFN- therapy can be achieved only in a minority of CHB patients. Both host and viral factors influence the IFN response during HBV infection and IFN- therapy , some of which could be used as predictors to improve the cost-effectiveness of IFN- therapy.
Table 1 Viral and host factors that affect IFN response during HBV infection and IFN therapy.
Don’t Miss: Does Hepatitis C Affect The Brain
Urgent Action Is Needed To Tackle Hepatitis B Stigma And Discrimination According To A New Report Released By The World Hepatitis Alliance
Across the world, stigma and discrimination impact people living with hepatitis B, with careers and personal relationships affected. The impact of stigma and discrimination also affects families and communities and negatively impacts testing strategies. The Stigma Report released by WHA brings together the latest research on stigma and discrimination and the stories of the people and communities affected by hepatitis B. The report highlights the need to address hepatitis B stigma and discrimination so that no one has to suffer the additional consequences of living with hepatitis B.
Danjuma Adda, president-elect of WHA, whose own story features in the report, said. Stigma and discrimination can have a huge impact on the lives of people living with hepatitis B. It impacts our rights to work, to travel and to live our lives. The Stigma report shows that it is time to tackle this issue to protect the rights of the millions of people living with hepatitis B. We can no longer suffer in silence the time for action is now.
Two hundred ninety-six million people live with hepatitis B worldwide, and for many, their lives are made infinitely more challenging by stigma and discrimination. In a 2017 survey of WHA members, 93% of respondents indicated that hepatitis-related stigma and discrimination impacted people in their countries, yet little is being done globally to tackle the issue.
Download the report at www.worldhepatitisalliance.org/stigma
About WHA
Exposure To A Source With Unknown Hbsag Status
Unvaccinated persons and persons with previous nonresponse to hepatitis B vaccination who have a discrete, identifiable exposure to blood or body fluids containing blood from a person with unknown HBsAg status should receive the hepatitis B vaccine series, with the first dose initiated as soon as possible after exposure and the series completed according to the age-appropriate dose and schedule. Exposed persons who are not fully vaccinated but started the series should complete the vaccine series. Exposed persons with written documentation of a complete hepatitis B vaccine series who did not receive postvaccination testing require no further treatment.
You May Like: How Do You Get Rid Of Hepatitis B
New Immunotherapy ‘highly Effective’ Against Hepatitis B
- Date:
- University College London
- Summary:
- Scientists have identified a new immunotherapy to combat the hepatitis B virus , the most common cause of liver cancer in the world.
Scientists at UCL have identified a new immunotherapy to combat the hepatitis B virus , the most common cause of liver cancer in the world.
Each year, globally, chronic HBV causes an estimated 880,000 deaths from liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma/liver cancer .
The pioneering study used immune cells isolated directly from patient liver and tumour tissue, to show that targeting acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase , an enzyme that helps to manage cholesterol levels in cells*, was highly effective at boosting immune responses.
Published in Nature Communications, the findings show that blocking the activity of ACAT with ACAT inhibitors boosts the specific immune cells that can fight both the virus and associated cancerous tumours, demonstrating its effectiveness as an immunotherapy. Inhibiting ACAT was also found to impede HBV’s own replication, thereby also acting as a direct antiviral. ACAT inhibitors such as avasimibe, taken orally, have previously been shown to be well-tolerated as cholesterol-lowering drugs in humans.
Explaining the study, lead author Professor Mala Maini , said: “Chronic hepatitis B virus infection is a major global health problem and the most common cause of liver cancer in the world.
Grant funding came from the Wellcome Trust and Cancer Research UK.
Story Source:
Incomplete Or Failed Response To Treatment
![Global Hepatitis B Virus [HBV] Treatment Market ...](https://www.hepatitisprohelp.com/wp-content/uploads/global-hepatitis-b-virus-hbv-treatment-market.jpeg)
Some people with autoimmune hepatitis have an incomplete response to treatment, meaning that treatment helps but does not lead to remission. If you have an incomplete response to treatment, you may need to take different medicines to help prevent liver damage.
Some people may fail to respond to treatment, meaning that the inflammation and liver damage of autoimmune hepatitis keep getting worse. Your doctor may recommend additional blood tests and higher doses of medicines. If liver damage leads to complications, you may need treatment for complications.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Effects Of Hepatitis B
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infection of your liver. Itâs caused by a virus. There is a vaccine that protects against it. For some people, hepatitis B is mild and lasts a short time. These âacuteâ cases donât always need treatment. But it can become chronic. If that happens, it can cause scarring of the organ, liver failure, and cancer, and it even can be life-threatening.
Itâs spread when people come in contact with the blood, open sores, or body fluids of someone who has the hepatitis B virus.
It’s serious, but if you get the disease as an adult, it shouldnât last a long time. Your body fights it off within a few months, and youâre immune for the rest of your life. That means you can’t get it again. But if you get it at birth, itâ unlikely to go away.
âHepatitisâ means inflammation of the liver. There are other types of hepatitis. Those caused by viruses also include hepatitis A and hepatitis C.
Treatment For Acute Hepatitis B
If you’re diagnosed with hepatitis B, your GP will usually refer you to a specialist, such as a hepatologist .
Many people do not have any troublesome symptoms, but if you do feel unwell, it can help to:
- get plenty of rest
- take over-the-counter painkillers, such as paracetamol or ibuprofen, for tummy pain
- maintain a cool, well-ventilated environment, wear loose clothing, and avoid hot baths or showers if itching is a problem
- take medication, such as metoclopramide, to stop you feeling sick, and chlorphenamine to reduce itching your doctor can give you a prescription for these if necessary
Most people recover completely in a couple of months, but you’ll be advised to have regular blood tests to check that you’re free of the virus and have not developed chronic hepatitis B.
You May Like: What Happens If You Have Hepatitis
Modulation Of The Adaptive Immune System
6.2.1. Therapeutic Vaccination
Previous attempts at different times during the past two decades, using existing prophylactic vaccines with varying vaccination strategies, have failed to restore HBV-specific immunity in chronically infected patients. When used in animal models, they provided promising results, which were not replicated in human subjects . Such vaccines which employed an adjuvant, although capable of stimulating a robust B cell response, failed to induce the cytotoxic arm of the immune response which was necessary to achieve a therapeutic outcome. In an attempt to overcome this disadvantage, DNA vaccine strategies were introduced employing coding sequences of HBsAg but, once again, yielded poor results in patients virally suppressed by analogue treatment. Notably, they failed to lead to either HBeAg or HBsAg seroconversion . Of similar faith, was the use of DNA prime followed by poxvirus boost, the latter containing the preS/S encoding region. Although promising results were obtained once again in the chimpanzee animal model , in a phase IIa trial this approach did not induce sustained T cell responses or achieve a sizeable reduction in viral load in chronic HBV carriers .
6.2.2. More Recent Approaches
6.2.3. Vector-Based Vaccines
6.2.4. Adoptive Transfer of Genetically Engineered T Cells
Ro7049389 Is Safe Well Tolerated In Chronic Hepatitis B Treatment
Disclosures: We were unable to process your request. Please try again later. If you continue to have this issue please contact .
Core protein allosteric modulator RO7049389 was safe and demonstrated antiviral activity in patients with chronic hepatitis B infection, according to research published in Lancet Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Current treatment options for patients with chronic HBV infection comprise two classes of drugs: subcutaneously administered interferon preparations and orally administered nucleotide analogues. Neither treatment achieves a high rate of functional cure, defined as sustained loss of hepatitis B surface antigen with or without seroconversion to antibody positivity,Man-Fung Yuen, MD, PhD, of the University of Hong Kong, and colleagues wrote. Thus, there is a huge unmet medical need for well-tolerated therapies for chronic HBV infection that can achieve a higher rate of functional cure with a finite course of treatment.
Adobe Stock
The data showed mean HBV DNA concentration declines from baseline of 2.44 log10 IU/mL in the 200 mg twice daily group, 3.33 log10 UI/mL in the 400 mg twice daily group, 3 log10 IU/mL in the 200 mg once daily group, 2.86 log10 IU/mL in the 600 mg once daily group and 3.19 log10 IU/mL in the 1,000 mg once daily group Mean HBV DNA concentration decline was 0.34 log10 IU/mL in the placebo group.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Flare Up Symptoms
The Next Frontier Of Daa Therapy
The use of DAAs has allowed for effective and well-tolerated treatment options for patients with HCV. The next focus of DAA therapy is the ongoing development of pan-genotypic regimens, treatment of patients who failed other DAA-based therapies and the feasibility of shortened treatment courses. Although many DAAs have resulted in cure rates exceeding 90% in many populations, effectively treating the 10% or so of patients that failed therapy has presented a challenge. Many of these patients develop RAVs after exposure to NS5As or NS3/4a inhibitors, which may limit their further treatment options.
The combination of the next-generation NS3/4A protease inhibitor glecaprevir and the next-generation NS5A inhibitor pibrentasvir has demonstrated activity against all genotypes and against frequently observed variants that have been resistant to other NS5A inhibitors. In the SURVEYOR trials, 12 weeks of treatment with glecaprevir/pibrentasvir in non-cirrhotic genotype 1 patients resulted in overall SVR12 rates > 98%. Reducing treatment duration to 8 weeks was equally effective in this population. A subsequent trial evaluated its efficacy in genotype 1 and 3 patients with compensated cirrhosis. SVR12 rates were 96% in genotype 1 patients and 98% across all genotype 3 patients. The presence of baseline RAVs had no significant impact on SVR rates.