Reversibility Of Hepatic Encephalopathy
Classically, hepatic encephalopathy was regarded as a reversible condition. Patients appeared to improve with either drug therapy or liver transplantation. However, a recent study assessed cirrhotic patients who had apparently recovered from an episode of overt hepatic encephalopathy. After careful psychometric testing, it was discovered that these clinically improved patients had residual cognitive impairment compared with cirrhotic patients with either minimal hepatic encephalopathy or no encephalopathy.
In 2009, Sotil et al evaluated 39 patients who had undergone liver transplantation about 1.5 years before the study. The 25 patients who had hepatic encephalopathy prior to transplantation, on the whole, performed worse on psychometric testing than the 14 patients with no history of overt encephalopathy prior to transplantation.
In 2011, Garcia-Martinez et al assessed the cognitive function in 52 patients who had undergone liver transplantation. Global cognitive function after transplantation was worse in patients with a history of alcohol-induced cirrhosis, patients with diabetes, and patients with a history of hepatic encephalopathy prior to transplantation. Furthermore, the brain volume after transplantation was smaller in patients with a history of hepatic encephalopathy prior to transplantation than in patients with no overt encephalopathy. These are provocative findings that require additional investigation.
Hepatic Encephalopathy Types And Stages
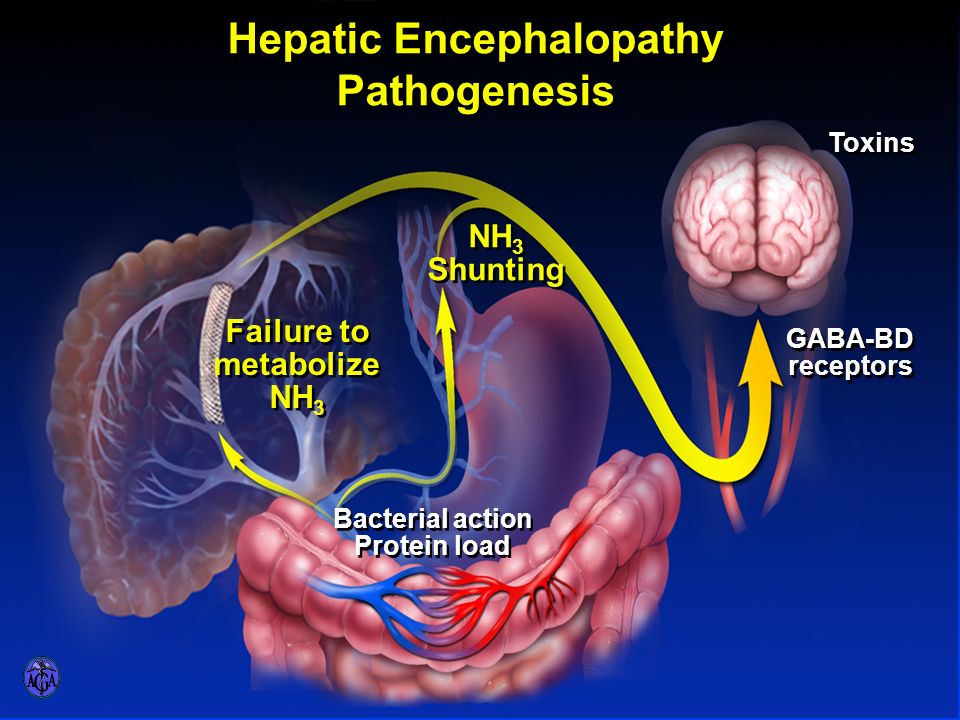
Hepatic encephalopathy , or portosystemic encephalopathy or PSE, is a condition that causes the worsening of brain function in people with advanced liver disease. When the liver is damaged, it can no longer remove toxic substances from the blood. These toxins may reach the brain and cause the brain cells to swell. This hampers brain function.
HE is classified into three types:
- Type A: It is associated with acute liver failure.
- Type B: It occurs when there is no primary liver damage, and encephalopathy occurs due to the portosystemic shunting of the blood . Portosystemic shunts can be either congenital or acquired.
- Type C: It is an encephalopathy associated with severe liver disease or severe liver damage. Encephalopathy can either be episodic or persistent .
The stages of HE include the following:
- Grade 0 : Difficult to detect clinically subtle impairment in memory, concentration, and intellectual functions. Slight impairment of coordination such as poor work performance or ability to drive
- Grade 1 : Presence of mood changes, depression, irritability, a decreased attention span, and sleep issues
- Grade 2 : Associated with increasing forgetfulness, slurred speech, inappropriate behavior, inability to do simple mental tasks such as basic math, shaking of hands, and writing difficulties
- Grade 3 : Characterized by marked sleepiness, disoriented in space and time, extreme anxiety, and strange behavior
- Grade 4 : The patient loses consciousness and passes into a comatose state.
Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatic Encephalopathy
Hepatic encephalopathy is often difficult to diagnose in the earliest stages of the disease. Forgetfulness, irritability, anxiety, and confusion are often the first signs, most of which easily missed even in persons with known liver disease.
Perhaps the first obvious symptom would be something called an inverted sleep-wake pattern, in which a person will literally sleep by day and remain awake at night. This is often followed by a range of later-stage symptoms, which can include:
- Lethargy
- Uninhibited behavior
- Amnesia
Severe cases can lead to a worsening state of consciousness, often progression to violent seizures and coma. Death is usually caused by the severe swelling of the brain .
You May Like: First Signs Of Hepatitis C
Postoperative And Rehabilitation Care
Patients with hepatic encephalopathy are at risk for recurrent episodes of encephalopathy.
Protein restriction is only of use in patients with acute flare-ups and is not justified in chronic cases. These patients need nutrition as they have a high catabolic rate and severe wasting.
Vegetable protein is better tolerated compared to animal protein.
Medications should be used with caution one should avoid constipation, blood thinners and use prophylaxis against spontaneous bacterial peritonitis.
Treatments For Hepatic Encephalopathy
The most important step in treating hepatic encephalopathy is for the patient to undergo the lifestyle changes needed to help reverse the underlying liver disease. This can include refraining from drinking alcohol, losing excess weight and controlling sugar intake.Additionally, steps can be taken to help reduce the toxins in the body. Antibiotics can help stop the growth of bacteria that produce natural toxins, and laxatives can help stimulate frequent bowel movements to help remove toxins.
Tampa General Hospitals liver disease and hepatology specialists offer comprehensive hepatology services to patients with diseases of the liver, biliary tree, gallbladder and pancreas.
You May Like: What Is The Cure For Hepatitis B
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Once hepatic encephalopathy has been diagnosed, it carries a poor prognosis. Close to 40% of patients are dead within 12 months. in view of this high mortality an interprofessional team that closely monitors and manages the patient is vital to improve the quality of life. At the onset of the diagnosis, the patient should be referred to a liver transplant surgeon to determine his or her eligibility.
The pharmacist plays a critical role in monitoring the medications, which cannot only exacerbate the condition but can remain in the body for prolonged periods because they are not broken down by the liver. All the doses of drugs have to be decreased, and one should avoid potentially liver-toxic drugs.
The nurse should educate the patient and the family on the disorder, its progression and potential complications. The mental status changes have to be closely monitored because they impart a very poor quality of life. Further, most patients have very little insight into their disease and may not be able to perform any daily living activities- hence a consult with a social worker, home care nurse, and a physical therapist are recommended. Finally, a dietitian should be consulted to ensure that the patient is receiving adequate calories.
Outcomes
Python Find Closest String Match In List
hepatic encephalopathy
Read Also: Hepatitis C Antibody Non Reactive Meaning
Glutamate Metabolism: A Coordinated Shuttle Between Astrocytes And Neurons
Astrocytes are known to play a major role in numerous functions of the central nervous system, including glutamate, ion and water homeostasis, defense against oxidative stress, energy storage in the form of glycogen, scar formation and tissue repair, modulation of synaptic activity via the release of gliotransmitters, and synapse formation and remodeling. Importantly, essential astrocytic functions involve strong metabolic cooperations with neighboring neurons. Such a metabolic interaction has been reviewed earlier in this chapter for GSH metabolism but is also operative for K+ and pH buffering, ascorbic acid recycling, energy substrate delivery, and glutamate metabolism in the so-called glutamate-glutamine shuttle . The latter represents a key function of astrocytes, which play a critical role in the regulation of glutamate neurotransmission.
Indeed, synaptically released glutamate is removed rapidly from the extracellular space by a transporter-mediated reuptake system that is particularly efficient in astrocytes. This mechanism contributes in a crucial manner to the fidelity of glutamate-mediated neurotransmission. Indeed, glutamate levels in the extracellular space are low , allowing for optimal glutamate-mediated signaling after depolarization while preventing overactivation of glutamate receptors, which could eventually result in excitotoxic neuronal damage.
Overview On Current Management Of Hepatic Encephalopathy
Zhixian Wang, MD, zujiang Yu, MD, Ke-Qin Hu, MD
Abstract
Hepatic encephalopathy is one of the most serious complications of chronic or fulminant liver failure. Its main clinical manifestations involving disturbance of consciousness, behavioral disorders and coma. According to the degree of impaired consciousness, neurological signs and EEG changes, the clinical course of HE may be divided into four phases, ranging from cognitive alteration to coma and even death, staging contribute to early diagnosis, prognosis and therapeutic evaluation. Management of HE primarily involves avoidance of precipitating factors, protect live function from further damage, treatment of ammonia poisoning and regulation of neurotransmitter. This review mainly discusses the current available options for therapy in Hepatic encephalopathy and some new studied agents.
Keywords
Full Text:
References
Poordad FF. Review article: the burden of hepatic encephalopathy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2007 25:3-9.
D’Amico G, Garcia-Tsao G, Pagliaro L. Natural history and prognostic indicators of survival in cirrhosis: a systematic review of 118 studies. J Hepatol. 2006 44:217-231.
Eroglu Y, Byrne WJ. Hepatic encephalopathy. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2009 27:401-414.
Ferenci P. Hepatic encephalopathy–definition, nomenclature, diagnosis, and quantification: final report of the working party at the 11th World Congresses of Gastroenterology, Vienna, 1998. Hepatology 35, 716-721 .
Read Also: What Causes Hepatitis C Symptoms
What Are The Stages Of Hepatic Encephalopathy
HE is assessed according to the severity of the symptoms. The most commonly used grading system is the West Haven grading system, which is as follows:
- Grade 0 Â Difficult to detect clinically subtle impairment in memory, concentration and intellectual functions. Slight impairment of coordination that may manifest as poor work performance or ability to drive . If such occurrences are brought to the physicianÂs notice, the patient may be referred for neuropsychiatric evaluation and followed up regularly to monitor the condition. At present, there are no drugs to treat minimal HE.
- Grade 1 Â Presence of mood changes, depression, irritability, a decreased attention span and sleep issues
- Grade 2 -Associated with increasing forgetfulness, slurred speech, inappropriate behavior, inability to do simple mental tasks like basic math, shaking of hands and writing difficulties
- Grade 3 ÂCharacterized by marked sleepiness, disoriented in space and time, extreme anxiety and strange behaviour
- Grade 4 Â Patient loses consciousness and passes into a comatose state
How Do You Treat Someone With Hepatic Encephalopathy
HE cannot be controlled without taking treatment. Symptoms will likely get worse without continuous treatment. Treatments for HE aims to control the disease, reduce hospitalization and prevent recurrence. Lactulose and antibiotics are most commonly used to treat HE and prevent toxins from building up.
Also Check: What Does Non Reactive Mean For Hepatitis C
When Should I Call The Doctor
You should call your doctor if you have liver disease and you notice signs of hepatic encephalopathy. Symptoms include impaired thinking, mood changes, sleep problems and hand flapping.
You should also notify your doctor if you have liver disease and become constipated. Bowel movements help rid the body of toxins. Having fewer bowel movements can cause toxins to build up in your body.
Brain Edema And Energy Metabolism
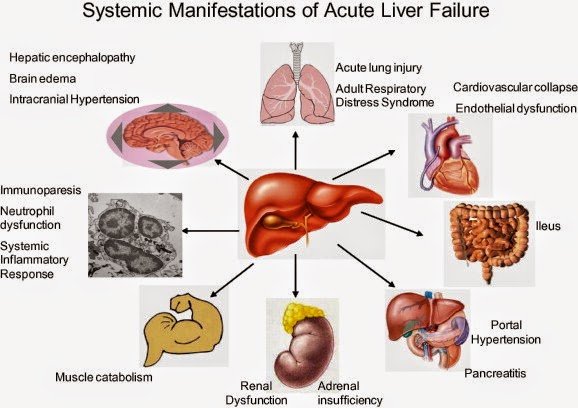
In acute liver failure , the deficiency of energy metabolism associated with brain edema has been fully described. This energy dysfunction is thought to be due to a compromised tricarboxylic acid cycle enzyme, -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase activity, limited anaplerotic flux and capacity of astrocytes to detoxify ammonium by glutamine synthesis, increased lactate synthesis as well as mitochondrial permeability transition induced by oxidative/nitrosative stress . At later stages of the disease, several mechanisms have been proposed where the circulating ammonia can increase glutamine, which could secondarily impact energy metabolism through an initial osmotic stress, while changes in the glutamateglutamine cycle will follow. Additionally, brain edema is life threatening and in these patients brainstem herniation and death can occur . However, instead of a severe edema seen in ALF, mild edema is seen in chronic liver failure , which correlates with lower and more variable ammonia concentrations . Finally, the presence of edema is described infrequently in ACLF patients where it is only present in 48% of patients .
Fig. 2
Also Check: Hepatitis C Is Curable Or Not
Risk Factors And Complications Of He
Risk factors that make it more likely you’ll get HE include:
- Cirrhosis or other severe liver disease.
- Having a TIPS procedure.
If you’ve had HE once, these things can trigger another bout:
- Not drinking enough water.
- Low levels of salt in the blood.
- Eating too much protein.
- Low oxygen levels.
- Surgery.
- Taking drugs that act on the central nervous system, including antidepressants, sleeping pills, opiates, and opioids.
Untreated, HE will get worse. It will not get better on its own.
How Liver Failure Affects The Brain
Hepatic encephalopathy typically occurs when the liver is no longer able to perform its usual metabolic functions.
In persons with a normal liver function, nitrogen-containing compounds from the intestines are transported to the liver, where they are processed and excreted from the body. When liver function is impaired, the nitrogen-containing compounds begin to gradually build up, which causes an increase in ammonia levels.
These ammonia particles then spread throughout the bloodstream and pass through the semi-permeable membrane that that surrounds the brain. There, they cause the swelling of brain cells called astrocytes, which eventually slows the production of neurotransmitters vital to cognitive thinking.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Vaccine Dosage For Newborns
Understanding The Psychiatric Aspects Of Liver Disease
When we hear the word “hepatitis,” we tend to associate it with cirrhosis and other disorders affecting the liver. But it’s not always the case. As with other persistent, chronic infections, hepatitis can directly impact one organ system while indirectly affecting other organ systems, as well.
One system indirectly impacted by liver disease is the central nervous system, and most specifically the brain. During an acute or chronic hepatitis infection, toxic substances from the liver can accumulate in the bloodstream and spread throughout the body. When these substances enter the brain, they can cause a neurological condition called hepatic encephalopathy.
Hepatic encephalopathy typically presents with confusion, lethargy, and sometimes dramatic changes in behavior and motor skills. If left untreated, the disease could gradually progress to a coma or even death.
All told, between 30 and 45 percent of people with cirrhosis will develop some signs of hepatic encephalopathy, whether it be mild forms of forgetfulness or more severe bouts of amnesia or seizures.
Types Of Hepatic Encephalopathy
There are two types of HE.
- Acute HE comes on fast and may be a sign of liver failure.
- Chronic HE takes longer to develop. Sometimes people recover only to have it recur later.
Doctors classify the severity of HE by stages.
- Stage 0: Minimal HE. Slight changes in memory and concentration.
- Stage 1: Mild HE. Mood changes and sleep problems.
- Stage 2: Moderate HE. Inappropriate behavior, slurred speech, trouble doing basic math.
- Stage 3: Severe HE. Disorientation, extreme sleepiness, or anxiety.
Read Also: How Do You Get Hepatitis C Symptoms
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatic Encephalopathy
HE may be considered either covert or overt:
Covert hepatic encephalopathy symptoms are minimal and can go unnoticed, even by a doctor.
Overt hepatic encephalopathy symptoms are more noticeable to other people.
Your doctor may tell you what Grade of HE you or your loved one has. Minimal and Grade 1 is considered covert. Grades 2, 3 and 4 are overt hepatic encephalopathy.
Grade 2 is the least severe overt HE and grade 4 is the most severe overt HE.
What Are The Causes Of Hepatic Encephalopathy
Hepatic encephalopathy can be precipitated by a variety of factors in an otherwise stable cirrhotic patient. These include:
- Excess nitrogen burden  Intake of large amounts of protein, bleeding from esophageal varices, kidney failure with impaired excretion of nitrogenous waste
- Fluid and electrolyte imbalance  Dehydration, hyponatremia , hypokalemia , alkalosis , hypoxia
Hepatic encephalopathy is sub-classified into three types based on the status of the liver.
- Type A: Associated with acute liver failure.
- Type B: Occurs when there is no primary liver damage and encephalopathy occurs due to portosystemic shunting of blood.
- Type C: Encephalopathy associated with chronic liver disease such as cirrhosis and portal hypertension. The encephalopathy can either be episodic or persistent . In some cases, the encephalopathy is subclinical, and the term Âminimal encephalopathy is used to describe such cases.
You May Like: Can Chronic Hepatitis C Be Cured
Treatments To Improve Sleep Disturbances
Sleep disturbances are more common in patients with cirrhosis than in control subjects. Whether or not this relates to hepatic encephalopathy is unclear. A trial compared the histamine H1 blocker hydroxyzine with placebo in patients with cirrhosis and minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Sleep efficiency and the patients’ subjective quality of sleep improved in patients receiving hydroxyzine at bedtime. However, there was no accompanying improvement in cognition, as measured by neurophysiologic tests. The authors urged caution when prescribing hydroxyzine, on account of the risk of worsening encephalopathy in some patients.
What Are The Treatment Options For Hepatic Encephalopathy
Treatment options for hepatic encephalopathy depend on the severity and underlying cause of the condition.
Youll likely need to eat less protein if eating too much protein caused the condition. Since protein is necessary for your body to function properly, a dietician or doctor can create a diet thatll allow you to get enough protein without making your symptoms worse. High-protein foods to avoid include:
- poultry
- eggs
- fish
Medications can also help slow the rate at which your blood absorbs toxins. Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics and lactulose , a synthetic sugar. These medications can draw ammonia, created by intestinal bacteria from your blood, into your colon. Your body will then remove the blood from your colon.
In severe cases that cause difficulty breathing, a ventilator or oxygen mask may be necessary.
Some people with the condition may be eligible to receive a liver transplant.
People with chronic hepatic encephalopathy have better recovery rates than those with the acute version of the condition. The rate of recovery increases if you receive treatment before the condition gets worse.
Hepatic encephalopathy and its symptoms can be reversible with proper treatment.
Also Check: How Do You Find Out If You Have Hepatitis C
What Are Hepatic Encephalopathys Possible Causes
Currently, the specific cause of Hepatic Encephalopathy is still unclear. However, experts theorize that it all starts with toxin accumulation or buildup in the blood. It can happen when there is a failure in the part of the liver to have the toxins broken down properly. The liver is responsible for the removal of chemicals that are toxic to the body, such as ammonia. These toxins are the result of leftovers of metabolized proteins that have been broken down to be used by the different bodily organs. The kidneys then convert these toxins into substances that are safer before having them excreted or removed via the urine.
Once there is damage to the liver, it can no longer have the toxins filtered out, which can then lead to the toxins building up and accumulating in the bloodstream. This toxic buildup can harm the brain and also the nerves and the organs. Several conditions can trigger Hepatic Encephalopathy, and these are imbalances in electrolytes, certain medications that suppressed nervous system, eating increased amounts of protein, medications that can have the immune system suppressed, recent trauma or surgery, low levels of oxygen or hypoxia, dehydration, problems with the kidney, and pneumonia and other similar infections.