The Nonresponder Situation As A Challenge
New vaccine formulations have been and are being developed to meet the challenges of nonresponse or low response among older adults and immunocompromised individuals to current hepatitis B vaccines, for example, third-generation hepatitis B recombinant vaccines containing HBsAg, preS1, and pre-S2 antigens or adjuvanted hepatitis B recombinant vaccines . These vaccines are showing improved immune response in immunocompromised populations and older adults and, in addition, these new vaccines can offer the possibility of simplified schedules, which might be very promising for the future, for example, a 0, 1-month schedule instead of the traditional 0, 1, 6-month schedule .
Reduced Risk Of Hepatocellular Carcinoma:
According to the CDC, the hepatitis B vaccine is recognized as the first anti-cancer vaccine because it can prevent primary liver cancer.3
A clear link has been demonstrated between chronic hepatitis B infection and the occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma. In a Taiwanese study, the institution of universal childhood immunization against hepatitis B virus has been shown to decrease the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma among children.4 In a Korean study in adult males, vaccination against hepatitis B virus has been shown to decrease the incidence of, and risk of, developing hepatocellular carcinoma in adults.5
What Happens When Patients Receive Ineffective Doses
Mishaps can affect vaccine potency. In busy clinics, healthcare staff members juggle many tasks. A distracted doctor or nurse can accidentally leave a vaccine vial on a countertop, instead of placing it back into a medical refrigerator. These small accidents can impact the potency of a vaccine.
These are known as temperature excursion events. They occur when vaccines are stored in ranges outside of the manufacturer’s recommended ranges. Unfortunately, ambient temperatures can damage the vaccine’s potency. Medical staff can’t tell whether these doses are still good by looking at them.
If a healthcare provider doesn’t follow CDC guidelines, they can administer these doses to unwitting patients. The vaccines may cause an inadequate immune response in their bodies and poorly protect patients against diseases.
These mishaps negatively impact both patients and their primary healthcare providers. Patients may need to return for revaccination. These mistakes can lower their opinion of the vaccine provider. The medical clinic can also lose thousands of dollars due to wasted doses.
Healthcare settings should have procedures in place to protect patients from ineffective doses. They should use a medical refrigerator to ensure that the cold chain remains intact. American Biotech Supply has several dedicated models that can safely store vaccines.
Read Also: What Does Chronic Hepatitis C Mean
What Is Hepatitis B
Viral hepatitis type B caused by the hepatitis B virus is a serious, potentially life-threatening disease that can be prevented by vaccination. Most people that are HBV infected remain asymptomatic and do not know their hepatitis status for many years. Only some individuals newly infected with HBV have symptoms . The symptoms can include extreme fatigue, abdominal pain, nausea, and jaundice. Most available scientific evidence suggests that HBV is not directly cytopathic, but that liver damage is caused by the cellular response to viral proteins in infected hepatocytes . For many people, hepatitis B is a short-term illness as clinical signs and symptoms of acute hepatitis B usually resolve within 1 to 3 months . Fulminant liver failure occurs in approximately 0.5% to 1.0% of adults with reported acute hepatitis B. In a subset of persons, the HBV can also cause a chronic liver infection that can later develop into cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma . The course of chronic HBV infection is dynamic with different clinical phases, each of which potentially lasts for decades . Most of the disease burden associated with HBV infection occurs among persons with chronic infection .
The Safety Of Hepatitis B Vaccination Programs

Numerous clinical trials and widespread practical applications have demonstrated that hepatitis B vaccines are very safe. Since 1982, over 1 billion doses of hepatitis B vaccine have been used worldwide. Adverse events after immunization against hepatitis B are infrequent and generally mild and transient. Except for localized pain, placebo-controlled studies have revealed that reported events occur no more frequently among vaccinees than among persons receiving placebo . Data from numerous long-term studies fail to causally link other serious adverse events to hepatitis B vaccination. Data do not indicate a causal association between hepatitis B vaccine and neurological disease , leukemia, diabetes mellitus, demyelinating disorders, chronic fatigue syndrome, arthritis, autoimmune disorders, asthma, hair loss, or sudden infant death syndrome. The Global Advisory Committee on Vaccine Safety has confirmed the excellent safety profile of hepatitis B vaccine and continues to monitor the safety of this vaccine. Furthermore, hepatitis B vaccination can be administered safely to pregnant women during any trimester of pregnancy and to breastfeeding women. Both low birth weight and premature infants and HIV-positive persons can receive hepatitis B vaccination. Hepatitis B vaccination is contraindicated only for persons with a history of allergic reactions to yeast or any of the vaccines components.
Read Also: Can You Get Hepatitis C Through Saliva
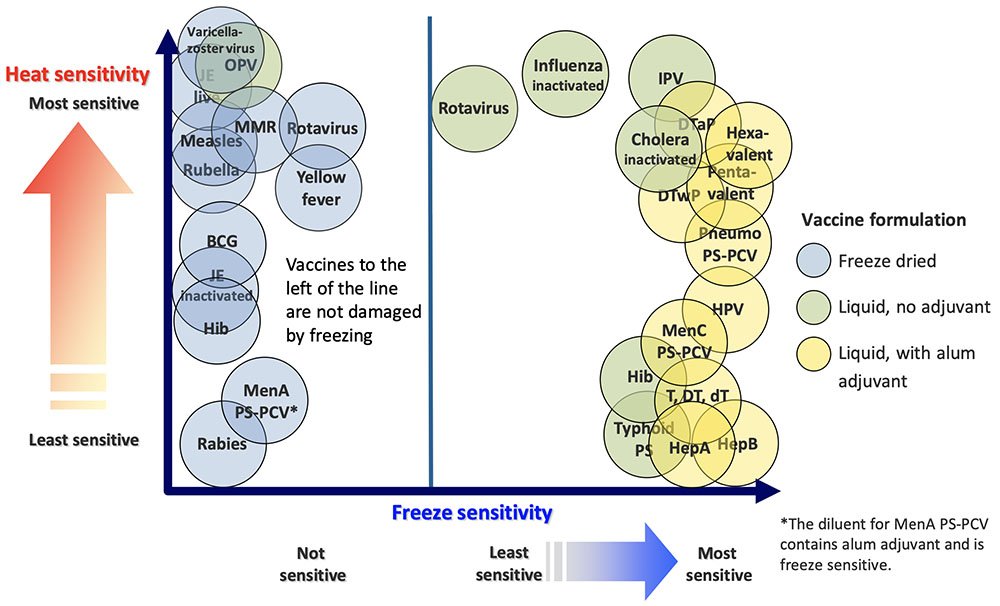
Why Is A Vaccine Cold Chain Necessary
According to the World Health Organization, vaccines are sensitive biological products that are sensitive to light, heat, and freezing. Vaccine potency, or the ability to adequately protect patients, can decrease when vaccines are exposed to extreme conditions. The CDC says that proper vaccine storage plays a critical role in stopping the spread of preventable illnesses.
A cold chain is a system that uses a temperature-controlled supply chain to keep vaccines in good condition. Ensuring vaccine potency starts at the manufacturing plant. Manufacturers protect doses at every step of the process using specialized equipment and procedures. These actions ensure that they store the vials at the correct ambient temperatures during their transportation and delivery.
Once they deliver them to a clinic, healthcare providers must manage the vaccines correctly. They must place these doses inside of a medical refrigerator that can maintain the optimal temperature settings. Next, they must follow correct CDC guidelines when administering these dosages to patients.
Use In Special Populations
Pregnancy
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies designed to evaluate RECOMBIVAX HB in pregnant women. Available post-approval data do not suggest an increased risk of miscarriage or major birth defects in women who received RECOMBIVAX HB during pregnancy.
Nursing Mothers
Data are not available to assess the effects of RECOMBIVAX HB on the breastfed infant or on milk productions/excretion. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mothers clinical need for RECOMBIVAX HB and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from RECOMBIVAX HB or from the underlying maternal condition.
Pediatric Use
Don’t Miss: What Are Some Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Establish A Storage And Handling Operation Procedures To Deal With Emergency Situations
Your organization should prepare a plan to deal with vaccines stored at out-of-range temperature settings. The CDC recommends that facilities should develop and maintain storage and handling operating procedures . It should be clearly written, detailed, and up-to-date. SOPs will help your facility stay organized and ensure that staff follows the proper vaccine management procedures. It will also serve as a reference. It should have information about three major areas.
-
General information Your plan should provide contact information for vaccine manufacturers, equipment service providers, and facility staff. Additionally, it must contain job descriptions, regularly used forms, and staff training requirements.
-
Routine storage and handling SOPs Every plan must have information about all aspects of vaccine inventory management, including ordering new vials to monitor storage conditions.
-
Emergency vaccine storage, handling, and transport SOPs These should outline steps that staff should take in case equipment malfunctions, natural disasters, power failures, improperly stored vials, and other emergencies that could compromise vaccines.
-
Clear instructions -Your plan should have clear steps about handling temperature excursion events and scenarios.
-
Emergency Contacts – Each plan should have emergency contacts when excursion events occur. These include e manufacturer, local health department, and vaccine program coordinators.
Interchangeability With Other Hepatitis B Vaccines:
Recombinant DNA vaccines are produced in yeast by expression of a hepatitis B virus gene sequence that codes for the hepatitis B surface antigen. Like plasma-derived vaccine, the yeast-derived vaccines are protein particles visible by electron microscopy and have hepatitis B surface antigen epitopes as determined by monoclonal antibody analyses. Yeast-derived vaccines have been shown by in vitro analyses to induce antibodies which are immunologically comparable by epitope specificity and binding affinity to antibodies induced by plasma-derived vaccine.13 In cross-absorption studies, no differences were detected in the spectra of antibodies induced in man to plasma-derived or to yeast-derived hepatitis B vaccines.13
Additionally, patients immunized approximately 3 years previously with plasma-derived vaccine and whose antibody titers were < 100 mIU/mL were given a 20-mcg dose of ENGERIX-B. All patients, including 2 who had not responded to the plasma-derived vaccine, showed a response to ENGERIX-B . There have been no clinical studies in which a 3-dose vaccine series was initiated with a plasma-derived hepatitis B vaccine and completed with ENGERIX-B, or vice versa. However, because the in vitro and in vivo studies described above indicate the comparability of the antibody produced in response to plasma-derived vaccine and ENGERIX-B, it should be possible to interchange the use of ENGERIX-B and plasma-derived vaccines .
Don’t Miss: Side Effects Of Autoimmune Hepatitis
Hepatitis A And Hepatitis B
Manufacturers make the Hepatitis A and B vaccines from yeast-derived recombinant DNA and are adsorbed onto aluminum. Providers should store the Hep A and Hep B vaccine between 2°C-8°C . Temperatures above 45°C can inactivate the vaccines. Never freeze these vaccines, because it damages their effectiveness. They form aggregates during freezing and aluminum sedimentation. Do not use these vaccines if they were frozen.
Use With Other Vaccines:
The ACIP states that, in general, simultaneous administration of certain live and inactivated pediatric vaccines has not resulted in impaired antibody responses or increased rates of adverse reactions.17 Separate sites and syringes should be used for simultaneous administration of injectable vaccines.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis A Is A Virus
Who Strategy For Hepatitis B Immunization
Although major progress has been achieved in hepatitis B immunization, a number of challenges remain. That is why the WHO called for comprehensive prevention and control of HBV infection and the development of time-specific immunization goals in its member states. The strategy includes the following: universal vaccination of infants within 24 hours of birth, full immunization of infants by routine immunization programs, catch-up vaccination of unimmunized cohorts, and monitoring progress and assessing the impact of immunization .
Universal Vaccination of Infants Within 24 Hours of Birth: a Real Challenge
Full Immunization of Infants by Routine Immunization Programs and Catch-Up Vaccination of Unimmunized Cohorts
Wider provision of the existing, safe and effective HBV vaccine, through universal childhood vaccination and by catch-up vaccination of unimmunized cohorts, will further reduce new hepatitis B infections, reducing rates of chronic illness and death. However, to achieve and/or sustain high coverage, stronger and resilient immunization delivery systems will be needed. Still, some countries adopt risk-grouptargeted vaccination only, instead of adding a universal vaccination program. However, changing demography, increasing immigration, and the current vaccine costs make the cost-benefit ratios in these remaining low-endemicity countries strongly in favor of universal HBV vaccination.
Monitoring Progress and Assessing the Impact of Immunization
Engerix B 20 Micrograms/1 Ml Suspension For Injection In Pre
This information is intended for use by health professionals
Engerix B 20 micrograms/1 ml
Suspension for injection in pre-filled syringe
Hepatitis B vaccine
1 dose contains :
Hepatitis B surface antigen1,2, 10 micrograms
1Adsorbed on aluminium hydroxide, hydrated Total: 0.25 milligrams Al3+
2Produced in yeast cells by recombinant DNA technology
1 dose contains :
Hepatitis B surface antigen1,2 , 20 micrograms
1Adsorbed on aluminium hydroxide, hydrated Total: 0.50 milligrams Al3+
2Produced in yeast cells by recombinant DNA technology
For the full list of excipients, see section 6.1
Suspension for injection in pre-filled syringe.
The suspension is turbid white.
Engerix B is indicated for active immunisation against hepatitis B virus infection caused by all known subtypes in non immune subjects. The 20 µg dose vaccine in 1.0 ml suspension is intended for use in subjects 16 years of age and above. The 10 µg dose vaccine in 0.5 ml suspension is intended for use in subjects up to and including 15 years of age, including neonates. The categories within the population to be immunised are determined on the basis of official recommendations.
It can be expected that hepatitis D will also be prevented by immunisation with Engerix B as hepatitis D does not occur in the absence of hepatitis B infection.
Posology
Dosage
Primary Immunisation schedules
Subjects up to and including 15 years of age:
Two primary immunisation schedules can be recommended:
Subjects 16 years of age and above:
Recommended Reading: How Long Can You Live With Hepatitis B
Vaccine Accidentally Left Out Of The Refrigerator 5 Steps To Take
Americans faced deadly health challenges from preventable diseases before the mid-20th Century. In the past, thousands died from communicable illnesses such as polio, rubella, measles, and whooping cough. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported that rubella infected more than 12.5 million adults and killed 2,000 babies during the 1964-65 outbreak in the United States.
Things changed once doctors began using vaccines. Disease rates plummeted, and dangerous diseases that caused disabilities and deaths were nearly wiped out of the nation. Since 2012, only 15 cases of rubella were reported to the CDC in the United States.
Vaccines can provide beneficial protection to individuals and protect immunocompromised people who cannot receive vaccines. Although they can save lives, they are only effective if healthcare providers manage, store, and administer them correctly. Additionally, they should also be stored in the right temperatures to maintain their potency. Unfortunately, these doses can easily degrade when exposed to out-of-range conditions.
If a healthcare provider accidentally leaves a vaccine on a countertop, it can ruin its effectiveness. What procedures should your medical facility have if a staff member forgot to put a vaccine back into your medical refrigerator? In today’s American Biotech Supply article, you’ll learn what steps to take to address a temperature excursion event.
The Impact Of Worldwide Hepatitis B Vaccination Programs: Model Of Success
A, Immunization coverage with third dose of hepatitis B in infants in 2019. B, Global immunization 19892019 HepB3 coverage in infants. Global coverage was 84% in 2019. Abbreviations: AFR,African region AMR,Americas region EMR,Eastern Mediterranean region EUR,European region SEAR,South-East Asia region WPR,Western Pacific region. Source: United Nations Children’s Fund /World Health Organization.
The success of HBV vaccination programs has been clearly demonstrated over the recent years in several regions around the world. Countries that have adopted the recommendation had a marked reduction in carrier rates as well as complications from HBV, including HCC. The low prevalence of chronic HBV infection in children younger than 5 years, reducing from 4.7% in the prevaccine era to less than 1% in 2019, can be attributed to the widespread use of hepatitis B vaccine. Due to the implementation of routinely birth-dose vaccination the greatest decrease appears to be in the Western Pacific region, from 8.3% HBsAg prevalence in the prevaccine era to 0.93% in 20022015 . Among health care workers, hepatitis B vaccination is highly effective for the prevention of healthcare associated HBV infection and chronic infection. Using mathematical models, it was estimated that since their implementation, HBV vaccination programs have averted 210 million new HBV infections globally .
Don’t Miss: First Signs Of Hepatitis C
Diphtheria And Tetanus Toxoid
There are several types of Diphtheria-tetanus-containing . Providers should store these vaccines between 2°C-8°C , and protect them from light. The inactivated forms of toxoids of diphtheria and tetanus are unaffected by rising temperatures until they reach 45°C when it loses its secondary structure. At 53 C, the vaccine’s degradation accelerates, causing it to lose its potency.
Adsorbed toxoids onto aluminum-based adjuvants allow these vaccines to have increased stability at elevated temperatures for a longer time. Do not freeze these vaccines, since they can lose their potency. Any frozen vaccine has a reduced immune response and an increased incidence of local reactions.
Hbv Vaccination Doses And Formulations
Given differences in the manufacturing processes and populations vaccinated, the quantity of HBsAg protein per dose that will induce a protective immune response differs in various vaccine products. Currently, hepatitis B vaccines are formulated to contain 540 g of recombinant HBsAg protein and an aluminum phosphate or aluminum hydroxide adjuvant . In general, based on immunogenicity data with different vaccine dosages in different age groups, the vaccine dosages to provide protection for infants, children, and adolescents are 50% lower than that required for adults . Marketed hepatitis B vaccines are to be administered by intramuscular injection on the anterolateral site of the thigh or into the deltoid muscle . The WHO has developed recommendations to ensure the quality, safety, and efficacy of recombinant hepatitis B vaccines and keeps a list of current hepatitis B vaccines prequalified by the WHO .
Hepatitis B vaccines are available as monovalent formulations for birth doses or for vaccination of adult persons at risk, and as combination vaccines . Major progress in the global response to viral hepatitis has been achieved through the introduction of routine hepatitis B vaccination via the WHOs Expanded Programme on Immunization, which was facilitated by the introduction of combination vaccines . Hepatitis B vaccines are generally stable for 3 to 4 years from the date of manufacture if stored between 2°C and 8°C.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Contagious Through Urine
Immunogenicity In Pediatric Patients:
In clinical trials with 242 children aged 6 months to, and including, 10 years given 10 mcg at months 0, 1, and 6, the seroprotection rate was 98% 1 to 2 months after the third dose the GMT of seroconverters was 4,023 mIU/mL.
In a separate clinical trial including both children and adolescents aged 5 to 16 years, 10 mcg of ENGERIX-B was administered at 0, 1, and 6 months or 0, 12, and 24 months . Immediately before the third dose of vaccine, seroprotection was achieved in 92.3% of subjects vaccinated on the 0-, 1-, and 6-month schedule and 88.8% of subjects on the 0-, 12-, and 24-month schedule . One month following the third dose, seroprotection was achieved in 99.5% of children vaccinated on the 0-, 1-, and 6-month schedule compared to 98.1% of those on the 0-, 12-, and 24-month schedule. GMTs were higher for children receiving vaccine on the 0-, 1-, and 6-month schedule compared to those on the 0-, 12-, and 24-month schedule . The clinical relevance of this finding is unknown.