Face Masks And Respiratory Hygiene
The WHO and the US CDC recommend individuals wear non-medical face coverings in public settings where there is an increased risk of transmission and where social distancing measures are difficult to maintain. This recommendation is meant to reduce the spread of the disease by asymptomatic and pre-symptomatic individuals and is complementary to established preventive measures such as social distancing. Face coverings limit the volume and travel distance of expiratory droplets dispersed when talking, breathing, and coughing. A face covering without vents or holes will also filter out particles containing the virus from inhaled and exhaled air, reducing the chances of infection. However, if the mask includes an exhalation valve, a wearer that is infected may transmit the virus through the valve. Many countries and local jurisdictions encourage or mandate the use of face masks or cloth face coverings by members of the public to limit the spread of the virus.
Global Hepatitis Work In Other Countries
To further decrease the burden of all types of viral hepatitis, CDC also helps countries build capacity for surveillance, testing, care, and treatment and assists with development and implementation of national control and elimination programs. CDC has recently supported other countries, including Pakistan, Uzbekistan, and Tanzania.
Learn more about CDCs work to prevent hepatitis B globally.
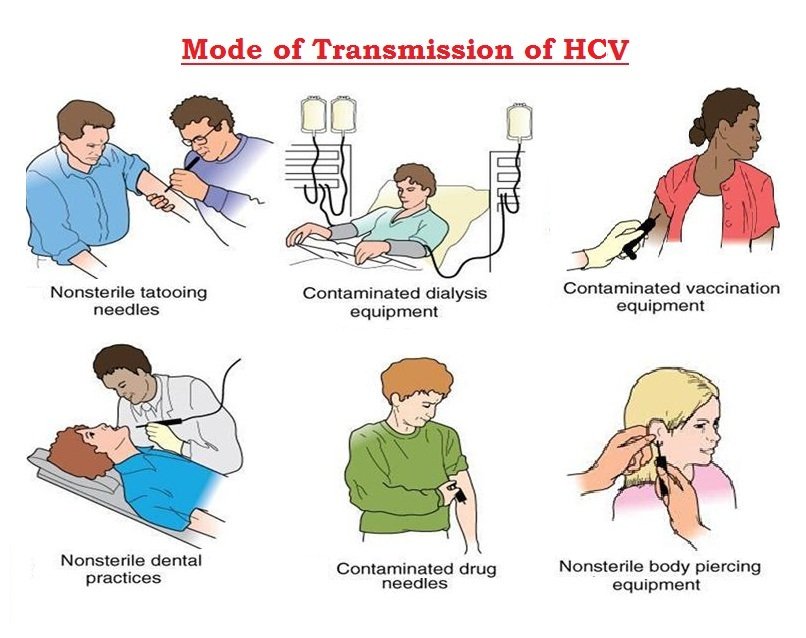
Body Piercings And Tattoos
Tattooing dyes, ink pots, stylets and piercing implements can transmit HCV-infected blood from one person to another if proper sterilization techniques are not followed. Tattoos or piercings performed before the mid 1980s, underground, or non-professionally are of particular concern since sterile techniques in such settings may have been or be insufficient to prevent disease.
Despite these risks, it is rare for tattoos to be directly associated with HCV infection and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Preventions position on this subject states that, no data exist in the United States indicating that persons with exposures to tattooing alone are at increased risk for HCV infection.
Recommended Reading: Symptoms Of Viral Hepatitis C
Asymptomatic And Symptomatic Hepatitis C Infection
Hepatitis C progresses in stages. During the initial acute phase, the disease is usually asymptomatic. As many as 30% will spontaneously clear the virus without knowing they had it. The rest will develop a chronic infection, of whom 15% to 30% will develop cirrhosis within 20 years.
As the disease slowly progresses, the likelihood of symptoms will increase. Even so, most people with chronic HCV infection will have either no symptoms or nonspecific signs such as chronic fatigue or depression.
While most people associate hepatitis C with liver-related symptoms, one in four people with a chronic HCV infection will develop extrahepatic symptoms .
These include skin-related symptoms that can occur during the acute and chronic stages and from hepatitis C treatment.
Indoor Ventilation And Avoiding Crowded Indoor Spaces

The CDC recommends that crowded indoor spaces should be avoided. When indoors, increasing the rate of air change, decreasing recirculation of air and increasing the use of outdoor air can reduce transmission. The WHO recommends ventilation and air filtration in public spaces to help clear out infectious aerosols.
Exhaled respiratory particles can build-up within enclosed spaces with inadequate ventilation. The risk of COVID19 infection increases especially in spaces where people engage in physical exertion or raise their voice as this increases exhalation of respiratory droplets. Prolonged exposure to these conditions, typically more than 15 minutes, leads to higher risk of infection.
Displacement ventilation with large natural inlets can move stale air directly to the exhaust in laminar flow while significantly reducing the concentration of droplets and particles. Passive ventilation reduces energy consumption and maintenance costs but may lack controllability and heat recovery. Displacement ventilation can also be achieved mechanically with higher energy and maintenance costs. The use of large ducts and openings helps to prevent mixing in closed environments. Recirculation and mixing should be avoided because recirculation prevents dilution of harmful particles and redistributes possibly contaminated air, and mixing increases the concentration and range of infectious particles and keeps larger particles in the air.
Also Check: Royal Canin Hepatic Canned Food
How Do You Get Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C spreads when blood or body fluids contaminated with the hepatitis C virus get into your bloodstream through contact with an infected person.
You can be exposed to the virus from:
- Sharing injection drugs and needles
- Having sex, especially if you have HIV, another STD, several partners, or have rough sex
- Being stuck by infected needles
- Birth — a mother can pass it to a child
- Sharing personal care items like toothbrushes, razor blades, and nail clippers
- Getting a tattoo or piercing with unclean equipment
You canât catch hepatitis C through:
- Have been on long-term kidney dialysis
- Have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
- Were born to a mother with hepatitis C
Since July 1992, all blood and organ donations in the U.S. are tested for the hepatitis C virus. The CDC says it is now rare that someone getting blood products or an organ would get hepatitis C. That said, The CDC recommends that anyone over the age of 18 get tested for Hepatitis C. If you haven’t been screened, you should consider having it done.
Learn more about the risk factors for hepatitis C.
Efficacy Of Treatment With Sofosbuvir And Ribavirin
In a study of the DAA combination, sofosbuvir and ribavirin, pan-genotypic clinical efficacy in HCV genotypes 16 was demonstrated.30,31 Another stage 3 clinical trial involving giving patients sofosbuvir in conjunction with ribavirin and PEGylated alpha interferon for a 12-week treatment period showed a sustained virological response in 27 out of 28 treatment-naïve patients with HCV genotype 4 .30 The efficacy of treatment has been profound to the extent that the European Association for the Study of the Liver and the WHO have recommended either a course of sofosbuvir, ribavirin and PEGylated alpha-interferon for a 12-week treatment period or 24 weeks of ribavirin in conjunction with sofosbuvir as an interferon-free treatment regime.3234 Other direct acting antiviral treatments include simeprevir, daclatasvir, a ledipasvirsofosbuvir combination tablet, and a paritaprevirombitasvir combination tablet.
You May Like: How To Cure Hepatitis C
Prognosis And Risk Factors
The severity of COVID19 varies. The disease may take a mild course with few or no symptoms, resembling other common upper respiratory diseases such as the common cold. In 34% of cases symptoms are severe enough to cause hospitalisation. Mild cases typically recover within two weeks, while those with severe or critical diseases may take three to six weeks to recover. Among those who have died, the time from symptom onset to death has ranged from two to eight weeks. The Italian Istituto Superiore di Sanità reported that the median time between the onset of symptoms and death was twelve days, with seven being hospitalised. However, people transferred to an ICU had a median time of ten days between hospitalisation and death. Abnormal sodium levels during hospitalization with COVID-19 are associated with poor prognoses: high sodium with a greater risk of death, and low sodium with an increased chance of needing ventilator support. Prolonged prothrombin time and elevated C-reactive protein levels on admission to the hospital are associated with severe course of COVID19 and with a transfer to ICU.
It is also assumed that those that are immunocompromised are at higher risk of getting severely sick from SARS-CoV-2. One research study that looked into the COVID19 infections in hospitalised kidney transplant recipients found a mortality rate of 11%.
Genotypes Of Hepatitis C
According to modern concepts of virologists, hepatitis C has six genotypes. The term genotype means the differences of the virus at the molecular level.
Most scientists recognize the existence of six genotypes. As a scientific hypothesis, the presence of three more genotypes is considered.
Since the genetic differences of the virus are indifferent to the average reader, let us dwell on the description of the six main genotypes.
Knowledge of the genotypes of their quasi-types is important for infectious disease doctors with:
-
choice of methods of treatment of the disease
-
determining the epidemic situation of hepatitis C.
Genotypes have a specific territorial distribution. In relation to the same genotypes of different territories, the same principles of treatment apply.
Genotypes are denoted by Arabic numerals , and quasitypes or subtypes are denoted by Latin letters and so on:
First genotype. It is ubiquitous, three quasi-types have been identified. If this genotype is confirmed, long-term treatment should be expected, for one year or more.
Second genotype. The ubiquitous distribution of the genotype and four quasitypes are characteristic. The duration of treatment is usually no more than six months.
Fourth genotype. Widespread in the Middle East and Central Africa. In the conditions of Russia it is little studied. Ten quasitypes have been identified.
Sixth genotype. Registered in Asian countries, has one quasi-type. In the conditions of Russia it is little studied.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Infected With Hepatitis B
What Drugs Treat And Cure Hepatitis C
The treatment of chronic hepatitis C has gone through several generations of medications. Not long ago, treatment was limited to interferon alpha-2b or pegylated interferon alpha-2b , and ribavirin . Interferon and pegylated interferon need to be injected under the skin , while ribavirin is taken by mouth. This combination therapy is infrequently used today, being recommended for only the least common genotypes of hepatitis C virus .
Since 2010, direct-acting antiviral drugs have been in use. The second generation of antivirals for HCV was the protease inhibitors telaprevir and boceprevir , both taken by mouth. These were used in combination with the earlier drugs to increase effectiveness . These drugs are also no longer in common use, and have been replaced by better options.
As more has been learned about how hepatitis C virus multiplies within the liver cells, new drugs continue to be developed to interfere with this multiplication at different stages. As such, we no longer think in terms of generations of drugs, but rather categories of action. Research and development of these direct-acting antivirals continue, with new agents coming to market every few months. Each category is improved and expanded by the addition of new drugs, which are safer and more effective.
Currently available and commonly used direct-acting antiviral drugs include:
Transmission And Prevention Research
Modelling research has been conducted with several objectives, including predictions of the dynamics of transmission, diagnosis and prognosis of infection, estimation of the impact of interventions, or allocation of resources. Modelling studies are mostly based on compartmental models in epidemiology, estimating the number of infected people over time under given conditions. Several other types of models have been developed and used during the COVID19 including computational fluid dynamics models to study the flow physics of COVID19, retrofits of crowd movement models to study occupant exposure, mobility-data based models to investigate transmission, or the use of macroeconomic models to assess the economic impact of the pandemic. Further, conceptual frameworks from crisis management research have been applied to better understand the effects of COVID19 on organisations worldwide.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Test Non Reactive
Skin Signs Of Liver Damage
Hepatitis C causes chronic inflammation of the liver, which over time causes progressive scarring known as fibrosis. Cirrhosis occurs when the scarring is severe enough to interfere with the function of the liver.
In rare cases, ongoing liver damage can cause cells to change at the genetic level, leading the hepatocellular carcinoma .
Hepatitis C Testing And Diagnosis
Doctors will start by checking your blood for:
Anti-HCV antibodies: These are proteins your body makes when it finds the hep C virus in your blood. They usually show up about 12 weeks after infection.
It usually takes a few days to a week to get results, though a rapid test is available in some places.
The results can be:
- Nonreactive, or negative:
- That may mean you donât have hep C.
- If youâve been exposed in the last 6 months, youâll need to be retested.
If your antibody test is positive, youâll get this test:
HCV RNA: It measures the number of viral RNA particles in your blood. They usually show up 1-2 weeks after youâre infected.
- The results can be:
- Negative: You donât have hep C.
- Positive: You currently have hep C.
You might also get:
Liver function tests: They measure proteins and enzyme levels, which usually rise 7 to 8 weeks after youâre infected. As your liver gets damaged, enzymes leak into your bloodstream. But you can have normal enzyme levels and still have hepatitis C. Learn the reasons why you should get tested for hepatitis C.
You May Like: How Can You Tell If You Have Hepatitis B
Common Symptoms Of Hepatitis
If you are living with a chronic form of hepatitis, like hepatitis B and C, you may not show symptoms until the damage affects liver function. By contrast, people with acute hepatitis may present with symptoms shortly after contracting a hepatitis virus.
Common symptoms of infectious hepatitis include:
It is crucial to understand what is causing hepatitis in order to treat it correctly. Doctors will progress through a series of tests to accurately diagnose your condition.
Rashes From Hcv Treatment
Hepatitis C is treated with a class of drugs called direct-acting antiviral . While DAAs can cure the vast majority of HCV infections, they can also cause side effects, including fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting.
Skin-related side effects can also occur during treatment, after treatment, or both, typically causing:
Read Also: How Can You Get Hepatitis
What Is Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a liver infection that can lead to serious liver damage. Itâs caused by the hepatitis C virus. About 2.4 million people in the U.S. have the disease. But it causes few symptoms, so most of them don’t know. The virus spreads through an infected personâs blood or body fluids.
There are many forms of the hepatitis C virus, or HCV. The most common in the U.S. is type 1. None is more serious than any other, but they respond differently to treatment.
Willowbrook State School Experiments
A New York University researcher named Saul Krugman continued this research into the 1950s and 1960s, most infamously with his experiments on mentally disabled children at the Willowbrook State School in New York, a crowded urban facility where hepatitis infections were highly endemic to the student body. Krugman injected students with gamma globulin, a type of antibody. After observing the temporary protection against infection this antibody provided, he then tried injected live hepatitis virus into students. Krugman also controversially took feces from infected students, blended it into milkshakes, and fed it to newly admitted children.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis And How Do You Get It
What Is Hepatitis C And How Do You Get It Expert Answers To Your Questions About This Curable Condition
If youve heard of hepatitis C , you might think of actress Pamela Anderson, who was diagnosed with the disease in the early 2000s. Or maybe you associate it with people who have piercings and tattooscommon culprits of hepatitis C transmission. Mostly, though, you probably dont think of it at all, because its the type of disease that flies under the radar. So it might surprise you to learn that hepatitis C is on the rise in the U.S., after decades of decline. So, whats going on?
Weve been seeing cases increase for the last seven or eight years, says Douglas T. Dieterich, MD, director of the Institute for Liver Medicine at Mount Sinai Hospital and professor in the division of liver diseases at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City. In fact, the rate of new hepatitis C cases more than quadrupled over the last decade, according to a study conducted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Dr. Dieterich attributes this increase to the growth in intravenous drug use among certain groups. Once people get addicted to oxycontin and cant get prescriptions anymore, they go out looking for other ways to satisfy their addiction, including heroin or other needle drugs, he says.
The scary news: Untreated, hepatitis C can be fatal. The really good news, though, is that if the disease is detected and treated, you can be cured of hepatitis C. Everybody should be screened at least once in their lifetime for hepatitis C, says Dr. Dieterich.
Related Skin Problems With Hepatitis C Infection
Some skin conditions share a possible association with chronic hepatitis C. For reasons not entirely clear, the risk of these is higher in people with hepatitis C than in the general population.
- Psoriasis: This autoimmune condition causes dry, raised, inflamed patches of skin covered with silvery-white scales. It is nearly twice as common in people with chronic hepatitis C as in those without.
- Dermatomyositis: This inflammatory autoimmune disease causes muscle weakness and a distinctive skin rash. In addition to a reddish-purple rash around the eyes, there may be dark red bumps on the knuckles, elbows, ankles, or knees.
- Erythema multiforme: This is a common skin reaction triggered by many different infections. It causes symmetric red, patchy skin lesions mostly on the arms and legs.
- Erythema nodosum: This is a skin symptom common in people with inflammatory bowel disease that causes tender red bumps on larger bony surfaces on the front of the lower leg. In the absence of IBD, hepatitis C may be suspected.
- Vitiligo: This is a condition that causes the destruction of pigment-producing skin cells called melanocytes, leading to patches of abnormally light skin. Hepatitis C may be suspected if vitiligo suddenly develops during adulthood.
Read Also: Is Hepatitis B A Virus