What Can Happen If Viral Hepatitis Is Not Treated
Most people recover from hepatitis A with no treatment or long-lasting health problems.
Chronic hepatitis B and C can lead to serious health problems, such as:19
- Cirrhosis, or scarring of the liver
- Liver cancer
- Liver failure
People with liver failure may need a liver transplant to survive. In the United States, cirrhosis caused by chronic hepatitis C is currently the most common reason for needing a liver transplant.20 Viral hepatitis is also the most common cause of liver cancer.21
Who Should Be Vaccinated
Children
- All children aged 1223 months
- All children and adolescents 218 years of age who have not previously received hepatitis A vaccine
People at increased risk for hepatitis A
- International travelers
- Men who have sex with men
- People who use or inject drugs
- People with occupational risk for exposure
- People who anticipate close personal contact with an international adoptee
- People experiencing homelessness
People at increased risk for severe disease from hepatitis A infection
- People with chronic liver disease, including hepatitis B and hepatitis C
- People with HIV
Other people recommended for vaccination
- Pregnant women at risk for hepatitis A or risk for severe outcome from hepatitis A infection
Any person who requests vaccination
There is no vaccine available for hepatitis C.
How Long Do The Hepatitis A And B Vaccines Protect You
During your lifetime, you need:
- One series of the hepatitis A vaccine
- One series of the hepatitis B vaccine
Most people dont need a booster dose of either vaccine. But if you have had dialysis, a medical procedure to clean your blood, or have a weakened immune system, your doctor might recommend additional doses of the hepatitis B vaccine.
You May Like: Can You Get Hepatitis A More Than Once
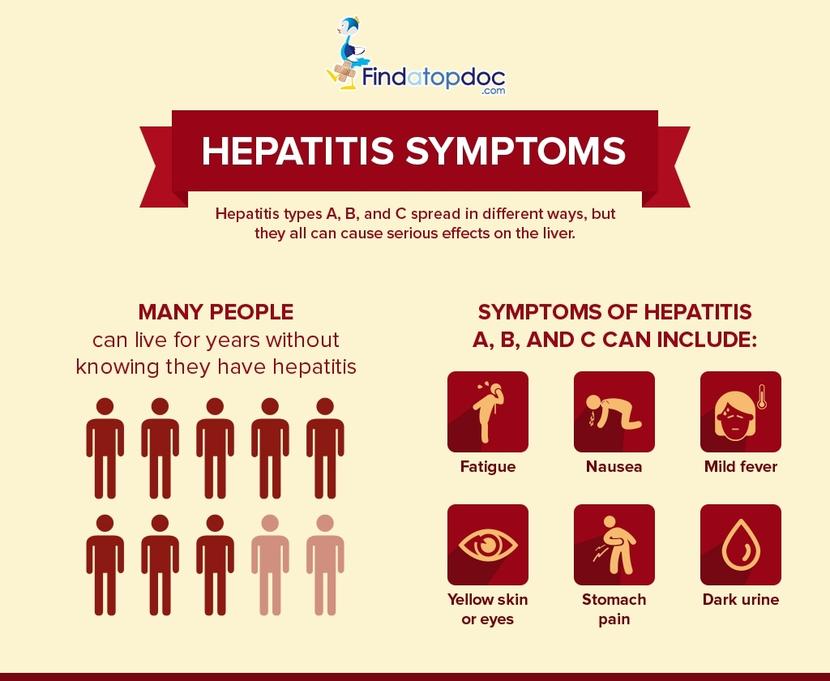
Symptoms Of Viral Hepatitis
Reading time:
When an individual is infected by one of these viruses it can result in acute hepatitis, which initially manifests with a similar clinical picture as that of flu, the symptoms being tiredness, fever and muscle aches. This may be accompanied by gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhoea, nausea or gastric discomfort and finally specific clinical signs of hepatitis may develop with the appearance of:
Yellow coloration of the skin and mucous membranes .
Dark brown or Coca-Cola coloured urine .
A whitish coloration of the faeces .
In a large proportion of cases hepatitis virus infections do not produce any symptoms and go totally unnoticed, the diagnosis is only made by chance if a test is performed at the right time. This disease pattern is called subclinical or asymptomatic hepatitis.
If the infection becomes chronic, it tends to course with very few symptoms. Some patients note a lack of concentration, tiredness, discomfort in the abdomen and in cases of advanced disease they may experience jaundice and an accumulation of fluid in the legs or abdomen. Other patients do not have any symptoms whatsoever and therefore follow a completely normal life.
The fact that cases of viral hepatitis are usually asymptomatic highlights the importance of performing regular blood tests and ruling out the presence of hepatitis in the event of altered liver function or a background of risk factors for transmission.
What Are The Signs Of Hep C
Most people with the hepatitis C virus dont show any symptoms, yet hep C can lead to serious health complications.
In people who do develop symptoms from acute infection, the average time from exposure to symptoms ranges from 2 to 12 weeks.Even without symptoms, a person with hep C can still spread the virus to others.
If youre at risk for hep C, and have experienced any of the symptoms listed below, speak with your healthcare professional and ask if you should be tested. Its important to note that you should never try to diagnose hep C yourself and that it can only be diagnosed by a healthcare professional.
Symptoms of acute and chronic hepatitis C infection may include:
- Fever
Recommended Reading: What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis C Infection
Also Check: Where Does Hepatitis Come From
Can Hepatitis Be Treated
There are no treatments to cure hepatitis A, aside from carefully monitoring liver function. If you know you have hepatitis A early enough, you might be able to stop the infection if you get a dose of the hepatitis A vaccine or something called hepatitis A immune globulin.
Hepatitis B, when chronic, can often be treated successfully. The most commonly used drugs to treat chronic hepatitis B are:
- Entecavir .
For hepatitis C, the following drugs are used:
- Simeprevir .
- Sofosbuvir sofusbuvir/velpatasvir sofusbuvir/velpatasvir/voxilaprevir ledipasvir/sofosbuvir .
- Ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir/dasabuvir .
- Elbasivir/grazoprevir .
- Glecaprevir/pibrentasvir .
These new drugs are sometimes given with older drugs like ribavirin and peginterferon alfa-2a and peginterferon-2b. You might have to take these medicines for some time, even as long as six months.
If you have chronic hepatitis D, your doctor may prescribe drugs with interferons and might also add medicines for hepatitis B. Hepatitis E treatments include peginterferon alfa-2a and ribavirin.
How Do You Get Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C spreads when blood or body fluids contaminated with the hepatitis C virus get into your bloodstream through contact with an infected person.
You can be exposed to the virus from:
- Sharing injection drugs and needles
- Having sex, especially if you have HIV, another STD, several partners, or have rough sex
- Being stuck by infected needles
- Birth — a mother can pass it to a child
- Sharing personal care items like toothbrushes, razor blades, and nail clippers
- Getting a tattoo or piercing with unclean equipment
You canât catch hepatitis C through:
- Breastfeeding
- Casual contact
- Have been on long-term kidney dialysis
- Have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
- Have HIV
- Were born to a mother with hepatitis C
Since July 1992, all blood and organ donations in the U.S. are tested for the hepatitis C virus. The CDC says it is now rare that someone getting blood products or an organ would get hepatitis C. That said, The CDC recommends that anyone over the age of 18 get tested for Hepatitis C. If you haven’t been screened, you should consider having it done.
Learn more about the risk factors for hepatitis C.
Recommended Reading: How Do People Get Hepatitis
When To Seek Medical Advice
See your GP if you persistently have any of the later symptoms listed, or if they keep returning. They may recommend having a blood test that can check for hepatitis C.
Read more about diagnosing hepatitis C
None of these symptoms mean you definitely have hepatitis C, but it’s important to get them checked out.
You should also speak to your GP about getting tested if there’s a risk you’re infected, even if you don’t have any symptoms. This particularly includes people who inject drugs or have done so in the past.
Read about the causes of hepatitis C for more information about who’s at risk of having the infection.
Page last reviewed: 27 October 2021 Next review due: 27 October 2024
What Are The Common Types Of Viral Hepatitis
Although the most common types of viral hepatitis are HAV, HBV, and HCV, some clinicians had previously considered the acute and chronic phases of hepatic infections as “types” of viral hepatitis. HAV was considered to be acute viral hepatitis because the HAV infections seldom caused permanent liver damage that led to hepatic failure. HBV and HCV produced chronic viral hepatitis. However, these terms are outdated and not currently used as frequently because all of the viruses that cause hepatitis may have acute phase symptoms . Prevention techniques and vaccinations have markedly reduced the current incidence of common viral hepatitis infections however, there remains a population of about 1 to 2 million people in the U.S. with chronic HBV, and about 3.5 million with chronic HCV according to the CDC. Statistics are incomplete for determining how many new infections occur each year the CDC documented infections but then goes on to estimate the actual numbers by further estimating the number of unreported infections .
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis C
Types D, E, and G Hepatitis
Individuals who already have chronic HBV infection can acquire HDV infection at the same time as they acquire the HBV infection, or at a later time. Those with chronic hepatitis due to HBV and HDV develop cirrhosis rapidly. Moreover, the combination of HDV and HBV virus infection is very difficult to treat.
- HIV patients
- People with hemophilia who receive blood clotting factors
Don’t Miss: Can Hepatitis C Spread Through Saliva
Contaminated Needles And Infected Blood
You can get hepatitis C from sharing contaminated needles, syringes and other injecting equipment during recreational drug use. Banknotes and straws used for snorting may also pass the virus on.
Being exposed to unsterilised tattoo and body piercing equipment can also pass hepatitis C on. Occasionally, you can get it from sharing a towel, razor blades or a toothbrush if there is infected blood on them.
Hepatitis C infection is also passed on in healthcare settings, from needle stick injuries or from medical and dental equipment that has not been properly sterilised. In countries where blood products are not routinely screened, you can also get hepatitis C by receiving a transfusion of unscreened blood and blood products.
You can prevent hepatitis C by:
- never sharing needles and syringes or other items that may be contaminated with infected blood
- only having tattoos, body piercings or acupuncture in a professional setting, where new, sterile needles are used
- following the standard infection control precautions, if youre working in a healthcare setting.
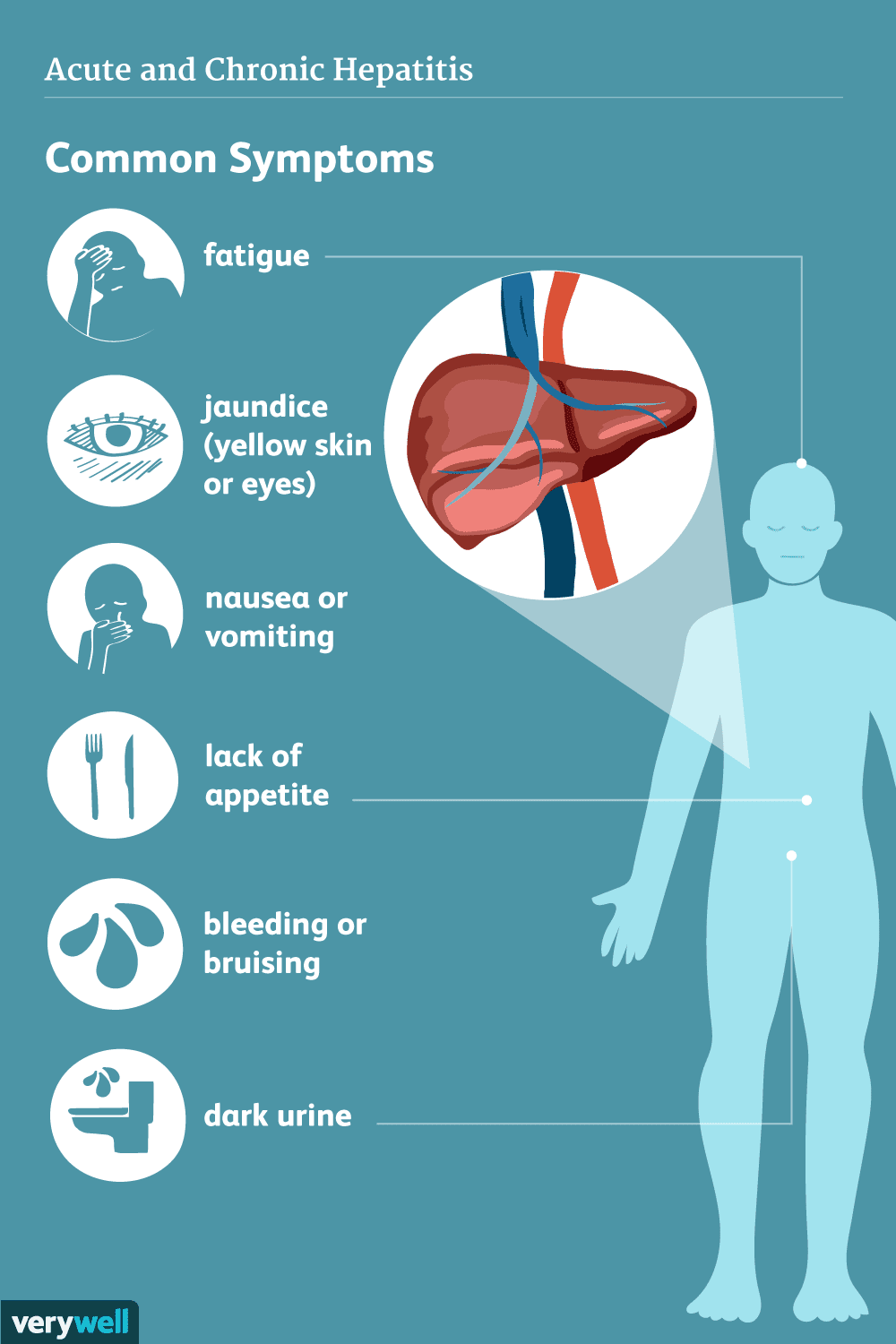
What Are The Symptoms Of Viral Hepatitis
The symptoms of viral hepatitis are similar for all types of hepatitis.9 They include:
- Low-grade fever
- Fatigue
- Joint pain
- Jaundice , which is when the skin and whites of the eyes turn yellow
People who are newly infected are most likely to have one or more of these symptoms, but some people with viral hepatitis do not have any symptoms. New hepatitis A infections usually cause symptoms, but as many as half the people with new hepatitis B and hepatitis C infections do not have symptoms.
Certain blood tests can show if you have hepatitis, even if you do not have symptoms. People with chronic hepatitis B or C often develop symptoms when their liver becomes damaged.
Don’t Miss: How To Live With Hepatitis B
Chronic Hepatitis C Symptoms
If you donât get diagnosed and treated, you could have the disease for years and not know it. Doctors call this the chronic form, because it lasts a long time. Some people who’ve had it for a while get scarring of the liver, which is called cirrhosis. or liver cancer.
In addition to the above symptoms, signs that your liver isnât working the way it should include:
- Ascites — fluid buildup in your belly
- Easy bleeding
- Hepatic encephalopathy — confusion, drowsiness, and slurred speech
- Jaundice of the skin
Questions For Your Doctor
When you visit the doctor, you may want to ask questions to get the information you need to manage your hepatitis C. If you can, have a family member or friend take notes. You might ask:
Don’t Miss: Definition Of Hepatitis B And C
What Is Acute Fulminant Hepatitis
Rarely, individuals with acute infections with HAV and HBV develop severe inflammation, and the liver fails . These patients are extremely ill with the symptoms of acute hepatitis already described and the additional problems of confusion or coma , as well as bruising or bleeding . In fact, up to 80% of people with acute fulminant hepatitis can die within days to weeks therefore, it is fortunate that acute fulminant hepatitis is rare. For example, less than 0.5% of adults with acute infection with HBV will develop acute fulminant hepatitis. This is even less common with HCV alone, although it becomes more frequent when both HBV and HCV are present together.
Who Should Get The Hepatitis A Vaccine
The hepatitis A vaccine is given in two doses, six to 18 months apart. Two doses are needed for lasting protection.
The vaccine is recommended for:27
- All children, starting at 1 year
- Men who have sex with men
- People who travel or work in a part of the world where hepatitis A is common, such as certain parts of Central or South America, Asia, Africa, and eastern Europe. See the CDCs Travelers Health Information.
- People who use illegal drugs
- People who are treated with clotting factor concentrates, such as people with hemophilia
- People with chronic liver disease
- People who work with hepatitis A in a laboratory or with hepatitis Ainfected primates
- Members of households planning to adopt a child, or care for a newly arriving adopted child, from a country where hepatitis A is common. See the CDCs Travelers Health information page for international adoptions.
You May Like: Can You Treat Hepatitis B
How Long Does It Last
Hepatitis A can last from a few weeks to several months.
Hepatitis B can range from a mild illness, lasting a few weeks, to a serious, life-long condition. More than 90% of unimmunized infants who get infected develop a chronic infection, but 6%10% of older children and adults who get infected develop chronic hepatitis B.
Hepatitis C can range from a mild illness, lasting a few weeks, to a serious, life-long infection. Most people who get infected with the hepatitis C virus develop chronic hepatitis C.
How Is It Spread
Hepatitis A is spread when a person ingests fecal mattereven in microscopic amountsfrom contact with objects, food, or drinks contaminated by feces or stool from an infected person.
Hepatitis B is primarily spread when blood, semen, or certain other body fluids- even in microscopic amounts from a person infected with the hepatitis B virus enters the body of someone who is not infected. The hepatitis B virus can also be transmitted from:
- Birth to an infected mother
- Sex with an infected person
- Sharing equipment that has been contaminated with blood from an infected person, such as needles, syringes, and even medical equipment, such as glucose monitors
- Sharing personal items such as toothbrushes or razors
- Poor infection control has resulted in outbreaks in health care facilities
Hepatitis C is spread when blood from a person infected with the Hepatitis C virus even in microscopic amounts enters the body of someone who is not infected. The hepatitis C virus can also be transmitted from:
- Sharing equipment that has been contaminated with blood from an infected person, such as needles and syringes
- Receiving a blood transfusion or organ transplant before 1992
- Poor infection control has resulted in outbreaks in health care facilities
- Birth to an infected mother
Don’t Miss: Which Hepatitis Is Not Curable
How Is Acute Hepatitis C Treated
Acute hepatitis C is typically monitored and not treated. Treatment during the acute stage doesnt change the risk that the disease will progress to the chronic form. An acute infection may resolve on its own without treatment. The following treatment may be all thats necessary:
- proper rest
- adequate fluids
- a healthy diet
Some people may need treatment with prescription medication. Your doctor will be able to work with you about what treatment options may be best for you.
Those most at risk for acute and chronic hepatitis C are people who use or share contaminated needles. Mothers can transmit HCV to their babies during childbirth, but not through breastfeeding. Other risk factors for transmission of HCV include:
- healthcare work, especially work around needles
- getting a tattoo or body piercing with unsterile equipment
- undergoing hemodialysis
- living in a household with someone with HCV
- sharing personal hygiene products, such as razors or toothbrushes
- engaging in sexual activity with multiple partners without condoms or dental dams
- having a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992 or receiving clotting factors before 1987
The most serious long-term risk of acute hepatitis C is developing chronic hepatitis C, which can lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer. In 75 to 85 percent of those with acute hepatitis C, the disease will progress to the more serious chronic hepatitis C.
What Should I Do If I Think I Have Been Exposed To Viral Hepatitis
- If you may have been exposed to hepatitis A or B, your doctor may recommend getting a vaccine to keep you from getting the infection.22,23
- The CDC recommends that people who are exposed to hepatitis C, such as a health care worker after an accidental needle stick, get tested for hepatitis C infection.18 New antiviral medicines for hepatitis C cure most of the people who take them. If you have health insurance, ask about your copay and coinsurance and which medicines are covered under your plan.
Learn more about hepatitis vaccines and testing.
Also Check: How Do I Know If I Have Hepatitis B
Getting Tested For Hepatitis C
Seek medical advice if you have persistent symptoms of hepatitis C or there’s a risk you’re infected, even if you do not have any symptoms.
A blood test can be carried out to see if you have the infection.
GPs, sexual health clinics, genitourinary medicine clinics or drug treatment services all offer testing for hepatitis C.
Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent or limit any damage to your liver, as well as help ensure the infection is not passed on to other people.