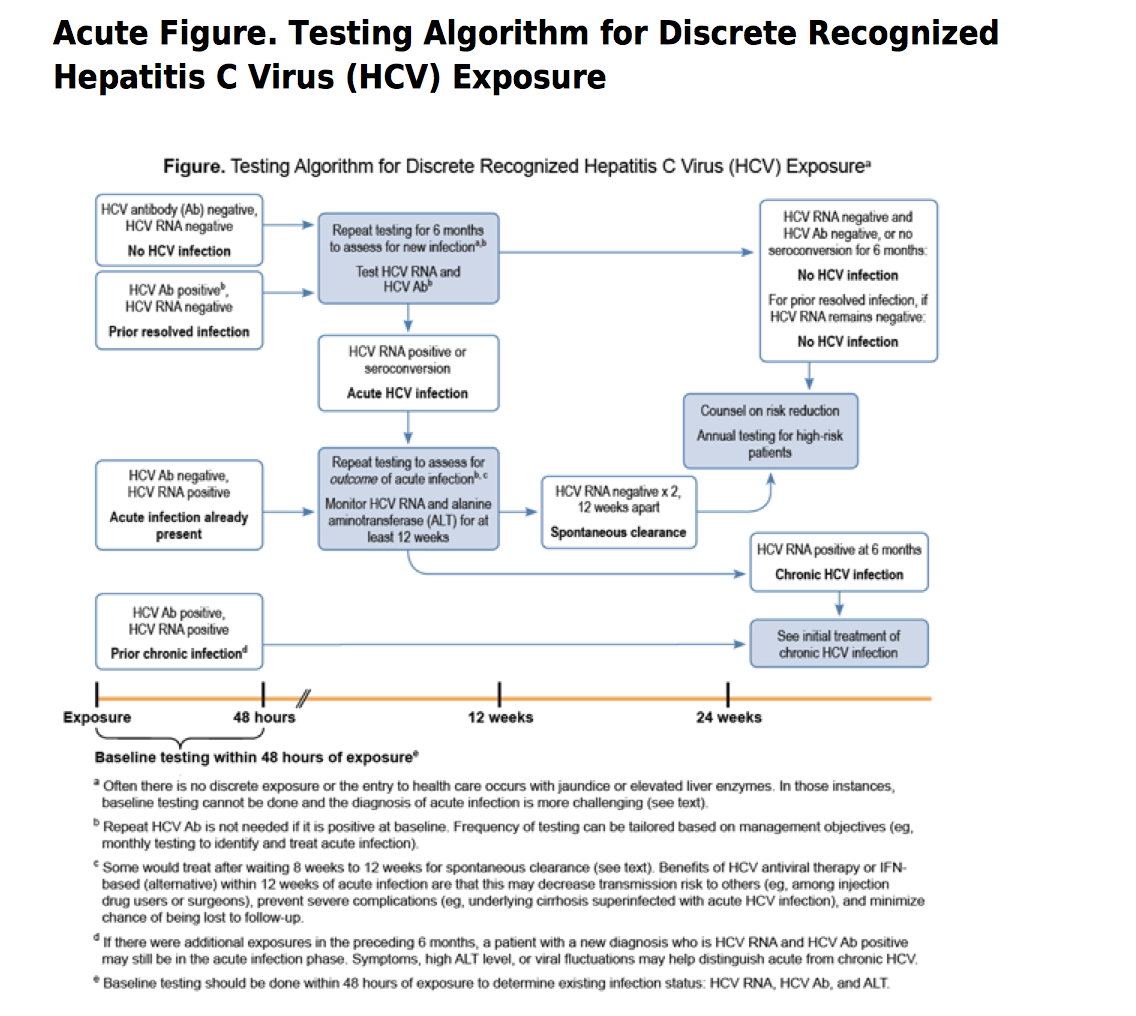
Other Things To Know:
- After a successful course of treatment for hepatitis C, the hepatitis C antibody remains detectable, but the hepatitis C RNA will be undetectable.
- If you plan to donate blood, you will be tested for the hepatitis C antibody and will be turned away even if you do not have an active infection.
- Any patient with a positive test result for the hepatitis C antibody should have additional tests to determine whether or not the virus is still active.
Discusses Conditions That May Cause Diagnostic Confusion Including Improper Specimen Collection And Handling Inappropriate Test Selection And Interfering Substances
A single negative hepatitis C virus RNA test result together with a reactive HCV antibody screen result with a signal-to-cutoff ratio of 8.0 or greater does not rule out the possibility of chronic HCV infection. Repeat testing for HCV RNA in 1 to 2 months is recommended in patient at risk for chronic hepatitis C.
Infants born to HCV-infected mothers may have false-reactive HCV antibody test results due to transplacental passage of maternal HCV IgG antibodies. HCV antibody testing is not recommended until at least 18 months of age in these infants.
Performance characteristics have not been established for the following types of serum specimen:
-Individuals under 10 years of age
-Grossly icteric
-Grossly lipemic
-Grossly hemolyzed
-Presence of particulate matter
Correlation Between Hcv Core Antigen Level And Hcv Rna Level
Numerous studies have explored the correlation between HCV RNA values and HCV core antigens also in relation to genotypes, and overwhelmingly high correlations were reported between 0.7 to > 0.9 for r-values. This would indicate that HCV core antigen might be a substitute for HCV RNA testing. Interestingly, the fluctuations in individual patients during a time course without any antiviral treatment were less pronounced with HCV core antigen vs the HCV RNA.
Furthermore, a significant lower correlation between HCV core antigen levels and HCV RNA levels is found in HBV coinfection patients with a r-value of 0.04, indicating that HCV core antigen actually may reveal additional information compared to HCV RNA levels, though this aspect has not been sufficiently explored yet.
The ability to commercialize an HCV antigen assay and need for a quantitative vs a qualitative assay will depend on the scenario, each of which will be addressed below in regard to where we stand and what we still need now: role in a diagnostic algorithm role in a blood bank/organ donor setting monitoring during natural history monitoring during and after therapy and predicting histological chances.
Recommended Reading: How Is Hepatitis B Contracted
How To Get Tested
Hepatitis C testing is performed by a doctor. Testing requires a blood sample, which can be collected in a hospital, lab, or other medical setting. Blood is often drawn from a vein in the arm or, in children, taken by pricking the skin. After blood is collected, the sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Potential Role Of Hcv Core Antigen In A Diagnostic Algorithm
An HCV core antigen assay can be useful in an diagnostic algorithm , but such use is even greater with a newer more sensitive assay .
Suggested algorithm for hepatitis C virus testing in anti-hepatitis C virus positive individuals. HCV: Hepatitis C virus.
As HCV RNA is still more sensitive, utility of HCV core antigen in such diagnostic algorithm will depend on potential cost saving for diagnosing HCV infection in a population setting. A big advantage is the ease to allowing reflex testing when the same testing-instrument is used for anti-HCV and HCV core antigen testing.
Thus anti-HCV positive results would be reflexed to HCV core antigen testing, and additional HCV RNA testing would only be required if HCV core antigen would be negative and potential confirmation of anti-HCV with RIBA only when both HCV core antigen and HCV RNA were negative.
In a setting where samples need to be shipped to a laboratory, HCV core antigen could prove to be more stable than HCV RNA in a setting where blood samples cannot be assessed soon after blood draw. But this would likely require some more data.
Also Check: How Do I Know If I Have Hepatitis C
What The Qualitative Results Mean
The qualitative results indicate that HCV is present in your blood. The test result will be either detected or undetected.
Detected means that you do have the virus in your blood. Undetected means that you dont have the virus in your blood, or you have a tiny amount that cant be detected by this test.
The qualitative test results may still be positive even if your viral load has decreased drastically due to treatment.
Role Of Hcv Core Antigen In A Blood Bank/organ Donor Setting
As outlined above, the sensitivity of HCV core antigen is inferior to HCV RNA, but superior to no testing. Thus, in a resource limited setting, where HCV RNA testing might be impossible due to cost restrains at present, HCV core antigen testing would allow for a compromise.
Given the cost of organ transplantation, HCV RNA testing cost is unlikely to be a rate limiting step, and therefore not likely to be relevant to organ donation. Still if currently no HCV RNA testing is performed, HCV core antigen might be better than no testing for infectivity.
Read Also: How Do I Know If I Have Hepatitis B
Role Of Hcv Core Antigen In Monitoring Untreated Patients
There currently is no role in monitoring the viral load of patients not undergoing antiviral therapy, but patients frequently want to know that their viral load has not significantly changed. For these circumstances HCV core antigen might be an alternative to quantitative HCV RNA testing.
Depending on country, there are or will soon be regimens available with a cure rate close to 100%. In such a setting it might well be that all patients who tested HCV viremic would get treated in an attempt to eradicate HCV. In such situation monitoring of untreated patients would become obsolete. However, likely the cost of such newer regimens might be prohibitive to treat all infected individuals in all countries.
Are Test Results Accurate
Although no test is perfect, hepatitis C testing is an important and accepted method of testing for HCV. In order to reduce the risk of inaccurate results, doctors take steps to verify a patients diagnosis. For example, a positive test result for hepatitis C antibody requires confirmation with HCV RNA testing.
Also Check: Do I Have Hepatitis C
What Does The Test Measure
Hepatitis C testing identifies antibodies to the hepatitis C virus, detects viral RNA, and/or determines the strain of hepatitis C. Hepatitis C testing may involve several different tests:
- Hepatitis C antibody test: Antibodies are a part of the bodys response to an infection. Testing for hepatitis C antibodies determines whether or not a patient has been exposed to the hepatitis C virus at some point in their life. If this test is positive, the next step is to test for hepatitis C RNA which can tell you if you have a current infection.
- Hepatitis C RNA test: RNA is a type of genetic material from the hepatitis C virus that can be detected in the blood. If test results are positive after a hepatitis C antibody test, doctors use a hepatitis C RNA test to look for and/or measure the amount of the virus in the blood. Qualitative HCV RNA tests can detect the presence of HCV RNA, while quantitative HCV RNA tests measure the amount of HCV RNA. Understanding the amount of HCV in the blood helps to monitor response to treatment.
- Genotype test: There are at least six types of hepatitis C, which are also called strains or genotypes. Treatment for hepatitis C depends on the strain, so genotype testing to guide treatment is performed in patients who are diagnosed with an HCV infection.
Interpreting Hcv Rna Test Results
It is essential that the provider understands how to interpret HCV RNA test results, especially during the course of HCV treatment.
| Result of HCV RNA Test | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| A quantified viral load — any exact number | Ongoing HCV infection |
| “Detected” | The HCV RNA is detectable but the number of international units is so low that it cannot be quantified accurately. This indicates extremely low level of virus is present. |
| “< 12 IU/mL” or “< 15 IU/mL” or “< 25 IU/mL” All of these are “less than the LLOQ” | HCV RNA is undetectable. No virus is detected at all in the patient’s serum specimen. |
You May Like: Colloidal Silver And Hepatitis C
Discusses Physiology Pathophysiology And General Clinical Aspects As They Relate To A Laboratory Test
Hepatitis C virus is recognized as the cause of most cases of posttransfusion hepatitis and is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. In the United States, HCV infection is quite common, with an estimated 2.4 million chronic HCV carriers.
Laboratory testing for HCV infection usually begins by screening for the presence of HCV-specific antibodies in serum, using an FDA-approved screening test. Specimens that are repeatedly reactive by screening tests should be confirmed with HCV tests with higher specificity, such as direct detection of HCV RNA by reverse transcription-PCR or HCV-specific antibody confirmatory tests.
HCV antibodies are usually not detectable during the first 2 months following infection, but they are usually detectable by the late convalescent stage of infection. These antibodies do not neutralize the virus and they do not provide immunity against this viral infection. Decrease in the HCV antibody level in serum may occur following resolution of infection.
Current screening serologic tests to detect antibodies to HCV include enzyme immunoassay and chemiluminescence immunoassays . Despite the value of serologic tests to screen for HCV infection, several limitations of serologic testing exist:
-There may be a long delay between exposure to the virus and the development of detectable HCV-specific antibodies
-False-reactive screening test result can occur
-Serologic tests cannot provide information on clinical response to anti-HCV therapy
Hepatitis C Viral Load / Hcv Rna Quantitative Testing
Hepatitis C
The viral load of hepatitis C refers to the amount of virus present in the bloodstream. The quantitative HCV RNA tests measure the amount of hepatitis C virus in the blood. The result will be an exact number, such as “1,215,422 IU/L.” Many people refer to the quantitative measurement as the hepatitis C “viral load.”
Viral load tests are used to confirm active hepatitis C infection and are used during treatment to help determine response. If you have lower levels of virus in your blood when you start treatment, you may have a better chance of getting rid of the virus.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis B Core Antibody
Enzyme Immunoassays For Detection Of Hepatitis C Antibody
The HCV Ab test is used for initial screening for hepatitis C. The test is performed by enzyme immunoassays , which detect the presence of hepatitis C antibodies in serum. The result of the test is reported as positive or negative. Third-generation EIAs have a sensitivity/specificity of approximately 99%. However, the presence of HCV Ab does not indicate whether the infection is acute, chronic, or resolved. A positive antibody test result should be followed up with an HCV RNA test to confirm that viremia is present.
Hepatitis C Antibody With Reflex To Pcr
- Hepatitis C Ab w/RFLX PCR
- Lab Code
- Hepatitis C Antibody w/Reflex PCR
- Description
-
The Qualitative detection of Hepatitis C virus IgG and IgM antibodies in human sera by the FDA approved Abbott ARCHITECT Anti-HCV test two-step chemiluminescent immunoassay.
In the first step, sample, assay diluent, and recombinant HCV antigen coated paramagnetic microparticles are combined. Anti-HCV present in the sample binds to the rHCV coated microparticles. In the second step, anti-human IgG/IgM acridinium-labeled conjugate is added, which binds to IgG and IgM anti-HCV. Then pre-trigger and trigger solutions are added to the reaction mixture. The resulting chemiluminescent reaction is measured as relative light units .
The presence or absence of IgG/IgM anti-HCV in the sample is determined by comparing the chemiluminescent signal in the reaction to the cutoff signal determined from an ARCHITECT Anti-HCV calibration. Specimens with signal to cutoff values 1.00 are considered reactive for IgG/IgM anti-HCV. Specimens with S/CO values < 0.79 are considered nonreactive and specimens with S/CO values between 0.80 and 0.99 are Indeterminate.
Reactive anti-HCV will reflex to Hepatitis C RNA, Quantitative for confirmation with an additional charge.
For anti-HCV testing without PCR reflex for REACTIVE results, see Hepatitis C Antibody without PCR reflex on reactive samples .
- Synonyms
Also Check: What Causes Hepatitis Of The Liver
The Quantitative Hcv Rna Test Is Checked Before A Patient Starts Treatment
For each patient, the result can be described as either a “high” viral load, which is usually > 800,000 IU/L, or a “low” viral load, which is usually < 800,000 IU/L. It’s not uncommon to have a viral load in the millions. Today’s hepatitis C treatments are very effective with both high and low viral loads. An undetectable HCV viral load 10-12 weeks after hepatitis C is completed is associated with a cure.
Hepatitis C Antibody Blood Test With Reflex On Positives
Assess exposure to hepatitis C virus infection and tests blood safety.
Also Known As: HCV, Hep C.
Methodology: Immunoassay
Preparation: No fasting required. Stop biotin consumption at least 72 hours prior to the collection.
Test Results: 2-3 days. May take longer based on weather, holiday or lab delays.
You May Like: What Is A Hepatitis B Shot
Hepatitis C Is Often Asymptomatic
Offer testing to anyone with a risk factor or clinical indication.
Risk factors:
- shared drug-use equipment, even once
- received personal services , with nonsterile equipment
- exposed to blood during sexual activity
- received blood, blood products, or organ transplant before 1992
- received medical care where non-sterile equipment may have been used
- born, travelled, or lived in a region where hepatitis C is common
- born to a mother with hepatitis C
- diagnosis of HIV or hepatitis B
- clinical clues or symptoms of liver disease
- occupational exposure
Hepatitis C Reflex Testing
To ensure complete and timely diagnosis of HCV, HCV reflex testing is recommended following a reactive hepatitis C antibody screening test. Reflex testing means the laboratory will perform the hepatitis C antibody test, and if the result is positive, the laboratory will immediately perform an HCV RNA test on the same specimen. If the subsequent HCV RNA test is negative, HCV infection is effectively ruled out for most patients. If the reflex HCV RNA test is positive, a diagnosis of active HCV infection has been confirmed, and the individual should be referred directly for HCV care and treatment.
Reflex testing obviates the need for the patient to return for follow-up testing should the initially HCV antibody test be reactive. If the RNA test is negative, the work-up is done, and the patient may be reassured.
- Rationale for reflex testing:
Read Also: Signs You Have Hepatitis B
How Much Does The Test Cost
The cost of hepatitis C testing depends on the tests that are performed, where the test is conducted, and a patients health insurance coverage. When testing is ordered by a doctor, patients with health insurance may find it helpful to discuss the cost of hepatitis C testing with their insurance company. In addition to the cost of testing, there may be other out-of-pocket costs such as copays and deductibles.
For patients without health insurance, or for whom insurance doesnt cover the cost of testing, it may be helpful to discuss the cost of hepatitis C testing with a doctor or hospital administrator.
At-home hepatitis C testing starts around $49. Some at-home kits test for multiple types of viral hepatitis at once, with the cost of these panels starting around $80.
Hepatitis C Testing And Diagnosis

Doctors will start by checking your blood for:
Anti-HCV antibodies: This blood test is the first — and sometimes only — one you may get. Also called the ELISA screen, it checks for antibodies that your body releases to fight the virus. These are proteins your body makes when it finds the hep C virus in your blood. They usually show up about 12 weeks after infection. Your test will be either negative or positive for antibodies. It usually takes a few days to a week to get results, though a rapid test is available in some places.
What the results mean
Negative . This is when your blood shows no signs of HCV antibodies. Most of the time, thatâs because you never came in contact with the virus and you do not have hep C.
Sometimes, your negative result can be false, meaning you have HCV. That may happen if you:
- Took the test too soon after your exposure. This test checks for only HCV antibodies, which can take several months to appear.
- Have HIV, a donated organ, or other conditions that weaken your immune system, which can suppress your antibodies
- Get hemodialysis for kidney problems
If youâve been exposed in the last 6 months, youâll need to be retested.
Positive . This means youâve been infected with HCV. But false positives are surprisingly common. More than 1 in 5 people who test positive donât actually have hepatitis C. Possible reasons include:
What the results mean
You May Like: Hepatitis C Causes Symptoms And Treatment
Taking A Hepatitis C Test
Hepatitis C testing is conducted on a sample of blood. Blood samples can be collected by a doctor, nurse, technician, or other health care provider from an adult patients vein using a small needle or a skin prick on a childs heel.
For an at-home hepatitis C test, patients collect a blood sample according to the manufacturers directions. Instructions provided in the test kit detail the steps to obtain a small sample of blood and mail it for testing.
What The Quantitative Results Mean
The quantitative test results indicate the exact amount of HCV in your blood. This number helps your doctor confirm whether you have a high or low viral load.
Measuring your viral load before treatment allows your doctor to monitor your viral load during and after treatment.
The viral load measurement doesnt indicate how severe your HCV infection or cirrhosis is. Your doctor will need to take a biopsy, or tissue sample, from your liver to learn more about how your liver has been affected by an HCV infection.
The viral load results from the quantitative PCR test can range from 15 to 100,000,000 IU/L.
If your results are:
- Fewer than 15 IU/mL: The virus is detected, but the amount cant be measured exactly. You may need to return later for another test to see if the measurement changes.
- Fewer than 800,000 IU/mL: A low viral load is detected.
- More than 800,000 IU/mL: A high viral load is detected.
- More than 100,000,000 IU/mL: The virus is detected and active infection is taking place.
- Inconclusive: HCV RNA cant be measured, and a new sample needs to be taken.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Test For Hepatitis C