When Should I Get This Test
Using hepatitis B tests to screen for HBV is recommended for certain groups at an increased risk of infection. You may benefit from hepatitis B screening if you:
- Were born in parts of the world where the disease is more common, including Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, South America, and parts of the Middle East
- Didnât receive a hepatitis B vaccine
- Are HIV-positive
- Use injectable drugs
- Are at risk of HBV infection due to sexual exposure
A doctor may order hepatitis testing based on your symptoms, medical and family history, and a physical exam. If you develop symptoms without recent exposure to HBV, doctors may recommend an acute viral hepatitis panel that looks for hepatitis A, B, and C in one sample of blood.
Hepatitis tests may also be performed as follow-up tests when other tests of liver health are abnormal.
Testing is common in those that show symptoms that could be caused by hepatitis B. Symptoms of hepatitis B include:
- Loss of appetite, nausea, or vomiting
- Pain in the joints or abdomen
- Yellowish skin and eyes
Using hepatitis B testing to assess immunity to HBV may take place before or after vaccination. Pre-vaccination testing is not always needed but may be performed if there is a chance that you have previously been infected with HBV or have already been vaccinated. Post-vaccination testing is used in certain groups of people at an especially elevated risk for HBV infection, including infants born to mothers with a hepatitis B infection.
Hepatitis B Serologic Testing And Hbv Dna
HBV serology and DNA assays were done every 6months according to Taiwan Rheumatology Association recommendations . HBV assays included serum HBsAg, anti-HBs and anti-HBc, measured by Architect i2000SR chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay . HBV immunization history of people with anti-HBs+/anti-HBcserostatus was not ascertained.
Anti-HBs titer < 10 mIU/ml was defined as seronegative. Low anti-HBs titer was defined as 10100 mIU/ml, based on evidence of significantly increased likelihood of anti-HBs loss and detectable HBV DNA at anti-HBs titers below 100 mIU/ml and protection against HBV reactivation above this threshold . Serum HBV DNA viral load was quantified by Abbott RealTime HBV , with a minimal sensitivity of 10 IU/ml. HBV DNA titer 10 mIU/ml was defined as detectable viral load , while the criteria defining clinical HBV reactivation at any serial 6-monthly follow-up check, were HBV replication 2 log increase from baseline or a new appearance of HBV DNA to 100IU/ml in people with previously stable or undetectable levels .
Whats The Procedure For A Hepatitis B Titer Test
A hepatitis titer test requires a healthcare professional to draw a small amount of blood for testing.
No special preparation is needed beforehand. If needles or the sight of blood make you anxious, you may want to arrange a drive ahead of time in case you feel faint.
Heres what will typically happen during this test:
Home tests that require a fingerpick are also available. The results of your tests are generally available within 3 days.
Also Check: Where Does Hepatitis B Come From
What Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
When you are exposed to HBV, your body mounts an immune defense to specifically target and neutralize the invader. Unlike innate immunity which mounts a generalized defense against all invaders, this type of immunity is disease-specific.
This immune response occurs whether you are exposed to HBV through blood or sexual contact, or if you are vaccinated with the hepatitis B vaccine.
The virus has proteins on its surface, called antigens, that serve as unique identification tags. When HBV enters the body, the immune system âencodesâ antibodies specific to these antigens so that it can recognize and attack the virus should it appear again.
There are two types of antibodies produced in response to the virus:
- Immunoglobulin M is the antibody that mounts the initial attack but eventually fades away.
- Immunoglobulin G is the antibody that provides long-lasting immune protection against HBV. The immunity can last for many years, but it gradually wanes over time.
You May Like: What Kinds Of Hepatitis Are There
Additional Specimen Collection Information
Collect blood in a lithium heparin, green-top, EDTA purple-topor red-top tube. PST and SST are acceptable. Serum orplasma should be separated from contact with the cells within 2hours of collection. Specimens not centrifuged within 4 hours ofcollection may be rejected. Refrigerate the specimen if unable toassay within 8 hours of collection. Samples with > 1+ lipemiamust be cleared prior to analysis.
You May Like: Does Alcohol Cause Hepatitis C
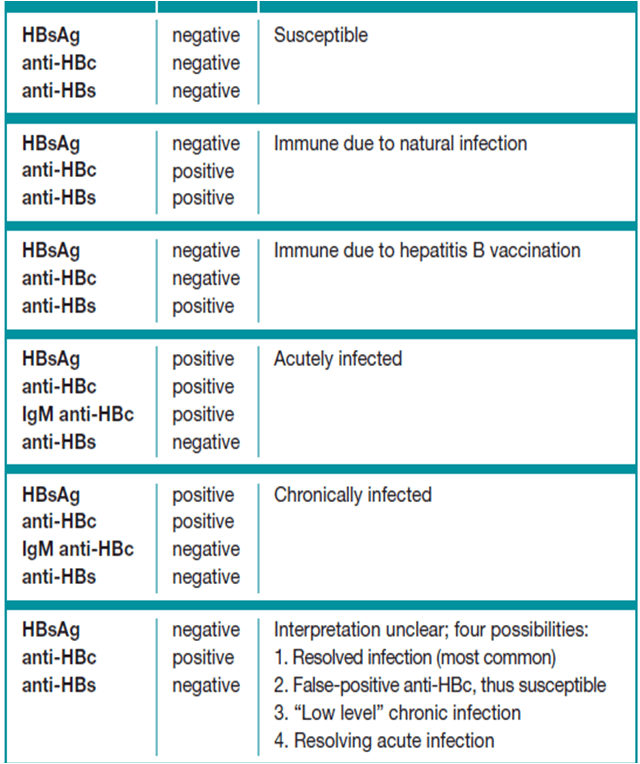
Module 3 Interpretation Of Hbv Diagnostic Test Results
This table describes 6 possible interpretations of diagnostic test results and subsequent recommended actions for clinicians.
In the first scenario of this table, a patient should be considered to be susceptible to hepatitis B when: hepatitis B surface antigen results are negative hepatitis B surface antibody results are negative total hepatitis B core antibody results are negative and the IgM marker of the hepatitis B core antibody is not available/or not done.
Itâs noted that approximately 5 percent to 10 percent of people will not respond to vaccine or else do not produce protective levels of antibody post-vaccination .
The recommended action when a patient is considered to be susceptible to hepatitis B is to vaccinate.
In the second scenario of this table, a patient should be considered to be immune to hepatitis B due to vaccination when: hepatitis B surface antigen results are negative hepatitis B surface antibody results are positive total hepatitis B core antibody results are negative and the IgM marker of the hepatitis B core antibody is not available/or not done. Regarding the hepatitis B surface antibody, clinicians are reminded that about 5 percent to 10 percent of people will not respond to the vaccine or else do not produce a protective level of antibody post-vaccination . Note that in immune individuals, levels of hepatitis B surface antibody may decline over time and become undetectable.
Hepatitis B Titer Test Panelmost Popular
The Hepatitis B Titer Test Panel panel contains 3 tests with 4 biomarkers.
Hepatitis B Titer Test
- Hepatitis B Surface Antigen with Reflex Confirmation
- Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Immunity, Quantitative
- Hepatitis B Core Antibody, Total
The Hepatitis B Titer Test is ordered when a person needs proof of immunity to Hepatitis B or just want to check their immune status.
The Hepatitis Titer Test includes immunity testing for Hepatitis B. Hepatitis is a viral disease which affects the liver. Vaccinations for Hepatitis B can provide protective antibodies which immunize a person from catching the virus. Additionally, a person who has been affected by Hepatitis B and recovers can develop natural immunity. Titer testing looks for the antibodies which typically indicate that a person is immune to a particular virus or infection.
Hepatitis B Immunity
Not Immune and no active or prior infection may be a good candidate for vaccine
- Hepatitis B Surface Antigen = Negative
- Hepatitis B Surface Antibody = Negative
- Hepatitis B Core Antibody, Total = Negative
Immunity due to vaccination
Don’t Miss: How Do You Treat Hepatitis C
Key Facts And Figures
- HBV is a vaccine-preventable disease that is highly infectious far more so than either HIV or HCV. It is transmitted through perinatal, percutaneous, or sexual exposure to an infected personâs blood / body fluids household contacts are also at risk of infection.
- Acute and chronic HBV infections are frequently asymptomatic or present with nonspecific symptoms about two-thirds of chronically infected people are unaware of their status, and most will only be detected through proactive screening.
- Of those infected as adults, 5% will become chronically infected in contrast, about 90% of infants infected at birth will develop chronic infection.Endnote 1
- Without intervention, 15%40% of chronically infected people will go on to develop cirrhosis, end-stage liver disease, and/or HCC.
HBV is a notifiable disease in all provinces and territories in Canada. As such, it must be reported to the regional/local Medical Officer of Health.
What Do The Results Mean
A hepatitis B blood panel consists of three tests that can be done with just one blood sample:
- Hepatitis B surface antigen . A positive test indicates that youre infected with hepatitis B and that you can spread it to other people. Further tests are needed to see if you have an acute or chronic infection.
- Hepatitis B core antibody . A positive result can indicate a past or current hepatitis B infection, but doesnt mean youre immune. A positive result needs to be interpreted by a doctor by examining the results of the other two tests.
- Hepatitis B surface antibody . A positive test indicates that youre protected from hepatitis B either through previous infection or vaccination .
The combination of these tests can indicate your hepatitis B status and whether you need to be vaccinated. Your test will give a negative or positive result for each category depending on whether your results are above or below the cutoff value.
Most peoples test results fall into the following categories. But its possible to have a result that doesnt fall into one of these groups. If youre reading your results yourself, be careful not to confuse HBsAb with HBcAb.
| HBsAG |
is associated with hepatitis B immunity after vaccination. But research has found that anti-HBs decline over time.
A found that more than 95 percent of people had anti-HBs levels greater than 10IU/L two years after vaccination. But this rate decreased to 70 percent after eight years.
You May Like: Can You Get Hepatitis C From Drinking After Someone
Screening Tests For Hepatitis B
Your blood may be screened for HBV for many different reasons. The three tests generally include HBsAg, antibody to HBsAg, and antibody to hepatitis B core antigen. This allows the healthcare provider to know whether you could benefit from vaccination, or if you have active or chronic hepatitis B and need counseling, care, or treatment.
You may be routinely screened if you are pregnant, are donating blood or tissue, need immunosuppressive therapy, or have end-stage renal disease. You will also be screened if you are in groups that are at higher risk for HBV.
Sequence Following An Initial Negative Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Titer
As you obtain documentation, please submit documentation of each step to CastleBranch
- Initial Hepatitis B titer negative for immunity
- Receive Hepatitis B challenge dose/booster
- Repeat Hepatitis B titer 4-6 weeks after challenge/booster vaccine
Donât Miss: Just Food For Dogs Hepatic Support
Don’t Miss: What Is The Treatment Of Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B Immunization And Postimmunizationserology
Michael John, MB, Ch.B., FRCP
Before the introduction of avaccine, hepatitis B virus was a major occupational risk to health care workers.Some of the highest infection rates were found in dentists and surgeons.1Infected health care workers have a 5-10% risk of developing chronic hepatitis B. A numberof clusters of dentist-to-patient HBV transmissions have been reported over the years,although these have decreased since the introduction of universal precautions.2Recent guidelines from Health Canada recommend restriction of practice of health careworkers who test positive for hepatitis B e antigen.3
The development of hepatitis vaccines in the 1980s has substantially decreased dentalworkers risk of acquiring HBV. A recent survey4 of dentists in Canadashowed that more than 90% had completed an immunization series and an additional 3% hadnatural immunity. However, rates of immunization among dental assistants and hygienistswas found to be much lower.
Hepatitis B Vaccines
The vaccine is administered intramuscularly into the deltoid muscle, as glutealinjection may result in decreased response rates. Response to vaccine following a 3-doseseries is typically greater than 95% in young, healthy people, although it decreases withage . Other factors such assmoking, obesity and chronic disease decrease vaccine efficacy and may be used to predictrisk of nonresponse.6 Adverse events are minimal, although mild injection-sitereactions may occur in 20% of recipients.
References
About The Hepatitis B Virus
The hepatitis B virus is a small DNA virus that belongs to the Hepadnaviridae family. Related viruses in this family are also found in woodchucks, ground squirrels, tree squirrels, Peking ducks, and herons.
Structure of the Hepatitis B Virus The hepatitis B virus contains an outer envelope and an inner core.
- The outer envelope of the virus is composed of a surface protein called the hepatitis B surface antigen or HBsAg. The HBsAg can be detected by a simple blood test and a positive test result indicates a person is infected with the hepatitis B virus.
- The inner core of the virus is a protein shell referred to as the hepatitis B core antigen or HBcAg, which contains the hepatitis B virus DNA and enzymes used in viral replication.
Life Cycle of the Hepatitis B Virus
The hepatitis B virus has a complex life cycle. The virus enters the host liver cell and is transported into the nucleus of the liver cell. Once inside the nucleus, the viral DNA is transformed into a covalently closed circular DNA , which serves as a template for viral replication . New HBV virus is packaged and leaves the liver cell, with the stable viral cccDNA remaining in the nucleus where it can integrate into the DNA of the host liver cell, as well as continue to create new hepatitis B virus. Although the life cycle is not completely understood, parts of this replicative process are error prone, which accounts for different genotypes or genetic codes of the hepatitis B virus.
Don’t Miss: How Many Hepatitis Shots Are Required
Hep B Titer Test Required By Most Schools And Employers
This assay is used to determine immune status for Hepatitis B. Also know as Hep B IGG titer
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody : The surface antibody is formed in response to the hepatitis B virus. Your body can make this antibody if you have been vaccinated, or if you have recovered from a hepatitis B infection. If this test is positive, then your immune system has successfully developed a protective antibody against the hepatitis B virus. This will provide long-term protection against future hepatitis B infection. Someone who is surface antibody positive is not infected, and cannot pass the virus on to others.
This is a Quantitative test required by many schools and medical programs. Levels of anti-HBs will be provided.
Diagnosis Of Acute And Chronic Hepatitis B
HBsAg is the first serologic marker to appear and may be detected within 1 to 2 weeks after exposure. It precedes the development of symptoms by an average of 4 weeks.104 The presence of HBsAg indicates ongoing infection. Qualitative but not quantitative methods are used by most clinical laboratories because the amount of antigen does not correlate with disease activity or with the presence of an acute or chronic infection.26 Some symptomatic patients may have self-limited, acute HBV infection without detectable HBsAg. These patients, up to 9% in some studies, have other detectable markers of infection.104 HBeAg appears virtually simultaneously, peaks, and then declines in parallel with HBsAg. It usually disappears before HBsAg. Adult patients who remain persistently positive for HBeAg for more than 10 weeks are likely to become chronically infected. HBeAg indicates a high level of viral replication and infectivity. Most patients with nondetectable HBeAg have resolving, minimal, or no active liver disease.26 Pre-core mutants of HBV do not express HBeAg they may be responsible for a more severe course and, in some cases, fulminant disease. Serum aminotransferase levels become raised but are nonspecific. They begin to increase just before the development of symptoms and then peak , with the development of jaundice.
Howard C. Thomas, Jennifer A. Waters, in, 1998
Don’t Miss: Sign And Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
Explainer: Lab Results And Their Interpretation
Dear 174, I am incredibly sad to hear about the loss of your husband to HCC. How devastating to you and the entire family. But as Thomas wrote, your blood test results indicate that you are protected from hepatitis B and have developed protective antibodies against any future exposure to this virus. Fortunately for you, even though you were exposed to the hepatitis B virus, you had a strong healthy immune response that was able to fight off an infection. Please stay in touch with us, especially if you have any other questions. And if you have children, hopefully they were vaccinated at birth. Thanks for posting and we all wish you the strength and comfort to endure your grief. Always, Joan
Hi,I had my first hepatitis B surface antigen test in Feb. 2019 the value was 832 iu/mL. I repeated the test a year later the value: 870 iu/mL. Both are marked red .My most recent AFP-L3% and total AFP test is 1.5, and the virus DNA is not detected .
What is your interpretation of the results? What is my risk for HCC?
Thanks,
Hi Thomas,
Dear ,
Welcome to the forum and thanks for sharing your result. Its very difficult for anyone to form an accurate picture of your liver from one low res image there is generally a ultrasonists report giving an interpretation of ALL the pictures of your liver taken together. That is the thing that will really tell you what is happening.
I hope this helps,
Thanks for sharing your results.
Regarding HCC risk:
MY results of tests:
Hi ,