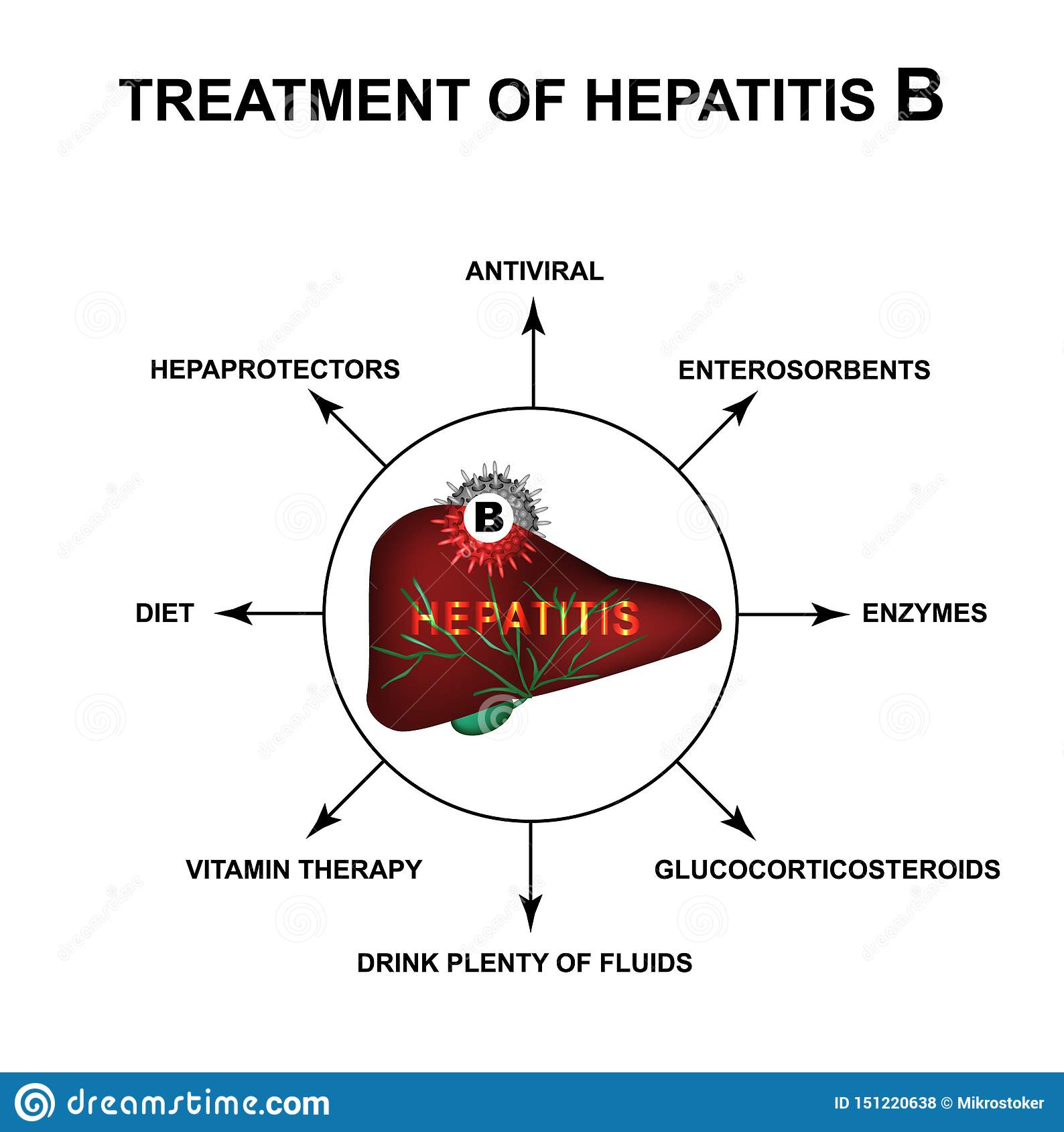
Treatment For Chronic Hepatitis B
If blood tests show that you still have hepatitis B after 6 months, your doctor may recommend medication to reduce the risk of complications of hepatitis B and regular tests to assess the health of your liver.
Treatment is usually offered if:
- your immune system is unable to control the hepatitis B by itself
- theres evidence of ongoing liver damage
Hepatitis B medications can help keep the virus under control and stop it damaging your liver, although they will not necessarily cure the infection and some people need lifelong treatment.
The main medicines for chronic hepatitis B include peginterferon alfa 2-a and antiviral medicines.
National Institutes Of Health Recommendations
The National Institutes of Health recommends nucleoside therapy for the treatment of patients with acute liver failure, as well as cirrhotic patients who are HBV DNA positive and those with clinical complications, cirrhosis or advanced fibrosis with positive serum HBV DNA, or reactivation of chronic HBV during or after chemotherapy or immunosuppression. In addition, immunoglobulin and vaccination should be administered to newborns born to women positive for hepatitis B surface antigen .
In general, for hepatitis B e antigen -positive patients with evidence of chronic HBV disease, treatment is advised when the HBV DNA level is at or above 20,000 IU/mL and when serum ALT is elevated for 3-6 months.
For HBeAg-negative patients with chronic hepatitis B disease, treatment can be administered when the HBV DNA is at or above 2,000 IU/mL and the serum ALT is elevated for 3-6 months.
In patients coinfected with HBV and HIV, initiate therapy against HBV and administer antiretroviral therapy as well.
The NIH also indicates that immediate therapy is not routinely indicated for patients who have the following :
-
Chronic hepatitis B with high levels of serum HBV DNA but normal serum ALT levels or little activity on liver biopsy
-
Low levels of or no detectable serum HBV DNA and normal serum ALT levels
-
Positive serum HBV DNA but not HBsAg , unless the patient is undergoing immunosuppression
What Are The Causes Of Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infection that is spread by the virus known a Hepatitis B. This disease spreads through the blood of an infected person or contact with bodily fluids.
There are many causes of Hepatitis B.
- Hepatitis B is caused by using an infected needle or blade.
- Hepatitis B can spread from an infected mother to her baby during pregnancy.
- It can occur by using the same razor or toothbrush as used by an infected person.
- Using unsterilized needles for ear piercing or tattooing can also be a reason.
- Hepatitis B may also be caused by the transfusion of infected blood to another person without examination.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Types Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B And Pregnancy
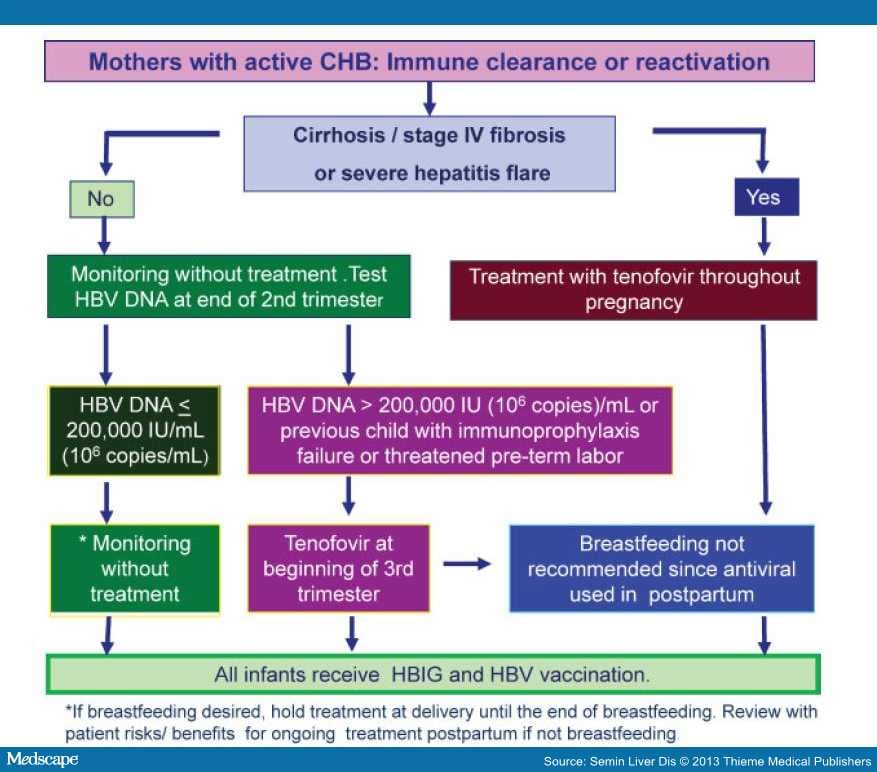
Because their immune systems arent fully developed, infants and young children are more likely to develop chronic hepatitis B, so its important to limit their exposure to the virus. All expecting women should be screened for hepatitis B. If a high viral load is detected through testing, your doctor will initiate treatment during your third trimester to reduce the likelihood that your baby will contract the disease during delivery.
Additionally, the infants of mothers with hepatitis B should receive the hepatitis B vaccination series and immune globulins at birth so they do not develop hepatitis B.
How Do People Get The Hbv Virus
Hepatitis B virus is found in the blood of people with HBV infection. It enters the body through blood-to-blood contact.
Reliable blood tests for HBV were developed many years ago. Since blood donors and blood products are tested for HBV, this is no longer the typical means of infection.
In many parts of the world, hepatitis B virus infects more than 8% of the population. HBV-infected women pass the infection to their babies during the birth process. People can also get hepatitis B by sharing needles for injection drug use, through sexual contact with an infected person, by an accidental needlestick with a contaminated needle, or from improperly sterilized medical, acupuncture, piercing, or tattooing equipment.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Core Antibody Igg And Igm
New Prospective Antiviral Treatment Strategies
Recently, there is a growing interest in some new therapeutic strategies, targeting viral life cycle or improving antiviral immune response, that could eliminate all replicative intermediates, including ccc-DNA. The drugs targeting different steps of HBV life cycle include entry inhibitors polymerase inhibitors core protein inhibitors HBsAg release inhibitors RNA silencers. On the other hand, the new therapies to improve anti-HBV immunity response include therapeutic vaccines, generating new T cells toll-like receptor 7 and toll-like receptor 8 agonists, stimulating antiviral effector cells retinoic acid-inducible gene I agonist anti-HBV antibodies checkpoint inhibitors programmed cell death protein 1 and PD1 ligand inhibitors, rescuing the T-cell exhaustion that can be observed in chronic HBV infection. Results of preclinical and early clinical studies are promising thus, soon, these treatment options could be available and could potentially transform the future indications for hepatitis B treatment.
Please Join The Fight Against Hbv
Over 850,000 people in the United States are estimated to be living with hepatitis B. The actual number may be as high as 2.2 million. There is no cure for chronic hepatitis B virus. Despite the huge human and economic toll of hepatitis B, research to cure the disease remains underfunded.
Through all of our research programs, the Baruch S. Blumberg Institute hopes to build upon the strides we have made to combat the hepatitis virus and other forms of liver disease. Of course, none of this could be accomplished without the continuous efforts of our researchers in the United States and other locations, such as China and Southeast Asia. Funding from these areas, and in other places like California, India, and Japan, is also one of the most significant ways that we, as a non-profit, can fund research efforts and discoveries pertaining to HBV.
To continue to make these developments, we need this funding to continue, and we can only do that with your help. You can join the fight against viral hepatitis by making a donation to the Baruch S. Blumberg Institute. No donation is too small, and any contribution can go a long way toward improving the lives of the millions who are living with Hep B today.
Also Check: What Drug Is Used To Treat Hepatitis B
Who Should Be Vaccinated For Hepatitis B
All newborns should be vaccinated. Also, people who are under 18 who were not vaccinated at birth should also get the vaccine. Other groups who should be sure to be vaccinated are those in certain high-risk categories, such as:
- People who have more than one sexual partner.
- Men who have sex with men.
- Adults with diabetes.
- Sexual partners of infected people and people who share households with infected individuals.
- People who are exposed to blood and other bodily fluids, including healthcare and public safety professionals, and people who work in jails and other places taking care of people who cant take care of themselves.
European Commission And Thervacb Join Forces
The role of viral hepatitis as a public health threat has long been underestimated. Only very recently, the United Nations in their 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development called for international action to combat viral hepatitis and reduce the disease burden. The major killer is the hepatitis B virus causing liver cirrhosis and liver cancer. Worldwide 880,000 humans die each year from the consequences of an HBV infection.
A prophylactic vaccine is available to prevent HBV infection, but more than 3% of the worlds population are chronically infected and do not profit from that vaccine anymore. For those suffering from chronic hepatitis B, until today no curative treatment option exists.
The European Commission therefore selected the project TherVacB led by Helmholtz Zentrum München for a five-year funding within the Horizon 2020 program. A consortium of leading virologists, immunologists and physicians specialized in treating viral hepatitis, will use a newly designed therapeutic vaccine, TherVacB, as an immunotherapy to cure HBV. TherVacB will be evaluated in a three-year clinical trial starting in 2022 conducted in Europe and in Africa. Integration of a partner site in Tanzania shall help building local capacities for diagnosing and treating hepatitis B and support an important goal of the consortium to raise awareness for hepatitis B.
Read Also: How Long Can A Person Live With Hepatitis C
How Is It Transmitted
Hepatitis B is highly infectious, and is spread from one person to another through exposure to infected blood and body fluids . It can be spread through:
- blood transfusions or organ transplantation in countries where blood or blood products have not been properly screened for hepatitis B and other viruses transmitted through blood
- unprotected sex with an infected person
- sharing needles or equipment for injecting drugs
- unsterilized medical/dental equipment and shared/contaminated materials or equipment used for tattooing, body piercing or acupuncture
- sharing toothbrushes or razors
- household contact between family members
Hepatitis B: Screening Prevention Diagnosis And Treatment
THAD WILKINS, MD, MBA RICHARD SAMS, MD, MA and MARY CARPENTER, PharmD Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University, Augusta, Georgia
Am Fam Physician. 2019 Mar 1 99:314-323.
Patient information: See related handout on hepatitis B, written by the authors of this article.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimated that in 2015 there were 21,900 cases of acute hepatitis B, with an overall incidence of 1.1 cases per 100,000.1 There are an estimated 850,000 to 2.2 million individuals in the United States with chronic hepatitis B.1,2 Approximately 25% of children and 15% of adults with chronic hepatitis B die prematurely from hepatocellular carcinoma or cirrhosis.3 However, treatment reduces morbidity and mortality from the disease.
WHAT IS NEW ON THIS TOPIC
Approximately 1,000 cases of perinatal hepatitis B occur annually in the United States, and nearly 90% of chronic hepatitis B cases in infants develop in the first year of life.
Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for all medically stable infants weighing 2,000 g or more within 24 hours of birth, unvaccinated infants and children, and unvaccinated adults requesting protection from hepatitis B or who are at increased risk of hepatitis B.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
Pregnant women should be screened for hepatitis B at the first prenatal visit.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
Pregnant women should be screened for hepatitis B at the first prenatal visit.
eFIGURE A
You May Like: Hepatitis A And B Vaccine Cost
What Do You Need To Know About Hepatitis B And C Coinfection
Hepatitis B and hepatitis C share some common transmission routes, including through blood-to-blood contact, and so hepatitis B and hepatitis C coinfection is possible. Anyone who is diagnosed with hepatitis C should also be screened for hepatitis B and vice versa.
Both hepatitis B and C affect the liver. When people have two active infections of the liver, one virus dominates the other. In most cases, the hepatitis C virus is the dominant virus and the hepatitis B virus is suppressed.
There are highly effective and widely accessible treatments available to cure hepatitis C called direct-acting antivirals. Anyone with hepatitis C should discuss treatment options with their healthcare provider, including people with a hepatitis B and C coinfection. Owing to the relationship between the two viruses in the liver, when a person is cured of hepatitis C, hepatitis B virus can flare up. When people are treated for hepatitis C with direct-acting antivirals, hepatitis B treatment may be considered to stop the reactivation of hepatitis B.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
After the virus enters the body, there is an incubation period lasting 1.5 to 6 months until illness begins. During the acute phase most persons have no symptoms or might experience a mild illness. Symptoms of acute HBV infection, when present, may include:
- Dark-colored urine, light-colored stools
During the chronic phase hepatitis B usually progresses silently, with no symptoms at all during the first 10-20 years. Signs of severe liver scarring may include:
- Star-shaped vein pattern developing on the swollen belly
- Easy bruising and bleeding
Chronic HBV infection can lead to serious liver disease, liver scarring , and hepatocellular cancer.
Because symptoms of hepatitis B are usually absent, persons with risk for HBV infection should be tested. If you think you have hepatitis B, or are at risk for hepatitis B, you should contact your doctor.
Read Also: How Long Does It Take To Cure Hepatitis C
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis B And C
In most patients, hepatitis B develops slowly over the course of several decades, and thus most patients have no symptoms. People who have advanced liver disease such as cirrhosis of the liver may experience complications and symptoms that reflect liver failure. Other symptoms include:
- A buildup of fluid within the abdominal cavity
- Confusion and tremors , which are complications due to the inability of the liver to filter out toxins that are normally cleaned out by a healthy liver
- Vomiting of blood, or blood within the stool . This is a complication in which enlarged veins within the esophagus or stomach bleed as a consequence of increased pressure around the diseased liver.
Most patients with chronic hepatitis C infection report no symptoms. But some patients may have very nonspecific symptoms related to fatigue and discomfort on the right side of the abdomen. Often, symptoms that lead to a diagnosis of hepatitis C are noticeable only at the end stage of liver disease, when the patient has developed liver cirrhosis and liver failure.
Because hepatitis B and C typically have no specific symptoms, many people who have the viruses dont even know it.
Donât Miss: Hepatitis B Vaccine Dose Schedule
American Association For The Study Of Liver Diseases Recommendations
The 2016 AASLD guidelines for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B as well as select recommendations from the 2018 AASLD guidance update on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B are outlined below and in the Guidelines section.
Adults with immune-active chronic hepatitis B infection
Administer antiviral therapy to lower the risk of morbidity and mortality associated with chronic hepatitis B infection.
The recommended initial agent for adults is PEG-IFN, entecavir, or tenofovir.
Adults with immune-tolerant chronic hepatitis B infection
Antiviral therapy is not recommended.
The AASLD suggests obtaining ALT levels at least every 6 months to monitor for potential transition to immune-active or -inactive chronic hepatitis B.
For select patients older than 40 years, the AASLD suggests antiviral therapy in the setting of normal ALT levels, elevated HBV DNA , and significant necroinflammation or fibrosis on liver biopsy specimens.
Adults with HBeAg-positive immune-active chronic hepatitis B who seroconvert to anti-HBe on nucleoside analog therapy
After a period of treatment consolidation , consider discontinuing NA therapy in noncirrhotic HBeAg-positive adults who seroconvert to anti-HBe while on NA treatment. If antiviral therapy is stopped, monitor the patient every 3 months for a minimum of 1 year for recurrent viremia, ALT flares, seroreversion, and clinical decompensation.
Adults with HBeAg-negative immune-active chronic HBV infection
Inpatient care
Also Check: What Does It Mean To Be Immune To Hepatitis B
Who Should Be Vaccinated
Children
- All children aged 1223 months
- All children and adolescents 218 years of age who have not previously received hepatitis A vaccine
People at increased risk for hepatitis A
- International travelers
- Men who have sex with men
- People who use or inject drugs
- People with occupational risk for exposure
- People who anticipate close personal contact with an international adoptee
- People experiencing homelessness
People at increased risk for severe disease from hepatitis A infection
- People with chronic liver disease, including hepatitis B and hepatitis C
- People with HIV
Other people recommended for vaccination
- Pregnant women at risk for hepatitis A or risk for severe outcome from hepatitis A infection
Any person who requests vaccination
There is no vaccine available for hepatitis C.
Mr And Miss Manu Testimonial
We began using the products almost 2 and half months and I am here to tell you that it is working, it worked for me and my wife.We were told we would need surgeries because of our fatty liver but we didnt need any surgery. Also, to my surprise, Im also, being treated for Macular Degeneration and I am now able to see better with my right eye and it is getting better very quickly. I havent done anything differently in diet or lifestyle so I have come to the conclusion that it is the Hepatitis and fatty liver Remedy.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Definition Of Hepatitis B
Medical Treatment For Hepatitis A B & C
Treatment for hepatitis A, B, or C is based on which type of hepatitis is present in the bloodstream and the severity of the resulting liver damage. Depending on the results of diagnostic tests, our specialists at NYU Langone may recommend antiviral medication to stop the virus from replicating and protect your liver from further damage.
Is Hepatitis B Curable
Theres no cure for hepatitis B. The good news is it usually goes away by itself in 4 to 8 weeks. More than 9 out of 10 adults who get hepatitis B totally recover.
However, about 1 in 20 people who get hepatitis B as adults become carriers, which means they have a chronic hepatitis B infection. Carriers are more likely to pass hepatitis B to other people. Most carriers are contagious meaning they can spread hepatitis B for the rest of their lives.
Hepatitis B infections that last a long time may lead to serious liver diseases like cirrhosis and liver cancer. About 1 in 5 people with chronic hepatitis B die from it. There are medicines that can help treat chronic hepatitis B infections.
Most babies who get hepatitis B during birth develop chronic infection, unless they get treated right away. But treatments are almost always effective if your baby gets them quickly. Thats why its important for pregnant people to get tested for hepatitis B.
Read Also: Causes Of Hepatitis C Infection