The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Getting the hepatitis B vaccine is one of the most effective ways to prevent hepatitis B. Its usually administered in two, three, or four doses. In many countries, infants receive their first dose of the vaccine at birth.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that infants receive their first dose of the vaccine at birth and finish all doses at 6 to 18 months old.
The CDC also recommends all children under the age of 19 years old be vaccinated if they havent already received the vaccination.
Adults can also get the hepatitis B vaccine. The vaccine is generally recommended if you have an increased risk of contracting the virus. Some of these risk factors include:
- traveling to or living in a region where hepatitis B is common
- being sexually active with more than one partner or with a partner who has hepatitis B
- working in a medical setting or other workplaces where youre exposed to bodily fluids
- using intravenous drugs and sharing drug equipment
- having chronic liver disease, a human immunodeficiency virus infection, a hepatitis C infection, diabetes, or kidney disease on dialysis
If youve been exposed to the hepatitis B virus and havent been vaccinated, try to see a doctor right away. They can administer the first dose of the vaccine, though youll need to follow up to receive the remaining doses over the next few months.
They may also prescribe a medication called
How Is Hepatitis B Prevented
Testing & Vaccination
- The hepatitis B vaccine offers excellent protection against HBV. The vaccine is safe and highly effective. Vaccination consists of 3 doses of vaccine over the course of 6 months. Protection lasts for 20 years to life.
- The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that all children should receive hepatitis B vaccine starting at birth. .
- The CDC recommends hepatitis B vaccine for persons traveling to countries where HBV is common .
- If you have one or more risk factors for hepatitis B infection, you should get a simple HBV blood test. The blood test will determine whether you are:
- immune to hepatitis B or
- susceptible to hepatitis B and need vaccination or
- infected with hepatitis B and need further evaluation by a physician
Perinatal Hepatitis
- California law requires testing of all pregnant women for hepatitis B infection
- If the mother is HBV-infected, she will pass the infection to the baby during the birth process, unless the baby gets immunized within hours of birth
- Giving the infant HBIG and HBV vaccine right away will reliably prevent infection of the infant
- Other family members should best tested for hepatitis B too, and given vaccine if they are not already infected or immune
Healthy Habits
After Exposure to Hepatitis B
Screening In Case Of Chronic Inactive Hepatitis Virus
Although most inactive carriers remain permanently in this state, there is a small percentage of individuals who may change their status to active infection.
For this reason, it is important that the person with asymptomatic hepatitis B undergoes regular checks of transaminases and the virus concentration in the blood .
Also Check: How Does Hepatitis B Affect The Body
Hepatitis B Vaccine Challenge Dose And Laboratory Testing
After written informed consent was obtained, information on demographics, height, weight, risk factors for HBV exposure , and vaccination history were collected from each participant. Blood was drawn for serologic testing immediately before and 2 weeks after a challenge dose of hepatitis B vaccine was administered by injection into the deltoid muscle with a standard-size needle. Serum specimens were frozen and shipped to the CDC Hepatitis Reference Laboratory for testing. Baseline specimens were tested for antibody to anti-HBsAg and total antibody to hepatitis B core antigen with the VITROS ECi Immunodiagnostic System . Specimens positive for anti-HBcAg were tested for HBsAg and HBV DNA. Postchallenge specimens were tested for anti-HBsAg only. A response to the challenge dose was defined as a postchallenge anti-HBsAg level of 10 IU/liter among persons with a baseline anti-HBsAg level of < 10 IU/liter. The results of serologic testing were not available for the investigators or participants until after completion of the study.
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a type of liver inflammation caused by the hepatitis B virus. When the liver is inflamed or damaged, it can impair liver function.
Hepatitis B may be mild and acute or chronic . Children are more likely to develop chronic hepatitis B if infected however, 95% of adults recover completely and do not become chronically infected.
Read Also: Which Oil Is Good For Hepatitis B Patient
What Is Involved In A Liver Transplant
A liver transplant is considered necessary when the liver is damaged and cannot function or in some cases of liver cancer. Your liver is very important. It is responsible for many functions related to making sure that your body stays healthy and is able to digest foods.
You may be eligible for a transplant if you have chronic hepatitis B infection or some of the diseases that may result from it, including liver cancer and cirrhosis. You will have to complete testing and be evaluated before being approved for a transplant. It is likely that you will be placed on a waiting list while an appropriate organ is found.
Donated livers come from two types of donors: living and deceased. Because the liver can regenerate, it is possible to use part of a liver for transplant. The remaining sections in both the donor and the receiver will grow into livers of adequate size.
People who get liver transplants must take anti-rejection drugs for the rest of their lives. These drugs make you more susceptible to infection. However, liver transplants have become more successful over time and continue to improve.
Complications Of Hepatitis B
A small proportion of people who become infected with the hepatitis B virus develop a long-term hepatitis B infection. They may have the virus in their bloodstream for most of their life without realising they are infected.
People with chronic hepatitis B infection may not notice any health problems until they develop liver problems such as liver disease or liver cancer later in life. Treatment for hepatitis B is essential because it is not possible to be a healthy carrier of the hepatitis B virus. Chronic hepatitis B infection occurs more commonly in some communities, including:
- Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander communities.
- In people from parts of the world where hepatitis B is more common, such as:
- North-East Asia
- Sub-Saharan Africa.
Don’t Miss: What Are Warning Signs Of Hepatitis C
How Is Hepatitis B Diagnosed
A diagnosis of hepatitis B infection is made using blood tests.
Because many people do not have symptoms when they get hepatitis B, they may never be diagnosed. Thats why screening for hepatitis B is recommended in a number of people including:
- people at higher risk
If you think you have been exposed to infected blood or body fluids, see a doctor as soon as possible. There are treatments that can reduce your risk of developing the infection, if given shortly after exposure.
What Should You Know About Hepatitis B Before You Travel
Hepatitis B is quite common in China and other Asian countries, where as many as 1 in 12 people have the virus, though many dont know it. Before traveling to those places, you should make sure youve been vaccinated against the virus.
In addition to getting the vaccine, you can take these additional precautions to reduce your risk of contracting the virus:
- Refrain from taking illegal drugs.
- Always use latex or polyurethane condoms during sex.
- Make sure new, sterile needles are used during all piercings, tattoos and acupuncture sessions.
- Avoid direct contact with blood and bodily fluids.
- Know the HBV status of all your sexual partners.
- Ask your doctor about possible vaccination before you travel to a place where hepatitis B is common.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Hepatitis B is a liver disease that can cause serious damage to your health. One reason that is dangerous is that it can easily go undetected for years while damaging your liver. Talk with your healthcare provider about being tested for hepatitis B if you have any reason to believe that you were not vaccinated or if you have engaged in risky behavior. If you do test positive, follow the directions from your healthcare provider so that you can live a longer, healthier and happier life.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 07/09/2020.
References
Recommended Reading: How Is Hepatitis A Transmitted
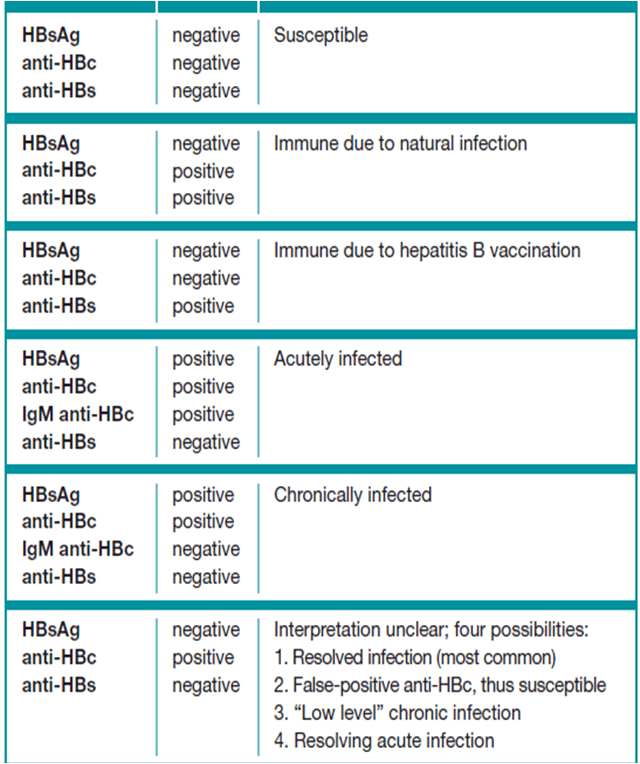
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test
A hepatitis B surface antigen test shows if you have an active infection. A positive result means you have hepatitis B and can transmit the virus to others. A negative result means you dont currently have hepatitis B.
This test doesnt distinguish between chronic and acute infection. This test is used together with other hepatitis B tests to determine the state of a hepatitis B infection.
Chronic Inactive Hepatitis B: What It Means
The condition of asymptomatic hepatitis B virus infection is now more correctly defined as inactive carrier status.
Although these individuals are chronic carriers of the B virus infection, they do not show signs of active disease.
This means that these people have the viral infection, but their blood test values are consistently normal and do not show the typical signs of hepatitis.
This condition is thought to be the result of constant monitoring of viral activity by the infected persons immune system and carries a very low risk of developing cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Read Also: Signs Of Hepatitis In Females
Whats The Difference Between Acute And Chronic Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B can be either acute or chronic:
- Acute hepatitis B lasts for a short period of time. If you have acute hepatitis B, you may be asymptomatic or have symptoms and develop icteric hepatitis. It can transition into chronic hepatitis B if the virus doesnt naturally go away after 6 months.
- Chronic hepatitis B lasts for at least 6 months. If you have this type of hepatitis, you may carry the hepatitis B virus for the rest of your life. Its possible to have chronic hepatitis B that started as acute, but many people dont have acute hepatitis B first.
Most people with acute hepatitis B make a full recovery. Some may never even show any symptoms. But those with chronic hepatitis B often need treatment to help manage the infection. Chronic hepatitis B also increases your risk of developing cirrhosis and certain types of liver cancer.
Your risk of developing chronic hepatitis B depends on when you first received your diagnosis of the virus. Children who receive a diagnosis of hepatitis B, especially those under the age of 5 years old, have a higher risk of the infection becoming chronic. Adults are less likely to develop chronic hepatitis B. Around 90 percent of adults who develop it will fully recover.
Keep in mind that hepatitis B can be present for years before you start to show any symptoms.
Understanding Immune Reaction To The Hepatitis B Virus
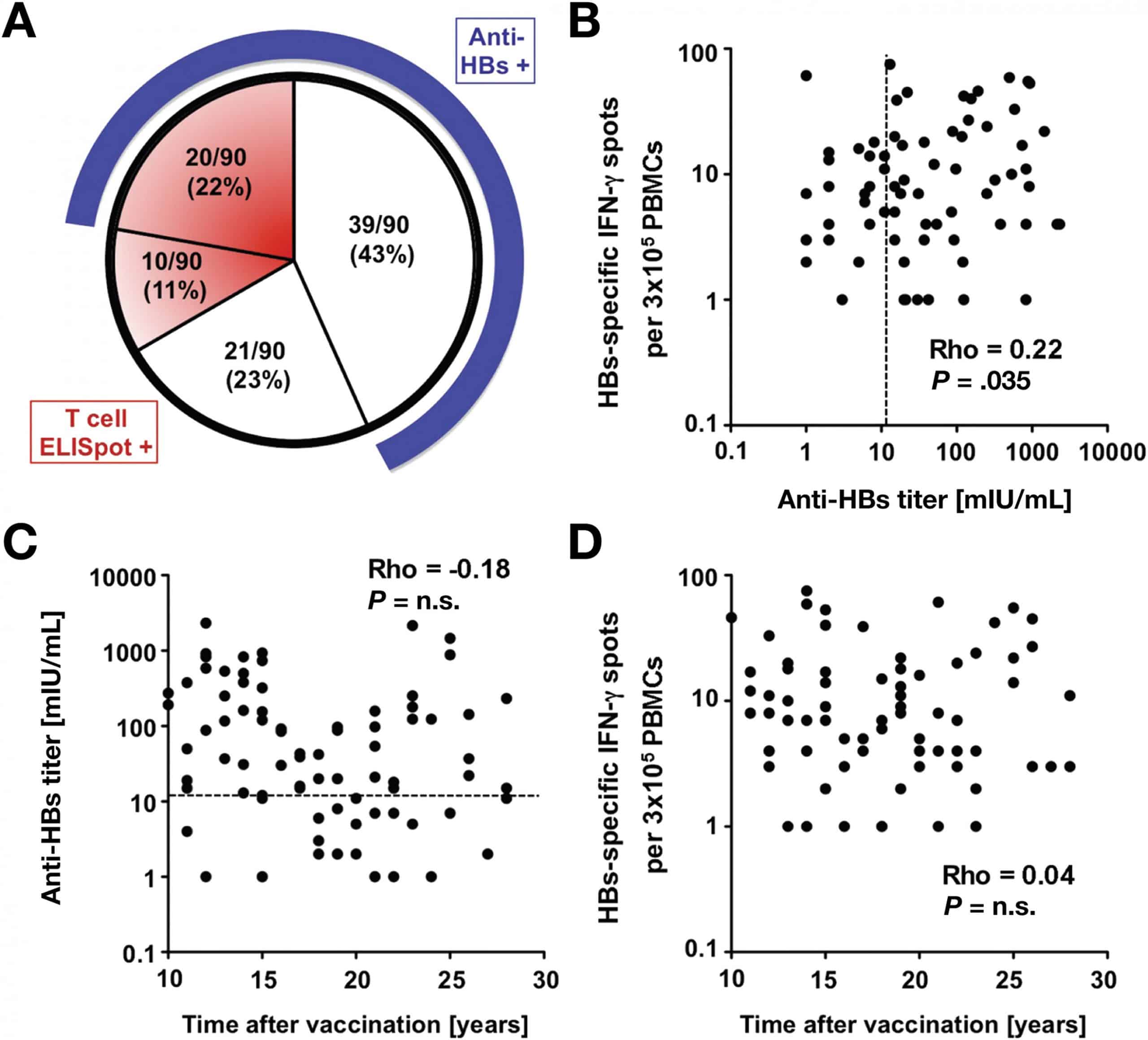
A collaboration of researchers from Japan and Malaysia has further clarified the immune response to hepatitis B virus through in vivo experimentation.
The innate immune system in mammals defends against infection from viruses and other microbial infections. Unfortunately, the human immune response to the hepatitis B virus is not yet fully understood. Without vaccination, hepatitis B causes both acute and chronic infections of the liver, and can lead to the development of cirrhosis and liver cancer. To gain a deeper understanding of how the immune system reacts to HBV, researchers from several institutions in Japan and Malaysia led by Professor Hiroyuki Oshiumi of Kumamoto University performed in vivo experiments on the tree shrew, a small mammal that is also prone to HBV infection.
Importantly, the researchers also found that extracellular vesicles are integral to the innate immune response to HBV infection. “We showed that EVs coming from HBV-infected hepatocytes carry viral nucleic acids which, in turn, stimulates the innate immune response against HBV,” said Professor Oshiumi. “However, we also found that HBV can escape the immune response by increasing the immunosuppressive microRNA levels in exosomes. The increase of these microRNAs eventually results in a reduction of NK cell activation which allows HBV to easily proliferate.”
More information:Frontiers in Immunology
Recommended Reading: How Can A Person Get Hepatitis B
Is Hepatitis B Curable
Theres currently no known cure for hepatitis B, but there are many ways you can prevent infection and avoid transmitting the virus to others.
The most effective and safe way to prevent hepatitis B is to get vaccinated. You can also use barrier methods, like condoms, when having sex and avoid sharing needles.
What To Do If You Miss A Scheduled Dose
The recommended schedule for the HBV vaccine follows a three-dose pattern, with all doses complete within 6 months. The good news is that if you miss a dose, you dont need to start the series of shots all over.
If you missed getting the second dose 1 month after the first, make an appointment as soon as possible. If you miss the third dose, you should also try to get it as quickly as possible. Keep in mind that the second and third doses
Also Check: Where Can I Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
Chronic Hepatitis Binfected Patients
A, Hepatitis A testing and immunity in patients with chronic hepatitis B. B, Hepatitis A testing and immunity in patients with chronic hepatitis C. C, Hepatitis B testing and immunity in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Abbreviations: anti-HA, hepatitis A antibody anti-HBc, hepatitis B core antibody anti-HBs, hepatitis B surface antibody.
In univariate analysis , the oldest patients were less likely to have immunity or vaccination than any other age group . Native American and black patients were less likely to have immunity or vaccination . Patients with no immunity or vaccination had fewer months of member coverage . After multivariable adjustment , factors significantly associated with immunity or vaccination included age 80 vs < 30 years , age 4049 vs < 30 years , Asian vs white race , male sex , and months of member coverage .
Review Of Current Recommendations
Table highlights the current recommendations for hepatitis A and B vaccinations. The Hepatitis C Task Force recommends both vaccines for newly diagnosed CHC patients without evidence of immunity to hepatitis A and/or B, based on expert opinion . The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommends hepatitis A vaccine for susceptible patients with chronic liver disease but not routinely for CHB or CHC patients without chronic liver disease . The American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver both recommend hepatitis A vaccine for all CHC patients with no evidence of preexisting antibody, but the AASLD similarly recommends vaccinating CHB patients with chronic liver disease . AASLD guidelines state that hepatitis B vaccine should be offered to CHC patients. The ACIP recommends hepatitis B vaccination of adults with chronic liver disease in addition to those at risk for infection by sexual exposure or exposure to blood . The Physician Quality Reporting System quality indicator from the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services counts all CHC patients with at least 1 hepatitis A vaccine or documented immunity to hepatitis A .
Hepatitis A and B Vaccination Recommendations and Quality Measures for Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B or C
| Recommending Agency . |
|---|
You May Like: How Do You Know If You Have Hepatitis
How You Can Get Hepatitis B
You can get hepatitis B from:
- injecting drugs using shared needles
- being injured by a used needle
- having a tattoo or piercing with unsterilised equipment
- having a blood transfusion in a country that does not check blood for hepatitis B. Blood transfusions in the UK are checked for hepatitis B.
If you’re pregnant and have hepatitis B, you can also pass it onto your baby during pregnancy or birth.
What If I Am Pregnant
It’s recommended that all pregnant women have a blood test for hepatitis B in early pregnancy.
If you have hepatitis B and are pregnant, treatments can reduce the risk of transmission of hepatitis B to the baby.
If you have hepatitis B, it is important to protect others from infection.
Important ways to prevent the spread of hepatitis B include:
- vaccination of all your close contacts
- practise safe sex until your sexual contacts are fully vaccinated and immune
- do not donate blood, organs or body tissue
- do not allow your blood to contact another person
- inform healthcare workers
- if your work involves potential for your blood or other body fluid to spread to other people, discuss your situation with your doctor
The hepatitis B vaccine is safe and effective in protecting against hepatitis B infection, providing protection in 95 in 100 vaccinated people.
In Australia, hepatitis B vaccination is part of the standard immunisation schedule for all newborn babies and infants. It’s also recommended for adults who are at high risk of exposure, people who are immunosuppressed or have other liver disease. People in these risk groups should be vaccinated against hepatitis B. Talk to your doctor about your level of risk and whether hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for you.
If you werent vaccinated against hepatitis B as a child, or if youre not sure whether you are vaccinated, talk to your doctor about whether you need a catch-up vaccine.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule For Child