How Can You Get Hepatitis C
Most people become infected with hepatitis C through blood-to-blood contact with an infected person, William Schaffner, MD, an Infectious Disease Specialist and Professor at the Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, tells Health. That can include blood transfusions, organ transplants, and IV drug use.
It’s less common, but the CDC says that you can also get hepatitis C by sharing personal care items that may have come into contact with an infected person’s blood, like razors or toothbrushes. Having sexual contact with someone infected with hepatitis C, being born to a mother with hepatitis C, or getting a tattoo or piercing with an infected needle are also less common causes of hepatitis C, the CDC says.
But even if you contract hepatitis C, you may not know you have itthat’s because both the acute and chronic forms of the infection don’t typically show symptoms. In some cases, however, the CDC says those infected with the virus might experience a fever, fatigue, dark urine, clay-colored bowel movements, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, joint pain, and jaundice. Still, because symptoms are rare, screening for hepatitis C is essential.
Are Test Results Accurate
Although no test is perfect, hepatitis C testing is an important and accepted method of testing for HCV. In order to reduce the risk of inaccurate results, doctors take steps to verify a patients diagnosis. For example, a positive test result for hepatitis C antibody requires confirmation with HCV RNA testing.
Over 250000 Canadians Believed To Be Infected But Many Unaware They Have Blood
Canadians born between 1945 and 1975 should be tested for the potentially liver-destroying virus hepatitis C, a new set of guidelines recommends.
More than 250,000 Canadians are believed to be infected with hepatitis C, but an estimated 40 to 70 per cent are unaware they harbour the blood-borne virus because it can take decades before symptoms become evident. Chronic infection can lead to cirrhosis of the liver or liver cancer.
The Canadian Association for the Study of the Liver, a national group of health-care providers and researchers, published its guidelines on testing and treating hepatitis C in Mondays edition of the CMAJ.
A key recommendation is that people be tested based on their age not only possible risk factors, said Dr. Jordan Feld, a liver specialist at Torontos University Health Network and a co-author of the guidelines.
And the reason weve done this is it just happens that somewhere between two-thirds and three-quarters of people with hepatitis C were born between 1945 and 1975 in Canada, he said.
So just the way someone gets a blood pressure check or a cholesterol check or a colonoscopy based on their age, we would recommend that they get a hepatitis C test if theyre born between those years.
And if we do that, we hopefully diagnose the vast majority of people living with hepatitis C.
Read Also: Rx Hepato Support For Dogs
Why Test All Your Adult Patients
- New cases of hepatitis C are on the rise, particularly among reproductive age adults. Rates of new HCV infections increased by more than 60% from 2015 to 2019. And in 2019, more than 63% of HCV infections occurred among adults 20-39 years of age.
- Your patients arent aware of their risk. Almost half of people with hepatitis C are unaware of their infection. Testing is the first step to accessing curative treatment. Without treatment, approximately 15-20% of adults with chronic HCV infection will develop progressive liver fibrosis and cirrhosis.
- Hepatitis C can be cured. Over 90 percent of people infected with HCV can be cured with 8-12 weeks of oral therapy. Treatment of hepatitis C is associated with reductions in mortality among persons with chronic hepatitis C.
What Does The Test Measure
Hepatitis C testing identifies antibodies to the hepatitis C virus, detects viral RNA, and/or determines the strain of hepatitis C. Hepatitis C testing may involve several different tests:
- Hepatitis C antibody test: Antibodies are a part of the bodys response to an infection. Testing for hepatitis C antibodies determines whether or not a patient has been exposed to the hepatitis C virus at some point in their life. If this test is positive, the next step is to test for hepatitis C RNA which can tell you if you have a current infection.
- Hepatitis C RNA test: RNA is a type of genetic material from the hepatitis C virus that can be detected in the blood. If test results are positive after a hepatitis C antibody test, doctors use a hepatitis C RNA test to look for and/or measure the amount of the virus in the blood. Qualitative HCV RNA tests can detect the presence of HCV RNA, while quantitative HCV RNA tests measure the amount of HCV RNA. Understanding the amount of HCV in the blood helps to monitor response to treatment.
- Genotype test: There are at least six types of hepatitis C, which are also called strains or genotypes. Treatment for hepatitis C depends on the strain, so genotype testing to guide treatment is performed in patients who are diagnosed with an HCV infection.
Also Check: What Organ Does Hepatitis B Affect
Cdc Recommendations For Hcv Screening
On April 10, 2020, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention issued new recommendations for hepatitis C screening among adults in the United States . This new guidance augments prior CDC guidance on HCV screening with two new major recommendations: all adults aged 18 years and older should have HCV screening at least once in their lifetime, except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection is less than 0.1%, and HCV screening should be performed for all pregnant persons during each pregnancy, except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection is less than 0.1%. The CDC continues to recommend screening persons for HCV regardless of age if risk factors for acquiring HCV are present, with repeat periodic screening in persons who have ongoing risk for acquiring HCV. These new CDC HCV screening recommendations expand prior guidance that recommended routine HCV screening for all persons born between 1945-1965.
Getting A Hepatitis C Test From Your Doctor
Ideally, you should talk with a doctor about hepatitis C screening. Theyll ask you about any potential exposures or risk factors and will probably order a blood test to check for HCV antibodies. You can get your blood tested anywhere that does routine blood work.
Its the same procedure as getting a routine blood test.
We reviewed each brands business and medical practices, checking:
- their BBB rating, if they have one
- whether theyve been involved in any lawsuits
- whether they provide help interpreting your results
- whether they make any unacceptable health claims
All companies on the list also state they use accredited labs to process their testing kits.
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis C Be Contracted Sexually
When Should I Test For Hep C
Many people dont feel sick when they first get hep C. If you are exposed to hep C, your body will try and fight the virus for 6 months. 1 in 4 people will clear hep C in those first 6 months.
People who dont clear their hep C will have whats called chronic hep C. You can get tested for hep C straight after you think you have been exposed, but you will need to go back for another test after 12 weeks and possibly again at 6 months.
You might be able to access testing and healthcare via your computer or phone.
Hepatitis C Virus Infection In Adolescents And Adults: Screening
Recommendations made by the USPSTF are independent of the U.S. government. They should not be construed as an official position of the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality or the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
| Adults aged 18 to 79 years | The USPSTF recommends screening for hepatitis C virus infection in adults aged 18 to 79 years. | B |
- View the Clinician Summary in PDF
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Without Hepatic Coma
Articles On Reasons For Hep C Tests
As far as viruses go, hepatitis C is among the sneakiest. Once it’s in your blood, it travels to your liver, where it may settle in for a silent, long-term stay. This can lead to cancer or cause the organ to fail if you don’t treat it. In fact, hepatitis C is among the top reasons for liver transplants in the U.S.
If you think youâve been exposed, here are five reasons to get tested right away:
What Health Professionals Need To Know About Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus is transmitted primarily through parenteral exposure to infectious blood or body fluids containing infectious blood. Hepatitis C is not a vaccine-preventable infection.
Hepatitis C infection is reportable by laboratories and clinicians to local public health authorities in all provinces and territories.
Consult the national case definition for additional information.
In Canada, screening of the blood supply was implemented in 1992. This has virtually eliminated the risk of HCV transmission via transfusion. Prior to this, thousands of people contracted HCV through receiving blood or blood products.
Also Check: How Long Can Someone Live With Hepatitis C
What Do The Results Mean
There are two results from a hepatitis C antibody test.
- A non-reactive or negative test result means that the person does not have the virus. The exception is if someone has come into contact with the virus recently, such as through contaminated blood. If this is the case, they will need to have another test.
- A reactive or positive test result means that the person has had the virus at some point but does not mean that they still have it. Further tests will be needed to check whether the virus is still active in the body and if treatment will be required.
Once diagnosed with hepatitis C, a person will need to undergo a series of different tests to see how the virus has affected their body.
These tests will check for any liver damage, identify how well the liver is working, and help a healthcare professional to decide on treatment.
Hepatitis C is treated with medication known as an antiviral. It gets this name because it aims to clear the virus out of the body.
Another aim of the medication is to slow down damage to the liver. It may also reduce the chance of a person getting liver cancer or developing serious liver scarring, known as cirrhosis.
A person with hepatitis C will require regular testing during treatment to see how well the medication is working. Keeping healthy, getting enough sleep, and avoiding drugs and alcohol can help treatment to work.
Eliminate Viral Hepatitis C By 2030
Bernadette Lettner, a registered nurse at the Regent Park Community Health Centre in Toronto, where Camara is now treated, points out that Canada has signed on to the WHO commitment to eliminate viral hepatitis C by 2030.
“I think that if you commit to doing something like that, then you’re going to have to make sure you’re able to test people who previously wouldn’t know that they’re hep C positive,” she said.
According to Lettner, many of those who are unaware are baby boomers. “The majority of new cases are in people who inject drugs or in prison populations,” she said.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Antibody Test Positive
Current Hepatitis C Testing Recommendations
Recently, several organizations have issued hepatitis C virus screening recommendations. In general, major guidelines now recommend routine one-time universal HCV testing for adults 18 years of age and older, routine HCV screening of pregnant individuals, screening younger persons at risk of acquiring HCV, and repeat screening for those with ongoing risk for HCV acquisition.
When Should I Get Hepatitis C Testing
When used for early detection in patients without symptoms of hepatitis C, screening is recommended at least once for all adults aged 18 years or older, except in locations with very low prevalence of HCV. Screening is also recommended during pregnancy and for patients of any age with risk factors for HCV infection. In patients with risk factors, periodic screening is recommended for as long as risk factors persist.
Risk factors for HCV include:
- Current or past injectable drug use
- Having a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992
- Receiving kidney dialysis
- Pain in the abdomen or joints
- Nausea, vomiting, or loss of appetite
- Jaundice or yellowish skin and eyes
Hepatitis C testing may also be performed when liver tests are abnormal or when diagnosing the cause of existing liver damage.
Also Check: What Is Drug Induced Hepatitis
Educating Clients About Viral Hepatitis
Clients may believe they know about viral , but their understanding of the disease may not be accurate. It is easy to confuse the three main types of viral , B, and C. Clients may have formed impressions based on limited or incorrect information. Counselors should briefly describe hepatitis A, B, and C, including their prevalence, , and relationship to drug use, as well as to other infections, such as HIV and sexually transmitted diseases. Specific strategies for speaking with clients include:
- Speak clearly and keep the message simple, focused, and brief.
- Use language, examples, and concepts that the client understands.
- Use appropriate visual aids.
- Frame numerical statements in terms that are easy to visualize. Say 5 out of 100 people rather than 5 percent of the population say more than half instead of the majority.
- Repeat the information at different times in different ways. The average client retains only approximately one-third of what he or she is told. Summarize essential points.
- Pay attention to a clients response to the information. For example, if a client stiffens his or her posture, consider saying, I notice that this topic seems to make you uncomfortable. It does for a lot of people. Please tell me what youre feeling right now. Id really like to help you with this.
- Use the opportunity to describe the potential detrimental effects of alcohol and other substance use on the liver of a person who is infected with HCV.
Counseling Practices That Educate Support And Motivate Clients Undergoing Screening
Clients might need help deciding whether to get screened, understanding the test results, and determining their next steps. Even when services offered through the substance abuse treatment program are limited, discussing testing with clients presents an opportunity for counselors to motivate clients for change by confronting substance use and by making choices that improve their overall health. However, this may also be true when services are offered on-site through substance abuse treatment programs. A study at one methadone clinic that offered hepatitis screening and vaccination revealed that although the majority of clients completed screening , only 54.7 percent of clients who lacked for hepatitis A received vaccinations and only 2.9 percent of clients who lacked immunity for received vaccinations .
The Consensus Panel makes the following general recommendations while recognizing that, in some programs, the counselors role may be limited:
Also Check: What Are The Common Symptoms Of Hepatitis
Identifying Patterns Of Risky Behavior
Screening is an opportunity to draw attention to the clients behaviors that put him or her at risk for contracting :
- Ask for the clients perception of his or her risk for having contracted : How likely do you think it is that the test will be positive?
- Listen for and identify behaviors that put the client at risk for contracting , B, and C and HIV, especially unprotected sex and sharing injection drug paraphernalia.
- Assess the clients alcohol consumption.
Determining The Prevalence Threshold For The Recommendations
Although the intent of public health screening is usually to identify undiagnosed disease, many persons previously diagnosed with hepatitis C are not appropriately linked to care and are not cured of their HCV infection, thereby representing an ongoing source of transmission. Therefore, the prevalence threshold of 0.1% should be determined on the basis of estimates of chronic hepatitis C prevalence, regardless of whether hepatitis C has been diagnosed previously.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis E Causes And Treatment
Can I Take The Test At Home
At-home hepatitis C tests are available that allow patients to collect a blood sample at home and mail it to a laboratory for testing. Test samples are collected through pricking a finger with a sharp object, called a lancet, thats included in the test kit.
At-home HCV testing is a form of hepatitis C antibody testing and does not test for hepatitis C RNA or the strains genotype. Testing for hepatitis C at home is not a substitute for testing performed by a health care professional, and positive test results may need to be confirmed by laboratory-based testing.
How To Get Tested
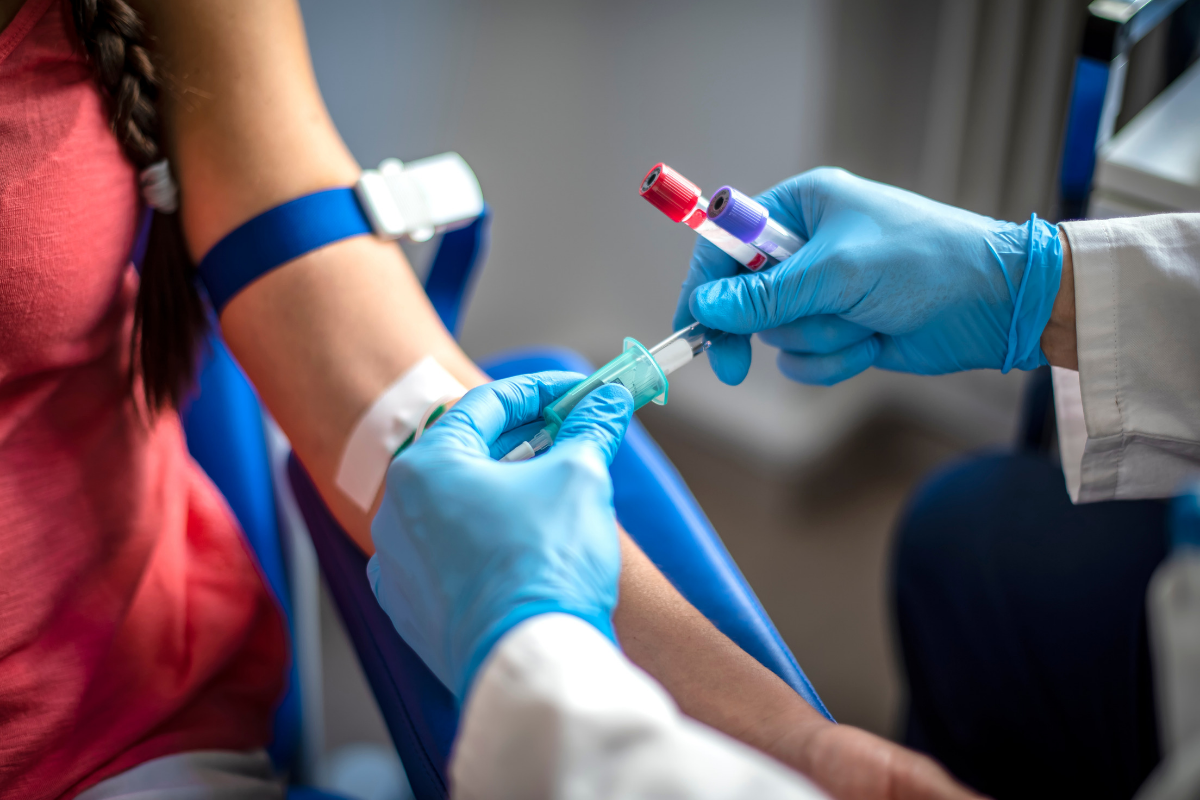
Hepatitis C testing is performed by a doctor. Testing requires a blood sample, which can be collected in a hospital, lab, or other medical setting. Blood is often drawn from a vein in the arm or, in children, taken by pricking the skin. After blood is collected, the sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Recommended Reading: What Medication Cures Hepatitis C
So Who Should Be Screened For Hepatitis C
Well, ideally, everyone should be screened for hepatitis C. The US Preventive Services Task Force recommends that doctors should ideally screen all of their patients by checking to see if they meet the at-risk criteria. “Hepatitis C should be routinely screened for in all adults at their routine medical visits,” says infectious disease expert Amesh A. Adalja, MD, Senior Scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security.
That criteria, according to the CDC, includes a long list of people:
- Current or former injection drug users
- Everyone born from 1945 to 1965
- Anyone who received clotting factor concentrates made before 1987
- Recipients of blood transfusions or solid organ transplants before July 1992
- Long-term hemodialysis patients
- People with known exposure to the hepatitis C virus, like healthcare workers after needle sticks involving blood from someone infected with hepatitis C
- People with HIV
- Children born to mothers with hepatitis C
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force also recommends screening for people in jail, those who snort drugs, and those who have received an unregulated tattoo.
Screening is crucial, Dr. Adalja says. “Hepatitis C is serious and contagious,” he says. “If you get screened now, you can get treatment and can prevent yourself from getting complications like liver cancer or liver cirrhosis.”