How Long Do The Hepatitis A And B Vaccines Protect You
During your lifetime, you need:
- One series of the hepatitis A vaccine
- One series of the hepatitis B vaccine
Most people dont need a booster dose of either vaccine. But if you have had dialysis, a medical procedure to clean your blood, or have a weakened immune system, your doctor might recommend additional doses of the hepatitis B vaccine.
Pregnancy And Hepatitis B
Treatment for Hepatitis B during pregnancy is available. It should be noted that any women infected with Hepatitis B during pregnancy should be treated on time under proper supervision so as the disease does not reach the infant.
Infants may die after being infected from Hepatitis B according to a survey conducted by a leading hospital of United States. As a treatment, antiviral therapy with tenofovir is recommended by many physicians.
When To See A Healthcare Provider
If you develop any of the symptoms of chronic hepatitis, liver damage, or liver cancer, see your healthcare provider. It takes only a blood test to detect the presence of a hepatitis virus in your body .
A blood test also can determine which hepatitis virus you’re infected with, which will determine what your treatment should be .
Read Also: How Do You Know You Have Hepatitis C
Hiv And Hbv Coinfection
About 2% of people with HIV in the United States are coinfected with HBV both infections have similar routes of transmission. People with HIV are at greater risk for complications and death from HBV infection. All people with HIV are recommended to be tested for HBV, and if susceptible, are further recommended to receive the hepatitis B vaccination or, if chronically infected, evaluated for treatment to prevent liver disease and liver cancer. For more information about HIV and HBV coinfection, visit HIV.govâs pages about hepatitis B and HIV coinfection.
Symptoms Of Hepatitis C In Women
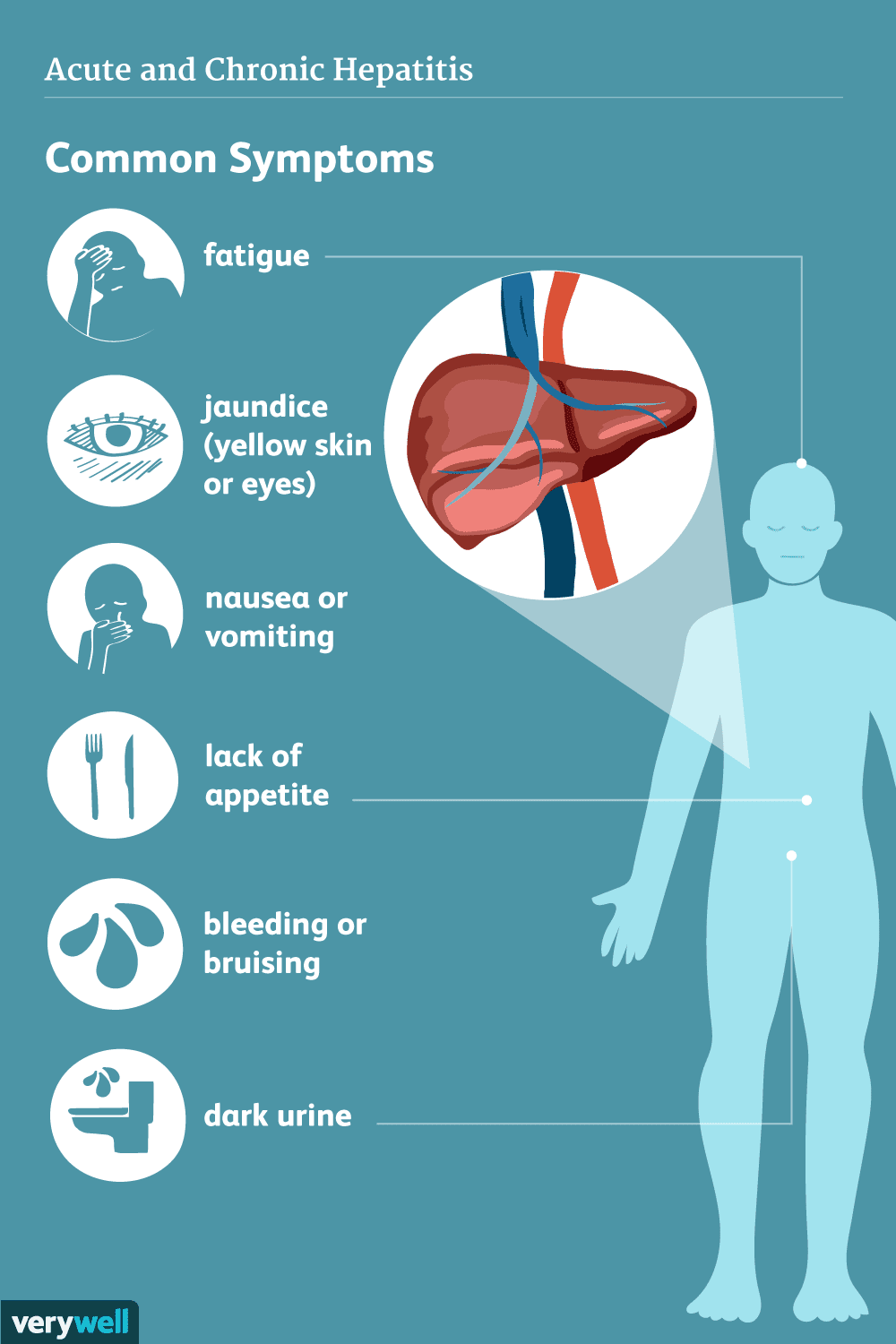
Many women dont have symptoms until the disease is in a later stage. Women who have signs of the disease in the earliest stage may brush off symptoms or attribute them to other factors, such as anemia, depression, or menopause.
Early symptoms of hepatitis C in women can include:
- fatigue
- muscle and joint pain
- poor appetite
Some hepatitis C infections are acute and the infection clears or improves on its own without treatment within a few months. Acute infections are more common in women .
Hepatitis C can also be chronic, meaning the infection doesnt clear on its own, but rather progresses and damages the liver. Symptoms of chronic hepatitis and liver damage include:
- bruising or bleeding
- spider veins
- confusion
The symptoms of chronic hepatitis C occur in both men and women, but the disease can progress slower in women. However, some women experience rapid progression of the disease and liver damage after menopause.
Having these symptoms doesnt mean you have hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C spreads from person-to-person through contact with infected blood. If you work in an industry where you might come in contact with blood, theres a slight risk of exposure. This includes personal care such as:
- manicurists
- housekeeping
- nursing
Hepatitis C can also be spread to a sexual partner during a menstrual cycle.
Also Check: Hepatitis A B C Difference
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Many people with hepatitis C don’t know they are infected. Symptoms typically don’t appear until years later in the course of chronic infection.
Signs of chronic infection include:
- Bleeding easily
- Confusion, drowsiness and slurred speech
- Spiderlike blood vessels on your skin
Because symptoms usually don’t appear until after hepatitis C has caused years of liver damage, the importance of screening is vital.
How Is Hepatitis B Diagnosed
If you think you may have hepatitis B or you might have been exposed to the virus through sex or drug use, see your doctor or gynecologist to get tested. The blood test also can tell whether someone has an acute infection or a chronic infection. Let the doctor know the best way to reach you confidentially with test results.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Acute Or Chronic
When To Seek Medical Advice
See your GP if you persistently have any of the later symptoms listed, or if they keep returning. They may recommend having a blood test that can check for hepatitis C.
Read more about diagnosing hepatitis C
None of these symptoms mean you definitely have hepatitis C, but it’s important to get them checked out.
You should also speak to your GP about getting tested if there’s a risk you’re infected, even if you don’t have any symptoms. This particularly includes people who inject drugs or have done so in the past.
Read about the causes of hepatitis C for more information about who’s at risk of having the infection.
Page last reviewed: 27 October 2021 Next review due: 27 October 2024
How Does Viral Hepatitis Affect Pregnancy
Hepatitis B and C can cause problems during pregnancy and can be passed to your baby. The risk of passing the virus to your baby is higher with hepatitis B than C.
Research shows that pregnant women with hepatitis B or C may have a higher risk for certain pregnancy complications:2
- Gestational diabetes
- Low-birth-weight baby
- Premature birth . Premature birth is the leading cause of infant death and raises the risk of health and developmental problems at birth and later in life.
Talk to your doctor if you think you may be pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Some antiviral medicines that treat hepatitis C, such as ribavirin, can cause serious birth defects if taken during pregnancy.
Recommended Reading: What Is Chronic Hepatitis B
Who Should Get The Hepatitis A Vaccine
The hepatitis A vaccine is given in two doses, six to 18 months apart. Two doses are needed for lasting protection.
The vaccine is recommended for:27
- All children, starting at 1 year
- Men who have sex with men
- People who travel or work in a part of the world where hepatitis A is common, such as certain parts of Central or South America, Asia, Africa, and eastern Europe. See the CDCs Travelers Health Information.
- People who use illegal drugs
- People who are treated with clotting factor concentrates, such as people with hemophilia
- People with chronic liver disease
- People who work with hepatitis A in a laboratory or with hepatitis Ainfected primates
- Members of households planning to adopt a child, or care for a newly arriving adopted child, from a country where hepatitis A is common. See the CDCs Travelers Health information page for international adoptions.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis C In Women
What is hepatitis C?
Hepatitis C is an infection caused by the hepatitis C virus . There are different types of hepatitis viruses, including hepatitis A, B, D, and E. Among the different viruses, hepatitis C is the most serious because it can be chronic and cause severe liver damage.
The virus spreads through contact with infected blood, so certain people have a higher risk of infection. This includes healthcare workers exposed to blood and drug users. Getting a tattoo or piercing with unsterilized equipment also increases the risk of infection.
Hepatitis C affects both men and women. As a whole, the symptoms and complications of the disease are the same for both sexes. But the virus can affect women differently.
Read Also: How You Contract Hepatitis B
Complications Of Hepatitis A
Around 10% of people who have had hepatitis A experience a relapse . Most people who have a relapse fully recover.
Hepatitis A does not cause chronic liver disease.
The severity of the disease is more severe in older age groups.
Complications of hepatitis A are rare, but the infection can lead to fulminant hepatitis. This is an acute form of hepatitis that can cause liver failure. The risk of death from fulminant hepatitis increases with age.
How Is Hepatitis B Transmitted
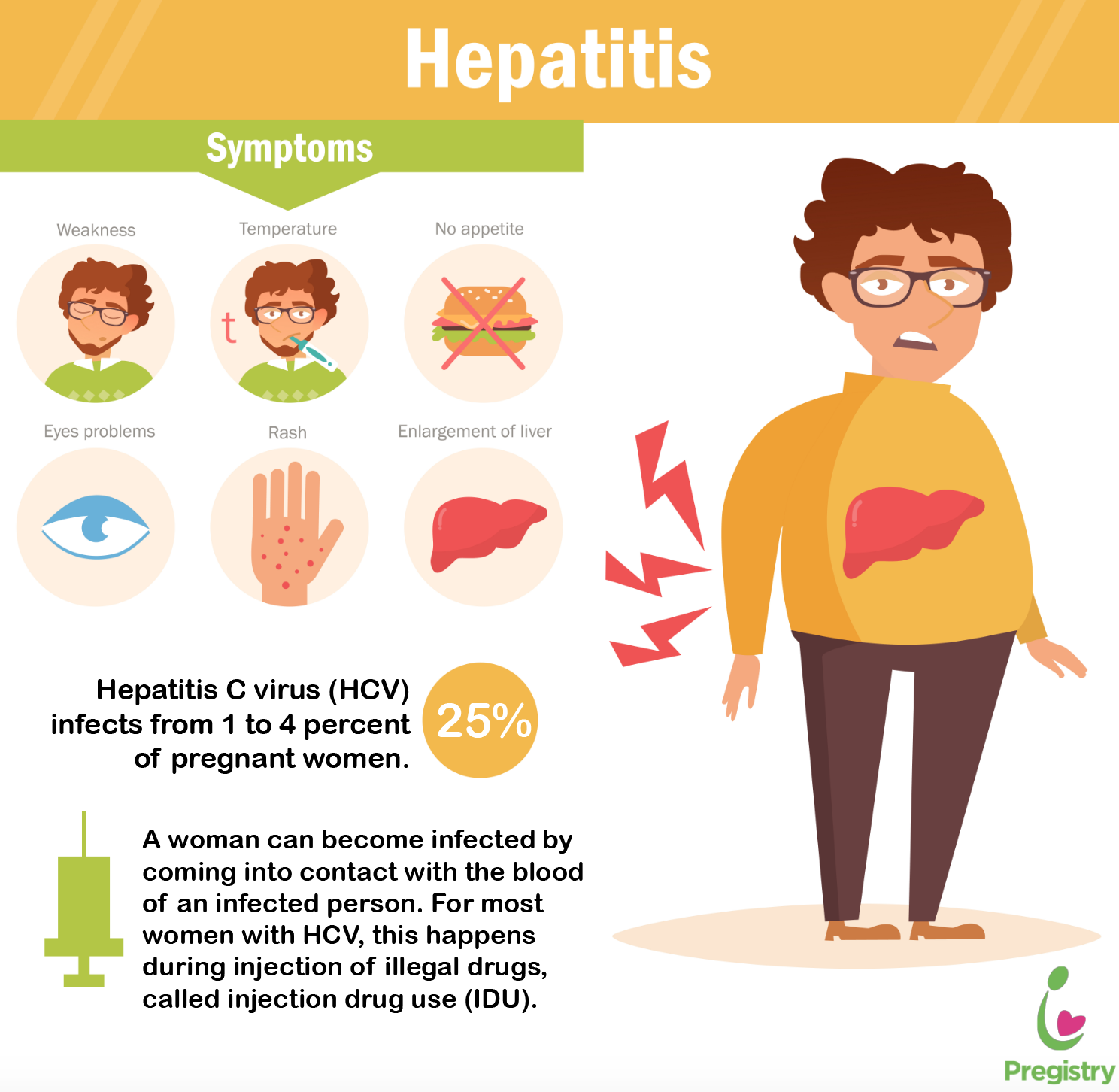
Hepatitis B is spread in several distinct ways: sexual contact sharing needles, syringes, or other drug-injection equipment or from mother-to-child at birth.
In the United States, in 2018, injection drug use was the most common risk factor reported among people with an acute HBV infection, followed by having multiple sex partners. Less commonly reported risk factors included accidental needle sticks, surgery, transfusions, and household contact with a person with HBV infection. In the United States, healthcare-related transmission of HBV is rare.
Mother-to-child transmission of HBV is especially concerning, because it is preventable. An estimated 25,000 infants are born to mothers diagnosed with HBV each year in the United States, and approximately 1,000 mothers transmit HBV to their infants. Without appropriate medical care and vaccinations, 90% of HBV-infected newborns will develop chronic infection, remaining infected throughout their lives. Up to 25% of people infected at birth will die prematurely of HBV-related causes. For this reason, the standard of care for pregnant women includes an HBV test during each pregnancy so that the appropriate steps can be taken to prevent HBV-positive mothers from transmitting the disease to her infant.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Surface Ab Ql Meaning
What Happens After A Hepatitis B Infection
Some people carry the virus in their bodies and are contagious for the rest of their lives. They should not drink alcohol, and should check with their doctor before taking any medicines to make sure these won’t cause more liver damage.
Anyone who has ever tested positive for hepatitis B cannot be a blood donor.
Who Should Be Tested
Testing for hepatitis A is not routinely recommended.
CDC recommends hepatitis B testing for:
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject drugs
- Household and sexual contacts of people with hepatitis B
- People requiring immunosuppressive therapy
- People with end-stage renal disease
- People with hepatitis C
- People with elevated ALT levels
- Pregnant women
- Infants born to HBV-infected mothers
CDC recommends hepatitis C testing for:
- All adults aged 18 years and older
- All pregnant women during each pregnancy
- About 24,900 new infections each year
- About 22,600 new infections in 2018
- Estimated 862,000 people living with hepatitis B
- About 50,300 new infections in 2018
- Estimated 2.4 million people living with hepatitis C
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis And What Causes It
Reducing The Risk Of Hepatitis A
Protecting yourself from hepatitis A
The most important action you can take to protect yourself against hepatitis A is to get vaccinated.
Practising strict personal hygiene is also essential to reducing the risk of hepatitis A. Steps you can take include:
- Wash your hands with soap and hot running water before handling food, after going to the toilet and after handling used condoms or having contact with nappies or the anal area of another person. Use a clean towel to dry your hands.
- Use barrier protection when engaging in oral-anal sex and avoid sex with someone who is infected with the hepatitis A virus.
- Vaccination may prevent illness if given within 2 weeks of contact with an infectious person.
- Clean bathrooms and toilets often, paying attention to toilet seats, handles, taps and nappy change tables.
- Boil your drinking water if it comes from an untreated source, such as a river.
- If you are travelling overseas, particularly to countries where hepatitis A is widespread, take special care to avoid hepatitis A. Before travelling, talk to your doctor about immunisation for protection.
Protecting others from hepatitis A
If you have hepatitis:
- Wash eating utensils in soapy water, and machine wash linen and towels.
Household contacts and sexual partners of an infectious person may need to be immunised.
All people who have hepatitis A should check with their doctor before returning to work or school.
Protecting yourself from hepatitis A when overseas
How Long Does It Last
Hepatitis A can last from a few weeks to several months.
Hepatitis B can range from a mild illness, lasting a few weeks, to a serious, life-long condition. More than 90% of unimmunized infants who get infected develop a chronic infection, but 6%10% of older children and adults who get infected develop chronic hepatitis B.
Hepatitis C can range from a mild illness, lasting a few weeks, to a serious, life-long infection. Most people who get infected with the hepatitis C virus develop chronic hepatitis C.
Don’t Miss: Lamivudine Dose In Hepatitis B
How Do You Get Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is found in an infected persons blood and other body fluids.
Hepatitis C is usually spread through:
- Sharing or reusing needles, syringes, and drug preparation equipment such as cookers and cotton when injecting drugs. This is the most common way hepatitis C is spread in the United States. Hands or drug preparation equipment that have even tiny amounts of blood on them can also spread hepatitis C.
- Accidental needle stick or other sharp instrument injury
Less common ways to spread hepatitis C:13
- Vaginal, oral, or anal sex
- Birth to a mother who has hepatitis, though this is rare
- Sharing personal items like razors and toothbrushes
- Tattoos or body piercings
- Blood transfusions done in the United States before the 1990s or in other parts of the world where hepatitis C testing is less common
What Is Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C, also known as hep C or HCV, is a virus that is associated with liver problems and chronic liver disease. Hepatitis C can be a mild illness that presents no real complications and lasts just a few weeks or months, but the infection can also present with more chronic forms that can last your entire life. Chronic forms of hepatitis C can lead to severe liver issues, including liver cancer and cirrhosis of the liver.
Read Also: Is Hepatitis C Contagious By Touch
Who Is At Risk
Anyone who has not been vaccinated or previously infected can get infected with the hepatitis A virus. In areas where the virus is widespread , most hepatitis A infections occur during early childhood. Risk factors include:
- poor sanitation
- living in a household with an infected person
- being a sexual partner of someone with acute hepatitis A infection
- use of recreational drugs
- travelling to areas of high endemicity without being immunized.
How Serious Is It
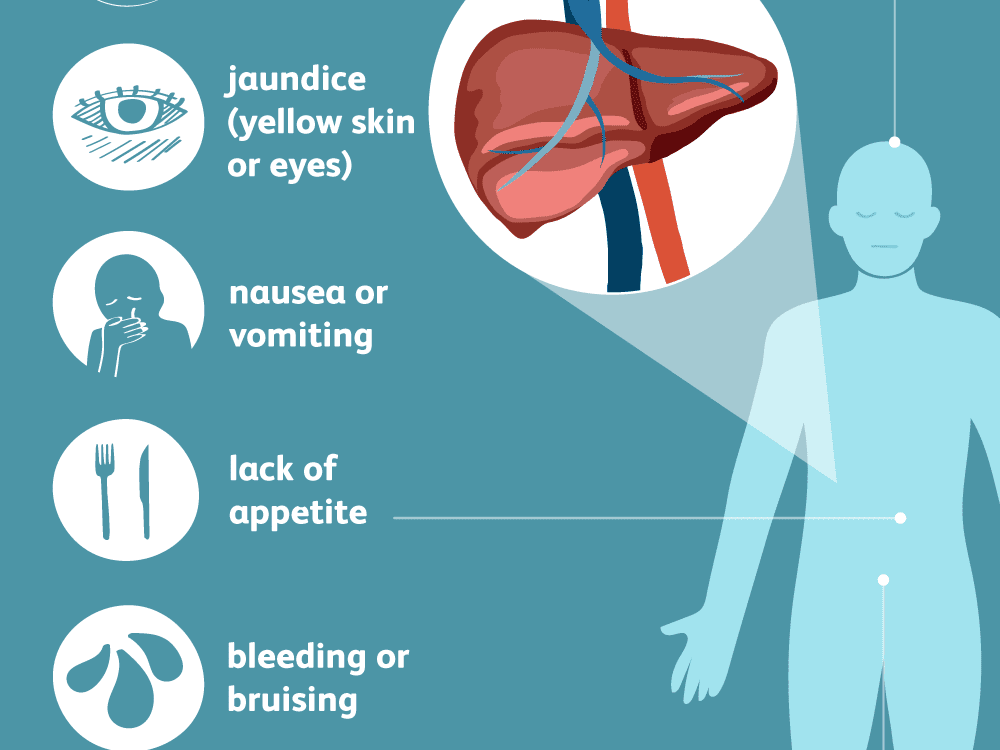
- People can be sick for a few weeks to a few months
- Most recover with no lasting liver damage
- Although very rare, death can occur
- 15%25% of chronically infected people develop chronic liver disease, including cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer
- More than 50% of people who get infected with the hepatitis C virus develop a chronic infection
- 5%-25% of people with chronic hepatitis C develop cirrhosis over 1020 years
You May Like: How Do You Get Hepatitis Of The Liver
How Do People Get The Hbv Virus
Hepatitis B virus is found in the blood of people with HBV infection. It enters the body through blood-to-blood contact.
Reliable blood tests for HBV were developed many years ago. Since blood donors and blood products are tested for HBV, this is no longer the typical means of infection.
In many parts of the world, hepatitis B virus infects more than 8% of the population. HBV-infected women pass the infection to their babies during the birth process. People can also get hepatitis B by sharing needles for injection drug use, through sexual contact with an infected person, by an accidental needlestick with a contaminated needle, or from improperly sterilized medical, acupuncture, piercing, or tattooing equipment.
Who Should Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
The hepatitis B vaccine is usually given in three doses over six months. The vaccine is recommended for:28
- All children at birth
- All children and teens younger than 19 who have not been vaccinated
- Men who have sex with men
- People who live with or have sex with someone who is infected with hepatitis B
- People with more than one sex partner
- People who share equipment to inject drugs
- People with chronic liver or kidney disease
- People with HIV
- People younger than 60 with diabetes
- People whose jobs expose them to human blood or other body fluids
- Residents and staff of facilities for people with developmental disabilities
- People who travel to parts of the world where hepatitis B is common, such as Southeast Asia, sub-Saharan Africa, the Amazon Basin in South America, the Pacific Islands, parts of Eastern Europe, and parts of the Middle East.29 See the CDCs Travelers Health information page.
Recommended Reading: Which Test For Hepatitis B
When Should I See A Doctor
Make an appointment if you have any of the symptoms and you recently:
- Traveled out of the country, especially if you went to Mexico, South America, Central America, or anywhere without good sanitation
- Ate at a restaurant that reported a hepatitis A outbreak
- Found out someone close to you, like a roommate or caregiver, was diagnosed with hepatitis A
- Had sex with someone who has hepatitis A
- Ate raw shellfish
- Used illegal drugs
When you see your doctor, they may spot some more signs that you’ve got the disease. For instance, they might find that you have:
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis A
You can get the first symptoms anytime between 15 and 50 days after you came in contact with the virus. But they usually show up between about 2 and 4 weeks later.
Most people with hepatitis A usually have sudden:
- Extreme tiredness
If your child has hep A, they may also have:
- Cold symptoms
- Cough
- Sore throat
If you’re over age 50 or have a long-term liver disease, you may have a more severe case of the disease called fulminant hepatitis A infection. You could have symptoms like:
- Spontaneous bleeding or easy bruising
- Confusion and changes in alertness
- Liver function that gets worse
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes that gets worse
Recommended Reading: Do They Have A Cure For Hepatitis C