How To Diagnose Autoimmune Hepatitis
It is difficult to suspect autoimmune hepatitis only based on the symptoms since several liver diseases cause similar symptoms. It is therefore important to rule out other causes of liver disease like viral hepatitis, alcoholic hepatitis and drug-induced hepatitis while making the diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis. Diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis is based on the following:
- Medical history of the patient where the patient will complain of the symptoms mentioned above. The patient may also give a history of suffering from another autoimmune disease
- Physical examination may reveal the presence of jaundice, pain over the liver, an enlarged liver, and other signs of liver disease as mentioned above.
- Blood tests: Blood tests done for autoimmune hepatitis include liver function tests and tests for autoantibodies
- Liver function tests will indicate high bilirubin levels, increase in liver enzymes, and prolonged bleeding and clotting times
What Are The Symptoms And Complications Of Autoimmune Hepatitis
Often, the symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis are minor. When symptoms do occur, the most common are fatigue, abdominal discomfort, aching joints, itching, jaundice , enlarged liver, nausea and spider angiomas on the skin. Other symptoms may include dark urine, loss of appetite, pale stools and absence of menstruation. More severe complications can include ascites and mental confusion. In 10%-20% of cases, autoimmune hepatitis may present with symptoms like an acute hepatitis.
What Are The Causes Of Autoimmune Hepatitis
Autoimmune hepatitis occurs when the white blood cells of the body produce an inappropriate immune response against the liver cells, thereby causing inflammation and damage. The exact cause of autoimmune hepatitis is not known. Affected people may have a genetic predisposition for the condition, which may be triggered by an environmental factor. Around 20% patients suffering from a genetic condition called autoimmune polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis-ectodermal dystrophy syndrome suffer from autoimmune hepatitis.
The environmental trigger could be:
- Drugs like infliximab, minocycline, atorvastatin, diclofenac, isoniazid, methyldopa, nitrofurantoin, and propylthiouracil, the hepatitis A vaccine, and herbal agents like black cohosh and dai-saiko-to. The autoimmune hepatitis may improve after stopping the medication
- Viruses such as hepatitis A, B, or C, or measles virus
Autoimmune hepatitis is of two main types, type 1 and type 2
- Type 1 autoimmune hepatitis usually first manifests in adolescence or young adults. Females are most commonly affected.
- Type 2 autoimmune hepatitis is less common than type 1 and usually first manifests in children. Its prognosis or outcome is often worse than type 1 disease.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis C Screening Test
What Is Autoimmune Disease
One job of the immune system is to protect the body from viruses, bacteria, and other living organisms. The immune system usually does not react against the bodys own cells. However, sometimes it attacks the cells it is supposed to protect this response is called autoimmunity. Researchers think certain bacteria, viruses, toxins, and drugs trigger an autoimmune response in people who are genetically susceptible to developing an autoimmune disorder.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test
When To Start Treatment
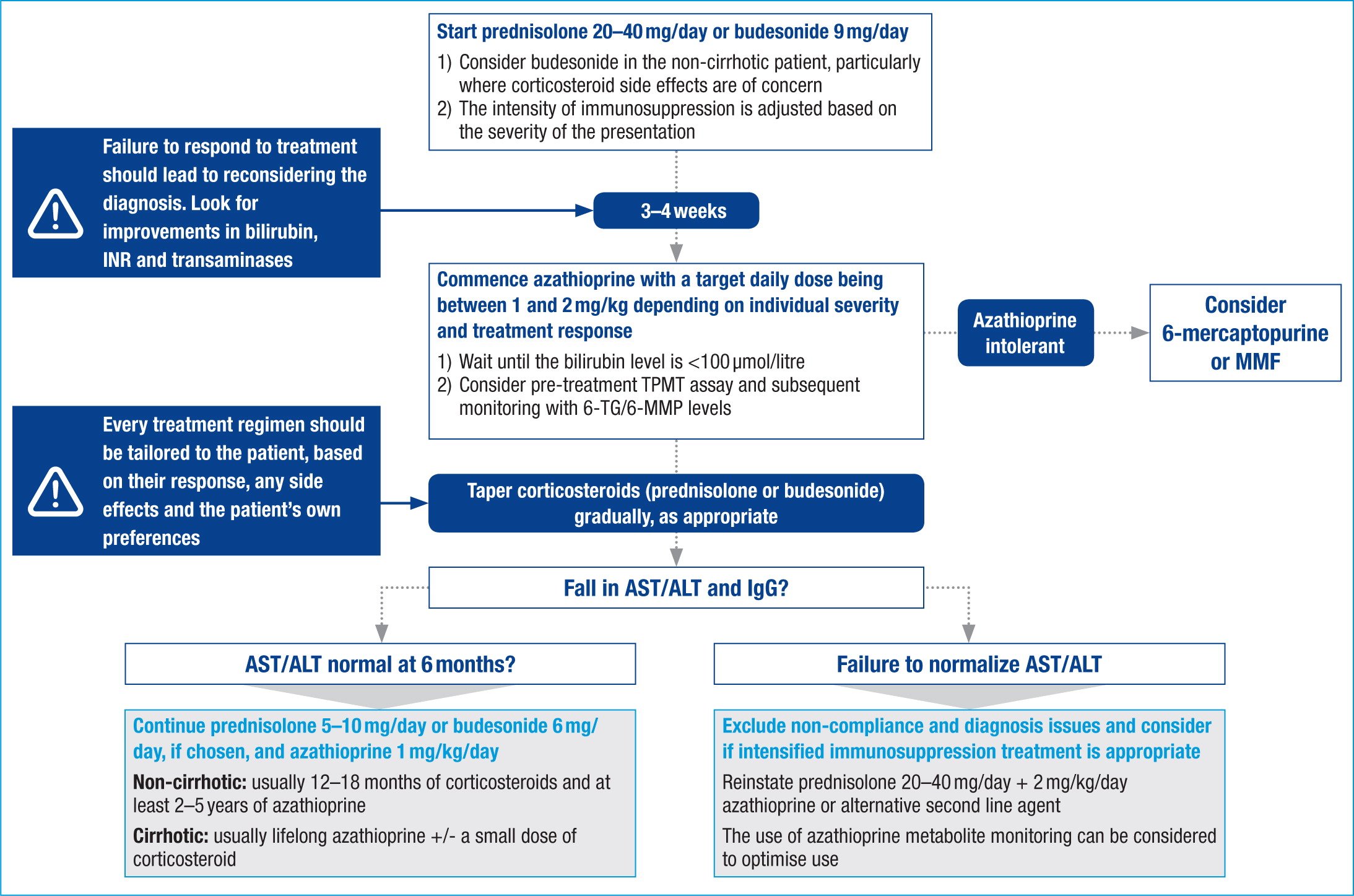
Treatment should be started in patients with significant disease, characterized by at least one of the following: AST or ALT > 10 times the upper limit of normal AST or ALT > 5 times the upper limit of normal and IgG > 2 times the upper limit of normal bridging necrosis or multiacinar necrosis on histology. Although uncommon, the presence of incapacitating symptoms has also been proposed as an indication of treatment regardless of laboratory values.
In asymptomatic patients with AST, ALT, and gamma globulins/IgG elevations that do not meet the criteria above, the benefit of treatment is less clear. The course of the disease in such patients has not been well established and there is little data to support treatment. Thus in asymptomatic patients with only mild laboratory and histological changes, the decision to start treatment should be individualized and the risks of therapy taken into account. Often treatment in this situation can be postponed and liver tests followed closely. Such patients should always be referred to a hepatologist or gastroenterologist for decision regarding therapy.
Asymptomatic patients with inactive disease on liver biopsy or burned out cirrhosis do not benefit from treatment.
Read Also: What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C
Treatments For Autoimmune Hepatitis
Treatment works best when AIH is diagnosed early. The goal in treating AIH is to slow or stop the bodys immune system from attacking the liver. The medications used are immunosuppressants, such as prednisone and Imuran® . Physicians usually prescribe a high initial dose of prednisone, and then taper it down progressively as symptoms and liver enzymes improve. Most people will need to take medication for the rest of their lives. Since prednisone can cause a wide range of side effects, Imuran® is often used in conjunction to allow for a lower dose of the prednisone.
Some people may go into remission, during which physicians can effectively discontinue treatment others will relapse after stopping treatment, and will then need to restart the medication and continue on long-term maintenance therapy. A few patients may eventually be tapered off the prednisone completely and stay solely on Imuran®. For those who do not respond to, or relapse from, the combination regimen, then stronger immunosuppressive agents such as mycophenolate mofetil, cyclosporine, or tacrolimus may be considered. When medications do not halt the progress of the disease, or complications from cirrhosis have developed, the remaining option is a liver transplant. Fortunately, the success rate of transplantation in people with AIH is excellent.
Recommended Reading: Hiv And Hepatitis B And C Are Incurable Bloodborne Pathogens
When The Liver Is Under Attack
In people with autoimmune hepatitis, immune cells inappropriately mistake the liver’s normal cells as abnormal and attack them. Over time, this can lead to inflammation, scarring , impaired liver function, and even cirrhosis , which can result in liver failure, and death if not treated. Some people may eventually need a liver transplant. The liver disease specialists at NewYork-Presbyterians Center for Liver Disease and Transplantation are experienced in diagnosing and treating autoimmune hepatitis.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatic Cirrhosis Of The Liver
What Is The Treatment For Autoimmune Hepatitis
Treatment is almost always needed. Early treatment can improve symptoms, reduce the risk of complications, and also greatly improve your outlook . Treatment aims to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system with immunosuppressant medicines:
- Steroid medication is the usual first treatment. Steroids are good at reducing inflammation. A high dose is usually needed at first. The dose is then gradually reduced over a few weeks. The aim is to find the lowest dose needed to control the inflammation. The dose needed varies from person to person. See the separate leaflet called Oral Steroids for more detail.
- Azathioprine is an immunosuppressant medicine that works in a different way to steroids. It is usually used in addition to the steroid. A steroid plus azathioprine tends to work better than either alone. Also, the dose of steroid needed is usually less if you also take azathioprine. This means that any side-effects from steroids may be less severe.
Treatment works well in most cases. Usually, the inflammation settles and symptoms improve within a few months of starting treatment. However, it may take a year or more to get the disease totally under control. Azathioprine is usually taken for at least two years.
For some people a liver transplant may be an option â for example:
Also Check: How Do You Get Hepatitis C
How Is Autoimmune Hepatitis In Children Diagnosed
Your childs health care provider will do several tests to look for autoimmune hepatitis and other related diseases. These tests may include:
- Blood tests
- Special scans of the liver, such as ultrasound and magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography
- Exam of the inside of the intestines , under anesthesia
You May Like: Hepatitis B Can It Be Cured
How Do Doctors Treat Autoimmune Hepatitis
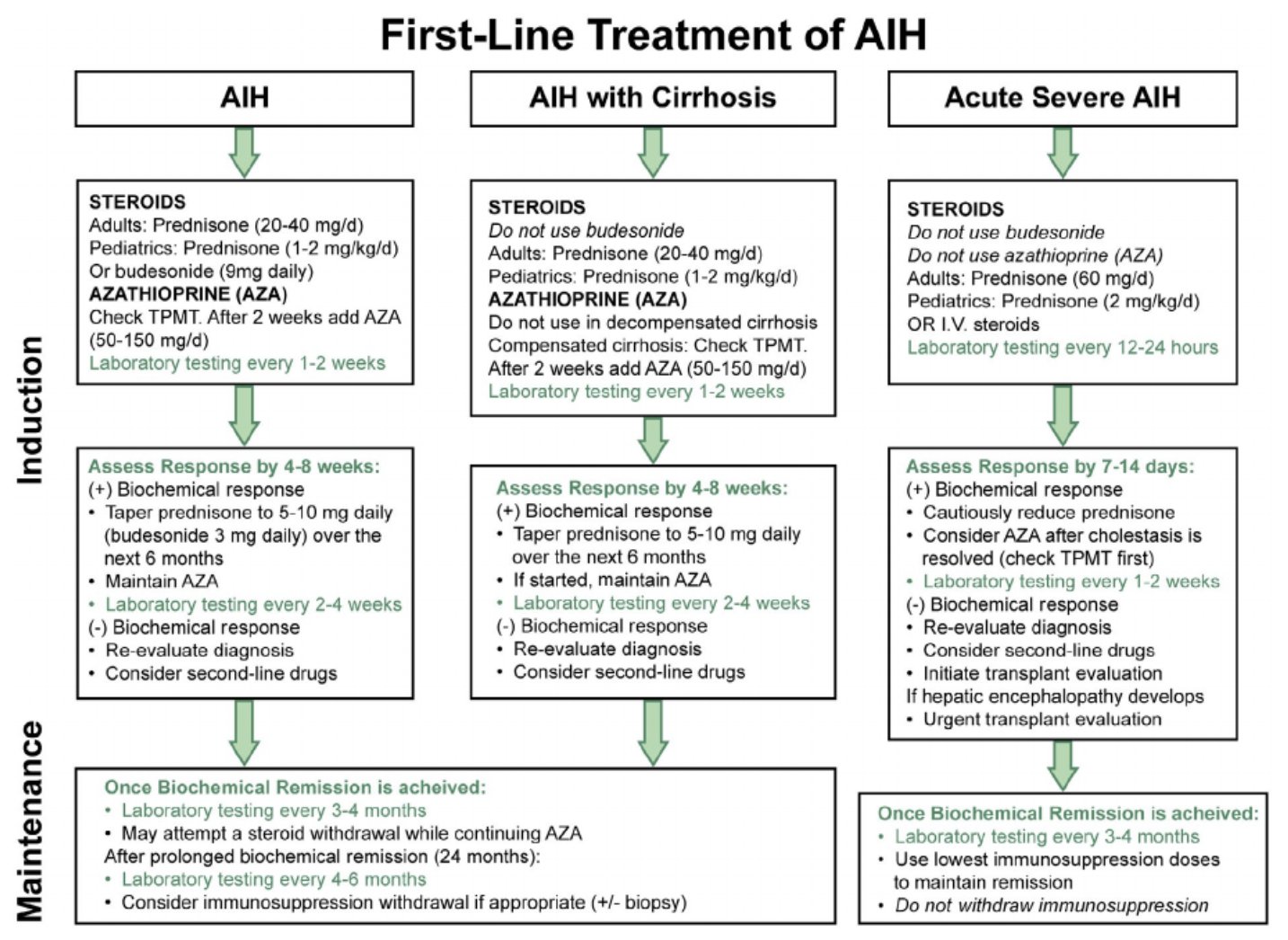
Doctors treat autoimmune hepatitis with medicines that suppress, or decrease the activity of, your immune system, reducing your immune systems attack on your liver. The medicines doctors most often prescribe are corticosteroidsprednisone or prednisolonewith or without another medicine called azathioprine.
Doctors typically start with a relatively high dose of corticosteroids and then gradually lower the dose. Your doctor will try to find the lowest dose that works for you. Your doctor will use blood tests to find out how you are responding to the treatment. A decrease in levels of the liver enzymes alanine transaminase and aspartate transaminase shows a response to treatment. ALT and AST falling to normal levels shows a full response. In some cases, a doctor may repeat a liver biopsy to confirm the response to treatment and find out whether the damage has resolved.
Treatment can relieve symptoms and prevent or reverse liver damage in many people with autoimmune hepatitis. Early treatment of autoimmune hepatitis can lower the chances of developing cirrhosis and other complications. A minority of people who have no symptoms or only a mild form of the disease may or may not need medicines.
Screening For Viral Hepatitis
The purpose of screening for viral hepatitis is to identify people infected with the disease as early as possible, even before symptoms and transaminase elevations may be present. This allows for early treatment, which can both prevent disease progression and decrease the likelihood of transmission to others.
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A causes an acute illness that does not progress to chronic liver disease. Therefore, the role of screening is to assess immune status in people who are at high risk of contracting the virus, as well as in people with known liver disease for whom hepatitis A infection could lead to liver failure. People in these groups who are not already immune can receive the hepatitis A vaccine.
Those at high risk and in need of screening include:
- People with poor sanitary habits such as not washing hands after using the restroom or changing diapers
- People who do not have access to clean water
- People in close contact with someone who has hepatitis A
- People who use illicit drugs
- People with liver disease
- People traveling to an area with endemic hepatitis A
The presence of anti-hepatitis A IgG in the blood indicates past infection with the virus or prior vaccination.
Hepatitis B
The CDC, WHO, USPSTF, and ACOG recommend routine hepatitis B screening for certain high-risk populations. Specifically, these populations include people who are:
Other
Alcoholic hepatitis
Read Also: Does Hepatitis C Affect The Brain
Although Considered Less Common Autoimmune Hepatitis Should Not Be Ignored Prompt Diagnosis And Treatment Can Prevent Liver Failure
Written by Editorial Team | Updated : July 6, 2022 2:11 PM IST
We say that a strong immune system is very important to keep diseases at bay. But, what about situations where the immune system itself turns against us? Autoimmune diseases are an example of what happens when the immune system starts considering the body’s own cells as foreign and destroys them. The result repeated inflammation and tissue damage induced by our own body.
We do not clearly know what causes most autoimmune diseases, though genetic changes over time and environmental as well as lifestyle factors have been known to trigger these diseases. Today, I am going to tell you about autoimmune hepatitis , which although considered less common, should not be ignored as prompt diagnosis and treatment are the only ways to prevent liver failure and ultimately transplantation.
Autoimmune Hepatitis Diagnosis And Treatment:
Prior to the Treatment:
- Your doctor will question you about your symptoms during your first visit for consultation
- Medications that you take as well as alcohol you drink will be asked in order to diagnose the problem
- Blood tests to rule out certain other viral hepatitis will be advised by your doctor to be taken.
- Autoimmune hepatitis blood tests can usually spot things which are called autoantibodies. It might be a sign of autoimmune hepatitis disease. Also certain other blood tests can also tell you whether your liver is affected
- Biopsy will also be asked by your doctor to be taken. Usually your doctor will take out a small piece of liver in order to look at the cells under the microscope
During the Treatment:
- Your doctor will prescribe you with prednisone which is a steroid that can ease inflammation
- You will be started off autoimmune hepatitis medication with a high dose and then your doctor will lower it with azathioprine or Imuran or with 6-mercaptopurine which otherwise called as Purinethol in order to weaken your immune system
- In certain cases your doctor will ask you to take prednisone or mycophenolate mofetil in order to weaken your immune system
Autoimmune Hepatitis Prognosis, Post Treatment and Recovery:Autoimmune Hepatitis Diet:Autoimmune Hepatitis Risk Factors:
- Being female
- Hereditary
- Having autoimmune disease
Autoimmune Hepatitis Complications:
- Enlarged veins in the esophagus
- Ascites or fluid in the abdomen
- Liver failure
- Liver cancer
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Hepatitis From Saliva
Boost Up Your Glutathione
Glutathione is considered the master anti-oxidant within the body and is produced by every cell in the body where it functions to protect our DNA. Glutathione is our cells security guard that protects the cellular components from outside free radical attack. Longevity scientists now believe that the level of glutathione in our cells has a direct relationship with how long we will live .
Glutathione plays a very important role in establishing immune tolerance . Studies have demonstrated that glutathione enhances the function of T cells and modulates immune activity . In this way, optimizing glutathione levels are extremely important for reducing collateral damage associated with inflammation and autoimmune reactions .
This article goes into more detail on glutathione and its role in reducing inflammation. Hopefully, this article has given you hope and several major action steps to reduce inflammation and heal autoimmune disease.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis B Vaccine For
About Autoimmune Liver Disease
Autoimmune liver diseases are typically long-lasting and recurring conditions. This means that you may experience persistent immune system attacks that destroy liver cells. As cells die, scar tissue known as fibrosis forms. Autoimmune diseases tend to progress slowly, and you may have long periods without symptoms. When scarring becomes extreme, liver function weakens and eventually may result in a condition known as cirrhosis. Cirrhosis is also known as liver failure or end-stage liver disease. The only cure for this condition is organ transplantation. While the only cure for severe cirrhosis is transplantation, we can help you manage the symptoms of the disease with medication before or instead of transplantation.
Our liver specialists work closely with other experts at Mount Sinai to provide a comprehensive approach to treating you if you have multiple autoimmune conditions. Our goal is to keep your immune system active and related symptoms under control.
Mount Sinai liver specialists work with colleagues in rheumatology, endocrinology, gastroenterology, radiology, and pathology to manage autoimmune liver disease. We use state-of-the-art methods of diagnosis and treatment.
If end-stage liver disease develops and you need liver transplantation, we have the expertise to help you. We have extensive experience treating patients with autoimmune liver disease. After living with chronic liver disease, through treatment, we can help restore your quality of life.
You May Like: Just Food For Dogs Hepatic Support
Autoimmune Hepatitis Diet: What Do Doctors Recommend
While there is no recommended diet for autoimmune hepatitis, diet considerations related to weight management and alcohol consumption may make an impact on both symptoms and disease progression. Following a healthy diet and talking with your doctor about alcohol consumption can help you avoid complications related to obesity, reduce weight gain from common steroid treatments, and avoid alcohol-related liver issues.
S To Reduce Inflammation
Here are the best action steps to get started with on your journey to prevent and/or heal chronic inflammation and autoimmune disease. You should always consult with your physician before stopping or changing medications or taking on new health strategies.
Additionally, you should be working with a functional health practitioner to help guide you through these strategies. This is not an exhaustive list and there are other natural therapeutic strategies that I and functional health practitioners will utilize to help individuals with chronic inflammation and autoimmune disorders.
Read Also: The Vaccine For Hepatitis B
Our Approach To Autoimmune Hepatitis
UCSF offers the most advanced diagnostic and treatment options for patients with autoimmune hepatitis. We generally begin with a high dose of prednisone to stop or slow the immune system’s attack on the liver. We then taper the dose and may supplement the regimen with additional immune-suppressing medications to manage the condition long term.
Autoimmune hepatitis can lead to severe liver damage or failure. In these cases, a liver transplant may be necessary. Our liver transplant program, designated a center of excellence by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, is known for outstanding outcomes and for helping pioneer techniques that have made transplants safer and more successful. We perform more than 100 transplants each year, and our survival statistics are among the best in the country.
Liver Transplantation For Autoimmune Hepatitis
In some people, the inflammation and liver damage of autoimmune hepatitis cannot be well controlled with medication alone. In these cases, our doctors may suggest a liver transplant. At NewYork-Presbyterian, you are ten times more likely to receive a liver transplant than at other hospitals in the region, with an average wait time of just nine months. Our surgeons have performed more than 2,000 liver transplants, with outcomes that meet or surpass national averages. They use a variety of liver transplant approaches, including living donor liver transplantation, to extend the limits of organ transplantation and provide the greatest number of transplants possible.
Read Also: How Long Can You Live With Hepatitis C Untreated
Read Also: Hepatitis C Non Reactive Test Result