Question 2 What Is The Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
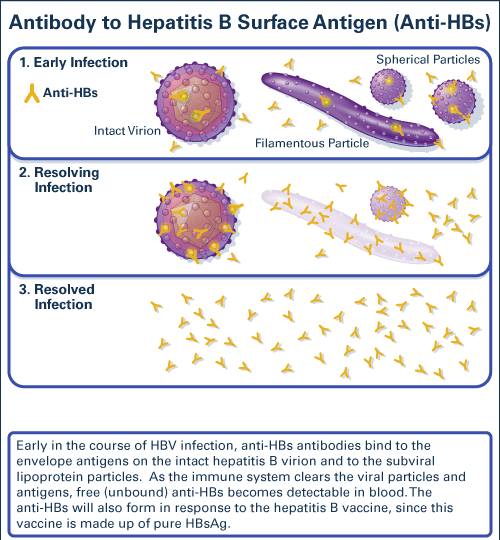
The hepatitis B surface antibody is the antibody that is produced in response to hepatitis B surface antigen , a protein present on the surface of the hepatitis B virus. Anti-HBs appears after convalescence from acute infection and lasts for many years. It can also be produced in response to hepatitis B vaccination.
Other hepatitis B antibodies are not produced in response to vaccination. This is because these antigens are not in the vaccine.
Read Also: What Does Hepatitis B Do To You
Cautions Discusses Conditions That May Cause Diagnostic Confusion Including Improper Specimen Collection And Handling Inappropriate Test Selection And Interfering Substances
Positive screen results without need for confirmation testing should be interpreted in conjunction with test results of other hepatitis B virus serologic markers .
Positive hepatitis B surface antigen test results should be reported by the health care provider to the State Department of Health, as required by law in some states.
Individuals, especially neonates and children, who recently received hepatitis B vaccination may have transient positive HBsAg test results because of the large dose of HBsAg used in the vaccine relative to the individualâs body mass.
Performance characteristics have not been established for the following specimen characteristics:
-Grossly icteric
-Containing particulate matter
What Does Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Ql Reactive Mean
If this test is positive or reactive, then your immune system has successfully developed a protective antibody against the hepatitis B virus. This will provide long-term protection against future hepatitis B infection. Someone who is HBsAb+ is not infected and cannot pass the virus to others.
Can reactive hepatitis B be cured?
Most adults with hepatitis B recover fully, even if their signs and symptoms are severe. Infants and children are more likely to develop a chronic hepatitis B infection. A vaccine can prevent hepatitis B, but theres no cure if you have the condition.
What is the normal level for Hep B surface AB?
For hepatitis B surface antibody , a level less than 5 mIU is considered negative, while a level more than 12 mIU is considered protective. Any value between 5 and 12 mIU is indeterminate and should be repeated.
Don’t Miss: Where Can I Get Tested For Hepatitis B
Can I Take The Test At Home
Samples for hepatitis B testing can be collected at home. At-home hepatitis B testing requires a patient to collect a blood sample, typically from a fingerstick using a very small needle provided in the test kit. Once a blood sample is collected, it is prepared according to the instructions contained in the test kit and mailed to a laboratory for testing.
Because there are numerous types of tests for HBV, it is important to look closely at the specific components of any at-home test kit. Many at-home test kits only look for hepatitis B surface antigen .
What Is The Difference Between The Hepatitis B Surface Antigen And The Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
The basic blood test for hepatitis B consists of three screening tests: a hepatitis B surface antigen test, which determines whether a person currently has the infection a hepatitis B core antibody test, which determines whether a person has ever been infected and a hepatitis B surface antibody test, which determines
Also Check: Can Hepatitis C Go Away By Itself
Taking A Hepatitis B Test
Testing for hepatitis B is performed on a sample of blood. A doctor, nurse, or other health care provider can obtain a blood sample using a small needle to draw blood from a vein.
At-home hepatitis B testing requires that users carefully follow instructions provided in the test kit to collect a small sample of blood, package the sample, and mail it to a lab for testing.
You May Like: Hepatitis A Is A Virus
Hbv Dna Hbv Genotype And Hbv Drug Resistance Assays
Specimen: Serum or plasma
Container: Red-top tube, yellow-top tube , gel-barrier tube, plasma preparation tube, or lavender tube
Collection method: Routine venipuncture
The specimen should be transfused to separate plasma/serum from cells within 6 hours and kept frozen when testing cannot be done promptly.
The tests use PCR amplification, DNA probe hybridization, and sequencing method.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Is More Infectious Than Hiv
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen
Health Streets Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test checks for a current infection of the hepatitis B virus. If the test is positive, then the person can be contagious to others.
Online registration is simple. You choose the lab location based on ZIP code during registration. An authorization barcode is instantly emailed to you and texted directly to the phone of the person being tested. A map of the clinic location will accompany the barcode. The registrant can then walk into the testing facility and show the barcode along with photo ID. Results are fast and stored securely online. Individuals and employers can register online or call to order tests.
Recommended Reading: Hepatic Porphyrias Diagnosis And Management
Sequence Following An Initial Negative Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Titer
As you obtain documentation, please submit documentation of each step to CastleBranch
- Initial Hepatitis B titer negative for immunity
- Receive Hepatitis B challenge dose/booster
- Repeat Hepatitis B titer 4-6 weeks after challenge/booster vaccine
Dont Miss: What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis C Infection
Recommended Reading: How To Treat Hepatic Steatosis
How Is The Hbcab Test Done
This is a blood test. A clinician will fill a tube with blood taken from a vein in your arm through which a needle is inserted. If you are giving blood, a sample will be taken from the blood you’re donating. The blood is sent to a lab, where it is tested. Sometimes HBcAb will be added on to lab orders when results from other tests indicate there may be a hepatitis B infection.
Preparation Prior To Transport
Label the specimen container with the patients full name, date of collection and one other unique identifier such as the patients date of birth or Health Card Number. Failure to provide this information may result in rejection or testing delay.
Centrifuge if using SST. Place specimen in biohazard bag and seal. Specimens should be stored at 2-8°C following collection.
Specimens more than the following number of days post collection will not be tested:
- > 6 days for Hepatitis B surface antigen
- > 7 days for Hepatitis B e Antigen and Hepatitis B e Antibody
- > 10 days for Hepatitis B core Antigen and Hepatitis B surface Antibody
Also Check: Where Can You Get Hepatitis A Vaccine
Antibody To Hepatitis B Surface Antigen
Harvest Order Choice: 90640
Synonyms: Anti-HBs HBs Ab Hepatitis B Post-vaccine screen
Program: Virology
Unit: Viral Serology
Useful For: Qualitative and quantitative enzyme immunoassay for the detection of antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen in human serum and EDTA, heparin, or citrated plasma. The assay results may be used as an aid in the determination of susceptibility to hepatitis B virus infection in individuals prior to or following HBV vaccination or where vaccination status is unknown. Assay results may be used with other HBV serological markers for the laboratory diagnosis of HBV disease associated with HBV infection.
Method: Enzyme Immunoassay
Request Form: SRD-1
Container/ Tube: The following tube types and anticoagulants, including those in both glass and plastic tubes, have all been evaluated and found to be acceptable: SST, EDTA, sodium citrate, lithium heparin, and sodium heparin.
Type: Human serum or plasma
Volume: Fill tubes as labeling indicates to avoid improper dilution
Collection Instructions: venipuncture
Storage: Serum/ plasma should remain at room temperature for no longer than eight hours. If assays are not completed within eight hours, serum/plasma should be refrigerated at 2-8C. Specimens may be stored at 2-8C for 7 days. For long-term storage, the specimens should be frozen . Specimen should not be used if they have incurred more than 5 freeze-thaw cycles. Mix specimens thoroughly after thawing.
Reference Interval: Negative, non-reactive
Hepatitis B Vaccine And Surface Antibody Titer Faqs
PLEASE NOTE: This is program specific some programs require 3 Hepatitis B vaccines AND a positive Hepatitis B Surface Antibody titer while others will accept 3 vaccines OR a titer. Please read the information in your CastleBranch account carefully so that you know exactly what you need to meet your programs requirements. If you have any questions, please email and a team member will respond.
Dont Miss: Which Hepatitis Is Transmitted Sexually
Recommended Reading: Symptoms Of Viral Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test
A hepatitis B surface antigen test shows if youre contagious. A positive result means you have hepatitis B and can spread the virus. A negative result means you dont currently have hepatitis B. This test doesnt distinguish between chronic and acute infection. This test is used together with other hepatitis B tests to determine the .
Also Check: Hepatitis C How Can You Get It
Educating Clients About Viral Hepatitis
Clients may believe they know about viral , but their understanding of the disease may not be accurate. It is easy to confuse the three main types of viral , B, and C. Clients may have formed impressions based on limited or incorrect information. Counselors should briefly describe hepatitis A, B, and C, including their prevalence, , and relationship to drug use, as well as to other infections, such as HIV and sexually transmitted diseases. Specific strategies for speaking with clients include:
- Speak clearly and keep the message simple, focused, and brief.
- Use language, examples, and concepts that the client understands.
- Use appropriate visual aids.
- Frame numerical statements in terms that are easy to visualize. Say 5 out of 100 people rather than 5 percent of the population say more than half instead of the majority.
- Repeat the information at different times in different ways. The average client retains only approximately one-third of what he or she is told. Summarize essential points.
- Pay attention to a clients response to the information. For example, if a client stiffens his or her posture, consider saying, I notice that this topic seems to make you uncomfortable. It does for a lot of people. Please tell me what youre feeling right now. Id really like to help you with this.
- Use the opportunity to describe the potential detrimental effects of alcohol and other substance use on the liver of a person who is infected with HCV.
You May Like: Hepatitis C Vaccine Side Effects
When Should I Get Hepatitis B Testing
Using hepatitis B tests to screen for HBV is recommended for certain groups that are at an increased risk of infection. Groups that may benefit from hepatitis B screening include:
- Pregnant people
- People born in parts of the world where hepatitis B is more common, including Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, South America, and parts of the Middle East
- People who didnât receive a hepatitis B vaccine
- HIV-positive people
- Pain in the joints or abdomen
- Loss of appetite, nausea, or vomiting
- Yellowish skin and eyes
Using hepatitis B testing to assess immunity to HBV may be used before or after vaccination. Pre-vaccination testing is not always needed but may be performed if there is a chance that a patient has previously been infected with HBV or has already been vaccinated. Post-vaccination testing is used in certain groups of people who are at an especially elevated risk for HBV infection, including infants born to mothers with a hepatitis B infection.
How To Get Tested
Hepatitis B testing is typically prescribed by a doctor and performed in a hospital, lab, or other medical setting. Taking a hepatitis B test requires a blood sample, which can be collected by a health care professional.
For laboratory-based testing, blood is drawn from a patientâs vein. After blood is collected, the sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Also Check: Hepatitis B And C Test Price
You May Like: Hepatitis C Causes Symptoms And Treatment
Question 5 What Is The Natural History Of Hepatitis B Surface Antibody During Acute Hepatitis B Infection And Convalescence
HBsAg can be detected in the blood 4 to 10 weeks after exposure. This corresponds to onset of symptoms and viremia detectable by nucleic acid amplification methods. Most hepatitis B infections are self-limited and are associated with disappearance of HBsAg within 4 weeks of onset of symptoms. The anti-HBs then appears and increases to a plateau level that persists indefinitely.2
Dont Miss: What Is Hepatitis C From
Does Hepatitis B Show Up In Routine Blood Tests
Routine blood tests do not detect hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatitis B tests are specifically done if blood tests show abnormal liver function results, or if a person experiences symptoms or falls into the high-risk category for HBV infection.
A panel of HBV-specific blood tests are required to detect HBV infection.
Recommended Reading: Natural Ways To Cure Hepatitis C
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a serious liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus . For some people, hepatitis B infection becomes chronic, meaning it lasts more than six months. Having chronic hepatitis B increases your risk of developing liver failure, liver cancer or cirrhosisa condition that causes permanent scarring of the liver.
Most people infected with hepatitis B as adults recover fully, even if their signs and symptoms are severe. Infants and children are more likely to develop a chronic hepatitis B infection.
Hepatitis B Surface Ab Reactive
![[Full text] Management of Hepatitis B Surface Antigen and Hepatitis C ...](https://www.hepatitisprohelp.com/wp-content/uploads/full-text-management-of-hepatitis-b-surface-antigen-and-hepatitis-c.jpeg)
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â its anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â its anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Read Also: What Is Hepatic Function Panel
Read Also: How To Reverse Hepatic Steatosis
Questions For Your Doctor About Test Results
Patients may find it helpful to ask questions about their hepatitis B test results. Questions that may be helpful include:
- What was my test result?
- Do I have an acute or chronic hepatitis B infection?
- Does the test result suggest that I have immunity for hepatitis B?
- Would I benefit from hepatitis B vaccination?
- Do I need any follow-up tests based on my hepatitis B test results?
When Should You Have The Test
Anyone who has symptoms of hepatitis B may benefit from having the test. Other people who may consider undergoing the hepatitis B panel test are those with known risk factors. These people include individuals born in places with a high incidence of HBV infection and those who use needles to inject drugs.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Surface Ab Ql Reactive
What Do Hepatitis B Test Results Mean
Hepatitis B test results help determine if HBV infection is negative or positive, and if positive, whether the infection is acute or chronic, or if recovery is complete. A combination of results are considered to identify and classify HBV infection status.
The following are some interpretations of hepatitis B test results:
Table: Hepatitis B test results and interpretations
| Test |
|---|
What Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
When you are exposed to HBV, your body mounts an immune defense to specifically target and neutralize the invader. Unlike innate immunity which mounts a generalized defense against all invaders, this type of immunity is disease-specific.
This immune response occurs whether you are exposed to HBV through blood or sexual contact, or if you are vaccinated with the hepatitis B vaccine.
The virus has proteins on its surface, called antigens, that serve as unique identification tags. When HBV enters the body, the immune system “encodes” antibodies specific to these antigens so that it can recognize and attack the virus should it appear again.
There are two types of antibodies produced in response to the virus:
- Immunoglobulin M is the antibody that mounts the initial attack but eventually fades away.
- Immunoglobulin G is the antibody that provides long-lasting immune protection against HBV. The immunity can last for many years, but it gradually wanes over time.
Also Check: What Does Hepatitis B Do To You
What Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Reactive Mean Clfeax
Reactive results from the hepatitis B surface antibody test means that people are now immune to the virus because they have been infected in the past and their immune systems produced antibodies to fight the infection, This protection can be the result of receiving the hepatitis B vaccine or successfully recovering from a past hepatitis B â¦
Recommended Reading: How Does One Contract Hepatitis C
Clinical Information Discusses Physiology Pathophysiology And General Clinical Aspects As They Relate To A Laboratory Test
Hepatitis B e antigen is a small polypeptide that exists in a free form in the serum of individuals during the early phase of hepatitis B infection, soon after hepatitis B surface antigen becomes detectable. Serum levels of both HBeAg and HBsAg rise rapidly during the period of viral replication. The presence of HBeAg in serum correlates with hepatitis B virus infectivity, the number of infectious virions, and the presence of HBV core antigen in the infected hepatocytes.
During recovery from acute hepatitis B, HBeAg level declines and becomes undetectable in the serum, while hepatitis B e antibody appears and becomes detectable in the serum. Anti-HBe usually remains detectable for many years after recovery from acute HBV infection.
In HBV carriers and patients with chronic hepatitis B, positive HBeAg results usually indicate presence of active HBV replication and high infectivity. A negative HBeAg result indicates very minimal or no HBV replication. Positive anti-HBe results usually indicate inactivity of the virus and low infectivity. Positive anti-HBe results in the presence of detectable HBV DNA in serum also indicate active viral replication in these patients.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Transmission Routes Cdc
Also Check: How Does A Person Catch Hepatitis C