Molecular Sieves And Desiccants
Apart from distillation, ethanol may be dried by addition of a , such as , , or . The desiccants can be dried and reused. can be used to selectively absorb the water from the 95.6% ethanol solution. Molecular sieves of pore-size 3 , a type of , effectively sequester water molecules while excluding ethanol molecules. Heating the wet sieves drives out the water, allowing regeneration of their dessicant capability.
Also Check: Is Hepatitis B The Same As Hiv
Signs And Symptoms Of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Initially, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease may have no symptoms at all. However, as the condition progresses, it may start to exhibit symptoms. Here are a few signs and symptoms of fatty liver disease:
- Fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
- Pain in the upper right quadrant of your abdomen
If nonalcoholic liver disease progresses to more serious conditions, it can cause more severe symptoms like ascites, jaundice, muscle wasting, and hepatic encephalopathy.
Keep in mind that fatty liver disease rarely occurs in isolation. Metabolic conditions are significant risk factors for developing fatty liver disease. Metabolic syndrome includes conditions like insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, elevated triglycerides, and high cholesterol. Fatty liver disease is also correlated with obesity and hypertension.
Read Also: How Do You Get Hepatitis A B C
Things You Can Do If You Have Non
Adopting a healthy lifestyle is the main way of managing NAFLD.
For example, it can help to:
- lose weight you should aim for a BMI of 18.5 to 24.9 losing more than 10% of your weight can remove some fat from the liver and improve NASH if you have it
- eat a healthy diet try to have a balanced diet high in fruits, vegetables, protein and carbohydrates, but low in fat, sugar and salt eating smaller portions of food can help, too
- exercise regularly aim to do at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity activity, such as walking or cycling, a week all types of exercise can help improve NAFLD, even if you do not lose weight
- stop smoking if you smoke, stopping can help reduce your risk of problems such as heart attacks and strokes
NAFLD is not caused by alcohol, but drinking may make it worse. It’s therefore advisable to cut down or stop drinking alcohol.
Page last reviewed: 19 November 2018 Next review due: 19 November 2021
You May Like: Blood Test For Hepatitis C Screening
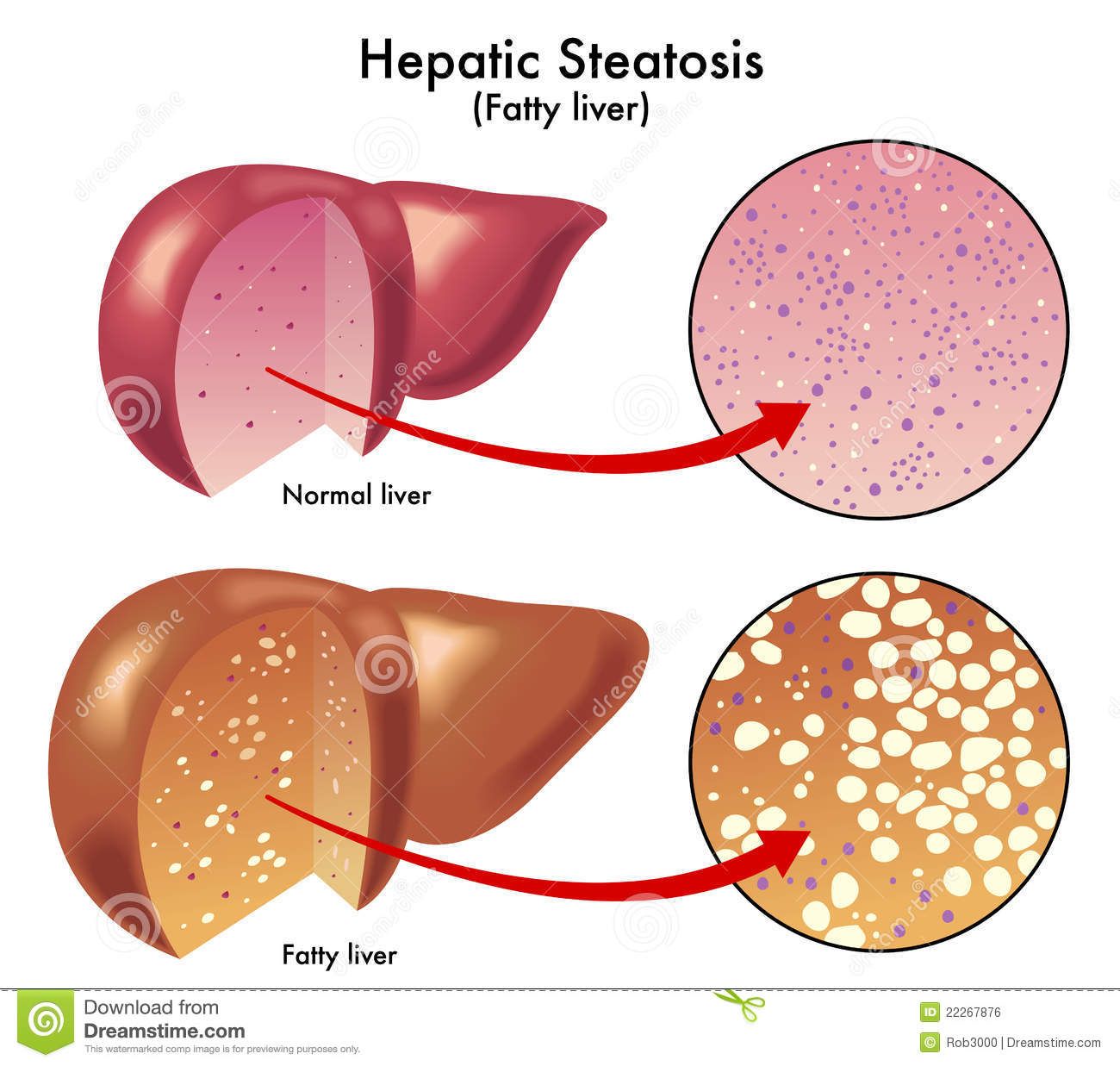
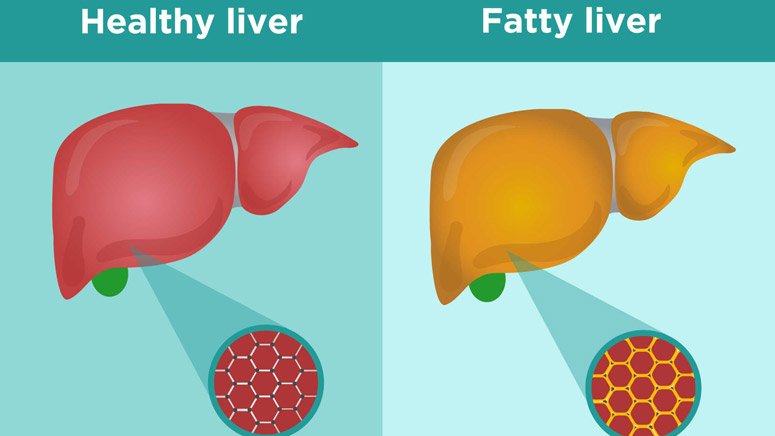
What Is Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease means you have extra fat in your liver. You might hear your doctor call it hepatic steatosis.
Heavy drinking makes you more likely to get it. Over time, too much alcohol leads to a buildup of fat inside your liver cells. This makes it harder for your liver to work.
But you can get fatty liver disease even if you donât drink a lot of alcohol.
How To Manage Fatty Liver With Diet
To combat fatty liver disease, its essential to make strategic and lasting changes to your diet, rather than just avoiding or integrating random foods here and there. The most important part of these changes is that they should be sustainable, says Aymin Delgado-Borrego, MD, pediatric and young adult gastroenterologist and public health specialist at Kidz Medical Services in Florida. Generally, the best diet for fatty liver includes:
- Adequate fiber
- Very limited saturated fats from animal products
- Very limited salt and sugar
- No alcohol
The American Liver Foundation recommends restricting calorie intake and modeling your eating habits after the Mediterranean diet. Dr. Delgado-Borrego says half of any plate of food you are eating should be fruits and vegetables, one quarter should be protein, and the other quarter should be starches. You can always reference the foods to eat and avoid, or just remember these two main rules to improve fatty liver:
The best way to ensure significant resolution or even cure is losing approximately 7%10% of your body weight, explains Sanaa Arastu, MD, a board-certified gastroenterologist with Austin Gastroenterology in Texas.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis A Shots At Costco
Treatment For Hepatic Steatosis
The most recommended treatment and the easiest is weight loss, as most causes of hepatic steatosis are obesity. Losing weight through exercise, nutrition, and healthy eating is often the treatment prescribed by doctors.
If the cause was something else like a medication side effect, then you should follow your doctors advice, and they will most likely have you stop taking it.
Never stop taking any medication without consulting a medical professional. In cases where the damage is so severe that the liver is irreversible, then a liver transplant or partial transplant may be necessary.
What Causes Fatty Liver Disease
Some people get fatty liver disease without having any pre-existing conditions. But these risk factors make you more likely to develop it:
- Having Type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance.
- Having metabolic syndrome .
- Taking certain prescription medications, such as amiodarone , diltiazem , tamoxifen or steroids.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C In Babies Symptoms
The Typical Treatments Treatment Of Hepatic Steatosis
The primary treatment for fatty liver disease is surgery. This involves removing or dissolving the fatty liver cell. Surgery can be used for treating both severe and moderate cases. But the downside to surgery is that it can leave you with scarring that could impede your progress in losing weight and even your ability to stand up.
A more common way to diagnose fatty liver disease is through the use of liver function tests called a CT scan and an MRI. These tests will show whether or not your liver is functioning to its fullest capacity. If it shows signs of inflammation then your doctor may want to prescribe medication that will reduce inflammation. If there is fluid buildup in your abdomen, then your doctor may use a procedure called a liposuction to remove some of the fluid and reduce the swelling in the abdominal area.
===> How To Cure A Fatty Liver In Just Days < < <
The diagnosis of fatty liver is a little more tricky. A biopsy of your liver from the abdominal area will reveal inflammation, but it might not be fatty liver. It could be something else like hepatitis B or C, or even HIV if it is contained in its early stages. If the biopsy indicates the presence of fatty liver, then your doctor will conduct a trial of anti viral medication to make sure that the hepatitis does not develop into cirrhosis of the liver which would be very serious.
Is Mild Hepatomegaly Serious
Rather than a disease in itself, hepatomegaly is a symptom or complication of other liver conditions, some of them life-threatening. For this reason, hepatomegaly is something to take seriously, as it points to an underlying problem that could be quite serious. Liver disease can develop for years with no overt symptoms at all.
Recommended Reading: How To Catch Hepatitis B
Fatty Liver Disease Theories
There are many different theories about how fatty liver disease develops. The two main contributing theories are:
1) an excess of lipids in the body due to a high-fat diet and sedentary lifestyle, or 2) genetic defects in the livers ability to metabolize lipids.
It is unclear which of these drivers is more significant for developing fatty liver disease. However, it is clear that once you have fatty liver disease, it becomes hard to stop its progression towards chronic liver failure and death.
How Is Fatty Liver Disease Managed
There are no medicines to treat fatty liver disease. Treatment involves making changes to your lifestyle. This can improve the condition and even reverse it.
If your fatty liver is caused by alcohol, then the most important thing to do is give up alcohol. This will prevent you from developing a more serious condition.
If you have non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, you will probably be advised to:
- drink no or very little alcohol
- quit smoking
Your doctor can help you. They may refer you to a dietitian, drug and alcohol counsellor or specialist.
Avoiding all fat in your diet is not necessary. However, your doctor may recommend that you avoid certain foods, such as those that contain fructose and trans fats .
There is no specific medicine for fatty liver disease. However, depending on your situation, your doctor may advise that you take medicine to lower your lipid levels, or improve the way your body manages glucose.
Also Check: Hepatitis A Shots At Costco
You May Like: How Long Can A Person Live With Hepatitis C
Hepatic Steatosis Hepatic Resection And Liver Transplantation
Macrovesicular steatosis is an important criterion defining extended-criteria donor organs. Several studies have reported a poor impact of steatosis on postoperative morbidity and mortality after liver resection. A national analysis of the Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients demonstrated that macrovesicular steatosis of greater than 30% was an independent predictor of reduced 1-year graft survival. Steatotic livers are particularly vulnerable to ischemia/reperfusion injury, resulting in an increased risk of postoperative morbidity and mortality after liver surgery, including liver transplantation. In a retrospective review of 450 living liver donors who underwent right hepatectomy, a mild degree of hepatic steatosis was associated with higher postoperative peak aspartate and alanine aminotransferase values. Furthermore, biliary complications remain a persistent problem in orthotopic liver transplantation. The presence of macrovesicular steatosis in 20% to 50% of a liver graft emerged as a newly defined risk factor for postoperative biliary complications in 175 adult patients undergoing living donor liver transplantation. Thus, hepatic steatosis poses a challenge after liver resection or transplantation.
How Are Fatty Liver Disease And Liver Fibrosis Diagnosed And Evaluated
Your doctor will begin by asking you about your medical history and symptoms. You will also undergo a physical exam.
In order to diagnose FLD and liver fibrosis, your doctor may order blood tests to evaluate liver function, including tests to assess the level of the liver enzymes ALT and AST, which can be high when the liver is fatty.
Your doctor may also order imaging tests of the liver such as:
Read Also: Natural Cure For Hepatitis B
Diagnosis Of Fatty Liver Disease
Your doctor may see something unusual in a blood test or notice that your liver is slightly enlarged during a routine check-up. These could be signs of a fatty liver. To make sure you dont have another liver disease, your doctor may ask for more blood tests , an ultrasound, a computed tomography scan or medical resonance imaging .If other diseases are ruled out, you may be diagnosed with NASH. The only way to know for sure is to get a liver biopsy. Your doctor will remove a sample of liver tissue with a needle and check it under a microscope.Some questions to ask your doctor after diagnosis include:
- What is the likely cause of my fatty liver?
- Do I have NASH? If not, how likely am I to develop NASH?
- Do I have cirrhosis? If not, how likely am I to develop cirrhosis?
- Do I need to lose weight? How can I do so safely?
- Should I be taking any medication to control my cholesterol and triglyceride levels?
- What medications or other substances should I avoid to protect my liver?
Can Hepatic Steatosis Cause Complications
When NAFLD is not noticed soon enough, damage to the liver can occur. This could lead to physical and mental symptoms. Sometimes treatments can fix the problem, but when hepatic steatosis goes on too long, the entire organ can fail, or liver cancer can develop.
Liver transplant and further treatments are required but are not guaranteed to bring you back to perfect health. The liver is in charge of a lot of essential things, and when it stops working correctly, the entire body suffers.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Contract Hepatitis C Virus
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
There are two different types of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease:
Simple fatty liver: This means you have fat in your liver, but you may not have any inflammation in your liver or damage to your liver cells. It usually doesnât get worse or cause problems with your liver. Most people with NAFLD have simple fatty liver.
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis : This is much more serious than a simple fatty liver. NASH means you have inflammation in your liver. The inflammation and liver cell damage that happen with NASH can cause serious problems such as fibrosis and cirrhosis, which are types of liver scarring, and liver cancer. About 20% of people with NAFLD have NASH.
Steatosis In Chronic Hepatitis C
In chronic hepatitis C patients, the prevalence of steatosis ranges from 40% to 86% . The majority of patients with steatosis have mild steatosis affecting less than 30% of hepatocytes. Thus, steatosis occurs more frequently in patients with chronic hepatitis C than in the general population of adults in the Western world. Macrovesicular steatosis is found in the periportal region of the liver-different from the centrilobular distribution characteristic of NASH patients. Mild steatosis had been reported in nearly 40% of patients with HCV genotype 4.
Moderate or severe steatosis is significantly less frequent in genotype 4 than 3 chronic hepatitis C patients and similar between genotype 4 and 1. In non-diabetic, overweight patients, moderate or severe steatosis is present in only 10%-15% of genotype 4 or 1 compared with 40% of genotype 3 patients. Thus, hepatic steatosis in genotype 4 is mostly associated with metabolic factors, similar to those in genotype 1.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis How Do You Get It
Prevention Of Hepatic Steatosis
A negative by-product of our modern civilization is little need for physical activity and an increased risk of chronic disease, such as heart disease, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and NAFLD. Physical inactivity is one of the causes of these associated metabolic disorders and is an actual known leading cause of death in the United States.-
What You Need To Know About Fatty Liver Disease
If a fatty liver disease diagnosis is made, your doctor will perform a series of tests to identify the cause of the condition. These may include a CT scan, blood test, liver enzymes test, albumin level, serum creatinine, and urine test. Blood tests may also reveal symptoms such as high calcium, low albumin, or polydipsia. Once these symptoms are present, your doctor will evaluate them to determine if you do have fatty liver disease and what course of treatment is appropriate.
Some factors that are known to cause fatty liver disease include being overweight or obese, being a woman, and being over 50 years of age. People who smoke cigarettes or use other tobacco products are at increased risk of developing this condition. There are also other risk factors that are not well understood but include genetic tendencies toward obesity and polydipsia. Other risk factors that are associated with this disease include being older than 50 years of age and having an unhealthy body mass index. Obese people are at greater risk than thinner people for developing fatty liver disease because obese people have excess fat deposits around their bellies, hips, and thighs.
About one of every five Americans has a fatty liver, which is also called steatosis. In fact, up to 9 of every 10 diabetics and people with obesity have fatty liver.
Here are the details of each of these disorders:
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis A Vaccine
Types Of Fatty Liver Disease
Health care providers divide fatty liver disease into two types. If you just have fat but no damage to your liver, the disease is called nonalcoholic fatty liver disease . If you have fat in your liver plus signs of inflammation and liver cell damage, the disease is called nonalcoholic steatohepatitis .
About 10% to 20% of Americans have NAFLD. About 2% to 5% have NASH.
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
- Am I taking any medications that could contribute to fatty liver disease?
- How much damage does my liver have?
- How long will it take to reverse the liver damage?
- What is a healthy weight for me?
- Can I talk to a nutritionist or go to classes to learn about healthy eating?
- How can I get treatment for alcohol use disorder?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Consider fatty liver disease an early warning sign to help you avoid a fatal liver condition, like cirrhosis or liver cancer. Even if you dont have symptoms or any liver function problems at this point, its still important to take steps to stop or reverse fatty liver disease.
You May Like: How Long Hepatitis B Vaccine Last
What Is Its Association With Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is closely tied to hepatic steatosis. It consists of several symptoms, including high blood pressure and sugar, an excessive amount of stomach fat, and high cholesterol. More research is needed to determine why: but most people with metabolic syndrome are also diagnosed with NAFLD.
It is uncertain if they are merely two different presentations of the same thing or if one tends to lead to the other: more research is required. Mothers with metabolic syndrome or who eat a high-fat diet while pregnant lead to their children being more likely to develop NAFLD in adulthood.
Herbal Medicine Improve Hepatic Lipid Metabolism
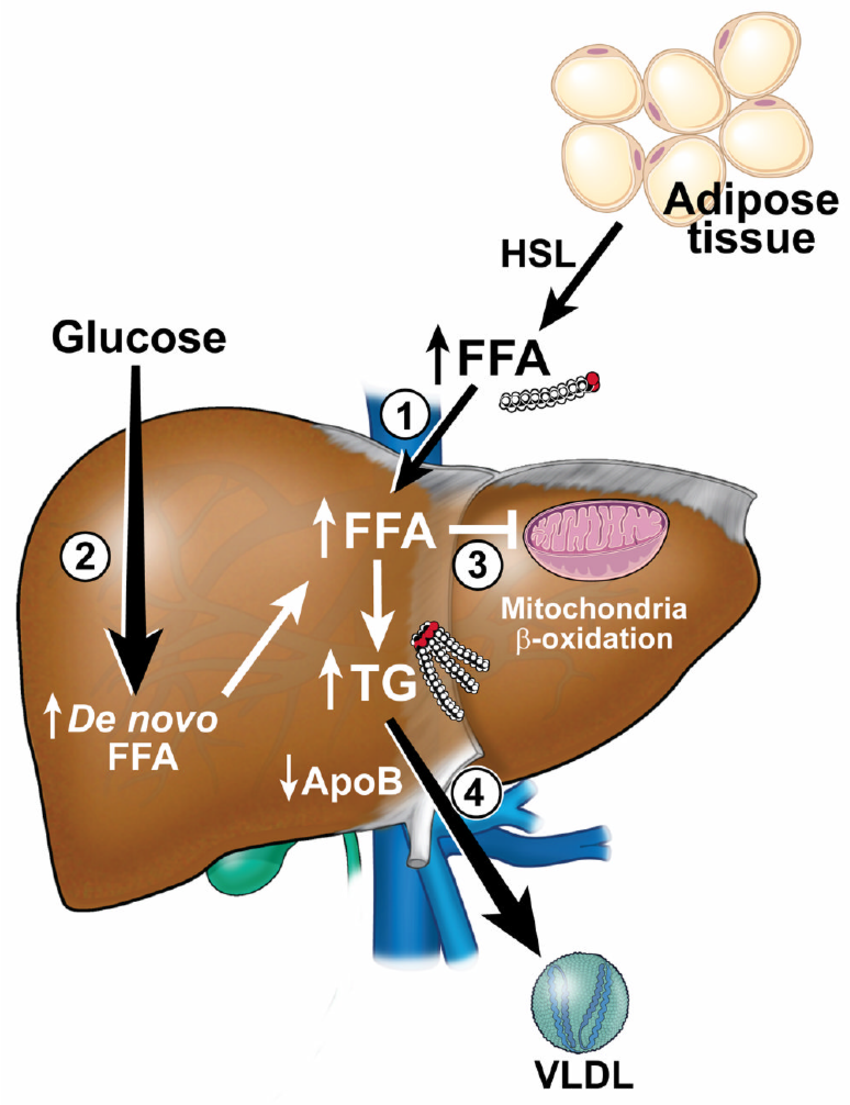
AMPK Pathway Involves in Herbal Medicine Modulation of Hepatic Lipogenesis and β-Oxidation
Oxidative Stress Action Involves in Herbal Medicine Modulation of Lipid Metabolism
Mitochondria Function Involves in Herbal Modulation of Hepatic Lipid Metabolism
Bile Acid Synthesis Involves in Herbal Medicine Modulation of Lipid Metabolism
Bile acids are synthesized in the liver and act as biological detergent to metabolite lipids and cholesterol into the bile. Gypenosides , palmatine and jatrorrhizine promote bile acid synthesis to prevent NAFLD, which involved the expression of cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase A1 . Punicalagin and pomegranate ellagic acid activate the CYP7A1/PPARγ signaling to promote hepatic diversion of cholesterol into bile acid . Celastrus orbiculatus Thunb. accelerated the hepatic cholesterol excretion in guinea pigs through suppressing oxidative stress via upregulation of the mRNA abundance of 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-CoA reductase and CYP7A1 . Glycyrrhizin modulated serum bile acid metabolism in MCD diet-fed mice by restoring inflammation-mediated hepatic farnesoid X receptor inhibition . The modulation of herbal medicine on lipid and cholesterol absorption and transport involved the bile acid regulation and shows its beneficial effects on treating NAFLD.
Figure 1 The lipid mechanistic insight into the anti-NAFLD effects of herbal medicine. NAFLD, Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Contract Hepatitis B