Prevent Infection After Contact With The Virus
If you think you have been in contact with the hepatitis B virus, see your doctor right away. Doctors typically recommend a dose of the hepatitis B vaccine to prevent infection. In some cases, doctors may also recommend a medicine called hepatitis B immune globulin to help prevent infection. You must get the vaccine dose and, if needed, HBIG shortly after coming into contact with the virus, preferably within 24 hours.
Whats The Prognosis For Hepatitis B
Your doctor will know youâve recovered when you no longer have symptoms and blood tests show:
- Your liver is working normally.
- You have hepatitis B surface antibody.
But some people don’t get rid of the infection. If you have it for more than 6 months, youâre whatâs called a carrier, even if you donât have symptoms. This means you can give the disease to someone else through:
- Unprotected sex
- Contact with your blood or an open sore
- Sharing needles or syringes
Doctors donât know why, but the disease does go away in a small number of carriers. For others, it becomes whatâs known as chronic. That means you have an ongoing liver infection. It can lead to cirrhosis, or hardening of the organ. It scars over and stops working. Some people also get liver cancer.
If youâre a carrier or are infected with hepatitis B, donât donate blood, plasma, body organs, tissue, or sperm. Tell anyone you could infect — whether itâs a sex partner, your doctor, or your dentist — that you have it.
Show Sources
CDC: âHepatitis B Questions and Answers for Health Professionals,â âHepatitis B Questions and Answers for the Public.â
Mayo Clinic: âHepatitis B.â
UpToDate: âHepatitis B virus: Screening and diagnosis.â
CDC.
HealthyPeople.gov: âHepatitis B in Pregnant Women: Screening.â
Annals of Internal Medicine: âScreening for Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Nonpregnant Adolescents and Adults: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement.â
Persons With Chronic Diseases
Refer to Immunization of Persons with Chronic Diseases in Part 3 for additional general information about vaccination of people with chronic diseases.
Chronic renal disease and patients on dialysis
People with chronic renal disease may respond sub-optimally to HB vaccine and experience more rapid decline of anti-HBs titres, and are therefore recommended immunization with a higher vaccine dose. Individuals undergoing chronic dialysis are also at increased risk for HB infection. In people with chronic renal disease anti-HBs titre should be evaluated annually and booster doses using a higher vaccine dose should be given as necessary.
Neurologic disorders
People with conditions such as autism spectrum disorders or demyelinating disorders should receive all routinely recommended immunizations, including HB-containing vaccine.
Chronic liver disease
HB immunization is recommended for non-immune persons with chronic liver disease, including those infected with hepatitis C, because they are at risk of more severe disease if infection occurs. Vaccination should be completed early in the course of the disease, as the immune response to vaccine is suboptimal in advanced liver disease. Post-immunization serologic testing may be used to confirm vaccine response.
Non-malignant hematologic disorders
Persons with bleeding disorders and other people receiving repeated infusions of blood or blood products are considered to be at higher risk of contracting HB and should be offered HB vaccine.
You May Like: How Can You Pass Hepatitis C
Treatment For Chronic Infection
Treatment for hepatitis B does not cure hepatitis B but works to delay or even to prevent complications from developing, like liver damage and ‘scarring’ of the liver . People with chronic hepatitis B usually need treatment to stop or to reduce the activity of the virus, so limiting liver damage. A liver specialist will usually advise on when treatment may be beneficial. There are two types of treatment currently given:
- Interferon. This medicine is similar to a substance produced in your body, which is also called interferon. It works to fight infections by boosting your immune system. Interferon is usually given as an injection each week.
- Antiviral medicines. These work by stopping the hepatitis B virus from multiplying in the body. They include lamivudine, adefovir, tenofovir, and entecavir. Your doctor will discuss these in more detail with you, as the medicine used can vary between people. A combination of antiviral medicines is sometimes used.
Treatment with medicines is usually continued for many years.
Side-effects with these medicines can occur. You will be monitored regularly while you are taking treatment, which includes blood tests. Some people need to change their medicines, or take a lower strength, if they have troublesome side-effects. Also, in some people, resistance can develop to their treatment medicine, which means that it does not work so well. If this happens then it is likely you will have to change the medicine you take.
Guidance On Reporting Adverse Events Following Immunization
Vaccine providers are asked to report, through local public health officials, any serious or unexpected adverse event temporally related to vaccination. An unexpected AEFI is an event that is not listed in available product information but may be due to the immunization, or a change in the frequency of a known AEFI.
Refer to Reporting Adverse Events Following Immunization in Canada and Adverse events following immunization in Part 2 for additional information about AEFI reporting.
Also Check: Where Can I Get A Hepatitis B Shot
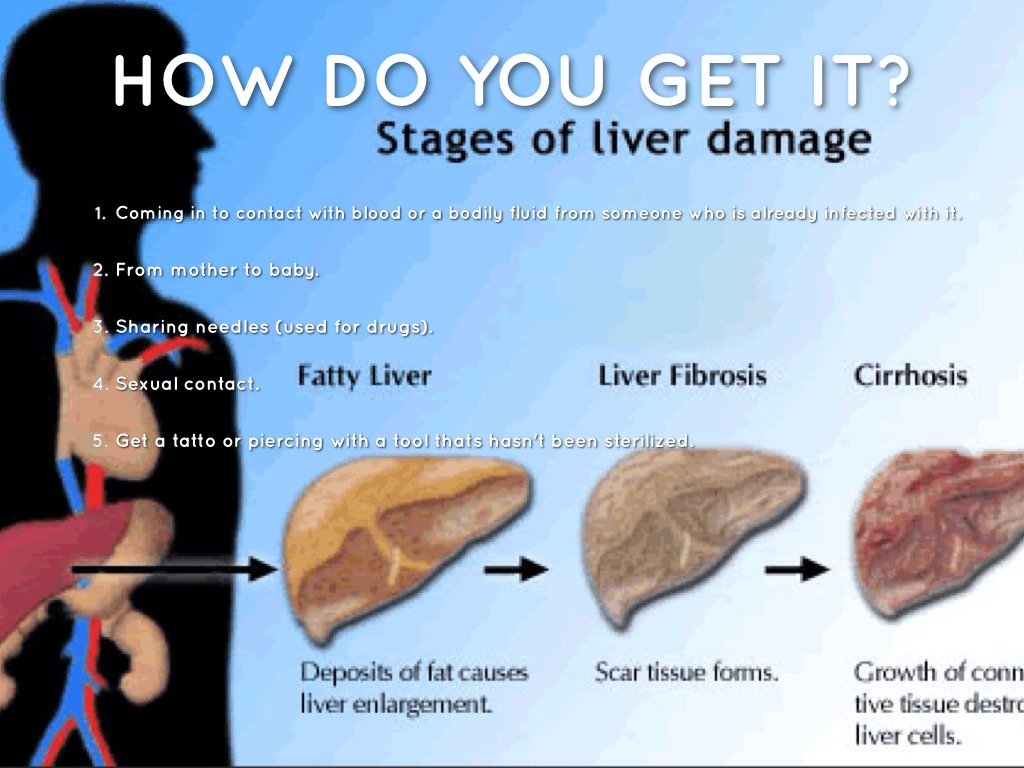
How Do You Get Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is really contagious. Its transmitted through contact with semen , vaginal fluids, and blood. You can get it from:
-
having vaginal, anal, or oral sex
-
sharing toothbrushes and razors
-
sharing needles for shooting drugs, piercings, tattoos, etc.
-
getting stuck with a needle that has the Hep B virus on it.
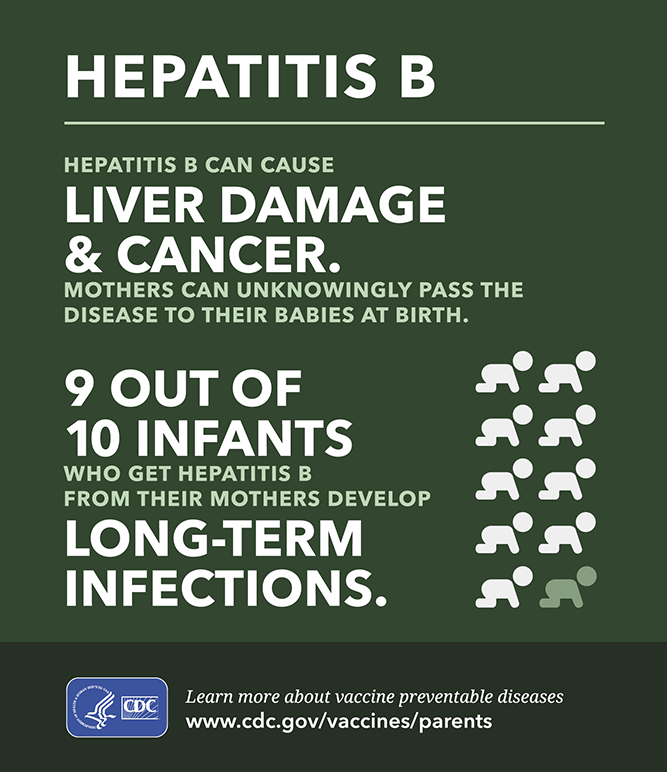
Hepatitis B can also be passed to babies during birth if their mother has it.
Hepatitis B isnt spread through saliva , so you CANT get hepatitis B from sharing food or drinks or using the same fork or spoon. Hepatitis B is also not spread through kissing, hugging, holding hands, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding.
Who’s Most At Risk Of Hepatitis B
People at highest risk of hepatitis B include:
- people born or brought up in a country where the infection is common
- babies born to mothers infected with hepatitis B
- people who have ever injected drugs
- anyone who has had unprotected sex, including anal or oral sex particularly people who have had multiple sexual partners, people who have had sex with someone in or from a high-risk area, men who have sex with men, and commercial sex workers
- close contacts, such as family members, of someone with a long-term hepatitis B infection
The risk of getting hepatitis B for travellers going to places where the infection is common is generally considered to be low if these activities are avoided.
Your GP can arrange for you to have a blood test to check for hepatitis B and have the hepatitis B vaccination if you’re at a high risk.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Symptoms In Women
How Can I Prevent Spreading Hepatitis B To Others
If you have hepatitis B, follow the steps above to avoid spreading the infection. Your sex partners should get a hepatitis B test and, if they arent infected, get the hepatitis B vaccine. You can protect others from getting infected by telling your doctor, dentist, and other health care professionals that you have hepatitis B. Dont donate blood or blood products, semen, organs, or tissue.
If I Am Infected How Can I Prevent Passing On The Virus To Others
If you have a current hepatitis B infection you should:
- Avoid having sex with anyone until they have been fully immunised and checked with a blood test to see that the immunisation has worked.
- Not share any injecting equipment such as needles, syringes, etc.
- Not donate blood or semen or carry a donor card.
- Not share razors, toothbrushes, etc, that may be contaminated with blood.
- Cover any cuts or wounds with a dressing.
- Make sure that, if any of your blood spills on to the floor or other surfaces following an accident, it is cleaned away with bleach.
You May Like: How Can You Get Rid Of Hepatitis C
How To Prevent Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a liver infection caused by a virus . It can be serious and theres no cure, but the good news is its easy to prevent. You can protect yourself by getting the hepatitis B vaccine and having safer sex. If you have oral, anal, and vaginal sex, use condoms and dental dams to help stop the spread of hepatitis B and other STDs.
Where Can I Get More Detailed Information On How To Live With Hepatitis B
More detailed information can be found in the Canadian Liver Foundations Healthy Living with Viral Hepatitis booklet, including:
- What to expect if you have hepatitis B
- The different types of blood tests and what they measure
- How to prepare for an appointment with your doctor
- What choices to make to prevent additional damage to your liver
- Who needs to know if you have hepatitis B and how to tell them
- How to recognize and deal with symptoms
- How to find financial assistance
- What questions to ask when considering alternative therapies.
Read Also: Hepatitis C And Liver Disease
What If I Am Exposed To Hepatitis B What Should I Do
You should see your GP or local health centre as soon as possible to discuss your options. You will need to have a blood test and in some cases you may start treatment immediately to stop your body becoming infected with Hepatitis B. Management may include hepatitis B immunoglobulin, an injection of plasma which contains high levels of antibodies to help prevent hepatitis B infection from developing in a person who has been exposed.
What Are The Risk Factors For Getting Hepatitis B

Due to the way that hepatitis B spreads, people most at risk for getting infected include:
- Children whose mothers have been infected with hepatitis B.
- Children who have been adopted from countries with high rates of hepatitis B infection.
- People who have unprotected sex and/or have been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection.
- People who live with or work in an institutional setting, such as prisons or group homes.
- Healthcare providers and first responders.
- People who share needles or syringes.
- People who live in close quarters with a person with chronic hepatitis B infection.
- People who are on dialysis.
Recommended Reading: Xifaxan Dose For Hepatic Encephalopathy
What Can I Do To Help Myself
- If you inject steroids or drugs NEVER share any equipment
- ALWAYS use a condom for sexual intercourse or during sexual contact
- Keep in regular contact with your GP and attend regular health checks
- Dont drink any alcohol. Drinking alcohol can speed up the progression of liver disease in people with Hepatitis B
- Eat a healthy diet, with regular meals, plenty of fruit and vegetables and avoid fatty and sugary foods
- Take regular exercise as this can help with the tiredness that is associated with chronic Hepatitis B. Ensure that you get adequate rest
- Try to keep your weight at a healthy level. Being overweight can sometimes cause more damage to the liver
How Can I Pay For My Medication
Private health insurance or drug plansIf you have private health insurance or a drug plan at work, you may be able to have the medication paid through your plan. Please consult your private health insurance or drug plan provider to see if your drug is covered.
Publicly funded drug plansEach province and territory has their own rules. Some provincial drug plans provide coverage for individuals 65 and older, or those on social assistance. Some provinces provide special support to low-income individuals. Please call your Provincial Ministry or Department of Health to get more information about the terms of the publicly funded drug plan in your province.
Quebec public drug programIn Quebec, everyone must be covered by prescription drug insurance either through private or publicly funded plans.
Each provincial and territorial government offers a drug benefit plan for eligible groups. Some are income-based universal programs. Most have specific programs for population groups that may require more enhanced coverage for high drug costs. These groups include seniors, recipients of social assistance, and individuals with diseases or conditions that are associated with high drug costs. For more details, please contact your provincial or territorial health care ministry, or click on the appropriate link below.
Yukon
Available Patient Assistance Program for Hepatitis B treatment VEMLIDY
Read Also: Signs N Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
What Are The Types Of Hepatitis B
There are two types of hepatitis B infection: acute and chronic.
Acute
An acute infection happens at the beginning, when you first get infected with hepatitis B. Many people are able to clear it from their bodies and recover. In fact, this is true of about 4 in 5 adults who are infected.
Chronic
If you are not able to clear the infection within six months or longer, you have chronic hepatitis B. It is chronic hepatitis B that leads to inflammation and the serious, and possibly fatal, illnesses of cirrhosis of the liver and liver cancer. Treatment can slow disease progress, reduce the chance of liver cancer and increase your chances of surviving.
Who Should Be Vaccinated For Hepatitis B
All newborns should be vaccinated. Also, people who are under 18 who were not vaccinated at birth should also get the vaccine. Other groups who should be sure to be vaccinated are those in certain high-risk categories, such as:
- People who have more than one sexual partner.
- Men who have sex with men.
- Adults with diabetes.
- Sexual partners of infected people and people who share households with infected individuals.
- People who are exposed to blood and other bodily fluids, including healthcare and public safety professionals, and people who work in jails and other places taking care of people who cant take care of themselves.
Also Check: How Long Can You Have Hepatitis C Without Knowing
Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
Many people with hepatitis B will not experience any symptoms and may fight off the virus without realising they had it.
If symptoms do develop, they tend to happen 2 or 3 months after exposure to the hepatitis B virus.
Symptoms of hepatitis B include:
- flu-like symptoms, including tiredness, a fever, and general aches and pains
- loss of appetite
- tummy pain
- yellowing of the skin and eyes
These symptoms will usually pass within 1 to 3 months , although occasionally the infection can last for 6 months or more .
Hepatitis: How Can I Protect Myself From Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a liver disease caused by the hepatitis B virus . The virus interferes with the functions of the liver and causes pathological damage. A small percentage of infected people cannot get rid of the virus and become chronically infected these people are at higher risk of death from cirrhosis of the liver and liver cancer.
HBV is spread by contact with blood or body fluids of an infected person the same way as the human immunodeficiency virus . However, HBV is 50 to 100 times more infectious than HIV.
The main ways of getting infected with HBV are:
- from mother to baby at the birth
- from child-to-child
- unsafe injections and transfusions
- unprotected sexual contact.
Worldwide, most infections occur from mother-to-child, from child-to-child , and from reuse of unsterilized needles and syringes. Before the widespread use of the hepatitis B vaccine, almost all children in developing countries used to become infected with the virus.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Treat Hepatitis C
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infection of your liver. Itâs caused by a virus. There is a vaccine that protects against it. For some people, hepatitis B is mild and lasts a short time. These âacuteâ cases donât always need treatment. But it can become chronic. If that happens, it can cause scarring of the organ, liver failure, and cancer, and it even can be life-threatening.
Itâs spread when people come in contact with the blood, open sores, or body fluids of someone who has the hepatitis B virus.
It’s serious, but if you get the disease as an adult, it shouldnât last a long time. Your body fights it off within a few months, and youâre immune for the rest of your life. That means you can’t get it again. But if you get it at birth, itâ unlikely to go away.
âHepatitisâ means inflammation of the liver. There are other types of hepatitis. Those caused by viruses also include hepatitis A and hepatitis C.
Common And Local Adverse Events
HB vaccine
HB vaccine is well tolerated. Reactions are generally mild and transient, and include: irritability, headache, fatigue and injection site reactions in 10% or more of recipients.
HAHB vaccine
There is no increase in adverse events when HAHB vaccine is compared with HA vaccine given alone or concomitantly with HB vaccine at a different injection site. When the adult formulation of HAHB vaccine is given to children in the 2 dose schedule, there is no increase in adverse events compared with those occurring after administration of the pediatric formulation of HAHB vaccine.
DTaP-HB-IPV-Hib vaccine
Reactions are usually mild and transient, and include fever, irritability, restlessness and injection site reactions .
HBIg
Headache, diarrhea, fever, urticaria, angioedema and injection site reactions may occur.
Also Check: How To Prevent Hepatitis A
What Are Clinical Trials For Hepatitis B
Clinical trialsand other types of clinical studiesare part of medical research and involve people like you. When you volunteer to take part in a clinical study, you help doctors and researchers learn more about disease and improve health care for people in the future.
Researchers are studying many aspects of hepatitis B, such as
- progression of hepatitis B and long-term outcomes
- new treatments for hepatitis B
- prevention of reactivated or worsening hepatitis B in people receiving cancer treatment