How Can I Contract Hepatitis B
You can contract hepatitis B by coming into contact with the bodily fluids of an infected person.
Resort activities that may put you at risk for hepatitis B include:
Getting a manicure, pedicure, tattoo, piercing, or acupuncture with improperly sterilized tools
Having sexual contact with an infected partner
Giving first aid to, or receiving it from, an infected person
Receiving a medical or dental procedure with contaminated equipment
Sharing personal grooming items with an infected person
Try To Control Itching
People who have hepatitis sometimes have itchy skin. You can control itching by keeping cool and out of the sun, wearing cotton clothing, or using over-the-counter antihistamines such as a non-drowsy one like loratadine or one that may make you sleepy like diphenhydramine . Talk to your doctor before taking these medicines.
What Increases Your Risk
People who have certain behaviours or certain jobs are at high risk for becoming infected with hepatitis B.
Job risk factors include:
- Handling blood or body fluids as a routine part of your job. This includes health care workers, such as doctors, dentists, nurses, and blood and lab technicians, and students in these jobs. It also includes morticians and embalmers.
- Being an employee or resident of an institution for people who have developmental disabilities.
- Being an employee or inmate of a prison.
Lifestyle risk factors include:
- Being born in, or travelling to, parts of the world where hepatitis B is common or where a large number of people have been infected for a long time. Such areas include Southeast and Central Asia, the islands of the South Pacific, the Amazon River basin, the Middle East, Africa, Eastern Europe, and China.
- Being a man who has sex with men.
- Being sexually active. This includes having unprotected sex with someone who is infected with the virus or whose sexual history is unknown to you.
- Having more than one sex partner.
- Living with someone who has a chronic hepatitis B infection.
- Getting body piercings or tattoos from someone who doesn’t sterilize his or her equipment.
- Sharing needles or other equipment to inject illegal drugs.
Other factors include:
- Hepatitis B and C: Should I Be Tested?
You May Like: Royal Canin Hepatic Dog Food Side Effects
How Is Hepatitis B Diagnosed
A simple blood test can tell your doctor if you have the hepatitis B virus now or if you had it in the past. Your doctor also may be able to tell if you have had the vaccine to prevent the virus.
If your doctor thinks you may have liver damage from hepatitis B, he or she may use a needle to take a tiny sample of your liver for testing. This is called a liver biopsy.
What To Think About
- Interferons have common side effects, including fever, headaches, and hair loss. They may also cause mental problems or make them worse.
- If you have cirrhosis, you cannot use interferons. But you can use adefovir, entecavir, lamivudine, telbivudine, and tenofovir.
- After any kind of treatment for hepatitis B, the virus may become active again .
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Antibody Test Cost
Where Does Hepatitis B Occur
Hepatitis B is found across the globe. From developed countries to those still developing, the disease can spread relatively easily. Some regions, like Africa, have an increased risk. While other more developed areas have a slightly lower risk due to increased use of vaccinations.
No matter the destination, vaccination is recommended.
Who Should Not Get The Vaccine
Speak with your health care provider if you have had a life-threatening reaction to a previous dose of hepatitis B vaccine, or any component of the vaccine such as yeast, or to latex.
There is no need to delay getting immunized because of a cold or other mild illness. However, if you have concerns speak with your health care provider.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Genotype 3 Treatment
Contagious And Incubation Periods
Symptoms appear about 3 months after you have contact with the virus . But they can appear as soon as 1 month to as late as 6 months after contact. Blood, semen, and vaginal fluids, whether fresh or dried, are highly contagious during this period and for several weeks after the start of symptoms.
If you have a short-term infection, in most cases you can’t spread the virus after your body starts making a certain type of hepatitis B antibody. This generally takes several weeks. If you have a long-term infection, you are able to spread the virus as long as you have an active infection.
How Is The Hepatitis B Vaccine Made
People are protected against hepatitis B virus infection by making an immune response to a protein that sits on the surface of the virus. When hepatitis B virus grows in the liver, an excess amount of this surface protein is made. The hepatitis B vaccine is made by taking the part of the virus that makes surface protein and putting it into yeast cells. The yeast cells then produce many copies of the protein that are subsequently used to make the vaccine. When the surface protein is given to children in the vaccine, their immune systems make an immune response that provides protection against infection with the hepatitis B virus.
The first hepatitis B vaccine was made in the 1980s by taking blood from people infected with hepatitis B virus and separating or purifying the surface protein from the infectious virus. Because blood was used, there was a risk of contaminating the vaccine with other viruses that might be found in blood, such as HIV. Although contamination with HIV was a theoretical risk of the early, blood-derived, hepatitis B vaccine, no one ever got HIV from the hepatitis B vaccine. That is because the blood used to make vaccine was submitted to a series of chemical and treatments that inactivated any possible contaminating virus. Today, there is no risk of contaminating the vaccine with other viruses because the surface protein is manufactured in the laboratory.
Also Check: Is Hepatitis C An Autoimmune Disease
What Is Hepatitis A And B Vaccine
Hepatitis A and B are serious diseases caused by virus.
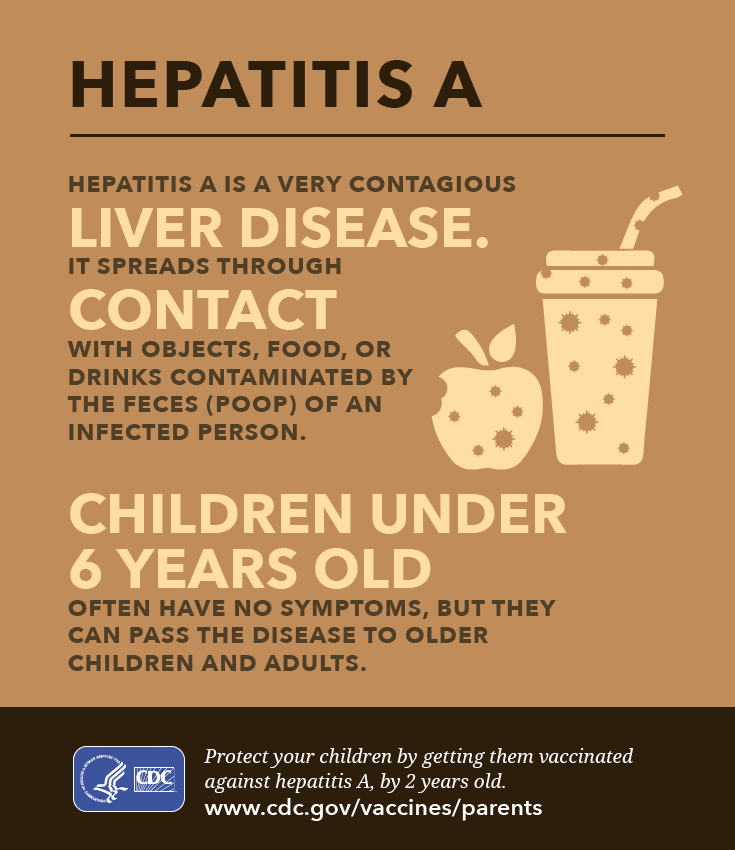
Hepatitis A is spread through contact with the stool of a person infected with the hepatitis A virus. This usually occurs by eating food or drinking water that has become contaminated as a result of handling by an infected person.
Hepatitis B is spread through blood or bodily fluids, sexual contact or sharing IV drug needles with an infected person, or during childbirth when a baby is born to a mother who is infected.
Hepatitis causes inflammation of the liver, vomiting, and jaundice . Hepatitis can lead to liver cancer, cirrhosis, or death.
The hepatitis A and B vaccine is used to help prevent these diseases in adults. The vaccine works by exposing you to a small dose of the virus, which causes the body to develop immunity to the disease. This vaccine will not treat an active infection that has already developed in the body.
This vaccine is recommended for adults with risk factors for getting hepatitis A or B, including:
Like any vaccine, the hepatitis A and B vaccine may not provide protection from disease in every person.
Who Should Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
- All children should get their first dose at birth, with a second dose between 1-2 months of age, and should have completed their vaccine series by 6-18 months of age.
- Children and adolescents through 18 years of age who did not get the vaccine when they were younger should be vaccinated.
- Adults at increased risk of acquiring hepatitis B, as well as any person who desires protection from hepatitis B.
- Persons at increased risk are as follows:
- Those whose sex partner is infected with hepatitis B
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject street drugs
- People with more than one sex partner
- People with chronic liver or kidney disease, or HIV infection
- People with jobs that expose them to human blood
- Household contacts of people infected with hepatitis B
- Residents and staff in institutions for the developmentally disabled
- Kidney dialysis patients
- People with hepatitis C infection
- People who travel to countries where hepatitis B is common
- People under 60 years of age with diabetes at the recommendation of their health care provider
Recommended Reading: How Long Is Hepatitis C Treatment
What Causes Hepatitis B
It’s caused by the hepatitis B virus. It is spread through contact with the blood and body fluids of an infected person.
You may get hepatitis B if you:
- Have sex with an infected person without using a condom.
- Get a tattoo or piercing with tools that weren’t sterilized.
A mother who has the virus can pass it to her baby during delivery. Medical experts recommend that all pregnant women get tested for hepatitis B. If you have the virus, your baby can get shots to help prevent infection with the virus.
You cannot get hepatitis B from casual contact such as hugging, kissing, sneezing, coughing, or sharing food or drinks.
Who Should Not Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine

- Anyone with a life-threatening allergy to baker’s yeast, or to any component of the vaccine should not get the hepatitis B vaccine. Tell your provider if you have any serious allergies.
- Anyone who has had a life-threatening allergic reaction to a previous dose of hepatitis B vaccine should not get another dose.
- Anyone who is moderately or severely ill should probably wait until they recover.
- Pregnant women who need protection from hepatitis B may be vaccinated, but should check with their doctor first.
Recommended Reading: Is Hepatitis The Same As Hiv
Should Pregnant Or Breast
The safety of hepatitis A vaccination during pregnancy has not been determined however, because hepatitis A vaccine is produced from inactivated virus, the risk to the developing fetus is probably low. The risk associated with hepatitis A vaccine should be discussed with your health care provider to determine if vaccination is right for you.
When Should You Call Your Doctor
If you see a person with hepatitis B become unconscious, call 911 or other emergency services.
if you have been diagnosed with hepatitis B and you have severe dehydration or these signs of liver failure:
- Extreme irritability.
- Extreme sleepiness.
- Swelling of the arms, legs, hands, feet, belly, or face.
- Heavy bleeding from the nose, mouth, or rectum , or under the skin.
- Yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes.
- You have risk factors for hepatitis B, such as handling blood or body fluids as a routine part of your job or having many sex partners.
- You have any symptoms of hepatitis B .
- Someone in your household has been diagnosed with hepatitis B.
- Your sex partner has been diagnosed with hepatitis B.
- You have been bitten by or exposed to the blood or body fluids of someone who has hepatitis B.
Also Check: How Often Should You Be Tested For Hepatitis C
Why Should I Vaccinate My Newborn Child If I Know That I Am Not Infected With Hepatitis B Virus
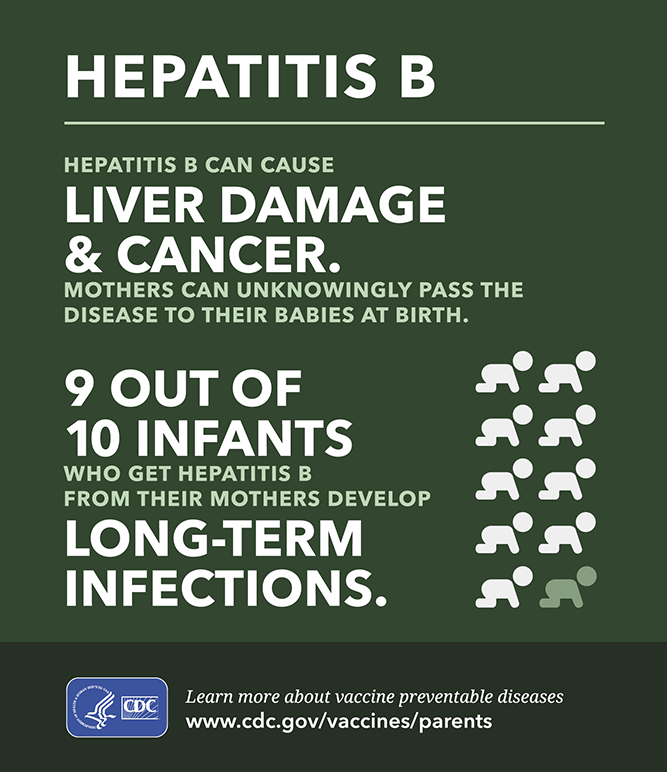
Before the hepatitis B vaccine, every year in the United States about 18,000 children were infected with hepatitis B virus by the time they were 10 years old. This statistic is especially important because people are much more likely to develop liver cancer or cirrhosis if they are infected early in life, rather than later in life .
About 9,000 of the 18,000 children infected in the first 10 years of life caught the virus from their mother during birth. However, many young children didn’t catch the disease from their mother. They caught it from either another family member or someone else who came in contact with the child. Because hepatitis B can be transmitted by relatively casual contact with items contaminated with blood of an infected person, and because many people who are infected with hepatitis B virus don’t know that they have it, it is virtually impossible to be “careful enough” to avoid this infection.
For these reasons, all young children are recommended to receive the hepatitis B vaccine. The best time to receive the first dose is right after birth. This will ensure that the child will be protected as early as possible from catching hepatitis B from people who dont know that they are infected with the virus.
Listen to Dr. Offit explain why newborns get the hepatitis B vaccine by watching this short video, part of the series Talking About Vaccines with Dr. Paul Offit.
Vaccination Is The Best Way To Prevent Hepatitis A And B Infection
Narrator: ÂYou are a traveller…Â .
Narrator: …and you are already dreaming of your next getaway. .
Disclaimer on-screen reads: TWINRIX is a combined hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccine used in adults, adolescents, children, and infants over the age of 1 year to prevent hepatitis A and hepatitis B diseases
Narrator: ÂWhile your travel plans probably donÂt include hepatitis A or hepatitis B…Â .
Disclaimer reads: 100% protection cannot be guaranteed and booster doses may be required.
Narrator: Â…you know that many common travel activities can put you at risk of acquiring these two serious liver diseases…Â .
Disclaimer reads: TWINRIX does not protect against hepatitis C or E, and is not indicated to treat or reduce the severity of hepatitis A or B infections. .
Narrator: Â…which is why you plan on talking to your doctor about TWINRIX, right? … Of course, right…Â Â…because you are a traveller.Â
Video concludes with TWINRIX logo, GSK logo, You are a traveller slogan, and safety information: Very commonly reported adverse events in adults were pain or discomfort, redness at the infection site, headache, and tiredness. Common adverse events were swelling at the injection site, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, and generally feeling unwell. Allergic reactions may also occur. Full product information can be found on Twinrix.ca. If you need to report an adverse event, please call 1-800-387-7374.
Twinrix.ca
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis A Vaccine Schedule For Adults
What You Need To Know
1. What is hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B is a serious disease that affects the liver. It is caused by the hepatitis B virus . HBV can cause:
Acute illness. This can lead to:
- loss of appetite
- jaundice
- pain in muscles, joints, and stomach
Acute illness is more common among adults.
Children who become infected usually do not have acute illness.
Chronic infection. Some people go on to develop chronic HBV infection. This can be very serious, and often leads to:
- liver damage
- liver cancer
- death
Chronic infection is more common among infants and children than among adults. People who are infected can spread HBV to others, even if they don’t appear sick.
- In 2005, about 51,000 people became infected with hepatitis B.
- About 1.25 million people in the United States have chronic HBV infection.
- Each year about 3,000 to 5,000 people die from cirrhosis or liver cancer caused by HBV.
Hepatitis B virus is spread through contact with the blood or other body fluids of an infected person. A person can become infected by:
- contact with a mother’s blood and body fluids at the time of birth
- contact with blood and body fluids through breaks in the skin such as bites, cuts, or sores
- contact with objects that could have blood or body fluids on them such as toothbrushes or razors
- having unprotected sex with an infected person
- sharing needles when injecting drugs
- being stuck with a used needle on the job.
2. Hepatitis B vaccine: Why get vaccinated?
3. Who should get hepatitis B vaccine and when?
Adults
Why Is The Hepb Vaccine Recommended
People who dont know they’re infected can spread the hepatitis B virus. So it cant be avoided just by being careful. That’s why health experts recommend that all babies get the vaccine right from birth.
The HepB injection usually creates long-term immunity. Most infants who get the HepB series are protected from hepatitis B infection beyond childhood, into their adult years.
Eliminating the risk of infection also decreases risk for cirrhosis of the liver, chronic liver disease, and liver cancer.
Don’t Miss: Is A Vaccine Available For Hepatitis B
Can Hepatitis B Be Prevented
The hepatitis B vaccine is the best way to prevent infection. The vaccine is a series of 3 or 4 shots. Check with your doctor or check your provincial immunization schedule to see if you or your child needs the hepatitis B vaccine.
A combination vaccine that protects against both hepatitis B and hepatitis A also is available.
To avoid getting or spreading the virus to others:
- Use a condom when you have sex.
- Don’t share needles.
- Wear disposable or plastic gloves if you have to touch blood.
- Don’t share toothbrushes or razors.
- Don’t get a tattoo, or make sure that the needles used have been cleaned properly and are sterile.
What Are The Side Effects Of The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Mild-to-moderate problems:
- Soreness, redness, or swelling where the shot was given
- Headache, tiredness, fever and loss of appetite
Severe problems :
- Dizziness
Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help ease pain and reduce fever.
It’s extremely rare for these vaccines to cause serious harm or death. If the person getting the vaccine has a serious reaction, call the doctor or seek immediate medical attention.
The hepatitis B vaccine is available at Walgreens Pharmacy. Ages vary by state.*
If you believe you have a medical emergency, please call 911.
Tell your doctor or a healthcare provider if the person getting the vaccine has any severe allergies.
Call the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention at 800-232-4636 or visit www.cdc.gov/vaccines for more vaccine information.
Read Also: Can Hepatitis C Be Treated
Persons With Inadequate Immunization Records
Evidence of long term protection against HB has only been demonstrated in individuals who have been vaccinated according to a recommended immunization schedule. Independent of their anti-HBs titres, children and adults lacking adequate documentation of immunization should be considered susceptible and started on an immunization schedule appropriate for their age and risk factors. Refer to Immunization of Persons with Inadequate Immunization Records in Part 3 for additional information.