Should I Be Screened For Hepatitis B
Screening is testing for a disease in people who have no symptoms. Doctors use blood tests to screen for hepatitis B. Many people who have hepatitis B dont have symptoms and dont know they are infected with hepatitis B. Screening tests can help doctors diagnose and treat hepatitis B, which can lower your chances of developing serious health problems.
Your doctor may recommend screening for hepatitis B if you9,14
- are pregnant
- were born in an area of the world where 2 percent or more of the population has hepatitis B infection, which includes Africa, Asia, and parts of the Middle East, Eastern Europe, and South America
- didnt receive the hepatitis B vaccine as an infant and have parents who were born in an area where 8 percent or more of the population had hepatitis B infection, which includes sub-Saharan Africa and parts of Asia
- are HIV-positive
- are a man who has sex with men
- have lived with or had sex with a person who has hepatitis B
- have an increased chance of infection due to other factors
How Is Hepatitis B Prevented
Testing & Vaccination
- The hepatitis B vaccine offers excellent protection against HBV. The vaccine is safe and highly effective. Vaccination consists of 3 doses of vaccine over the course of 6 months. Protection lasts for 20 years to life.
- The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that all children should receive hepatitis B vaccine starting at birth. .
- The CDC recommends hepatitis B vaccine for persons traveling to countries where HBV is common .
- If you have one or more risk factors for hepatitis B infection, you should get a simple HBV blood test. The blood test will determine whether you are:
- immune to hepatitis B or
- susceptible to hepatitis B and need vaccination or
- infected with hepatitis B and need further evaluation by a physician
Perinatal Hepatitis
- California law requires testing of all pregnant women for hepatitis B infection
- If the mother is HBV-infected, she will pass the infection to the baby during the birth process, unless the baby gets immunized within hours of birth
- Giving the infant HBIG and HBV vaccine right away will reliably prevent infection of the infant
- Other family members should best tested for hepatitis B too, and given vaccine if they are not already infected or immune
Healthy Habits
After Exposure to Hepatitis B
How To Control Hepatitis B In Pregnant Women
Study has shown that the most common mode of transmitting hepatitis B is by mother to child infection. Babies that are infected with hepatitis B have an increased risk of developing a serious liver disease or cancer in the future. It is necessary for pregnant women to test and take preventive steps to avoid the transmission of the virus to their children.
If a pregnant woman tests positive to hepatitis B, during delivery two shots of the hepatitis B vaccine should be administered to her. The first dose of the vaccine and one dose of hepatitis B immune globulin . These vaccines have to be available during delivery and be injected at different points during delivery.
If these vaccines are being administered correctly within the first 12 hours of life, the newborn has 95% chance of not developing hepatitis B in future.
After delivery, the baby has to complete the vaccine according to the schedule as part of a three or four dose series. After this regular checkups should be carried out.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Rapid Test Kit
Hepatitis C Symptoms In Women
Liver disease C infection isnt the like other sort of liver disease. Heres where to discover why and to discover the symptoms and signs to look out for.
Liver disease C is an infection caused by the hepatitis C infection . There are various types of liver disease infections, including hepatitis A, B, D, and E. Amongst the various infections, liver disease C is the most serious because it can be chronic and cause severe liver damage.
The infection spreads out through contact with infected blood, so particular individuals have a higher risk of infection. This includes healthcare workers exposed to blood and drug users.
Hepatitis C impacts both males and females As a whole, the symptoms and complications of the disease are the same for both sexes. But the infection can impact women in a different way.
How Do You Test For Hepatitis B

A simple blood test carried out by a healthcare professional will show whether you have the virus. You may also be given extra tests to see if your liver is damaged.
If youve got hepatitis B you should be tested for other STIs. Its important that you tell your recent sexual partner/s so they can also get tested and treated. Many people who have hepatitis B dont notice anything wrong, and by telling them you can help to stop the virus being passed on. This can also stop you from getting the infection again.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis B Vaccine For
Hepatitis B Causes And Risk Factors
Itâs caused by the hepatitis B virus, and it can spread from person to person in certain ways. You can spread the hepatitis B virus even if you donât feel sick.
The most common ways to get hepatitis B include:
- Sex. You can get it if you have unprotected sex with someone who has it and your partnerâs blood, saliva, semen, or vaginal secretions enter your body.
- Sharing needles. The virus spreads easily via needles and syringes contaminated with infected blood.
- Accidental needle sticks.Health care workers and anyone else who comes in contact with human blood can get it this way.
- Mother to child.Pregnant women with hepatitis B can pass it to their babies during childbirth. But thereâs a vaccine to prevent newborns from becoming infected.
Hepatitis B doesnât spread through kissing, food or water, shared utensils, coughing or sneezing, or through touch.
Treatment For Hepatitis C
The goal of treatment is to clear the virus from the body. If you have acute hepatitis C, you probably wont have symptoms, and the virus will clear on its own without treatment. In the case of chronic hepatitis, your doctor may treat the virus with antiviral medication for 12 to 24 weeks.
Until 2011, there were only two drugs available to treat hepatitis C: pegylated interferon and ribavirin . These drugs were often used in combination with each other.
The drugs currently used to treat hepatitis C include:
- ribavirin
Also Check: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Positive
What Should You Know About Hepatitis B Before You Travel
Hepatitis B is quite common in China and other Asian countries, where as many as 1 in 12 people have the virus, though many dont know it. Before traveling to those places, you should make sure youve been vaccinated against the virus.
In addition to getting the vaccine, you can take these additional precautions to reduce your risk of contracting the virus:
- Refrain from taking illegal drugs.
- Always use latex or polyurethane condoms during sex.
- Make sure new, sterile needles are used during all piercings, tattoos and acupuncture sessions.
- Avoid direct contact with blood and bodily fluids.
- Know the HBV status of all your sexual partners.
- Ask your doctor about possible vaccination before you travel to a place where hepatitis B is common.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Hepatitis B is a liver disease that can cause serious damage to your health. One reason that is dangerous is that it can easily go undetected for years while damaging your liver. Talk with your healthcare provider about being tested for hepatitis B if you have any reason to believe that you were not vaccinated or if you have engaged in risky behavior. If you do test positive, follow the directions from your healthcare provider so that you can live a longer, healthier and happier life.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 07/09/2020.
References
What If I Am Pregnant
It’s recommended that all pregnant women have a blood test for hepatitis B in early pregnancy.
If you have hepatitis B and are pregnant, treatments can reduce the risk of transmission of hepatitis B to the baby.
If you have hepatitis B, it is important to protect others from infection.
Important ways to prevent the spread of hepatitis B include:
- vaccination of all your close contacts
- practise safe sex until your sexual contacts are fully vaccinated and immune
- do not donate blood, organs or body tissue
- do not allow your blood to contact another person
- inform healthcare workers
- if your work involves potential for your blood or other body fluid to spread to other people, discuss your situation with your doctor
The hepatitis B vaccine is safe and effective in protecting against hepatitis B infection, providing protection in 95 in 100 vaccinated people.
In Australia, hepatitis B vaccination is part of the standard immunisation schedule for all newborn babies and infants. It’s also recommended for adults who are at high risk of exposure, people who are immunosuppressed or have other liver disease. People in these risk groups should be vaccinated against hepatitis B. Talk to your doctor about your level of risk and whether hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for you.
If you werent vaccinated against hepatitis B as a child, or if youre not sure whether you are vaccinated, talk to your doctor about whether you need a catch-up vaccine.
Read Also: Difference Between Hepatitis A And B
How Do You Know If You Have Hepatitis B
The only way to know if you have hepatitis B is bya medical exam. There are several blood tests yourhealth care provider can use to diagnose hepatitis B.These tests can tell you:
- If it is an acute or a chronic infection
- If you have recovered from infection
- If you are immune to hepatitis B
- If you could benefit from vaccination
What Is Chronic Hepatitis B
Doctors refer to hepatitis B infections as either acute or chronic:
- An acute HBV infection is a short-term illness that clears within 6 months of when a person is exposed to the virus.
- A person who still has HBV after 6 months is said to have a chronic hepatitis B infection. This is a long-term illness, meaning the virus stays in the body and causes lifelong illness. An estimated 850,000 to more than 2 million people in the U.S. have chronic HBV.
The younger someone is when infected, the greater the chances for chronic hepatitis B.
Recommended Reading: Is There A Treatment For Hepatitis C
What Is Hbv Treatment
Not everyone infected with HBV will need treatment. Doctors usually only recommend treatment if the virus is damaging your liver.
Antivirals: These are oral medications that make it hard for HBV to reproduce, but they usually work for only as long as you take them. They are able to lower the amount of HBV in your body and stop liver damage in about 70% to 90% of patients. Unfortunately, these treatments cannot cure hepatitis B to date.
What Causes Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is caused by the hepatitis B virus. It can happen through exposure to infected blood and other bodily fluids in the following situations:
- sharing needles and other injecting drug equipment
- sharing razors, toothbrushes or nail clippers
- sexual contact
- tattooing with unsterilised needles and equipment
- close family contact with someone who has hepatitis B
- being born to a mother with hepatitis B
- accidental exposure such as a needle stick injury or being splashed with infected blood or body fluid
- blood transfusion this is now very rare as blood in Australia is screened for hepatitis B
You cannot catch hepatitis B through being coughed or sneezed on by infected people or by consuming contaminated food and drink. You cannot catch the virus from saliva, breast milk or tears.
Recommended Reading: How To Contract Hepatitis B And C
What Are The Risk Factors For Getting Hepatitis B
Due to the way that hepatitis B spreads, people most at risk for getting infected include:
- Children whose mothers have been infected with hepatitis B.
- Children who have been adopted from countries with high rates of hepatitis B infection.
- People who have unprotected sex and/or have been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection.
- People who live with or work in an institutional setting, such as prisons or group homes.
- Healthcare providers and first responders.
- People who share needles or syringes.
- People who live in close quarters with a person with chronic hepatitis B infection.
- People who are on dialysis.
Causes Of Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is spread through contact with blood that contains the hepatitis B virus. If infected blood or body fluids enter another persons bloodstream, that person may become infected.
The time from exposure to the hepatitis B virus to the appearance of the illness is 45 to 180 days.
Risky activities that can cause infection include:
- Sharing unsterile or unclean equipment for injecting drugs.
- Piercing the skin with equipment that is not properly cleaned, disinfected and sterilised.
- Sharing razor blades or toothbrushes.
- Coming into contact with infected blood through open cuts or the mucous membranes of another person.
- Having unprotected sex , especially if there is blood present.
Mothers who have hepatitis B can pass the virus to their babies or children at the time of birth or after birth. If the newborn baby is quickly immunised with 2 vaccines, they can be protected from getting hepatitis B.
All blood and blood products produced for medical purposes in Australia are carefully screened for hepatitis B and other blood-borne viruses. The risk of getting infected with hepatitis B from a blood transfusion is extremely low .
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get Tested For Hepatitis B
What Should You Know About Pregnancy And Hepatitis B
A pregnant woman who has hepatitis B can pass the infection to her baby at delivery. This is true for both vaginal and cesarean deliveries.
You should ask your healthcare provider to test you for hepatitis B when you find out you are pregnant. However, while it is important for you and your healthcare provider to know if you do have hepatitis B, the condition should not affect the way that your pregnancy progresses.
If you do test positive, your provider may suggest that you contact another healthcare provider, a liver doctor, who is skilled in managing people with hepatitis B infections. You may have a high viral load and may need treatment during the last 3 months of your pregnancy. A viral load is the term for how much of the infection you have inside of you.
You can prevent your infant from getting hepatitis B infection by making sure that your baby gets the hepatitis B vaccine in the hours after they are born along with the hepatitis B immunoglobulin. These two shots are given in two different locations on the baby. They are the first shots needed.
Depending on the type of vaccine used, two or three more doses must be given, usually when the baby is 1 month old and then 6 months old, with the last by the time the baby is 1 year old. It is critical that all newborns get the hepatitis B vaccination, but even more important if you have hepatitis B yourself.
If I Am Infected How Can I Prevent Passing On The Virus To Others
If you have a current hepatitis B infection you should:
- Avoid having sex with anyone until they have been fully immunised and checked with a blood test to see that the immunisation has worked.
- Not share any injecting equipment such as needles, syringes, etc.
- Not donate blood or semen or carry a donor card.
- Not share razors, toothbrushes, etc, that may be contaminated with blood.
- Cover any cuts or wounds with a dressing.
- Make sure that, if any of your blood spills on to the floor or other surfaces following an accident, it is cleaned away with bleach.
Also Check: Where Can I Get A Hepatitis B Shot
What About Pregnancy
If you have hepatitis B, your baby has a very highchance of getting it. Pregnant women should bechecked for hepatitis B by a health care provider. Ifyou are at risk for hepatitis B, ask your provider aboutgetting vaccinated. The hepatitis B vaccine is safe forpregnant women and their baby. The vaccine can helpyour baby if:
- It is given to the baby within 12 hours of birth.
- The baby finishes the vaccine series. Note: babies should be tested after the last vaccine shot to make sure they are protected from the disease.
Don’t breastfeed until you have discussed it withyour health care provider. Avoid breastfeeding if yournipples are cracking or bleeding until the sores heal.Until they heal, you can pump your milk to keep upyour milk supply. Do not feed this milk to your baby.Throw it away.
Hepatitis B is a very serious disease for babies. 9 out of 10 babies infected develop chronic hepatitis B.
What Is My Risk
Your risk depends of several factors: destination, length of stay, what you do when you are travelling and whether you have direct contact with blood or other body fluids. In certain destinations, your risk may be higher, as some areas have higher numbers of people with chronic hepatitis B in the general population.
The risk increases with certain activities, such as unprotected sex, sharing needles, tattooing and acupuncture.
Aid and health care workers and anyone who receives medical or dental care with unsterilized or contaminated equipment in a country where hepatitis B occurs are also at greater risk.
You May Like: Hepatitis A Vaccine At Cvs
Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
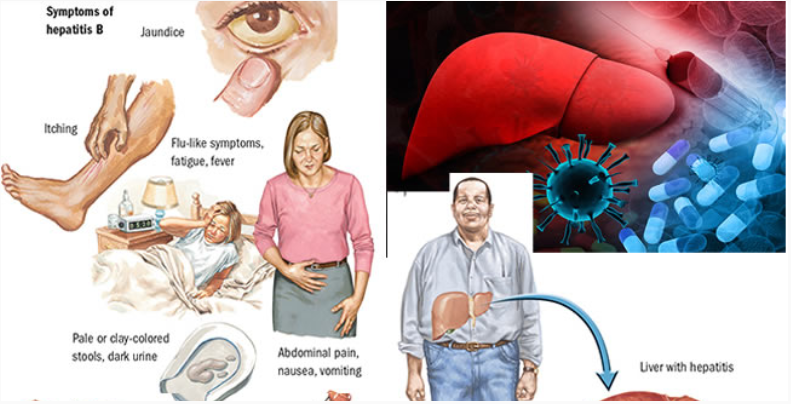
The majority of people experience no significant symptoms during the acute phase of infection. However, some people develop a rapid onset of the disease with symptoms that last a few weeks, including extreme fatigue, yellowing of eyes and skin, dark urine, abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting.
A small amount of people with acute hepatitis experience liver failure which can result in death. Sometimes the Hepatitis B virus can end up in a chronic infection that can develop such consequences as liver cancer or cirrhosis. However, more than 90% of adults recover naturally within the first year without any special treatment. But its important to remember that an infected person can transmit HBV to other people even if he or she has no symptoms.