Who Should Get Screened For Hepatitis B
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control calls for HBV screening of all foreign-born persons from regions where hepatitis B is common regardless of their vaccination history.
Additionally, all pregnant women should be screened for HBV at an early prenatal visit during each pregnancy, even if they have been previously tested or vaccinated.
Other groups recommended for HBV screening include:
- Anyone seeking protection from the HBV infection
- Healthcare and public safety workers
- Household, sex, or needle-sharing contacts of persons infected with HBV
- Intravenous drug users
What Is The Purpose Of A Hepatitis B Test
Hepatitis B test is performed to detect, classify, and treat hepatitis B virus infection.
Hepatitis B blood tests involve the measurement of several HBV-specific antigens and antibodies. In addition, HBV blood tests also include liver enzymes and liver function tests to assess and monitor the condition of the liver and provide appropriate treatment.
The HBV specific tests include the following:
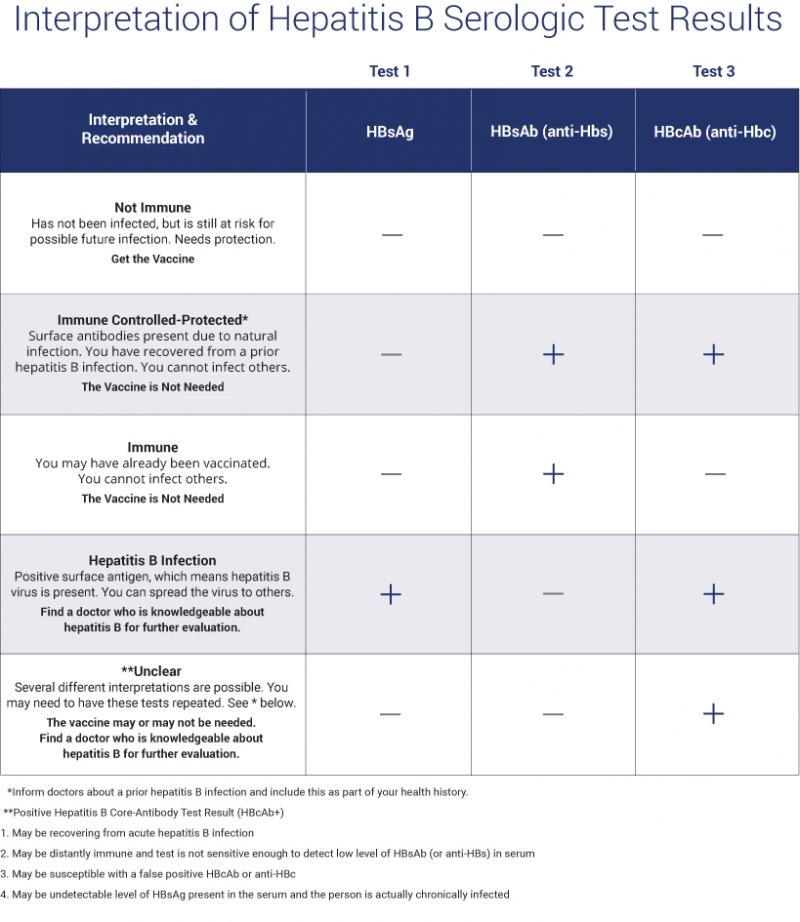
- HBsAg: HBsAg is an antigen found on the surface of hepatitis B virus. HBsAg may be detected in the blood any time after 1 week post-exposure to HB virus, but usually appears after 4 weeks.
- Anti-HBs: Anti-HBs are antibodies produced by the bodys immune system to fight HBsAg. Anti-HBs from a prior infection or vaccination provides immunity against further infection.
- Hepatitis B core antigen : HBcAg is an antigen found in the core layer which covers the hepatitis B viral DNA.
- Hepatitis B core antibody : Anti-HBc is the antibody that fights HBcAg. Anti-HBc is the first detectable antibody after HBV infection. There are two kinds of Anti-HBc:
- Immunoglobulin M hepatitis B core antibody : IgM anti-HBc indicates acute or reactivated recent infection within the previous 6 months.
- Immunoglobulin G hepatitis B core antibody : IgG anti-HBc may indicate previous or chronic infection. Once present, IgG anti-HBc persists for a lifetime.
Pregnancy And Hepatitis B
Doctors must closely monitor pregnant people who have HBV.
There is a risk that the virus can pass from parent to child during delivery without the correct treatment. Therefore, all people should receive hepatitis B testing during pregnancy. A person with chronic hepatitis B should talk with a doctor about the risks and benefits of antiviral treatment while pregnant.
According to the Hepatitis B Foundation, if someone has HBV, their newborn must immediately receive the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine and hepatitis B immune globulin within 12 hours of birth. The infant should then receive the second and third doses of the vaccine according to the standard childhood immunization schedule.
Pregnant people unsure of their vaccination status can receive the hepatitis B vaccine during pregnancy and breastfeeding or chestfeeding.
However, there is currently not enough safety information about Heplisav-B and PreHevbrio, so pregnant people
Recommended Reading: How Long Can You Live With Hepatitis B Untreated
What Do The Hepatitis B Immunity Results Mean
If an individual is positive for both surface and core antibodies, it can indicate that they had a natural HBV infection and recovered. If only surface antibodies are positive, it can indicate that the individual was vaccinated. In both of these cases, immunity is confirmed, meaning that further vaccination is not generally required.
What Does The Test Measure
Hepatitis B testing looks for antigens, antibodies, or the genetic material of the hepatitis B virus. HBV antigens are substances from the virus that cause a patientâs body to produce an immune response. Antibodies are substances made by the immune system in response to the hepatitis B virus.
Initial tests for hepatitis B measure antibodies and antigens related to HBV including:
If a patient is diagnosed with hepatitis B based on these initial tests, additional hepatitis B testing may be used to monitor the disease, guide treatment, and determine if a person can spread hepatitis B to others. These additional tests may include:
- Hepatitis B e antigen : Hepatitis B e antigen is a protein from the hepatitis B virus found in some patients who are positive for hepatitis B surface antigen. Measuring this antigen can help doctors understand infectivity, which describes a personâs ability to spread HBV to others.
Recommended Reading: How To Live With Hepatitis B
What Is The Normal Range For Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are measured in blood samples in milli-International Units/milliliter mIU/mL). The ranges for hepatitis B surface antibodies are:
- Anti-HBs greater than 10-12 mIU/mL: Protected against hepatitis B virus infection, either from vaccination or successful recovery from a previous HBV infection.
- Anti-HBs less than 5 mIU/mL: Negative for HBV infection, but susceptible and hence requires vaccination.
- Anti-HBs from 5-12 mIU/mL: Inconclusive results and the test should be repeated.
However, there is no standardization of these values so it is advisable to check the manufacturers values it is the reason values are mainly reported as positive or negative.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
Not all individuals infected with acute hepatitis B will experience symptoms. In fact, the CDC estimates that only about 30-50% of infected people age 5 and older will have symptoms. When symptoms are present, they will develop about 3 months after exposure and will include the following:
Individuals with chronic hepatitis B will generally not have any symptoms. When symptoms are present, they are generally very similar to the symptoms of acute hepatitis B. Given the serious nature of hepatitis B and the effects it can have on your liver and overall health, it is important to talk to your doctor about hepatitis B if you believe you may have been exposed to the disease.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis Panel Acute With Reflex To Confirmation
About Our Hepatitis B Immunity Status Test
This blood test is used to confirm immunity against the hepatitis B virus by detecting the presence of surface antigens, surface antibodies, and core antibodies specific to HBV .
Hepatitis B is a sexually transmitted disease caused by the double-shelled hepatitis B virus. It is preventable through vaccination.
An individual develops hepatitis B surface antibodies from a successful vaccination or if they have had hepatitis B and recovered from the infection. The hepatitis B vaccine stimulates the body to make these antibodies to protect against the virus. If an individual has been infected but cleared the virus, the surface antibodies they developed protect against the virus for life, preventing reinfection. The hepatitis B surface antibody is detectable after clearing the virus.
The presence of hepatitis B core antibody can indicate a past or present HBV infection. People vaccinated for hepatitis B will not have the core antibody in their blood.
How You Can Get Hepatitis B
You can get hepatitis B from:
- injecting drugs using shared needles
- being injured by a used needle
- having a tattoo or piercing with unsterilised equipment
- having a blood transfusion in a country that does not check blood for hepatitis B. Blood transfusions in the UK are checked for hepatitis B.
If youâre pregnant and have hepatitis B, you can also pass it onto your baby during pregnancy or birth.
Read Also: What Does Hepatitis C Antibody Mean
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test
A hepatitis B surface antigen test shows if you have an active infection. A positive result means you have hepatitis B and can transmit the virus to others. A negative result means you dont currently have hepatitis B.
This test doesnt distinguish between chronic and acute infection. This test is used together with other hepatitis B tests to determine the state of a hepatitis B infection.
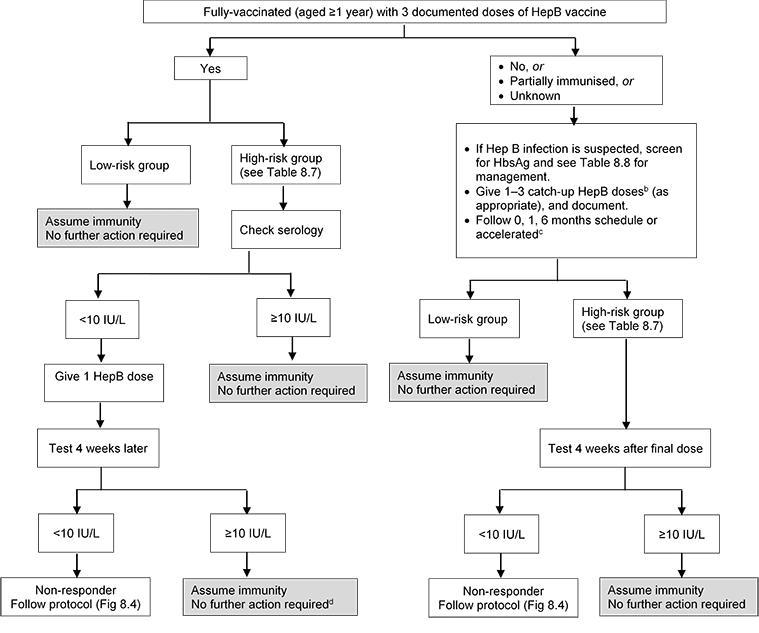
What To Do If You Miss A Scheduled Dose
The recommended schedule for the HBV vaccine follows a three-dose pattern, with all doses complete within 6 months. The good news is that if you miss a dose, you dont need to start the series of shots all over.
If you missed getting the second dose 1 month after the first, make an appointment as soon as possible. If you miss the third dose, you should also try to get it as quickly as possible. Keep in mind that the second and third doses
Also Check: Where Can I Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
Also Check: Cvs Hepatitis A Vaccine Cost
Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis B
Anyone can contract hepatitis B. However, certain groups are at greater risk. According to the CDC, the following groups are at highest risk for contracting hepatitis B:
- Infants born to infected mothers
- People who inject drugs or share needles
- Sexual partners of people infected with hepatitis B
- Men who have sex with men
- People living in close proximity to a person with hepatitis B
- Health care workers or others exposed to blood in their work environments
- Hemodialysis patients
What Do The Results Mean
A hepatitis B blood panel consists of three tests that can be done with just one blood sample:
- Hepatitis B surface antigen . A positive test indicates that youre infected with hepatitis B and that you can spread it to other people. Further tests are needed to see if you have an acute or chronic infection.
- Hepatitis B core antibody . A positive result can indicate a past or current hepatitis B infection, but doesnt mean youre immune. A positive result needs to be interpreted by a doctor by examining the results of the other two tests.
- Hepatitis B surface antibody . A positive test indicates that youre protected from hepatitis B either through previous infection or vaccination .
The combination of these tests can indicate your hepatitis B status and whether you need to be vaccinated. Your test will give a negative or positive result for each category depending on whether your results are above or below the cutoff value.
Most peoples test results fall into the following categories. But its possible to have a result that doesnt fall into one of these groups. If youre reading your results yourself, be careful not to confuse HBsAb with HBcAb.
| HBsAG |
is associated with hepatitis B immunity after vaccination. But research has found that anti-HBs decline over time.
A found that more than 95 percent of people had anti-HBs levels greater than 10IU/L two years after vaccination. But this rate decreased to 70 percent after eight years.
Also Check: How Do You Get Hepatitis C Virus
Chronic Hepatitis Binfected Patients
A, Hepatitis A testing and immunity in patients with chronic hepatitis B. B, Hepatitis A testing and immunity in patients with chronic hepatitis C. C, Hepatitis B testing and immunity in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Abbreviations: anti-HA, hepatitis A antibody anti-HBc, hepatitis B core antibody anti-HBs, hepatitis B surface antibody.
In univariate analysis , the oldest patients were less likely to have immunity or vaccination than any other age group . Native American and black patients were less likely to have immunity or vaccination . Patients with no immunity or vaccination had fewer months of member coverage . After multivariable adjustment , factors significantly associated with immunity or vaccination included age 80 vs < 30 years , age 4049 vs < 30 years , Asian vs white race , male sex , and months of member coverage .
Counseling Practices That Educate Support And Motivate Clients Undergoing Screening
Clients might need help deciding whether to get screened, understanding the test results, and determining their next steps. Even when services offered through the substance abuse treatment program are limited, discussing testing with clients presents an opportunity for counselors to motivate clients for change by confronting substance use and by making choices that improve their overall health. However, this may also be true when services are offered on-site through substance abuse treatment programs. A study at one methadone clinic that offered hepatitis screening and vaccination revealed that although the majority of clients completed screening , only 54.7 percent of clients who lacked for hepatitis A received vaccinations and only 2.9 percent of clients who lacked immunity for received vaccinations .
The Consensus Panel makes the following general recommendations while recognizing that, in some programs, the counselors role may be limited:
Recommended Reading: Low Protein Diet For Hepatic Encephalopathy
Complications Of Hepatitis B
A small proportion of people who become infected with the hepatitis B virus develop a long-term hepatitis B infection. They may have the virus in their bloodstream for most of their life without realising they are infected.
People with chronic hepatitis B infection may not notice any health problems until they develop liver problems such as liver disease or liver cancer later in life. Treatment for hepatitis B is essential because it is not possible to be a healthy carrier of the hepatitis B virus. Chronic hepatitis B infection occurs more commonly in some communities, including:
- Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander communities.
- In people from parts of the world where hepatitis B is more common, such as:
- North-East Asia
About The Hepatitis B Immunity Test
-
What this test is for
The kit tests for hepatitis B antibodies to see whether you are immune. Please note that this is not a test kit for a current hepatitis B infection. The result will tell you whether you have immunity to hepatitis B.
Unsure if you should be purchasing hepatitis B vaccines or an immunity test? Our clinicians can advise you.
-
When to take the test
The test should be done at least 4 weeks after completing a course of hepatitis B injections or at least 4 weeks after a booster injection.
-
How to take the test
You will need to produce a blood sample using a small finger prick device, contained in the kit. You will only need to produce a small amount of blood and it shouldn’t hurt. Full instructions come with the test kit.
You should send your blood sample back to our partner laboratory in the pre-paid envelope provided.
Don’t Miss: How Long Can Hepatitis C Live Outside The Body
Review Of Current Recommendations
Table highlights the current recommendations for hepatitis A and B vaccinations. The Hepatitis C Task Force recommends both vaccines for newly diagnosed CHC patients without evidence of immunity to hepatitis A and/or B, based on expert opinion . The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommends hepatitis A vaccine for susceptible patients with chronic liver disease but not routinely for CHB or CHC patients without chronic liver disease . The American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver both recommend hepatitis A vaccine for all CHC patients with no evidence of preexisting antibody, but the AASLD similarly recommends vaccinating CHB patients with chronic liver disease . AASLD guidelines state that hepatitis B vaccine should be offered to CHC patients. The ACIP recommends hepatitis B vaccination of adults with chronic liver disease in addition to those at risk for infection by sexual exposure or exposure to blood . The Physician Quality Reporting System quality indicator from the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services counts all CHC patients with at least 1 hepatitis A vaccine or documented immunity to hepatitis A .
Hepatitis A and B Vaccination Recommendations and Quality Measures for Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B or C
| Recommending Agency . |
|---|
What Does No Immunity To Hepatitis B Mean
NOT IMMUNE has not been infected. but is still at risk for possible future. infection needs vaccine. Get the vaccine.
How do you know if you have Hep B immunity?
A hepatitis B surface antibody test is used to check for immunity to HBV. A positive test means you are immune to hepatitis B. There are two possible reasons for a positive test. You may have been vaccinated, or you may have recovered from an acute HBV infection and are no longer contagious.
Also Check: Can You Get Hepatitis C From Kissing
Hepatitis B Blood Tests
The Hepatitis B Panel of Blood Tests
Only one sample of blood is needed for a hepatitis B blood test, but the Hepatitis B Panel includes three parts. All three test results are needed to fully understand whether a person is infected or not. Below is an explanation of the 3-part Hepatitis B Panel of blood test results.
How Do Doctors Test For Hepatitis B Immunity
Doctors may order a panel of blood tests to check if someone has HBV:
- Hepatitis B surface antigen : This test looks for the presence of HBV in the blood by looking for antigens found on the virus. A positive result means that a person has HBV.
- Hepatitis B surface antibody : This test can show if a person is immune and protected against HBV. A positive result indicates that the person has overcome a past HBV infection or it is the result of receiving the hepatitis B vaccine.
- Hepatitis B core antibody : This test looks for another antibody in the HBV, but this one does not provide protection. A positive result indicates that a person had a past infection or currently has HBV.
Some people with certain risk factors for hepatitis B infection, such as those who inject drugs, pregnant people, and other populations, may require testing postvaccination to check their immunity.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis A And How Do You Get It