Overall Prevalence Of Hbv Infection
Over the 10-years period from 2000 to 2010, 877,892 individuals were screened for HBV infection and 5,055 positive cases were reported in Bahrain. On average 79,808 individuals are screened for chronic HBV infection every year and the prevalence of HBV infection during the period 20002010 was 0.58% . The global prevalence of HBV was 0.7% . Although there was no big difference in the prevalence over the period of 10 years, the actual number of positive cases has almost doubled in the later years especially in 2007 and 2008 .
Survey Had High Rates Of Missing Data
In the study, Beste and her colleagues used survey data and stored blood serum collected in a 2005 study on hepatitis C prevalence in Veterans.
In a 36-item questionnaire in the 2005 study, the Veterans self-reported on potential military and non-military risk factors, such as exposure to combat and to blood in combat vaccination with pneumatic jet guns drug use history and sexual behavior. The participants also underwent blood tests that Beste and her team reanalyzed to determine the prevalence of hepatitis B infection, exposure, and immunity, before assessing the links between military risk factors and hepatitis B.
We used the blood test results to tell whether someones been either exposed to hepatitis B or infected with hep B, Beste says, because a lot of people who are exposed dont necessarily get a chronic infection. The blood tests can tell us if youve ever been exposed or are currently infected. By linking the risk factors and the blood test results, we were able to tell that combat is associated with hep B exposure, even after we accounted for more typical risk factors like drug use history and sexual history.
Combat questions included:
- Were you ever in a combat zone during your years of active service?
- Were you ever wounded in combat?
- Did someone else’s blood ever get on your skin during combat?
Sexual behavior questions included:
Description Of The Study Population
One hundred fifty-one mothers attended the mobile health camp, which comprised 37% of the total study population. Among them, 125 mothers were HBsAg seronegative and the remaining 26 mothers were HBsAg seropositive. The proportion of HBsAg positive mothers was significantly lower than the proportion of HBsAg negative mothers in the population with the difference being greater than 2 standard error .One child refused to give a blood sample, therefore only 25 mother-children pairs were included in the data analysis .
Fig. 1
Recommended Reading: How Long Can A Person Live With Hepatitis C
Seroprevalence Of Hbsag And Sociodemographic Characteristics Of Study Participants
A total of 1000 adolescent voluntary blood donors aged between 18 years and 25 years, spread across the counties Kisumu, Siaya, and Homa Bay, were enlisted into the study. Of the thirty-seven samples that initially tested positive for HBsAg, thirty-four were confirmed HBsAg-positive, giving an overall seroprevalence of 3.4%. The two test methodologies used as initial and confirmatory tests in this study were notably applied because of the good analytical agreement between the methods and could therefore reliably detect and confirm HBV infection in the study population. Nevertheless, some discrepancies in quantitative measurement as reported between the initial test and the confirmatory test may have been due to factors such as variations in the standard calibrators used in each assay, difficulties in quality assurance occasioned by sample transport, assay degeneration, and operator error. Comparatively across the counties, seroprevalence was highest in Siaya at 1.3% followed by Homa Bay at 1.1% while Kisumu recorded the least at 1.0% . Generally, there was no statistically significant association between sociodemographics such as age, age group, gender, county of origin, and number of donations to HBsAg test results. This is summarized in Table 1.
Study Design And Population
This study was conducted between January 2007 and December 2009 in Malatya City. This city is located in mid-eastern Anatolia and has an estimated urban population of 555,000 and an estimated rural population of 15,000. The study was performed in the Public Health Office with the participation of two state hospitals. To identify risk factors for HBV acquisition, we conducted a case-control study. The Public Health Department generated the case and control groups. All patients who were diagnosed with acute HBV infection within the study periods were eligible for inclusion. The case definition of acute HBV infection was made, with some modifications, using criteria per the Council of State and Territorial Epidemiologists . Control groups consisted of healthy residents who met the demographic characteristics of the study population and who could be documented as negative for any current and/or previous HBV infection. Chronic HBV patients, vaccinated persons, healthy carriers, and formerly infected individuals were not included. Patients and controls were requested to provide written informed consent. All adult patients and controls were volunteers. Nonadult patients were included only with their parents’ permission.
Read Also: How To Know If I Have Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B And Pregnancy
Hepatitis B can be transmitted from a birthing parent to a newborn infant. This is because the newborn is exposed to blood and bodily fluids during delivery.
In fact, 90% of mothers with an acute hepatitis B infection and 10% to 20% of mothers with chronic hepatitis B will transmit the virus to their newborn, estimates the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
For this reason, birthing parents are routinely screened for hepatitis B during each pregnancy.
Additionally, the hepatitis B vaccine and hepatitis B immune globulin are both administered to infants with an HBV-positive birthing parent within of birth to prevent infection.
According to the
- people with hepatitis C infection
- men who have sex with men
- people with multiple sexual partners
- people who are seeking treatment for a sexually transmitted infections
- people with current or recent injection drug use
- family members or sexual partners of those with hepatitis B
- people with chronic liver disease
- people traveling to areas with high rates of hepatitis B
- people on maintenance dialysis
- people who are incarcerated
The hepatitis B vaccine is usually administered in three shots, given 1 month and 6 months after the first dose. Another recently approved vaccine is completed in two doses spaced 1 month apart.
Hiv And Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C Coinfection
Hepatitis B and hepatitis C are liver infections caused by a virus. Because these infections can be spread in the same ways as HIV, people with HIV in the United States are often also affected by chronic viral hepatitis.
Viral hepatitis progresses faster and causes more liver-related health problems among people with HIV than among those who do not have HIV. Liver disease, much of which is related to HBV or HCV, is a major cause of non-AIDS-related deaths among people with HIV.
Given the risks of hepatitis B or hepatitis C coinfection to the health of people living with HIV, it is important to understand these risks, take steps to prevent infection, know your status, and, if necessary, get medical care from someone who is experienced in treating people who are coinfected with HIV and HBV, or HIV and HCV.
You May Like: Royal Canin Veterinary Diet Hepatic Formula Dry Dog Food
Who Is Most Affected
In the United States, rates of new HBV infections are highest among adults aged 30-59 years, reflecting low hepatitis B vaccination coverage among adults at risk. The most common risk factor among people with new HBV infections is injecting drugs, related to the opioid crisis.
The highest rates of chronic hepatitis B infection in the United States occur among foreign-born individuals, especially people born in Asia, the Pacific Islands, and Africa. Approximately 70% of cases in the United States are among people who were born outside of the United States. CDC developed this map of the geographic distribution of hepatitis B around the world – PDF. Other groups who have higher rates of chronic HBV infection include people who inject drugs and men who have sex with men.
Risk Factors For Acute Hepatitis B
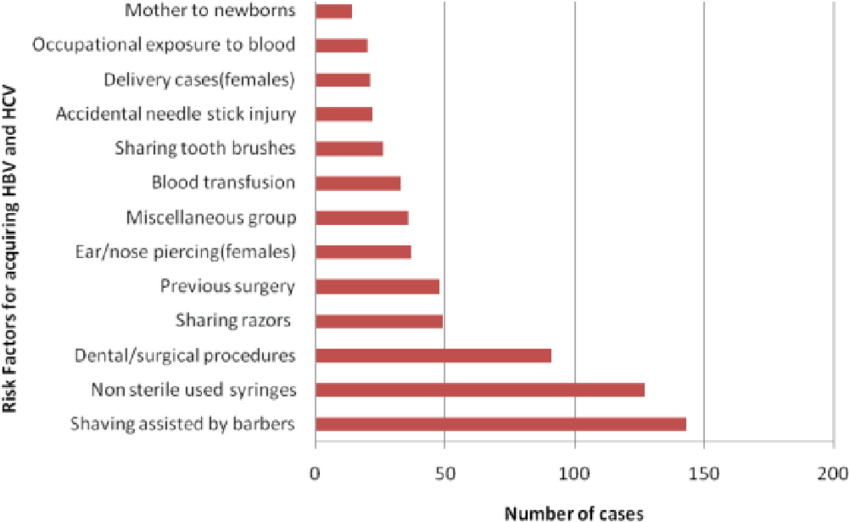
In the univariate regression analysis, statistically significant ORs were obtained for household contact with chronic hepatitis B , liver cirrhosis , and hepatocellular carcinoma , undergoing invasive medical procedures including intramuscular injection , intravenous injections or infusions , endoscopy , and surgery , body care and beauty treatment in public places including pedicure four or more times , and barber shop shaving four or more times , eating out twice or more per week , and lack of HBV vaccination in the patients with AHB . Piercing and tattooing in women ), bleeding during pedicure ) were also risk factors for AHB. No associations were suggested with the other reported risk factors, such as dental surgery, acupuncture, haemodialysis, blood transfusion, promiscuous sexual contact, being with a user of injectable drugs.
In multivariate regression analysis, household contact with a person or persons with liver cirrhosis and chronic hepatitis B , intramuscular injection , intravenous injections or infusions , receipt of pedicure in bath centres , eating out twice or more per week and lack of HBV vaccination were independently associated with AHB.
You May Like: How Can You Catch Hepatitis B And C
Characteristics Of Children And Hbsag Seroprevalence
A greater proportion of male children were HBsAg seropositive compared to female children . Children with average or greater size at birth were less frequently HBsAg seropositive compared to those that were smaller than average size at birth . Children who were fed colostrum within 1 h after delivery were less HBsAg seropositive compared to no colostrum fed ones .
Table 5 Childrens characteristics and HBsAg sero-prevalence
Administration of the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine was high among the children however, only half of the children that had been vaccinated were HBsAg seronegative. Nearly two-thirds of children were vaccinated with the second dose, but nearly half of them were HBsAg seronegative. Only one-third of children were vaccinated with full series of the hepatitis B vaccine , although more than half of children were HBsAg seropositive . Furthermore, the percentage of HBsAg seropositivity increased in older age groups with rates of 20, 50, and 72% respectively in age groups 0 to 12 months, 12 to 24 months, and 24 to 60 months .
Fig. 2
Ethics Approval And Consent To Participate
Ethical approval for the study was obtained from Institutional Research and Ethical Committee of Moi University/Moi Teaching and Referral Hospital. The ethical committee waived the need for written consent since this analysis was done retrospectively. All the clinical data has been de-identified as per the ethical board requirement.
Also Check: What Are The Effects Of Hepatitis C
How Long Can You Live With Hepatitis B
Most people who contract hepatitis B during adulthood fully recover within 1 to 3 months.
People with chronic hepatitis B may have a higher risk of developing long-term liver problems, like cirrhosis or liver cancer, which require treatment and may be life threatening.
Keep in mind that the risk of developing chronic hepatitis B is higher for babies and children, especially if they have not been vaccinated against the virus.
Blood Collection And Serological Analysis
After donor blood collection, whole blood samples from donor bags were dispensed into red top vacutainer tubes and left to clot at room temperature. Thereafter, 75l of serum was pipetted from the vacutainer tube for analysis using Murex HBsAg Version 3 as per the manufacturer’s instructions. Samples that turned positive for HBsAg using this initial test were shipped to the Regional Blood Transfusion Laboratory in Nairobi, where a confirmatory test was done by Chemiluminescence Immunoassay using the ARCHITECT HBsAg Qualitative Confirmatory assay as per the manufacturer’s instructions. A result was considered positive if the first test and the confirmatory test were all reactive.
Don’t Miss: Is Hepatitis C Contagious Through Saliva
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test
A hepatitis B surface antigen test shows if you have an active infection. A positive result means you have hepatitis B and can transmit the virus to others. A negative result means you dont currently have hepatitis B.
This test doesnt distinguish between chronic and acute infection. This test is used together with other hepatitis B tests to determine the state of a hepatitis B infection.
Hepatitis Types And Liver Risks
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. It can be caused by several viruses. The main types in the United States are A, B, and C. Type A symptoms are often similar to a stomach virus. But most cases resolve within a month. Hepatitis B and C can cause sudden illness. However, they can lead to liver cancer or a chronic infection that can lead to serious liver damage called cirrhosis.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Hepatitis B
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis B
If you think you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a healthcare professional as soon as possible.
A doctor or other healthcare professional may administer the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine and a shot of hepatitis B immunoglobulin. This is a combination of antibodies that provide short-term protection against the virus.
Though both can be given up to a week after exposure, theyre most effective at preventing infection if administered within 48 hours.
If you receive a diagnosis of acute hepatitis B, a doctor may refer you to a specialist. They may advise you to get regular blood tests to ensure you dont develop chronic hepatitis.
Many people with acute hepatitis B dont experience serious symptoms. But if you do, it can help to:
- get plenty of rest
- take over-the-counter pain mediation, like naproxen, when needed
Other lifestyle changes may also be needed to manage your infection, such as:
- eating a nutritious, balanced diet
- avoiding substances that can harm your liver, such as:
- alcohol
- certain herbal supplements or medications, including acetaminophen
If blood tests show you still have an active infection after 6 months, your doctor may recommend further treatment, including medications to help control the virus and prevent liver damage.
Strengths Of The Study
This study was the first of its kind to be done within western Kenya covering a range of high-risk populations. Female sex workers, MSM and substance users have not been previously screened for HBV infection in Kenya. Overall, many persons were screened for Hepatitis B although some groups were smaller than others depending on the available numbers from these groups. The persons selected into the risk group were all screened, this represented 100% of all persons presenting to primary care or otherwise. This project was important in showing feasibility of screening.
Also Check: How To Get Tested For Hepatitis
Characteristics Of Mothers And Status Of Their Childrens Hbsag Seroprevalence
The HBsAg seroprevalence was higher among children who lived with mothers having no ANC services compared to those having some ANC services . The prevalence was higher among children with mothers that drank alcohol during pregnancy compared to those that did not . The prevalence was higher among children with mothers that consumed alcohol daily .
Table 4 Mothers socio-demographic, serological characteristics and HBsAg sero-prevalence of children
The prevalence of HBeAg and HBeAb seropositive mothers was 76% with 10 mothers HBeAg positive and 9 mothers HBeAb positive out of a total of 25 mothers. All mothers were HBcAb positive. The majority of children with HBeAg positive mothers were HBsAg positive, whereas less children were HBsAg positive with HBeAg negative mothers. Less children were HBsAg positive with HBeAb positive mothers, where as an overwhelming number of children were HBsAg positive with HBeAb negative mothers .
Measurement Of Chronic Hbv Infection
Hepatitis B surface antigen was measured in all participants at the baseline visit, using a point of care, lateral flow rapid diagnostic test , where participants venous whole blood was applied to an on-site rapid test strip . Results were recorded as positive, negative, or unclear. HBV antibodies to hepatitis B core antigen and hepatitis B e antigen were additionally measured in stored plasma samples from a randomly selected subcohort of 2000 participants who were alive and cancer free after two years of follow-up, using a Luminex-based multiplex serology panel.
Read Also: Is Hepatitis B Virus A Std
What Are The Symptoms
- Symptoms can take 2 to 6 months to appear.
- Many people who are infected with hepatitis B have either no symptoms or only mild symptoms.
- Symptoms of acute hepatitis B can include fatigue, loss of appetite, joint pain, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, and dark urine. A small number of people will develop jaundice .
- Some people develop chronic hepatitis B and most remain contagious for the rest of their lives. Chronic infection may lead to cirrhosis and/or liver cancer. Most people with chronic hepatitis B are unaware of their infection.
What Is My Risk
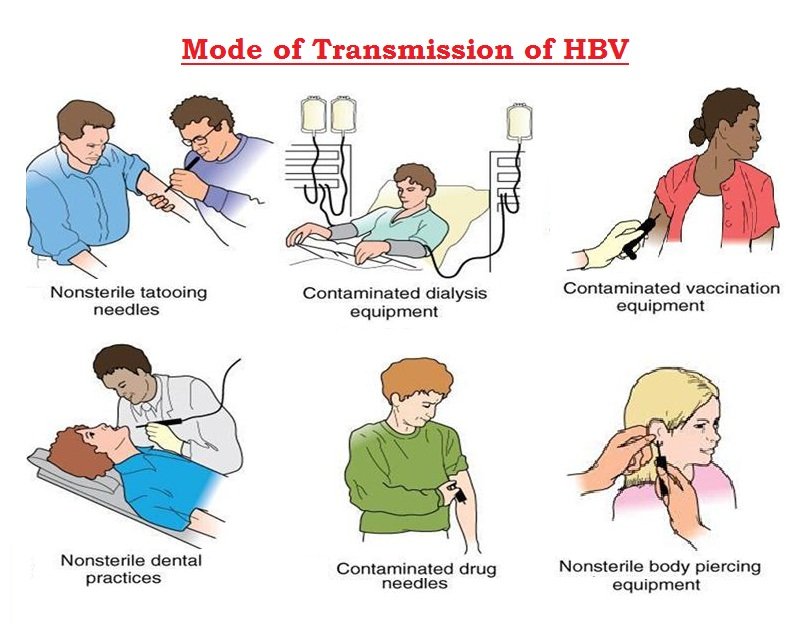
Your risk depends of several factors: destination, length of stay, what you do when you are travelling and whether you have direct contact with blood or other body fluids. In certain destinations, your risk may be higher, as some areas have higher numbers of people with chronic hepatitis B in the general population.
The risk increases with certain activities, such as unprotected sex, sharing needles, tattooing and acupuncture.
Aid and health care workers and anyone who receives medical or dental care with unsterilized or contaminated equipment in a country where hepatitis B occurs are also at greater risk.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Effects On Liver
How Can You Prevent Hepatitis B
You can reduce your risk of contracting hepatitis B by avoiding contact with bodily fluids. For example, do not share drug injection needles or equipment. Use a barrier method, like a condom, during penetrative sex.
Its also important to talk with a doctor about whether youre up to date on your hepatitis B vaccinations.
The recommends that the following groups receive HBV vaccines:
- all infants
- unvaccinated children under the age of 19
- adults ages 19 to 59
- adults over the age of 60 who are considered high risk
- any child or adult who may be considered high risk
If you think you may have been exposed to HBV, talk with a doctor about getting a hepatitis B booster shot. They may also recommend taking a medication called hepatitis B immune globulin within