Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C often doesn’t have any noticeable symptoms until the liver has been significantly damaged. This means many people have the infection without realising it.
When symptoms do occur, they can be mistaken for another condition. Symptoms can include:
- flu-like symptoms, such as muscle aches and a high temperature
- feeling tired all the time
- loss of appetite
Read more about the complications of hepatitis C.
How Is Hepatitis C Diagnosed
Your doctor will determine if you have hepatitis C by using a blood test. The test is called the Hepatitis C Antibody Test. The test checks your blood for antibodies to the hepatitis C virus. If antibodies are detected, it means you have been exposed to hepatitis C. If your viral load is positive, it means you are currently actively infected with hepatitis C. A negative test means that you do not have hepatitis C antibodies and likely do not have hepatitis C.
What If I Am Pregnant And I Have Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C can be passed from a mother to her child during pregnancy and during delivery. Per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , approximately 6 of every 100 infants born to HCV-infected mothers become infected with the virus. The risk is 2-3 times greater when the mother has HIV as well.
You and your doctor should discuss and decide if you should receive treatment for hepatitis C during your pregnancy.
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatitis B Vaccine
How Do People Get Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C virus is found in the blood of people with HCV infection. It enters the body through blood-to-blood contact.
Until reliable blood tests for HCV were developed , people usually got hepatitis C from blood products and blood transfusions. Now that blood and blood products are tested for HCV, this is no longer the typical means of infection.
Currently, people usually get hepatitis C by sharing needles for injection drug use. An HCV-infected woman can pass the infection to her baby during birth. It is also possible to get hepatitis C from an infected person through sexual contact, an accidental needlestick with a contaminated needle, or improperly sterilized medical, acupuncture, piercing, or tattooing equipment.
What Are The Some Of The Most Common Side Effects Of Hepatitis C Medications
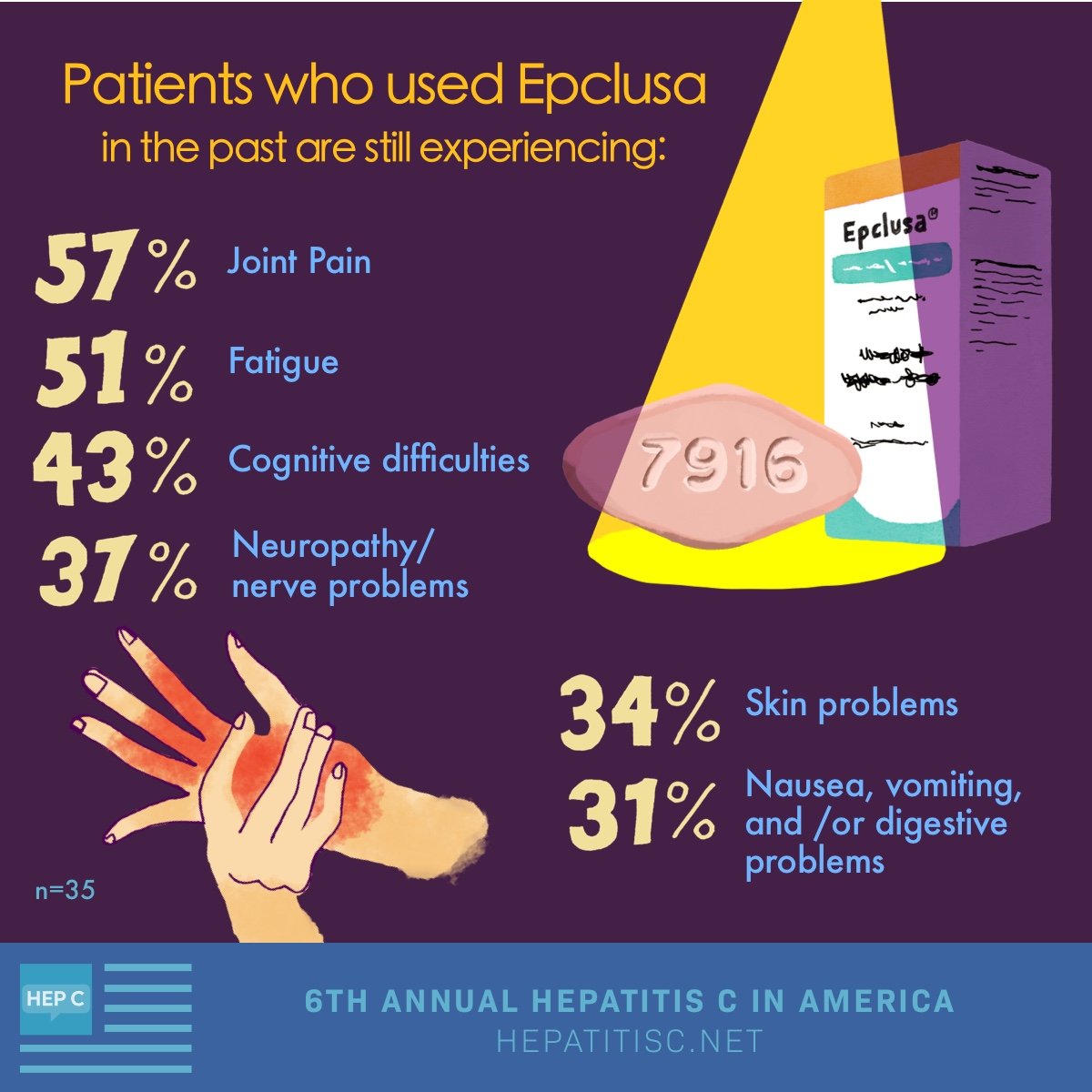
It depends on which drugs you take to treat hepatitis C.
This once-a-day tablet could cure hepatitis in 12 to 16 weeks.
You may have:
- Depression
- Low blood cell counts
Talk to your doctor if youâve had an organ transplant, or if youâre pregnant, breastfeeding, or plan to get pregnant while taking it. It can cause miscarriages. Also tell your dentist or other doctor youâre on it before you have surgery or any other type of procedure.
This comes as a tablet, capsule, or liquid. You take it with food twice a day, in the morning and evening, for 24 to 48 weeks or longer.
You can expect to have:
- Flu-like side effects
- Gastrointestinal problems
- Low blood cell counts
- Low red blood cell count
- Itching
Donât take St. Johnâs wort while youâre on this medication. Also, youâll need to use two methods of birth control to prevent pregnancy in you or your partner while taking ribavirin and for 6 months after you stop.
Youâll take it once a day for 12 weeks. Itâs OK for people who have cirrhosis and have already had some treatment.
It could cause side effects like:
- Headache
- Fatigue
You May Like: How Us Hepatitis C Transmitted
Causes And Risk Factors
HCV causes hepatitis C. People contract the virus through blood-to-blood contact with contaminated blood. For transmission to occur, blood containing HCV must enter the body of a person without HCV.
A speck of blood, invisible to the naked eye, can carry hundreds of hepatitis C virus particles, and the virus is not easy to kill.
The report the following risk factors for developing hepatitis C:
- using or having used injectable drugs, which is currently the most common route in the U.S.
- receiving transfusions or organ transplants before 1992, which is before blood screening became available
- having exposure to a needle stick, which is most common in people who work in healthcare
- being born to a mother who has hepatitis C
The CDC offer advice on cleaning syringes if it is not possible to use clean and sterile ones. Although bleach can kill the HCV in syringes, it may not have the same effect on other equipment. Boiling, burning and using alcohol, peroxide, or other common cleaning fluids to wash equipment can reduce the amount of HCV but might not stop a person from contracting the infection.
It is extremely dangerous to inject bleach, disinfectant, or other cleaning products, so people should make sure they rinse the syringe thoroughly. A person should only ever use bleach to clean equipment if new, sterile syringes and equipment are not available.
People who are at risk due to these factors can have screening to rule out HCV.
- peginterferon alfa-2a
- sofosbuvir
Questions For Your Doctor
When you visit the doctor, you may want to ask questions to get the information you need to manage your hepatitis C. If you can, have a family member or friend take notes. You might ask:
Recommended Reading: How Common Is Hepatitis C
List Of People With Hepatitis C
The infectious disease hepatitis C is caused by the hepatitis C virus , which affects the liver. During the initial infection, people often have mild or no symptoms, and there is typically no symptoms early during chronic infection. This condition can progress to scarring of the liver , and advanced scarring . Over many years however, it often leads to liver disease and occasionally cirrhosis. In some cases, those with cirrhosis will develop complications such as liver failure, liver cancer, or dilated blood vessels in the esophagus and stomach.
What Drugs Treat And Cure Hepatitis C
The treatment of chronic hepatitis C has gone through several generations of medications. Not long ago, treatment was limited to interferon alpha-2b or pegylated interferon alpha-2b , and ribavirin . Interferon and pegylated interferon need to be injected under the skin , while ribavirin is taken by mouth. This combination therapy is infrequently used today, being recommended for only the least common genotypes of hepatitis C virus .
Since 2010, direct-acting antiviral drugs have been in use. The second generation of antivirals for HCV was the protease inhibitors telaprevir and boceprevir , both taken by mouth. These were used in combination with the earlier drugs to increase effectiveness . These drugs are also no longer in common use, and have been replaced by better options.
As more has been learned about how hepatitis C virus multiplies within the liver cells, new drugs continue to be developed to interfere with this multiplication at different stages. As such, we no longer think in terms of generations of drugs, but rather categories of action. Research and development of these direct-acting antivirals continue, with new agents coming to market every few months. Each category is improved and expanded by the addition of new drugs, which are safer and more effective.
Currently available and commonly used direct-acting antiviral drugs include:
- simeprevir
- Muscle aches
Recommended Reading: Best Juice For Hepatitis B
What Do You Do If You Become Ill
Talk to your health care provider about getting tested if you think you:
- are at risk
- may have hepatitis C
If you have hepatitis C, tell those who may have been exposed to your blood or bodily fluids. They should get tested and be treated if necessary. Bodily fluids, like semen and vaginal fluid, are a concern because they could be carrying small amounts of infected blood.
Some adults with hepatitis C will recover from the disease on their own within 6 months. Until your health care provider confirms your recovery status, you are still contagious and can spread the disease.
After recovery, you are no longer contagious because you will not have the disease anymore. But you can get hepatitis C again.
Unfortunately, most adults with hepatitis C:
- cannot recover on their own
- develop a more serious form of the disease if they are sick for longer than 6 months
What Laboratory Tests Diagnose Hepatitis C
Laboratory blood tests will be done to evaluate the patient’s liver function and to look for hepatitis C antibodies . If these tests indicate that the person has hepatitis C, a hepatitis C “viral load” test will be done. This looks for genetic material from the hepatitis C virus and measures the quantity of hepatitis C virus that is circulating in the patient’s blood. This is helpful in determining if treatment is appropriate and to monitor the success of the treatment .
Individuals who had hepatitis C in the past and cleared the virus on their own will have a positive HCV antibody test, but there will be no hepatitis C virus genetic material in the blood. If a person is immunosuppressed due to an immunological condition, cancer chemotherapy, immunotherapy or HIV/AIDS, the test results may be different and need to be evaluated accordingly.
Read Also: What Does Hepatitis Do To The Body
How Do You Get Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C spreads when blood or body fluids contaminated with the hepatitis C virus get into your bloodstream through contact with an infected person.
You can be exposed to the virus from:
- Sharing injection drugs and needles
- Having sex, especially if you have HIV, another STD, several partners, or have rough sex
- Being stuck by infected needles
- Birth — a mother can pass it to a child
- Sharing personal care items like toothbrushes, razor blades, and nail clippers
- Getting a tattoo or piercing with unclean equipment
You canât catch hepatitis C through:
- Breastfeeding
- Casual contact
- Have been on long-term kidney dialysis
- Have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
- Have HIV
- Were born to a mother with hepatitis C
Since July 1992, all blood and organ donations in the U.S. are tested for the hepatitis C virus. The CDC says it is now rare that someone getting blood products or an organ would get hepatitis C. That said, The CDC recommends that anyone over the age of 18 get tested for Hepatitis C. If you haven’t been screened, you should consider having it done.
Learn more about the risk factors for hepatitis C.
Testing For Hepatitis C

Hepatitis C is usually diagnosed using 2 blood tests: the antibody test and the PCR test. These can be as part of a routine blood test or are often combined as a dried blood spot test. The dried blood spot test is similar to a blood sugar test in pricking the finger to get a blood spot that is put on a testing card. This is then sent to a laboratory to be tested.
Another similar test is an antigen test, which if used can often get the results back in 90 minutes. This is very expensive and not many services have access to the machine needed.
Read Also: Does Hepatitis C Cause Itching
Contaminated Needles And Infected Blood
You can get hepatitis C from sharing contaminated needles, syringes and other injecting equipment during recreational drug use. Banknotes and straws used for snorting may also pass the virus on.
Being exposed to unsterilised tattoo and body piercing equipment can also pass hepatitis C on. Occasionally, you can get it from sharing a towel, razor blades or a toothbrush if there is infected blood on them.
Hepatitis C infection is also passed on in healthcare settings, from needle stick injuries or from medical and dental equipment that has not been properly sterilised. In countries where blood products are not routinely screened, you can also get hepatitis C by receiving a transfusion of unscreened blood and blood products.
You can prevent hepatitis C by:
- never sharing needles and syringes or other items that may be contaminated with infected blood
- only having tattoos, body piercings or acupuncture in a professional setting, where new, sterile needles are used
- following the standard infection control precautions, if youre working in a healthcare setting.
How Do Doctors Treat Hepatitis C
Doctors treat hepatitis C with antiviral medicines that attack the virus and can cure the disease in most cases.
Several newer medicines, called direct-acting antiviral medicines, have been approved to treat hepatitis C since 2013. Studies show that these medicines can cure chronic hepatitis C in most people with this disease. These medicines can also cure acute hepatitis C. In some cases, doctors recommend waiting to see if an acute infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
Your doctor may prescribe one or more of these newer, direct-acting antiviral medicines to treat hepatitis C:
You may need to take medicines for 8 to 24 weeks to cure hepatitis C. Your doctor will prescribe medicines and recommend a length of treatment based on
- which hepatitis C genotype you have
- how much liver damage you have
- whether you have been treated for hepatitis C in the past
Your doctor may order blood tests during and after your treatment. Blood tests can show whether the treatment is working. Hepatitis C medicines cure the infection in most people who complete treatment.
Hepatitis C medicines may cause side effects. Talk with your doctor about the side effects of treatment. Check with your doctor before taking any other prescription or over-the-counter medicines.
For safety reasons, talk with your doctor before using dietary supplements, such as vitamins, or any complementary or alternative medicines or medical practices.
You May Like: Medications Used For Hepatitis C
How Will I Know If My Treatment Works
The goal of treatment is to reduce the amount of the hepatitis C virus in your blood to levels that cant be detected after 24 weeks of therapy. The amount of the virus in your blood is called your viral load. At the end of your treatment, your doctor will need to measure your viral load and find out how healthy your liver is. He or she may repeat many of the same tests that were done when you were first diagnosed with hepatitis C.
If your blood has so few copies of the virus that tests cant measure them, the virus is said to be undetectable. If it stays undetectable for at least 6 months after your treatment is finished, you have what is called a sustained virologic response . People who have an SVR have a good chance of avoiding serious liver problems in the future.
Treatment may not reduce your viral load. You may not have an SVR after treatment. If thats true, your doctor will discuss other treatment options with you. For example, if 1 round of treatment did not decrease your viral load enough, your doctor may recommend a second round. Even if treatment doesnt keep you from having active liver disease, lowering your viral load and controlling chronic liver inflammation may help you feel better for a longer time.
The Connection Between Sleep Problems And Hepatitis C
Sleep disturbances affect about 50 percent of people with hepatitis C, according to a study published in November 2014 in the Journal of Circadian Rhythms. Some sleep issues may be due to psychiatric problems, substance abuse issues, or advanced liver disease. In turn, not getting proper rest can increase your risk for depression, anxiety, and not feeling well in general, Graham says.
Effectively treating hepatitis C can alleviate some of the fatigue and sleep problems once the virus is cleared, she says. And although sleep disturbances may also be a side effect of certain hepatitis C treatments, including DAAs, Graham emphasizes that the treatment lasts only 8 to 12 weeks, so these issues are likely temporary.
Also Check: How Soon Can You Test For Hepatitis C
Transmission Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is transmitted through blood, primarily via sharing needles and syringes used for drugs. However, it can also spread via needles used for piercings or tattoos that havenât been properly sanitized. The virus can also be passed through blood transfusion, and a mother with hepatitis C can potentially pass the virus on to their child during birth.
Hepatitis C is not strictly a sexually transmitted infection, but the virus can be transmitted through sexual contact. This primarily can happen if you have sex during menstruation or during anal sex .
Demographic And Clinical Characteristics
summarizes demographic data for the total sample and by group. Groups did not significantly differ in terms of age or race. Although the SUD+ group included a significantly higher percentage of men than the SUDâ groups, all groups were composed primarily of men . The HCV+ groups had completed significantly fewer years of education than the HCVâ group. Groups did not significantly differ in rates of current psychiatric diagnoses or medical conditions.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Test Results Non Reactive
How Can You Get Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a blood-borne disease. The main source of infection is from blood from an infected person.
- Most cases are caused by using contaminated needles or injecting equipment to inject drugs . Even a tiny amount of an infected person’s blood left on a needle is enough to cause spread to others.
- Some people who received blood transfusions or blood prior to 1991 were infected with hepatitis C from some donor blood. Since 1991 all blood and blood products donated in the UK are screened for HCV.
- There is also a risk of contracting hepatitis C from needlestick accidents, or other injuries involving blood spillage from infected people.
- There is a small risk of contracting the virus from sharing toothbrushes, razors and other such items which may be contaminated with infected blood.
- There is even a small risk from inhaling drugs like cocaine, as these can make the inside of your nose bleed. If that happens, tiny spots of blood can fall on to the note you are using and, if that is used by someone else, your blood can travel up their nose and into their bloodstream.
- There is also a small risk from re-used equipment used for tattooing, body piercing, acupuncture, etc.
- There is a small risk that an infected mother can pass on the infection to her baby.
- There is a small risk that an infected person can pass on the virus whilst having sex.
The virus is not passed on during normal social contact, such as holding hands, hugging, or sharing cups or crockery.