Where Can I Find A Hepatitis B Core Antibody Igm Test Near Me
Check our lab finder to locate a collection site in your area.
Note: Result turn around times are an estimate and are not guaranteed. Our reference lab may need additional time due to weather, holidays, confirmation/repeat testing, or equipment maintenance.
Detection Period:
IgM core antibodies are typically detectable within a few weeks of infection and fade to undetectable levels after 4-6 months.
Requirements:
It is recommended that someone taking Biotin stop consumption at least 72 hours prior to the collection of a sample.
Description:
What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis B Surface Antibody And Antigen
An antigen is a substance that induces antibody production. Hepatitis B surface antigen is a protein on the surface of hepatitis B virus.
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are produced by the bodys immune system in response to HBsAg. The presence of adequate hepatitis B surface antibodies in the blood indicates protection against hepatitis B virus infection.
About Our Hepatitis B Core Antibody Test Igm
This blood test detects IgM antibodies to hepatitis B core antigen to indicate an acute hepatitis B infection. After infection with HBV, the IgM antibody is the first antibody produced by the body to fight off the virus.
The recommended minimum window period for Hepatitis B Core Antibody, IgM is:
- 6 weeks post potential exposure hepatitis B can occasionally be detected as early as 3 weeks post-exposure. For the most accurate results, we recommend getting tested after 6 weeks.
Recommended Reading: What Is Acute Hepatic Porphyria
Why Do I Need This Test
You may need this test if your healthcare provider suspects you have a liver infection caused by HBV. You may also need this test if you have symptoms of hepatitis B. Symptoms usually start slowly. Many people have no symptoms or only feel like they have a mild case of the flu. You may not have symptoms until the infection is chronic or severe.
The most common symptom is extreme tiredness. Other symptoms may include:
-
Swelling and confusion. This is in extreme cases.
You may also have this test if you have a history that puts you at risk for being in contact with the virus. Risk factors for hepatitis B infection include:
-
Having sex with someone infected with the virus
-
Living in close contact with someone who has the virus
-
Being a man who has sex with men
-
Being a child born to a mother who has the virus
-
Sharing needles for intravenous drug use
-
Working in a healthcare center where you are exposed to blood
-
Getting a blood transfusion or organ transplant. This is less common with active screening.
Hepatitis B Core Antibody
- Hepatitis B Core Antibody, Total
- Description
-
The Qualitative detection of Hepatitis B virus Core IgG and IgM antibodies in human sera using the FDA approved Abbott ARCHITECT CORE test two-step chemiluminescent immunoassay.
In the first step, sample, assay diluent, and Hepatitis Core Antigen coated paramagnetic microparticles are combined. Anti-HBc antibodies present in the sample binds to the HBcAg coated microparticles. In the second step, anti-human IgG and IgM acridinium-labeled conjugate is added, which binds to IgG and IgM anti-HBc. Then pre-trigger and trigger solutions are added to the reaction mixture. The resulting chemiluminescent reaction is measured as relative light units .
The presence or absence of anti-HBc antibodies in the sample is determined by comparing the chemiluminescent signal in the reaction to the cutoff signal determined from an active ARCHITECT CORE calibration. Specimens with signal to cutoff values 1.00 are considered reactive for HBcAb. Specimens with S/CO values < 1.00 are considered nonreactive.
For Batteries containing HBCA see:
Hepatitis B Antibodies , Quantitative detection of Hepatitis B virus Surface IgG antibody and Hepatitis B virus Core IgG and IgM antibodies
Hepatitis B Battery , Quantitative detection of Hepatitis B virus Surface IgG antibody , Qualitative detection of Hepatitis B virus Surface Antigen and Qualitative detection of Hepatitis B virus Core IgG and IgM antibodies
- Synonyms
Also Check: Who Should Get Tested For Hepatitis C
Acute Hepatitis B Infection
High titers of immunoglobulin M anti-HBc, thought to be predominantly a thymus-independent response, appears early in the course of acute HBV infection, together with HBsAg and HBeAg . Anti-pre-S1 may also occur early in the course of infection. This is accompanied by a vigorous major histocompatibility complex class I restricted cytolytic T lymphocyte response against multiple epitopes throughout the structural and nonstructural proteins of the virus. The CTLs, by direct lysis of infected hepatocytes, are thought to be important in clearance of the virus. There is also some evidence for a role in viral elimination of the cytokines interferon γ and tumor necrosis factor α .
Figure 2. The natural history of acute HBV infection. HBsAg and HBeAg can be detected early in the serum, prior to the onset of clinical hepatitis. Antibody to pre-S1 can sometimes be detected during this early phase. AST (aspartate aminotransferaseis an indication of lysis of infected hepatocytes.
There is a strong MHC class II restricted T helper cell proliferative response to the nucelocapsid antigens, HBcAg and HBeAg, but not to the envelope proteins, during the early phase of acute hepatitis B. The association of recovery with the presence of the MHC class II locus DRB1*-1302 supports an important role for the CD4 response in recovery.
Louis M. Katz MD, Roger Y. Dodd PhD, in, 2013
How Is My Privacy Protected When I Take A Sti Test Online
We guarantee complete discretion, we won’t disclose your results to your GP, employer or insurers under any circumstances.
Your data security is hugely important to us. We take strict measures to ensure result integrity with the minimum of data sharing. We only share the essential details need to conduct testing with our laboratory provider.
We don’t believe in selling your data, individually or in aggregate. And you can request to wipe your account data at any time.
All samples are disposed of following analysis.
You May Like: Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection
Taking A Hepatitis B Test
Testing for hepatitis B is performed on a sample of blood. A doctor, nurse, or other health care provider can obtain a blood sample using a small needle to draw blood from a vein.
At-home hepatitis B testing requires that users carefully follow instructions provided in the test kit to collect a small sample of blood, package the sample, and mail it to a lab for testing.
Read Also: What Is Autoimmune Hepatitis C
What Medical Professionals Are Involved With My Sti Test
All STI testing is conducted entirely by trained biomedical scientists and other healthcare professionals. As a medically-led laboratory, a team of up to 16 consultant doctors are responsible for laboratory clinical governance.
Once test analysis has been completed to our high standards, your results are processed and a personalised report created.
Your report clearly explains your test results and can include comparison against normal ranges, current NHS & NICE guidelines, general health guidance and recommended actions for follow up.
In the event of positive sexual health results, we partner with HealthExpress, the UK’s premier online clinic & registered pharmacy. A GMC registered team UK doctors can review your details and prescribe safe treatment. We will also connect you with specialist sexual health advisors.
And of course, as our results are professional quality, your GP can also find them directly actionable.
Don’t Miss: Symptoms Of Hepatitis B And C In Females
Why It Is Done
Hepatitis B testing is done to:
- Find the type of infection and see if an infection has occurred recently or in the past.
- Screen people who have a higher chance of getting or spreading hepatitis B. This includes doctors, dentists, and nurses.
- Screen blood donors and donor organs to prevent the spread of hepatitis B.
- Find out if a person has antibodies after getting a hepatitis B vaccination. Having antibodies means the vaccine worked.
- Find out if hepatitis B is the cause of abnormal liver function tests.
- See how well treatment of chronic hepatitis B is working.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis And How Do You Get It
Sample Collection And Preparation
Ninety-two blood donors in Ile-Ife, Osun State were enrolled for the study between July and August 2009. Five millilitres of blood was collected from each donor by venepuncture into a labelled sterile container free of anticoagulants or preservative. Each blood specimen was separated by low centrifugation at 500 g for 5 minutes and the serum transferred into labelled cryovial. Thereafter, the sera were kept frozen at -20C until analysed.
Recommended Reading: How Would You Know If You Had Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B Core Antibody Igm
The measurement of IgM antibodies against hepatitis B virus core antigen is used to diagnose acute hepatitis B infection, to determine acute hepatitis B virus infection in the serological window period, that is, hepatitis B surface antigen and the corresponding antibodies are negative, as well as for the differentiation between acute and chronic or previous hepatitis B infection in the presence of positive anti-HBc antibodies.
Hepatitis B virus , has an incubation period of 6 to 23 weeks . It is mainly transmitted by blood and certain secretions of the body. Hepatitis B can also be transmitted through the use of infected needles. This form of hepatitis is more severe than hepatitis A. It damages the liver cells and can lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer. The treatment involves the use of interferon and antiviral drugs in an attempt to control the virus’s proliferation. Vaccination for HBV provides protection for over 20 years.
Hepatitis B virus consists of an outer shell that surrounds an inner “core”. The outer shell contains a protein called hepatitis B surface antigen or Australian antigen. The inner core contains the hepatitis B core antigen . The inner core also contains another protein called e antigen. The human body reacts to the presence of these antigens by producing antibodies against them. Thus, laboratory testing includes tests for the presence of antigens as well as antibodies .
Hepatitis B Core Antibody – Total and IgM
Important Note
Understanding Your Test Results
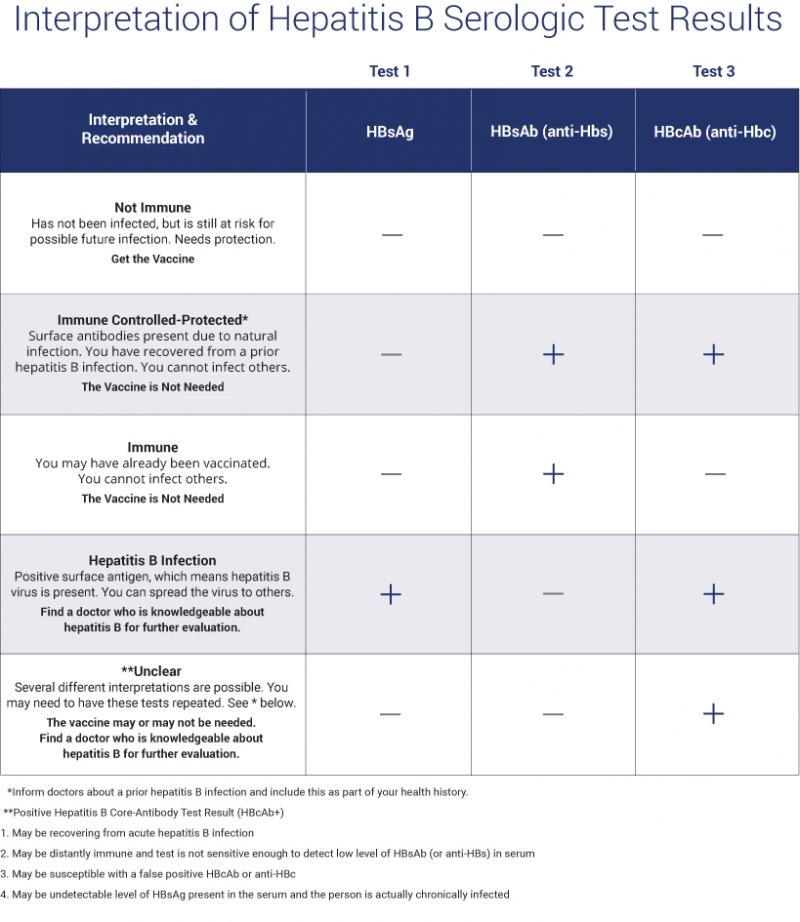
Understanding your hepatitis B blood tests can be confusing. It is important to talk to your health care provider so you understand your test results and your hepatitis B status. Are you infected? Protected? Or at risk? The Hepatitis B Panel of blood tests includes 3 tests and all three results must be known in order to confirm your status.
Below is a chart with the most common explanation of the test results, but unusual test results can occur. Please note that this chart is not intended as medical advice, so be sure to talk to your health care provider for a full explanation and obtain a printed copy of your test results. In some cases, a person could be referred to a liver specialist for further evaluation.
More Detailed Information About Hepatitis B Blood Tests
An acute hepatitis B infection follows a relatively long incubation period – from 60 to 150 days with an average of 90 days. It can take up to six months, however, for a person to get rid of the hepatitis B virus. And it can take up to six months for a hepatitis B blood test to show whether as person has recovered from an acute infection or has become chronically infected .
The following graphic from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention represents the typical course of an acute hepatitis B infection from first exposure to recovery.
According to the CDC, a hepatitis B blood test result varies depending on whether the infection is a new acute infection or a chronic infection.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Treatment For Autoimmune Hepatitis
Counseling Practices That Educate Support And Motivate Clients Undergoing Screening
Clients might need help deciding whether to get screened, understanding the test results, and determining their next steps. Even when services offered through the substance abuse treatment program are limited, discussing testing with clients presents an opportunity for counselors to motivate clients for change by confronting substance use and by making choices that improve their overall health. However, this may also be true when services are offered on-site through substance abuse treatment programs. A study at one methadone clinic that offered hepatitis screening and vaccination revealed that although the majority of clients completed screening , only 54.7 percent of clients who lacked for hepatitis A received vaccinations and only 2.9 percent of clients who lacked immunity for received vaccinations .
The Consensus Panel makes the following general recommendations while recognizing that, in some programs, the counselors role may be limited:
You May Like: Is Hepatitis C Caused By A Virus Or Bacteria
Can I Take The Test At Home
Samples for hepatitis B testing can be collected at home. At-home hepatitis B testing requires a patient to collect a blood sample, typically from a fingerstick using a very small needle provided in the test kit. Once a blood sample is collected, it is prepared according to the instructions contained in the test kit and mailed to a laboratory for testing.
Because there are numerous types of tests for HBV, it is important to look closely at the specific components of any at-home test kit. Many at-home test kits only look for hepatitis B surface antigen .
Don’t Miss: How Long Does Hepatitis C Live On Surfaces
Does Hepatitis B Show Up In Routine Blood Tests
Routine blood tests do not detect hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatitis B tests are specifically done if blood tests show abnormal liver function results, or if a person experiences symptoms or falls into the high-risk category for HBV infection.
A panel of HBV-specific blood tests are required to detect HBV infection.
Hepatitis B Igm Antibody Test
The Hepatitis B IgM Antibody test is used to detect antibodies called IgM in your blood. The test is used to find out whether you are actively infected with the hepatitis B virus . The HBV has an envelope surrounding the central core. During the active stage of infection, your immune system will make IgM antibodies to the core of HBV. These antibodies usually appear in the blood after several weeks after you are first infected with HBV. The core antibodies will not be present in the bodies of people who have had the Hepatitis B vaccine.
Wear a half-sleeved shirt as full sleeved shirt might pose difficulty in pulling up the sleeves. Do not wear sweater or jacket. The patient should avoid taking multivitamins or dietary supplements containing biotin or vitamin B7 which are present in hair, skin and nail supplements and multivitamins for 24 hours before this blood collection. If your blood sample is needed for other tests then fasting may be required in some cases. Please kindly follow the instructions given by the lab.
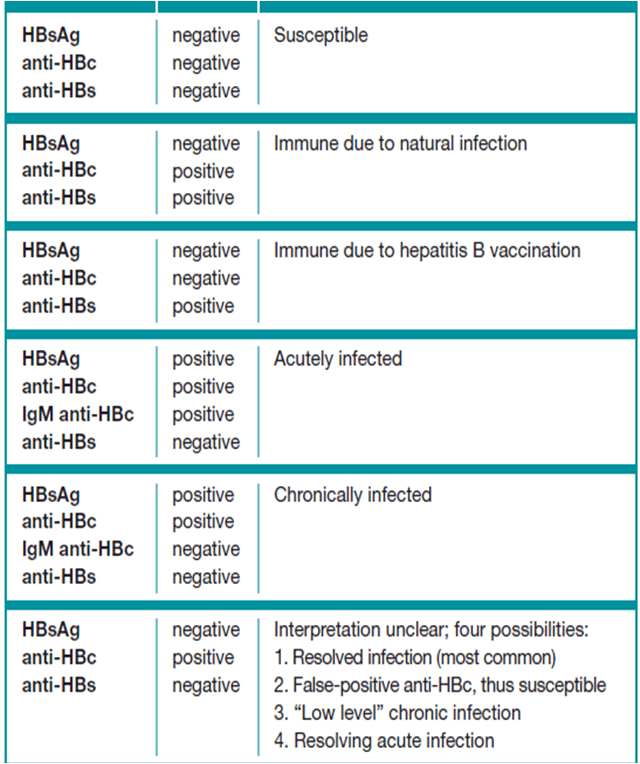
As said earlier the major use of this IgM serum test is to find out whether a person is infected with HBV virus or not. From the test reports, we can conclude that:
If HBsAg negative, anti-HBc positive, anti-HBs negative, then the interpretation is unclear, which means:
- Resolved infection
- Resolving acute infection
| Type |
|---|
| Antibodies are not normally present |
Read Also: Is Chronic Hepatitis C Curable
Hepatitis B Core Antibody Igm Serum
Diagnosis of acute hepatitis B infection
Identifying acute hepatitis B virus infection in the serologic window period when hepatitis B surface antigen and antihepatitis B surface are negative
Differentiation between acute and chronic or past hepatitis B viral infections in the presence of positive anti-hepatitis B core
Can Hepatitis B Antibodies Disappear
With the passage of time, the body hepatitis protective antibodies continuously decreased or disappeared, Therefore, in order to maintain the hepatitis protective antibodies capable of continuous, effective presence needed every three to four booster vaccination once hepatitis b vaccine, hepatitis B core antibody can
Donât Miss: What Does Hepatitis B Come From
You May Like: Can Hepatitis C Be Cured
What Does Hepatitis B Core Antibody Positive Mean
Hepatitis B is an inflammation of the liver caused by a virus. Signs of hepatitis include tiredness or fatigue, fevers, loss of appetite, nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, headache, itchy skin, muscle soreness , jaundice , dark urine, and light stools.Here are some hepatitis B facts:
1. HBV infections will occur in one out of every 20 people at some time in the United States
2. Your risk of HBV is greater if you have sex with someone who has HBV.
3. Your risk is greater if you have a job that places you in contact with human blood.
4. Your risk is greater if you travel to areas where HBV is common.
Some people who donate blood get a letter from the blood bank saying that they are hepatitis B core antibody positive. Dont panic. This does not mean that you have hepatitis B, but you should get a more thorough screening. There are three blood tests that are used to diagnose hepatitis B: hepatitis B surface antigen, hepatitis B surface antibody, and hepatitis B core antibody positive. If your blood tests show that you are hepatitis B core body positive, it means that you either have a present infection or that you were infected in the past. There is a possibility of having a false hepatitis B core antibody positive. Blood banks only screen for hepatitis B core antibody positive and not for surface antigens or antibodies.
You May Like: Can Hepatitis C Spread Through Saliva
Mutant Viruses And Chronic Infection
Anti-HBe-positive patients in the reactivated phase of the disease are also referred to as the HBeAg-negative viremic group. Genomic analyses has revealed that such patients carry natural mutants of the virus that have either reduced levels or complete abrogation of HBeAg production. These variants are selected at the time of, or soon after, seroconversion, and become dominant during the reactivation phase. The most common precore mutation is the G1896A substitution, which creates a premature stop codon in the precursor protein from which HBeAg is elaborated. This mutation affects the stem of the encapsidation signal, but leads to stronger base pairing with the A1896 change in genotypes with a T at position 1858 of the precore region, such as B, C, D, and E. The double mutation affecting the core promoter region is thought to result in decreased transcription of the precore mRNA, with a knockon effect on HBeAg production, while pgRNA production remains the same or is even upregulated. It is now apparent that additional mutations in this region may contribute to this phenotype.
Geoffrey M. Dusheiko, in, 2003
Don’t Miss: How To Treat Hepatic Encephalopathy