Is There Any Treatment For A Coma
Once an individual is out of immediate danger, the medical care team focuses on preventing infections and maintaining a healthy physical state. This will often include preventing pneumonia and bedsores and providing balanced nutrition. Physical therapy may also be used to prevent contractures and deformities of the bones, joints, and muscles that would limit recovery for those who emerge from coma.
Are There Risk Factors For The Development Of Mild Cognitive Impairment
Scientists know that the strongest risk factors for the development of mild cognitive impairment are the same as those for dementia: older age, family history of dementia, and conditions that increase the risk of cardiovascular disease including high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, diabetes, obesity, and stroke.
Why Does Liver Disease/failure Lead To Brain Dysfunction
Unhealthy liver, unhealthy brain.The liver is an important organ which is responsible for a lot of essential tasks in life. Everything that is consumed passes down into the intestines where the food and drink are metabolized into various molecules which are passed into the bloodstream and sent to the liver.
Not only does the liver filter out the bad from the good from what is sent from the intestines, it also plays an important role in producing blood clotting factors and helping to control glucose levels in the blood. When your liver is severely damaged, it can no longer remove these toxic molecules or produce the vital elements. In addition, the sick liver releases toxic molecules. A combination of all these factors affects the brain from properly functioning, causing HE.
What factors cause HE?
Brain edema
Brain edema, an accumulation of water which leads to swelling of the brain, is commonly associated with HE. In acute liver failure, brain edema contributes to an increase in pressure in the skull which can be fatal. In cirrhosis, even though an increase in pressure within the skull is not observed, brain edema is still present. An accumulation of water in the brain is primarily due to swelling of the astrocytes . Astrocytes work very closely with neurons to help maintain normal brain function. However, swollen astrocytes lead to dysfunction in neurons and therefore brain function is impaired.
The following triggers can cause or worsen HE:
You May Like: Unspecified Hepatic Cirrhosis Type Hcc
How Is Hepatic Encephalopathy Managed Or Treated
Treatment varies depending on your symptoms and overall health and how severe the condition is. Its important to take medications for hepatic encephalopathy exactly as prescribed. With treatment, its possible to slow, and sometimes stop, the disease from getting worse. Your doctor may recommend one or both of these treatments:
- Antibiotics: Bacteria in your body make natural toxins from digested foods. Antibiotics, such as rifaximin , stop bacterial growth. As a result, the body produces fewer toxins.
- Laxatives:Lactulose oral solution, a laxative made from lactose sugar, draws toxins into the colon. The laxative stimulates frequent bowel movements that help remove toxins from the body.
Differential Diagnosis For Hepatic Encephalopathy
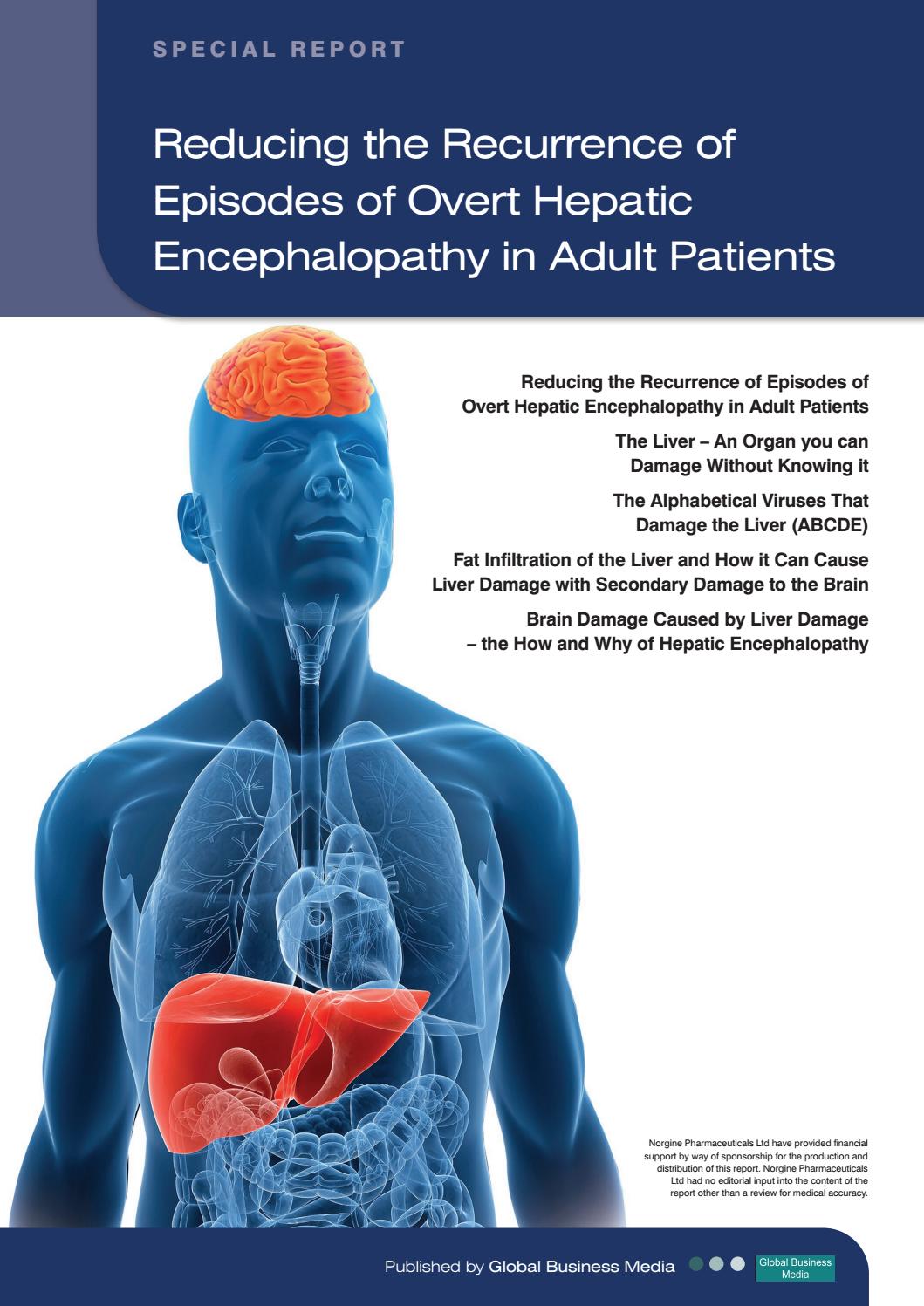
Distinguishing hepatic encephalopathy from other acute and chronic causes of altered mental status may be difficult in patients with cirrhosis. A decision to perform additional neurologic studies should be based on the severity of the patient’s mental dysfunction, the presence of focal neurologic findings , and the patient’s responsiveness to an empiric trial with cathartic agents. Even patients with severe hepatic encephalopathy should demonstrate steady improvement in mental dysfunction after initiation of treatment with lactulose.
Differential diagnoses of encephalopathy are as follows :
-
Intracranial lesions, such as subdural hematoma, intracranial bleeding, stroke, tumor, and abscess
-
Infections, such as meningitis, encephalitis, and intracranial abscess
-
Metabolic encephalopathy, such as hypoglycemia, electrolyte imbalance, anoxia, hypercarbia, and uremia
-
Hyperammonemia from other causes, such as ureterosigmoidostomy and inherited urea cycle disorders
-
Toxic encephalopathy from alcohol intake, such as acute intoxication, alcohol withdrawal, and Wernicke encephalopathy
-
Toxic encephalopathy from drugs, such as sedative hypnotics, antidepressants, antipsychotic agents, and salicylates
-
Organic brain syndrome
Recommended Reading: If You Have Hepatitis B Do You Have Hiv
Ventilator Or Oxygen Mask
Hepatic encephalopathy can cause many mental and physical changes, and even after taking all precautions, there is a possibility for the illness to progress. If it creates difficulty in breathing, a ventilator or oxygen mask may be needed to support the patient until toxins can be removed from the body. Without assistance with breathing, a patient could suffer catastrophic events and need additional medical support.
A ventilator is a machine hooked up to a tube that goes down the throat into the lungs. This means the machine is breathing for the patient. The oxygen mask is less intrusive and covers both the nose and mouth and has oxygen pumped through it. It can help force more oxygen down the throat of the patient to aid in breathing. As the hepatic encephalopathy starts being controlled through different interventions, the patient may be able to come off the ventilator or no longer need the oxygen mask.
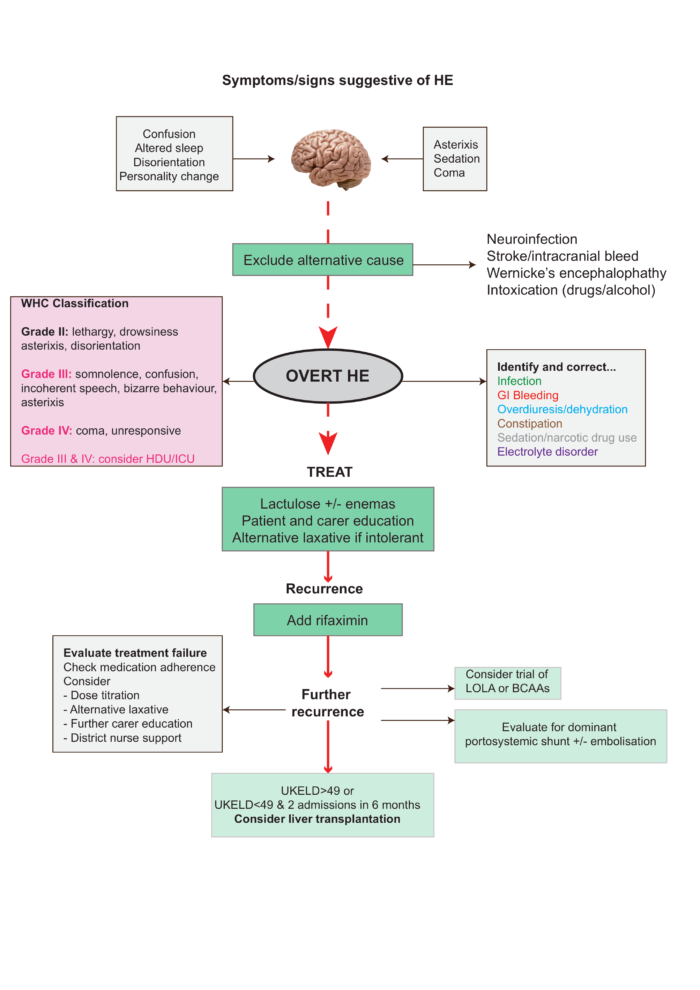
Clinical Scales For Grading He
A number of scales have been devised for the diagnosis of HE the first of its kind was proposed by Parsonsmith and colleagues in 1957. For patients with moderate to severe HE, the Glasgow Coma scale can also be employed.
Table 1: West-Haven Criteria for Hepatic Encephalopathy
| Stage |
|---|
MHE, minimal hepatic encephalopathy.
The West-Haven Classification Table
Stage 0. MHE . Lack of detectable changes in personality or behavior. Minimal changes in memory, concentration, intellectual function, and coordination. Asterixis is absent.
Stage 1. Trivial lack of awareness. Shortened attention span. Impaired addition or subtraction. Hypersomnia, insomnia, or inversion of sleep pattern. Euphoria, depression, or irritability. Mild confusion. Slowing of ability to perform mental tasks. Asterixis can be detected.
Stage 2. Lethargy or apathy. Minimal disorientation. Inappropriate behavior. Slurred speech. Obvious asterixis. Drowsiness, lethargy, gross deficits in ability to perform mental tasks, obvious personality changes, inappropriate behavior, and intermittent disorientation, usually regarding time.
Stage 3. Somnolent but can be aroused, unable to perform mental tasks, gross disorientation about time and place, marked confusion, amnesia, occasional fits of rage, present but incomprehensible speech.
Dont Miss: Liver Cancer From Hepatitis C
Read Also: Can Hepatitis C Be Transmitted Through Sex
What Are The Treatment Options For Hepatic Encephalopathy
Treatment options for hepatic encephalopathy depend on the severity and underlying cause of the condition.
Youll likely need to eat less protein if eating too much protein caused the condition. Since protein is necessary for your body to function properly, a dietician or doctor can create a diet thatll allow you to get enough protein without making your symptoms worse. High-protein foods to avoid include:
- poultry
- eggs
- fish
Medications can also help slow the rate at which your blood absorbs toxins. Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics and lactulose , a synthetic sugar. These medications can draw ammonia, created by intestinal bacteria from your blood, into your colon. Your body will then remove the blood from your colon.
In severe cases that cause difficulty breathing, a ventilator or oxygen mask may be necessary.
Some people with the condition may be eligible to receive a liver transplant.
People with chronic hepatic encephalopathy have better recovery rates than those with the acute version of the condition. The rate of recovery increases if you receive treatment before the condition gets worse.
Hepatic encephalopathy and its symptoms can be reversible with proper treatment.
What Is The Prognosis For People With Hepatic Encephalopathy
People with hepatic encephalopathy can slow, stop or reverse the disease by sticking to their prescribed treatment plan. People who have chronic liver disease may need to keep treating hepatic encephalopathy to stop symptoms from getting worse or coming back.
Its important to see a doctor right away when you first notice signs of hepatic encephalopathy. Untreated hepatic encephalopathy can get worse and increase your risk of serious complications, such as coma.
People who develop end-stage liver disease may need to consider a liver transplant. Youll undergo testing to see if you can withstand such a major procedure. A new liver often gets rid of hepatic encephalopathy.
Also Check: How Soon Can You Test For Hepatitis C
Common Precipitants Of Hepatic Encephalopathy
Some patients with a history of hepatic encephalopathy may have normal mental status while under treatment. Others have chronic memory impairment in spite of medical management. Both groups of patients are subject to episodes of worsened encephalopathy. Common precipitating factors are as follows:
Renal failure: Renal failure leads to decreased clearance of urea, ammonia, and other nitrogenous compounds.
Gastrointestinal bleeding: The presence of blood in the upper gastrointestinal tract results in increased ammonia and nitrogen absorption from the gut. Bleeding may predispose to kidney hypoperfusion and impaired renal function. Blood transfusions may result in mild hemolysis, with resulting elevated blood ammonia levels.
Infection: Infection may predispose to impaired renal function and to increased tissue catabolism, both of which increase blood ammonia levels.
Constipation: Constipation increases intestinal production and absorption of ammonia.
Medications: Drugs that act upon the central nervous system, such as opiates, benzodiazepines, antidepressants, and antipsychotic agents, may worsen hepatic encephalopathy.
Diuretic therapy: Decreased serum potassium levels and alkalosis may facilitate the conversion of NH4+ to NH3. At the authorâs institution, diuretic-induced hypovolemia is the most common reason for patients with previously well-controlled hepatic encephalopathy to present to the emergency room with worsening mental function.
How Should I Use This Medicine
Take this medicine mouth. Follow the directions on the prescription label. Shake well before using. Use a specially marked spoon or container to measure your medicine. Ask your pharmacist if you do not have one. Household spoons are not accurate. Take your doses at regular intervals. Do not take your medicine more often than directed.
You may be directed to take this medicine rectally. If so, you must follow specific directions from your doctor or healthcare professional. Please contact him or her.
Talk to your pediatrician regarding the use of this medicine in children. Special care may be needed.
Overdosage: If you think you have taken too much of this medicine contact a poison control center or emergency room at once.
NOTE: This medicine is only for you. Do not share this medicine with others.
You May Like: Can You Ever Get Rid Of Hepatitis B
Does Having Mild Cognitive Impairment Always Lead To The Development Of Dementia
There are some cases in which the cause of the mild cognitive impairment is due to the effects of a treatable illness or disease. However, researchers have now determined that for most patients with mild cognitive impairment , the MCI is a point along the pathway to dementia. The MCI is considered the stage between the mental changes that are seen in normal aging and early-stage dementia. MCI can be due to a variety of diseases, such as Alzheimers or Parkinsons disease, just as dementia can be due to a variety of reasons such as Alzheimers or Parkinsons disease, dementia with Lewy bodies, vascular dementia, frontotemporal dementia, and other causes.
According to the American Academy of Neurology, of people aged 65 or older who have mild cognitive impairment:
- About 7.5 percent will develop dementia in the first year after diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment
- About 15 percent will develop dementia in the second year
- About 20 percent will develop dementia in the third year
What Are The Symptoms Of Mild Cognitive Impairment
Examples of memory and thinking problems that might be seen in someone with mild cognitive impairment include:
- Memory loss. Forgets recent events, repeats the same questions and the same stories, forgets the names of close friends and family members, forgets appointments or planned events, forgets conversations, misplaces items often.
- Language problems. Has trouble coming up with the desired words. Has difficulty understanding written or verbal information.
- Attention. Loses focus. Is easily distracted.
- Reasoning and judgment. Struggles with planning and problem solving. Has a hard time making decisions.
- Complex decision-making. May struggle, but can complete complex tasks such as paying bills, taking medications, shopping, cooking, household cleaning, driving.
You May Like: Is Hepatitis B And C Contagious
Hepatic Encephalopathy In Small Animals
, DVM, DACVIM, Department of Clinical Sciences, College of Veterinary Medicine, Cornell University
Hepatic encephalopathy develops in liver disorders associated with portosystemic shunting, fulminant hepatic failure, or cirrhosis . Clinical signs vary but involve disturbed sensorium ranging from mild dullness and an inability to respond to basic commands to overt abnormalities, including propulsive circling, head pressing, aimless wandering, weakness, ataxia, amaurosis , ptyalism, dementia, behavior change , collapse, seizures, and coma. Although the pathophysiologic mechanisms of HE are not completely known, synergistic effects between the failure of the liver to detoxify ammonia and other endogenous substances, increased cerebral inflammatory cytokines, impaired brain perfusion, development of neuronal edema, hypoxia, mitochondrial dysfunction, neuroglycopenia, and oxidative injury are important interdependent mechanisms. Increased production of reactive oxygen and nitrogen oxide species are thought to trigger protein and RNA modifications that deleteriously influence brain function. The integrated concept of HE explains episodic variability and heterogeneous precipitating factors that correlate with diverse clinical scenarios.
What Causes Mild Cognitive Impairment
All possible causes of mild cognitive impairment have not been completely discovered. In a small number of cases, another condition may be causing the symptoms seen in mild cognitive impairment. Some of the possible conditions include:
- Depression, stress, and anxiety
- Diseases or conditions that affect blood flow in the brain
- Low vitamin B12 levels or other nutrient levels
- Eye or hearing problems
- An infection
- Side effects of certain prescription or illegal drugs
- History of alcoholism
Many of these causes of mild cognitive impairment are treatable.
Most cases of MCI, however, are due to a variety of diseases, such as Alzheimers or Parkinsons disease.
Read Also: Hepatitis C And Liver Cirrhosis
Could I Have It
HE often starts slowly, and at first, you may not be aware you have it. The stages of HE span from mild to severe and involve numerous symptoms. It is important for you and your family to become familiar with the signs and symptoms of HE so you can tell your doctor right away if you think you may have it. Prompt diagnosis is essential in order that your doctor can initiate the treatment of HE.
If you have been diagnosed with a chronic liver disease, you could have HE if you are experiencing the following symptoms:
- Trouble sleeping at night
If you are experiencing any of the symptoms listed above, please talk with your healthcare provider.
Whats The Difference Between Mild Cognitive Impairment And Decline Due To Normal Aging
Some gradual mental decline is seen with normal aging. For example, the ability to learn new information may be reduced, mental processing slows, speed of performance slows, and ability to become distracted increases. However, these declines due to normal aging do not affect overall functioning or ability to perform activities of daily living. Normal aging does not affect recognition, intelligence, or long-term memory.
In normal aging, a person may occasionally forget names and words and misplace things. With mild cognitive impairment, the person frequently forgets conversations and information that one would ordinarily remember such as appointments and other planned events.
Read Also: What Are Some Symptoms Of Hepatitis
Is Lactulose An Effective Therapy
Using lactulose for hepatic encephalopathy is a very effective therapy. But remember that it does not in any way cure H.E. It only helps to manage the symptoms, especially when it comes to your mental status. However, ensure to follow all of your doctors directions and carry him or her along with how you feel as you use the medication.
Hepatic Encephalopathy Recommended Diet
Have you been diagnosed with hepatic encephalopathy ? This liver-related brain condition can cause various symptoms like lack of focus, confusion, and personality changes. It can result from various conditions but is closely linked to liver cirrhosis. This is one of the various complications linked to cirrhosis of the liver. Its critical to know different facts about this condition including the signs/symptoms, causes, treatments, and prevention. Besides mental changes, HE can also cause other symptoms like sluggish movement, problems moving hands, and even bad breath. The good news is the hepatic encephalopathy diet can help to treat the condition. This involves knowing what to eat and avoid in order to treat the condition effectively.
There are various traditional ways to treat HE. They include prescription medicines to reduce the amount of ammonia the body produces. Meanwhile, there are also certain treatments to avoid like sedatives/tranquilizers due to their stress on the liver. Meanwhile, you can also use diet changes like less protein to help treat HE effectively in a natural/holistic way. This is a safe and effective way to deal with serious cirrhosis complications without using treatments with strong chemicals. Good protein sources include well-cooked white meats and beans.
Also Check: Can Hepatitis B Cause Meningitis
What Causes Hepatic Encephalopathy
When you have liver disease, the liver struggles to filter natural toxins out of the body. Toxins, such as ammonia, accumulate in the blood. Toxins in the bloodstream can travel to the brain and temporarily affect brain function.
People with chronic liver disease are at risk for hepatic encephalopathy. Something usually triggers the condition, such as:
What Is Hepatic Encephalopathy
Hepatic encephalopathy is an often-temporary neurological disorder due to chronic, severe liver disease. A diseased liver struggles to filter toxins from the bloodstream. These toxins build up in the body and travel to the brain. Toxicity affects brain function and causes cognitive impairment.
People with hepatic encephalopathy may seem confused or have difficulty processing their thoughts. Treatments can remove the toxins and reverse the problem. As liver disease progresses, the condition may worsen and become less treatable. Hepatic encephalopathy is also known as portosystemic encephalopathy .
You May Like: Is There Treatment For Hepatitis B