Hepatitis D Virus And Hepatitis B Virus Infection In Amerindian Communities Of The Amazonas State Colombia
Grupo de Gastrohepatologia, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad de Antioquia, UdeA, Calle 70 No. 52-21, Medellin, Colombia
Present Address: Facultad de Investigación Judicial, Forenses y Salud, Tecnologico de Antioquia, Medellín, Colombia
Grupo de Gastrohepatologia, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad de Antioquia, UdeA, Calle 70 No. 52-21, Medellin, Colombia
Grupo de Investigación e Innovación Biomedica, Instituto Tecnológico Metropolitano, Medellin, Colombia
Read Also: What Are The Stages Of Hepatitis B
Causes And Risk Factors Of Hepatitis D
The primary route of transmission for hepatitis D is contact with infected blood or other bodily fluids. This can happen through sharing needles or drug materials with an infected person or having unprotected sex with an infected person.
Although it is rare, hepatitis D can be passed from mother to child during birth.
People cant get hepatitis D through everyday close contact that doesnt involve blood or bodily fluids.
What Else Causes Viral Hepatitis
Some cases of viral hepatitis cannot be attributed to the hepatitis A, B, C, D, or E viruses, or even the less common viruses that can infect the liver, such as cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus, herpesvirus, parvovirus, and adenovirus. These cases are called non-AE hepatitis. Scientists continue to study the causes of non-AE hepatitis.
Read Also: How Many Types Of Hepatitis Are There
What Is Hepatitis E
Hepatitis E, also called enteric hepatitis , is similar to hepatitis A, and more prevalent in Asia and Africa. It is also transmitted through the fecal-oral route. It is generally not fatal, though it is more serious in women during pregnancy and can cause fetal complications. Most patients with hepatitis E recover completely.
How Can Hepatitis B Be Prevented
The hepatitis B vaccine offers the best protection. All infants and unvaccinated children, adolescents, and at-risk adults should be vaccinated. For people who have not been vaccinated, reducing exposure to the virus can help prevent hepatitis B. Reducing exposure means using latex condoms, which may lower the risk of transmission not sharing drug needles and not sharing personal items such as toothbrushes, razors, and nail clippers with an infected person.
You May Like: Autoimmune Hepatitis Primary Biliary Cholangitis
The Hepatitis E Virus
The hepatitis E virus is an RNA virus which is positive-sense, non-enveloped and single-stranded. It is also a self-limiting virus which means it limits its growth by its actions. This means hepatitis E will not lead to any long-term illness or sickness as the host recovers by themselves. It has a fecal to mouth transmission route. It could be clinically compared with hepatitis A. hepatitis e could sometimes develop into an acute severe disease which is rare. Hepatitis e could be very dangerous for a pregnant woman as they mostly die of it.
Will Medicare Pay For A Hepatitis C Vaccine
Hepatitis C is contracted in the same manner as hepatitis B. Unfortunately, theres no vaccine yet to help prevent this type.
Yet, Medicare Part B provides coverage for a one-time hepatitis C screening if you:
- Have a date of birth between the years 1945 and 1965
- Received a blood transfusion before 1992
- Have used or currently use illegal drugs via injection
For those who are high-risk, Medicare Part B covers an annual screening for hepatitis C. Qualifying screenings receive full coverage.
Don’t Miss: How Can Hepatitis B Be Transmitted
Prognosis Of Hepatitis D
Your health outlook depends on whether you were coinfected or superinfected with hepatitis D the prognosis is better for people who were coinfected.
The vast majority of coinfected people experience only the acute phase of the disease most of these people will get better over two to three weeks. Liver enzyme levels typically return to normal within four months.
About 10 percent of people infected with hepatitis D develop a chronic liver infection.
Chronic hepatitis D leads to cirrhosis, or scarring of the liver, in about 70 to 80 percent of cases. Once a person has cirrhosis, the disease may remain stable for as long as 10 years, although a high percentage of people with chronic hepatitis D and cirrhosis eventually die of acute liver failure or liver cancer unless they get a liver transplant.
The overall mortality rate of hepatitis D is unclear, with estimates placing it between 2 and 20 percent. As with most forms of hepatitis, prevention is the best strategy.
Ways Hepatitis B Is Spread
Blood-to-blood and sexual contact
Most infections in Australia are associated with:
- immigration from a high prevalence country
- sharing injecting equipment
- mother-to-baby transmission at or around the time of birth
- child-to-child contact through open sores and wounds
- tattooing or body piercing
- household contact sharing razors and toothbrushes
- receiving blood or blood products before 1971 when screening commenced for hepatitis B virus
You May Like: How Can You Contract Hepatitis
How Do You Get Hepatitis D E
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Ways Hepatitis A Is Spread
Faecal-oral
Faeces containing the virus are transferred from the infected person to another persons mouth.
Most infections in Australia are associated with:
- contaminated food, drink and eating utensils
- hands contaminated via contact with nappies, toys or towels soiled with faeces from an infected person
- oral/anal sexual contact
- travel to countries where hepatitis A is endemic
- injecting and non-injecting drug use
Recommended Reading: How Much Does Hepatitis B Vaccine Cost
How Can Hepatitis D Be Prevented
-
Avoiding hepatitis B infection is the only way to prevent hepatitis D infection. All methods to prevent hepatitis B infection will lead to prevention and reduce the risk of getting hepatitis D.
-
Getting vaccinated: Vaccination is bliss vaccination of hepatitis B is available. All children should be vaccinated. Adults with a high risk of infection are recommended for vaccination. This vaccination is usually an episode of three consecutive injections over six months.
-
Be cautious during tattooing and piercing, inquire about the sterilization of the equipment, and make sure they use sterile needles. Go to a trustworthy place.
-
Stop using drugs, and avoid injectable recreational drugs like heroin and cocaine. Use sterile needles each time in case you are not able to avoid drugs and never share the needle with other people.
-
Always practice safe sex, and use protection such as condoms. Never have unprotected sex with someone who has been infected by any type of hepatitis or any STDs .
You May Like: What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis Ab And C
What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis B

Drugs approved for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B include alpha interferon and peginterferon, which slow the replication of the virus in the body and also boost the immune system, and the antiviral drugs lamivudine, adefovir dipivoxil, entecavir, and telbivudine. Other drugs are also being evaluated. Infants born to infected mothers should receive hepatitis B immune globulin and the hepatitis B vaccine within 12 hours of birth to help prevent infection.
People who develop acute hepatitis B are generally not treated with antiviral drugs because, depending on their age at infection, the disease often resolves on its own. Infected newborns are most likely to progress to chronic hepatitis B, but by young adulthood, most people with acute infection recover spontaneously. Severe acute hepatitis B can be treated with an antiviral drug such as lamivudine.
Also Check: Can Hepatitis C Kill You
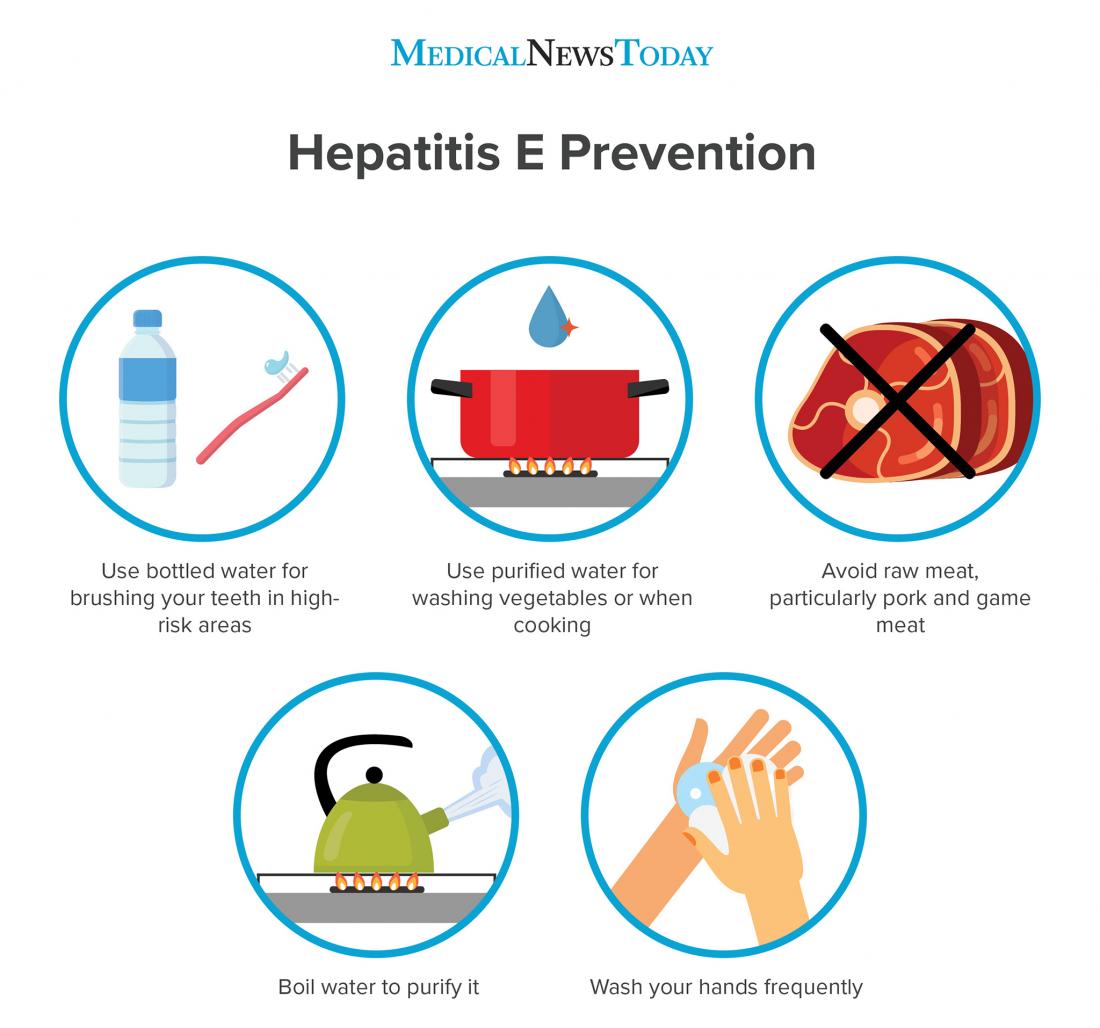
Treatment Prevention Of Hepatitis E
Although, hepatitis E is being cured by itself, and there is no vaccine for it. But somethings should still be done when you find out you have it. Some of this includes
- Visit the nearest hospital and get prescriptions from your doctor.
- Follow the doctors advice.
- Reduce stress by cutting away part of your daily actions till you feel strong again.
- Eat good food and do not drink alcohol or take hard drugs.
Hepatitis E could be prevented by trying to
- Avoid taking contaminated or uncovered water and food.
- Avoid uncooked food or fruit that you didnt peel yourself.
- Stop your child from putting objects in their mouth.
- Wash your dishes in soapy hot water.
Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis A
People most likely to get hepatitis A are
- international travelers, particularly those traveling to developing countries
- people who live with or have sex with an infected person
- people living in areas where children are not routinely vaccinated against hepatitis A, where outbreaks are more likely
- day care children and employees, during outbreaks
- men who have sex with men
- users of illicit drugs
Read Also: Can You Die From Hepatitis B
What Is The Treatment
If you have been diagnosed with hepatitis C, it is important to talk to your healthcare provider about what your options are. Since it can vary, so can the treatment options. If your case is mild, you may have coverage under Medicare Part B with outpatient services.
A doctor may also prescribe a medication to help with treatment. Medicare does not cover most of the prescriptions that are used to treat hepatitis C, except in special inpatient and outpatient situations.
Medicare Part D will cover certain prescription drugs in special situations.
Also Check: How Can You Catch Hepatitis
What Costs Should I Expect To Pay
Even with Medicare coverage, medication treatments for hepatitis C can still be costly. According to a 2017 analysis, the cost could range from $6,297 to $10,889 for the entire treatment course.
Depending on your income, you may be able to qualify for a low-income subsidy. This means youd get assistance to pay for your medication costs. According to the same analysis, Medicare beneficiaries with a low-income subsidy paid between $10.80 and $1,191 for their total hepatitis C treatment costs.
Several FDA-approved medications can treat hepatitis C. The following are some commonly prescribed medications that Medicare plans cover, as well as their estimated costs according to GoodRx.com.
| Medication | |
|---|---|
| 81% | $211$28,658 |
Cost is certainly a factor to consider in your hepatitis C treatment. However, complications from hepatitis C can be life threatening. Ideally, you and your doctor can find a treatment plan that will be affordable, safe, and effective for you.
You May Like: Causative Agent Of Hepatitis C
Don’t Miss: If You Have Hepatitis C Can It Go Away
View 2 Section 8 Wheelchair Accessible Apartments For Rent In Hamilton County Oh Browse Photos Get Pricing And Find The Most Affordable Apartmentsbeautifully Remodeled Handicap Accessible Home 8 $249900 4 Bed 2 Bath 0 Square Feet Property Also For Rent Contact Agent For Details Newly And Beautifully Renovated Handicap Accessible Home Ready For New Owners Depending On The Length Of Tenancy The Property Owner Should Request A Rent Increase On Either March 2 Or January 2 If The Property Owner Chooses To Keep The Tenant On A Month
- 2021. 7. 2. ·AASLD-IDSA HCV Guidance Panel. Hepatitis C guidance 2018 update: AASLD-IDSA recommendations for testing, managing, and treating hepatitis C virus infection. Clin Infect Dis 2018 67: 1477-1492
- 2017. 7. 12. ·The BOP- recommended approach to evaluation and management of HCV includes five basic steps. STEP1: Test for HCV infection with anti-HCV test. See Section 2, Screening for HCV Infection. All sentenced inmates Diagnostic evaluation of other conditions Upon inmate request
- 2013. 11. 6. ·Epidemiology. In the United States, the prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection is 0.2% among children aged 1 to 11 years and 0.4% among adolescents aged 12 to 19 years. 1,2 Modeling based on a recent U.S. census predicts that ~7,200 new cases of pediatric HCV infection occur annually. 3 At least six HCV genotypes are known , with
- 2019. 8. 27. ·HCV Screening. The US Preventive Services Task Force has posted new draft recommendations advising that essentially all US adults aged 18 to 79 years should be screened for hepatitis C virus (HCV
- The USPSTF recommends screening for hepatitis C virus infection in adults aged 18 to 79 years. Grade: B Recommendation. Resources Newly Reported Hepatitis C Infections and Recommendations for Universal Hepatitis C Screening Slide set from April 9, 2020 webinar
Clinical And Laboratory Criteria For Diagnosis
Because cases of hepatitis D are not clinically distinguishable from other types of acute viral hepatitis, diagnosis can be confirmed only by testing for the presence of antibodies against HDV and/or HDV RNA. HDV infection should be considered in any person with a positive hepatitis B surface antigen who has severe symptoms of hepatitis or acute exacerbations.
You May Like: Royal Canin Hepatic Diet For Dogs
What Is Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A accounts for 20 percent to 25 percent of hepatitis cases in developed countries. Hepatitis A is usually transmitted through the fecal-oral route, meaning a person somehow ingests contaminated feces from an infected person. If an infected person did not wash his or her hands properly after using the bathroom, the disease may spread from the persons hands. The incubation period is two to six weeks, during which the infected individual is contagious.
Another cause of hepatitis A is eating shellfish harvested from contaminated water. Developing countries experience hepatitis A epidemics caused by drinking water contaminated with raw sewage.
The prognosis for hepatitis A patients is excellent with self-limiting course, and recovery is complete. About 85 percent of people with hepatitis A recover within three months, and almost all recover within six months. The disease does not become chronic, and there are no long-term health implications.
What Is Hepatitis D
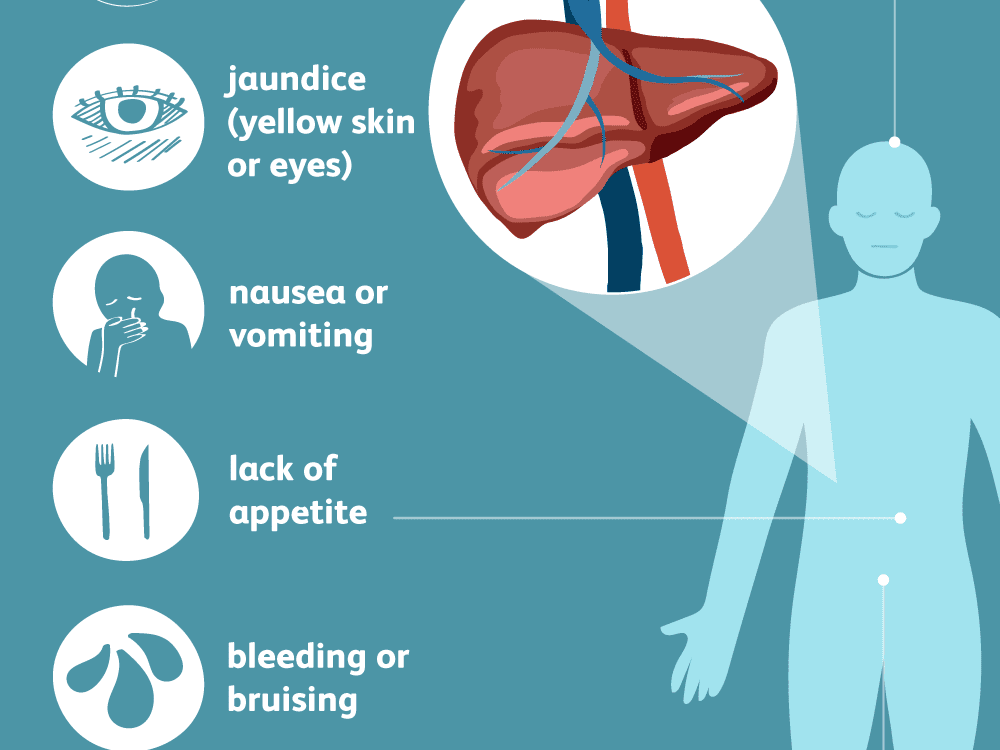
Hepatitis D is a viral infection that causes liver inflammation and damage. Inflammation is swelling that occurs when tissues of the body become injured or infected. Inflammation can damage organs.
Viruses invade normal cells in your body. Many viruses cause infections that can spread from person to person.
The hepatitis D virus is unusual because it can only infect you when you also have a hepatitis B virus infection. In this way, hepatitis D is a double infection. You can protect yourself from hepatitis D by protecting yourself from hepatitis B by getting the hepatitis B vaccine.
Hepatitis D spreads the same way that hepatitis B spreads, through contact with an infected persons blood or other body fluids.
The hepatitis D virus can cause an acute or chronic infection, or both.
You May Like: How Long Is A Hepatitis C Shot Good For
Diagnosis Of Hepatitis D
-
Chronic hepatitis B Hepatitis B, Chronic Chronic hepatitis B is inflammation of the liver that is caused by the hepatitis B virus and that has lasted more than 6 months. Most people with chronic hepatitis B have no symptoms, but some… read more suddenly becomes much worse in people who are chronically infected with hepatitis B.
-
Chronic hepatitis B progresses more rapidly than it typically does.
If hepatitis D is suspected, a blood test to detect antibodies produced by the person’s immune system in response to the hepatitis virus D is done to confirm the diagnosis.
Risk Of Becoming Chronic
The risk for chronic infection varies according to the age at infection and is greatest among young children. Approximately 90% of infants and 25%50% of children aged 15 years will remain chronically infected with HBV. By contrast, approximately 95% of adults recover completely from HBV infection and do not become chronically infected
Read Also: Hepatitis B Antigens And Antibodies
Read Also: How Can One Get Hepatitis C
Does Medicare Cover Hep C Testing
Medicare typically does cover Hepatitis C testing one time if you have risk factors that put you at a high risk for getting Hepatitis C.
Medicare Advantage plans may also cover Hep C testing that meets eligible criteria and is ordered by a doctor. Many Medicare Advantage plans also cover prescriptions drugs, which Original Medicare doesnt cover.
Hepatitis And The Liver
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. The liver is important for a range of functions in the body. These include regulating metabolism, making proteins, storing vitamins and iron, removing toxins and producing bile.
If the liver doesnt work properly, it can cause serious illness or sometimes even death.
Hepatitis may be caused by infection, viruses, chemicals, alcohol and other drug use and other factors.
Chronic hepatitis means ongoing inflammation of the liver, irrespective of the underlying cause.
You May Like: New Drugs For Hepatitis C
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B virus spreads through blood, saliva, tears etc. Still, unlike hepatitis A it is not concentrated in urine, sweat or faeces. One can spread this virus by sharing personal products like toothbrushes, syringes, needles for drug use, etc. This virus can also invade your body if you get tattoos under unhygienic conditions through infected needles.
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis C Cause Low Platelets
Did You Know Hepatitis Facts
- Did you know those diagnosed with both hepatitis b and d are coinfectious?
- Did you know anyone with chronic hepatitis b and develops hepatitis d is called superinfection?
- Did you know that people who have had any kind of viral hepatitis since they are young are not allowed to donate blood?
- Did you know there are four genomes of hepatitis E which infect humans only?
- Did you know hepatitis E is the most common causative of acute viral hepatitis worldwide?
Also Check: What Does Hepatitis C Cause
Who Should Be Vaccinated
Children
- All children aged 1223 months
- All children and adolescents 218 years of age who have not previously received hepatitis A vaccine
People at increased risk for hepatitis A
- International travelers
- Men who have sex with men
- People who use or inject drugs
- People with occupational risk for exposure
- People who anticipate close personal contact with an international adoptee
- People experiencing homelessness
People at increased risk for severe disease from hepatitis A infection
- People with chronic liver disease, including hepatitis B and hepatitis C
- People with HIV
Other people recommended for vaccination
- Pregnant women at risk for hepatitis A or risk for severe outcome from hepatitis A infection
Any person who requests vaccination
There is no vaccine available for hepatitis C.