Do I Need To Have This Test
It’s your choice to be tested for any or all of these infections.
The tests are recommended to:
- protect your health through early treatment and care
- reduce any risk of passing an infection on to your baby, partner or other family members
If you test positive for hepatitis B, HIV or syphilis, your partner and other family members may be offered a test for the infection.
Explainer: Lab Results And Their Interpretation
Before posting your lab results, please read through and abide by the best practices thread first
We all know that its important to have blood tests to know your current Hep B status or to know if youre protected against it. There are a lot of different tests in a panel for Hep B and these can be confusing. Here are short explanations for some of the common ones:
Use this thread to get help if you dont understand your results.
Hi Everich,
You need to be a bit more specific about what the exact test was. What is all the information you have about the test? We cannot answer your question without that information.
Thomas
Hi Everich, there are basically 3 blood tests that are required for a new vs. a chronic hepatitis B infection. Below is a simple summary of these tests. If you could let us know which blood test was indeterminate that would be very helpful.
Hepatitis B surface antigen â If or means the hep b virus is present. This could mean a new infection or a chronic infection . If this test is or , then the hep b virus is not present in the blood.
Hepatitis B surface antibody â this tests for a protective antibody against the hep b virus. This can occur through getting the hep b vaccine or recovery from an exposure to the virus. If or , then it means a person has been protected against the hep b virus either through vaccination or recovery from an infection. Generally, the above test will be or .
Her report says HBV VIRAL LOAD < 34. IU/ml
Screening For Viral Hepatitis During The Domestic Medical Examination Of Newly Arrived Refugees
- New arrivals from certain countries may have been tested for hepatitis B surface antigen and receive 1-2 doses of the hepatitis B vaccine overseas through the Vaccination Program for US-bound Refugees. Domestic clinicians should review the DS-3025 .
- All newly arriving refugees who were born in or have lived in countries with intermediate or high prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus infection should be tested for HBV infection. Serologies for hepatitis B should include HBsAg, hepatitis B surface antibody , total hepatitis B core antibody , and IgM antibody to hepatitis B core antigen .
- Those who do not have HBV infection should be offered hepatitis B vaccination series according to the ACIP-recommended schedule.
- Clinicians should consider further evaluation and management for people whose serologic testing indicates prior HBV infection. In this case, hepatitis B vaccination is not indicated.
You May Like: Hepatitis C Is Caused By
Counseling Practices That Educate Support And Motivate Clients Undergoing Screening
Clients might need help deciding whether to get screened, understanding the test results, and determining their next steps. Even when services offered through the substance abuse treatment program are limited, discussing testing with clients presents an opportunity for counselors to motivate clients for change by confronting substance use and by making choices that improve their overall health. However, this may also be true when services are offered on-site through substance abuse treatment programs. A study at one methadone clinic that offered hepatitis screening and vaccination revealed that although the majority of clients completed screening , only 54.7 percent of clients who lacked for hepatitis A received vaccinations and only 2.9 percent of clients who lacked immunity for received vaccinations .
The Consensus Panel makes the following general recommendations while recognizing that, in some programs, the counselors role may be limited:
Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis B
Anyone can contract hepatitis B. However, certain groups are at greater risk. According to the CDC, the following groups are at highest risk for contracting hepatitis B:
- Infants born to infected mothers
- People who inject drugs or share needles
- Sexual partners of people infected with hepatitis B
- Men who have sex with men
- People living in close proximity to a person with hepatitis B
- Health care workers or others exposed to blood in their work environments
- Hemodialysis patients
Recommended Reading: Herbal Cure For Hepatitis B
What Happens During A Hepatitis Panel
A health care professional will take a blood sample from a vein in your arm, using a small needle. After the needle is inserted, a small amount of blood will be collected into a test tube or vial. You may feel a little sting when the needle goes in or out. This usually takes less than five minutes.
At-home testing kits are available for hepatitis B and C. Usually the test kit will include a sharp device, to prick your finger so you can collect a drop of blood to send to a lab for testing. For more information on at-home testing for hepatitis, talk to your provider.
Dont Miss: What Do You Do If You Have Hepatitis C
Whats The Procedure For A Hepatitis B Titer Test
A hepatitis titer test requires a healthcare professional to draw a small amount of blood for testing.
No special preparation is needed beforehand. If needles or the sight of blood make you anxious, you may want to arrange a drive ahead of time in case you feel faint.
Heres what will typically happen during this test:
Home tests that require a fingerpick are also available. The results of your tests are generally available within 3 days.
Also Check: How Can You Tell If You Have Hepatitis B
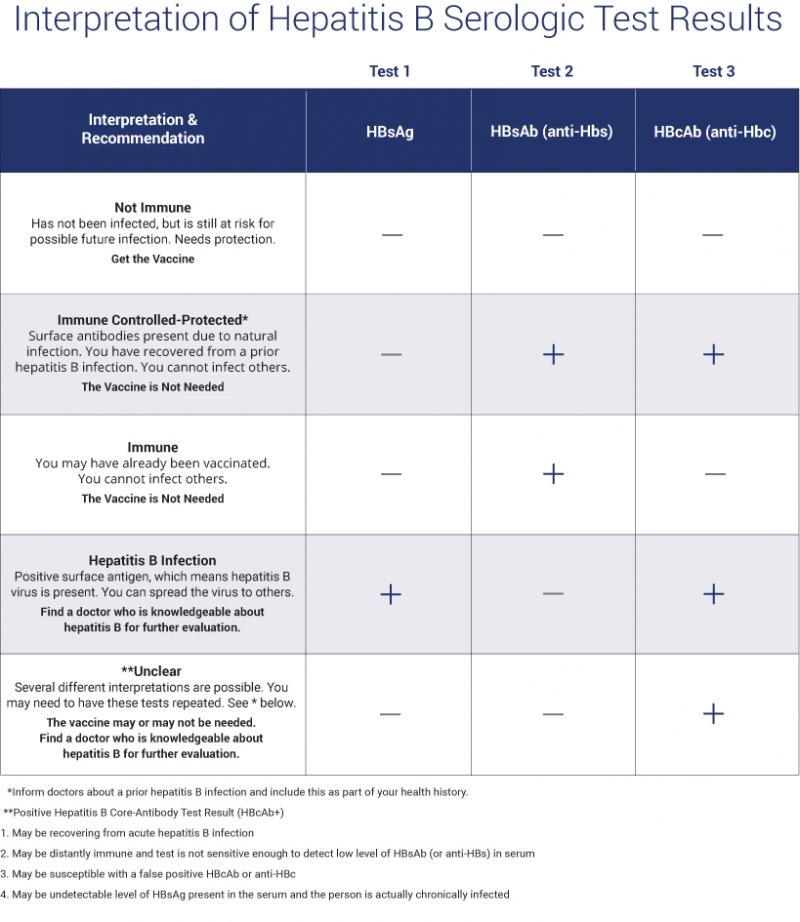
What Do The Results Mean
A hepatitis B blood panel consists of three tests that can be done with just one blood sample:
- Hepatitis B surface antigen . A positive test indicates that youre infected with hepatitis B and that you can spread it to other people. Further tests are needed to see if you have an acute or chronic infection.
- Hepatitis B core antibody . A positive result can indicate a past or current hepatitis B infection, but doesnt mean youre immune. A positive result needs to be interpreted by a doctor by examining the results of the other two tests.
- Hepatitis B surface antibody . A positive test indicates that youre protected from hepatitis B either through previous infection or vaccination .
The combination of these tests can indicate your hepatitis B status and whether you need to be vaccinated. Your test will give a negative or positive result for each category depending on whether your results are above or below the cutoff value.
Most peoples test results fall into the following categories. But its possible to have a result that doesnt fall into one of these groups. If youre reading your results yourself, be careful not to confuse HBsAb with HBcAb.
| HBsAG |
is associated with hepatitis B immunity after vaccination. But research has found that anti-HBs decline over time.
A found that more than 95 percent of people had anti-HBs levels greater than 10IU/L two years after vaccination. But this rate decreased to 70 percent after eight years.
Whats The Hepatitis B Titer Test Used For
A hepatitis B titer test measures antibodies in your blood to see if youre immune either due to vaccination or previous infection.
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that targets your liver. It can be transmitted by coming into contact with the bodily fluids of an infected person. A person with the virus can also infect their child during birth.
Hepatitis B can develop into a chronic infection. Chronic infection occurs when your body cant fight off the virus within six months. Chronic hepatitis B infections most commonly develop less than six years old, especially in infants.
Hepatitis B titer tests can be used to evaluate:
- whether a high-risk person is immune to hepatitis B
- whether hepatitis B immunoglobulin is needed after a needle prick
- men who have sex with men
- people born in countries with a hepatitis B prevalence greater than 2 percent
- people born in the United States not vaccinated as children and with parents born in regions with more than 8 percent hepatitis B prevalence
You may need your titer test results as proof of hepatitis B immunity in order to get into healthcare programs at many schools for example, the nursing program at Lone Star College. In the United States, employers are not allowed to withdraw a job offer if they learn you have hepatitis B.
Read Also: What To Do If I Have Hepatitis B
Classical Hbv And Hcv Virological Tests
Key pointi.e.
- European Association for the Study of the Liver
J Hepatol.
- European Association for the Study of the Liver
J Hepatol.
- European Association for the Study of the Liver
J Hepatol.
- European Association for the Study of the Liver
J Hepatol.
Ann Intern Med.Gastroenterology.
- European Association for the Study of the Liver
J Hepatol.
- European Association for the Study of the Liver
J Hepatol.
- European Association for the Study of the Liver
J Hepatol.
- European Association for the Study of the Liver
J Hepatol.
Ann Intern Med.
- European Association for the Study of the Liver
J Hepatol.
Evolution Of Serologic Tests After Infection And Vaccination
To optimally understand and interpret HBV serologic diagnostic tests, it is important to understand how serologic markers evolve over time after initial infection and after receiving hepatitis B vaccine. Following acute HBV infection, the evolution of the pattern of serologic markers depends on the outcome of the host immune response, which typically correlates with the patient’s age. Adults have resolution of HBV infection approximately 90% of the time, whereas 30 to 90% of young children will fail to resolve the infection and thus develop chronic HBV infection. The following discussion will summarize the evolution of key serologic markers during acute HBV infection with recovery, chronic HBV, and post-immunization, with each topic accompanied by corresponding animations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Hepatitis B Serology Training as audio-visual guides to aid in understanding.
You May Like: The Signs Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B Blood Test Panel
A Hepatitis B Blood Test Panel includes a Hepatitis B Core Antibody Total , Hepatitis B Surface Antigen , Hepatitis B Surface Antibody .
CPT Code: See Individual Tests
Also Known As:
No fasting required. Stop biotin consumption at least 72 hours prior to the collection.
Test Results:
2-3 days. May take longer based on weather, holiday or lab delays.
CPT Code: See Individual Tests
Also Known As:
No fasting required. Stop biotin consumption at least 72 hours prior to the collection.
Test Results:
You May Like: Hepatitis B And Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
Evaluation Of Individuals Suspected Of Having An Hbv Infection
Given the perinatal and childhood vaccination programs already in place in North America, most HBV-infected individuals will likely present with chronic infection. Such individuals are likely to have risk factors that include immigration from high endemicity regions, injection drug use or sexual contact with an infected person 1) . Therefore, the present guideline will provide diagnostic recommendations first for individuals suspected of having chronic HBV infection and, subsequently, for those with acute infection. The diagnosis of HBV infection in any individual has important management implications, including appropriate counselling, monitoring and/or treating and vaccinating family or at-risk contacts.
Read Also: Why Does Hepatitis Cause Joint Pain
What Are The Risk Factors For Contracting Hepatitis B
You are at high risk if you:
- Have unprotected sex with an infected person
- Have unprotected sex with multiple partners
- Have a sexually transmitted infection
- Were born to a Hepatitis b infected mother
- Use injection drugs and share contaminated materials
- Receive a tattoo or piercing with unsterilized equipment
What To Expect From Your Doctor
Hep B can be very complex and not every doctor has a good understanding of it. You can check our directoryfor a hep B specialist doctor or use our resources to help you and your doctor through hep B testing.
Your doctor might ask you about your family history of hep B or liver disease, where you were born, and any other possible exposures to hep B such as unprotected sex or injecting drug use.
You can tell your doctor as much or as little as you feel comfortable with. More information can help your doctor make the best decisions for your health, but what you share with them is up to you.
You might be able to access healthcare via your computer or phone.
Don’t Miss: How Do I Know If I Have Hepatitis
Addressing Hepatitis For The First Time
It is crucial that a treatment counselor or health professional use a nonjudgmental and compassionate tone. Clients need to feel comfortable disclosing information about their health and risky behaviors. The following strategies can help initiate the conversation:
- Display posters, literature, or other -related items that could help prompt the client to ask questions about hepatitis. .
- Assess clients ability to discuss , based on their degree of openness in the counseling session, the amount of detail they provide in their responses, and the length of the therapeutic relationship.
- Raise the subject in a way that avoids making clients feel defensive or afraid. Consider introducing the subject by making parallels with other conditions that have been discussed. Say, for example, You said you were tested for HIV several times. Were you ever tested for viral ? or You mentioned that your friend is sick with HIV. Have you been tested for HCV or HIV? Tell me about those tests.
- Be patient and allow time for multiple, short conversations about the subject. This might ease feelings of fear, anxiety, or shame.
Detection Of Antiviral Resistance
Lamivudine monotherapy has been reported to be associated with the rapid emergence of antiviral resistance in 15% to 60% of treated individuals . Resistant HBV genomes have mutations in codon 552 within the YMDD motif of the reverse transcriptase/polymerase where a valine or isoleucine replaces the methionine. Resistance is typically clinically manifested by significant elevations in ALT after an initial decline in response to treatment. Prolonged treatment after development of the YMDD mutant is controversial, although improvement in liver pathology with decreased fibrosis may occur with continuation of treatment. Concerns about disease flares after stopping lamivudine have been raised . The development of genotypic resistance can be documented by molecular sequencing or by the INNO-LiPA HBV DR assay , which involves hybridization of amplified HBV-DNA fragments onto specific nucleotide probes that have been immobilized on nitrocellulose strips .
Don’t Miss: Where Can I Get Hepatitis A Vaccine
Understanding Your Test Results
Understanding your hepatitis B blood tests can be confusing. It is important to talk to your health care provider so you understand your test results and your hepatitis B status. Are you infected? Protected? Or at risk? The Hepatitis B Panel of blood tests includes 3 tests and all three results must be known in order to confirm your status.
Below is a chart with the most common explanation of the test results, but unusual test results can occur. Please note that this chart is not intended as medical advice, so be sure to talk to your health care provider for a full explanation and obtain a printed copy of your test results. In some cases, a person could be referred to a liver specialist for further evaluation.
More Detailed Information About Hepatitis B Blood Tests
An acute hepatitis B infection follows a relatively long incubation period – from 60 to 150 days with an average of 90 days. It can take up to six months, however, for a person to get rid of the hepatitis B virus. And it can take up to six months for a hepatitis B blood test to show whether as person has recovered from an acute infection or has become chronically infected .
The following graphic from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention represents the typical course of an acute hepatitis B infection from first exposure to recovery.
According to the CDC, a hepatitis B blood test result varies depending on whether the infection is a new acute infection or a chronic infection.
Preparation Prior To Transport
Label the specimen container with the patients full name, date of collection and one other unique identifier such as the patients date of birth or Health Card Number. Failure to provide this information may result in rejection or testing delay.
Centrifuge if using SST. Place specimen in biohazard bag and seal. Specimens should be stored at 2-8°C following collection.
Specimens more than the following number of days post collection will not be tested:
- > 6 days for Hepatitis B surface antigen
- > 7 days for Hepatitis B e Antigen and Hepatitis B e Antibody
- > 10 days for Hepatitis B core Antigen and Hepatitis B surface Antibody
You May Like: Hepatitis B Core Ab Total