Where Is It Found
HAV is common in areas with poor sanitation and restricted access to clean water. In countries with high HAV endemicity, as in some African and Asian countries, many adults are immune to HAV as a result of infection during childhood, and epidemics of hepatitis A are uncommon. In areas such as Central and South America, Eastern Europe and parts of Asia with intermediate HAV endemicity, childhood transmission is less common and so more adolescents and adults are vulnerable to infection outbreaks then become more likely. In countries such as Australia, the United States and Western Europe where there is low HAV endemicity, infection is less common in the general community, but disease occurs among people in high-risk groups as community-wide outbreaks.
How Can I Learn More
- Ask your health care provider.
- Visit the website of the Food and Drug Administration for vaccine package inserts and additional information at www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/vaccines.
- Contact the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention :
- Call 1-800-232-4636 or
- Visit CDC’s website at www.cdc.gov/vaccines.
Vaccine Information Statement
Hepatitis A & B Combination Vaccine
Hepatitis A & B combination vaccineHepatitis A & B Quick facts4 doses 0, 7, 2130 days and 12 months apart at least 21 days prior to travel
-
Hepatitis A and B are two viruses that affect your liver’s ability to function.
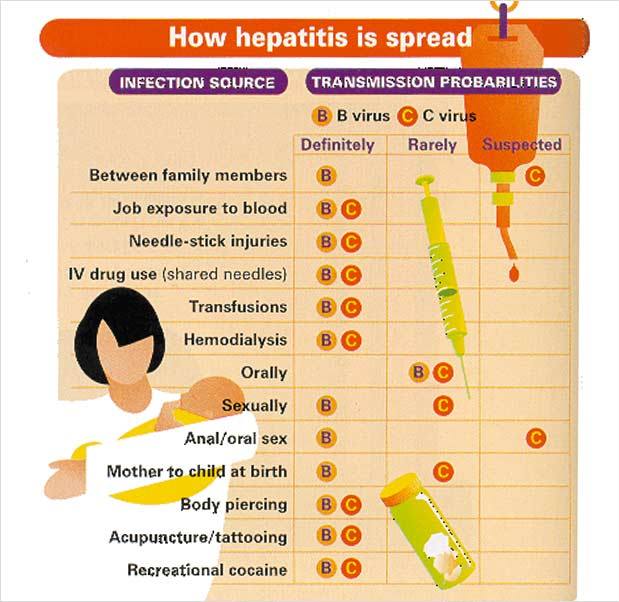
Hepatitis A is usually spread through ingesting contaminated food or water or close contact with an infected person. The hepatitis A virus can cause a flu-like illness, a yellowing of the skin or eyes along with severe stomach pains and diarrhea.
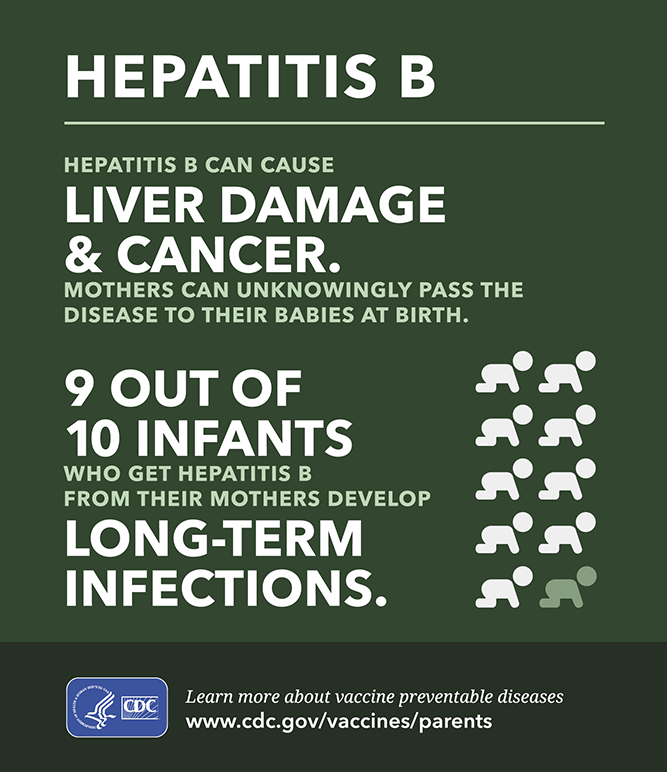
Hepatitis B is a highly contagious, serious liver disease caused by the hepatitis B virus. It spreads through contact with the blood or other body fluids of an infected person, including contact with objects that could have blood or body fluids on them such as toothbrushes and razors. It can cause a short-term flu-like illness, or long-term infection that can lead to liver damage, liver cancer or death. Babies and young children infected with hepatitis B are more likely to get this chronic form of the disease.
-
The hepatitis A & B combination vaccine contains both hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccines to prevent these two forms of hepatitis. Its administered either as 3 doses over 6-month period or 3 shots administered over 1 month with the addition of a booster shot after 1 year.
Learn more about the hepatitis A & B vaccines from the CDC:
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Surf Ab Quant 3.1
Persons With Chronic Diseases
Refer to Immunization of Persons with Chronic Diseases in Part 3 for additional general information about vaccination of people with chronic diseases.
Chronic renal disease and patients on dialysis
HA vaccine is recommended for people with chronic renal disease or undergoing dialysis if they are at increased risk of HA infection or severe HA . A study assessing the immune response of hemodialysis patients to standard doses of HA vaccine demonstrated a good HA antibody response and no serious adverse effects.
Chronic liver disease
HA immunization is recommended for susceptible persons with chronic liver disease, including those infected with hepatitis C and chronic HB carriers, because they are at risk of more severe disease if infection occurs. Vaccination should be completed early in the course of the disease, as the immune response to vaccine is suboptimal in advanced liver disease.
Non-malignant hematologic disorders
For Those Needing The First Dose Of The Hepatitis A Vaccine
Individuals
If you are 19 and older and have health insurance:
- Your healthcare provider
- University of Louisville Pharmacy, 550 S. Jackson St.
- 7:30am – 7:00pm Monday – Thursday
- 7:30am – 5:00pm Friday
If you are 19 and older and do NOT have health insurance:FOR THOSE ON MEDICARE: Medicare Part D should cover the cost of your Hepatitis A vaccination. Click HERE for more information you can share with your healthcare provider or pharmacy. Call Medicare or your plan provider first to understand any restrictions or cost that may be involved.
For hepatitis A vaccines for children contact:
- Your healthcare provider
You May Like: Medicine For Hepatitis C Virus
Where Can People Get The Hepatitis A Vaccine
Talk to your medical provider about the hepatitis A vaccine. In South Carolina, adults 18 years and older can get vaccinated at some local pharmacies without a prescription, depending on your insurance coverage. To search for a nearby pharmacy that offers vaccines, visit www.vaccinefinder.org.
DHECs local health departments also provide hepatitis A vaccines. DHEC has an Adult Vaccine Program that provides low-cost vaccines for uninsured or underinsured individuals who are 19 years and older.DHECs local health departments are currently providing no-cost hepatitis A vaccines to individuals in at-risk groups .
What Happens If I Miss A Dose
Contact your doctor if you miss a booster dose or if you get behind schedule. The next dose should be given as soon as possible. There is no need to start over.
Be sure you receive all recommended doses of this vaccine. You may not be fully protected against disease if you do not receive the full series.
You May Like: How Did I Get Hepatitis B
What Is The Hepatitis A Vaccine
Hepatitis A vaccination provides the best form of protection against the virus. Most vaccinations come in two doses given six months apart. Most children are vaccinated around one-year-old.
Studies indicate the vaccine protects for 40 years or more.
Immune globulin is an alternative to hepatitis A vaccination that provides short-term protection for travellers. This is also offered at Passport Health locations across North America.
Who Should Have The Hepatitis A Vaccine
People usually advised to have the hepatitis A vaccine include:
- close contacts of someone with hepatitis A
- people planning to travel to or live in parts of the world where hepatitis A is widespread, particularly if sanitation and food hygiene are expected to be poor
- people with any type of long-term liver disease
- men who have sex with other men
- people who inject illegal drugs
- people who may be exposed to hepatitis A through their job this includes sewage workers, people who work for organisations where levels of personal hygiene may be poor, such as a homeless shelter, and people working with monkeys, apes and gorillas
Contact your GP surgery if you think you should have the hepatitis A vaccine or you’re not sure whether you need it.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Quant
The Above Policy Is Based On The Following References:
How Is This Vaccine Given
This vaccine is given as an injection into a muscle. You will receive this injection in a doctor’s office or other clinic setting.
The hepatitis A and B vaccine is given in a series of 3 shots. The booster shots are given 1 month and 6 months after the first shot.
If you have a high risk of hepatitis infection, you may be given 3 shots within 30 days, and a fourth shot 12 months after the first.
Your individual booster schedule may be different from these guidelines. Follow your doctor’s instructions or the schedule recommended by the health department of the state you live in.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis A Symptoms And Treatment
Who Is At Risk For Infection
Anyone who is not immune to hepatitis A can get hepatitis A infection. Food-borne outbreaks occur sporadically throughout the USA. Certain groups of people do have a higher risk of developing HAV infection and should be vaccinated:
- Persons experiencing homelessness
- People who eat raw or under-cooked shellfish
Hepatitis A Vaccine: Canadian Immunization Guide
For health professionals
Last partial chapter update
: The immunoglobulin dosage for Hepatitis A pre-exposure and post-exposure prophylaxis was increased based on the Product Monograph update for GamaSTAN®, which is available on Health Canada’s Drug Product Database.
Last complete chapter revision: March 2018
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Hepatitis From Saliva
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a contagious liver infection with potentially severe symptoms. It can lead to lifelong illness if it becomes chronic.
The two most common forms of hepatitis B are:
- Acute Hepatitis B A short-term illness occurring 6 months after exposure. It can lead to chronic hepatitis infection.
- Chronic Hepatitis B A long-term illness that affects the liver. Nearly 250 million people worldwide have chronic infection.
Hepatitis A And B Vaccine Side Effects
Get emergency medical help if you have any of these signs of an allergic reaction:hives difficulty breathing swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Keep track of any and all side effects you have after receiving this vaccine. When you receive a booster dose, you will need to tell the doctor if the previous shot caused any side effects.
You should not receive a booster vaccine if you had a life-threatening allergic reaction after the first shot.
Becoming infected with hepatitis is much more dangerous to your health than receiving this vaccine. However, like any medicine, this vaccine can cause side effects but the risk of serious side effects is extremely low.
You may feel faint after receiving this vaccine. Some people have had seizure like reactions after receiving this vaccine. Your doctor may want you to remain under observation during the first 15 minutes after the injection.
-
numbness, tingling, or burning pain
-
red or blistering skin rash with burning or tingly feeling
-
easy bruising or bleeding or
-
unexplained muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness.
Common side effects include:
-
headache or
-
tired feeling.
This is not a complete list of side effects and others may occur. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report vaccine side effects to the US Department of Health and Human Services at 1-800-822-7967.
Also Check: How Do You Catch Hepatitis B And C
Who Should Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
The CDC recommends it for all babies, who should get their first dose as newborns.
Other people who need it include:
- People younger than age 19 who haven’t been vaccinated
- Anyone who has a sex partner with hepatitis B
- People who are sexually active but arenât in a long-term relationship in which both partners are monogamous
- Anyone being evaluated or treated for an STD
- Men who have sex with men
- People who share needles used to inject drugs
- Anyone who lives with someone who has hep B
- Anyone whose job routinely puts them at risk for coming in contact with blood or blood-contaminated body fluids
- People with end-stage kidney disease
- People who live and work in facilities for people who are developmentally disabled
- Travelers to regions with moderate to high rates of hepatitis B
- People with chronic liver disease
- People with HIV infections
You should not get the vaccine if you had a severe allergic reaction to an earlier dose or are allergic to yeast, because yeast is used to make the vaccine.
What Is Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is a virus affecting the liver. It usually spreads through contaminated food or water. Unlike other forms of hepatitis, A cannot become a chronic infection.
Symptoms often appear two to six weeks after exposure. This means a traveler can visit a country and return not knowing theyre infected.
Some common hepatitis A symptoms include:
- Fatigue
These will persist for a few weeks, severe cases can last months. Death is rare.
Also Check: What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis B
How And When Do Doctors Give Vaccines
For the hepatitis A vaccine:
You should get two doses, given as shots, 6 months apart for complete protection. The virus in the vaccine is killed .
Children should get the first dose between 12 and 23 months of age. Children older than age 2 can get the first dose at their next doctorâs visit.
If you need the vaccine because of upcoming travel, get it at least 1 month before you go.
For the hepatitis B vaccine:
For long-lasting immunity, you need three to four doses, depending on which type of vaccine is used. You get them as shots.
Children should get their first dose at birth and complete the series by age 6 months. Usually, the baby would get a second dose at 1 month old and the third dose at 6 months.
Babies born to women who have hepatitis B need a shot of hep B antibodies, as well as their first hep B vaccine shot, when theyâre born. They will also need follow-up blood tests to make sure theyâre OK.
Catch-up vaccinations are recommended for children and teens who were never vaccinated or who did not get all three shots.
If you’re an adult who wants to be vaccinated, you should talk about it with your doctor or pharmacist. If you are considering both vaccines, ask your doctor about vaccines that combine hep A and B.
Show Sources
What If There Is A Serious Problem
An allergic reaction could occur after the vaccinated person leaves the clinic. If you see signs of a severe allergic reaction , call 9-1-1 and get the person to the nearest hospital.
For other signs that concern you, call your health care provider.
Adverse reactions should be reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System . Your health care provider will usually file this report, or you can do it yourself. Visit the VAERS website at www.vaers.hhs.gov or call 1-800-822-7967. VAERS is only for reporting reactions, and VAERS staff members do not give medical advice.
Read Also: Is Hepatitis C Related To Aids
Should I Get The Hepatitis A Vaccine
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A vaccination is recommended for:
- Travelers to countries that have high rates of hepatitis A
- Family members or caregivers of a recent adoptee from countries where hepatitis A is common
- Men who have sex with men
- People who use injection and non-injection drugs
- People with chronic liver diseases, such as hepatitis B or hepatitis C
- People who are teated with clotting-factor concentrates
- People who work with hepatitis A infected animals or in a hepatitis A research laboratory
- People who are experiencing homelessness
- People age 40 and older at increased risk for hepatitis A infection, or who are at increased risk for severe disease from hepatitis A infection who also have other risk factors
- People age 19 or older at increased risk for hepatitis A infection, or who are at increased risk for severe disease from hepatitis A infection who also have other risk factors
Health care providers recommend that all children receive a hepatitis A vaccination at around 1 year of age, but many adults have never received the vaccine because it only became available in 1995.
Health care personnel and patients with the following conditions should discuss the hepatitis A vaccination with their health care provider: pregnancy, immunocompromising conditions, HIV infection, heart disease, chronic lung disease, chronic alcoholism, asplenia, kidney failure.
You should NOT get the hepatitis A vaccination or you should wait, if you:
Before Taking This Medicine

Hepatitis A and B vaccine will not protect you against infection with hepatitis C or E, or other viruses that affect the liver. It will also not protect you from hepatitis A or B if you are already infected with the virus, even if you do not yet show symptoms.
You should not receive this vaccine if you are allergic to yeast or neomycin, or if you have ever had a life-threatening allergic reaction to any vaccine containing hepatitis A or hepatitis B.
Before receiving this vaccine, tell the doctor if you have:
-
an allergy to latex rubber or
-
a weak immune system caused by disease, bone marrow transplant, or by using certain medicines or receiving cancer treatments.
You can still receive a vaccine if you have a minor cold. In the case of a more severe illness with a fever or any type of infection, wait until you get better before receiving this vaccine.
FDA pregnancy category C. Tell your doctor if you are pregnant. It is not known whether hepatitis A and B vaccine will harm an unborn baby. However, not vaccinating the mother could be harmful to the baby if the mother becomes infected with a disease that this vaccine could prevent. Your doctor will decide whether you should receive this vaccine, especially if you have a high risk of infection with hepatitis.
If you are pregnant, your name may be listed on a pregnancy registry. This is to track the outcome of the pregnancy and to evaluate any effects of this vaccine on the baby.
You May Like: What Are The Symptoms Of Having Hepatitis C