Needlestick Injuries In Healthcare Settings
Nurses, physicians, and all healthcare professionals who routinely use needles while providing medical care are at risk for needlestick injuries. In fact, it is estimated that more than 600,000 needlestick injuries happen each year, with nurses being at highest risk. An average of about 2 percent of needlestick injuries where there has been exposure to the virus will result in acute hepatitis C.
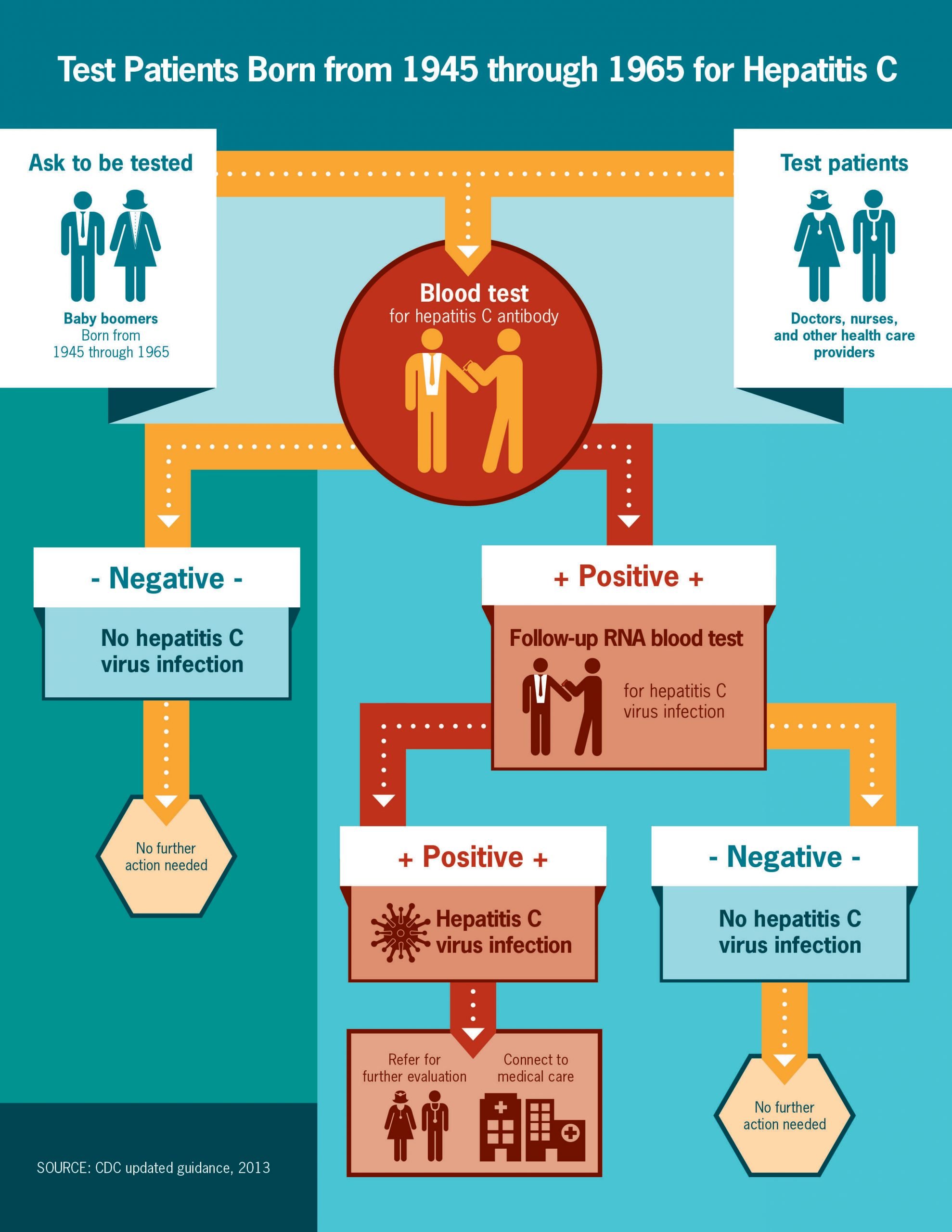
Hepatitis C Antibody Test
Certain foreign substances that enter your body trigger your immune system to make antibodies. Antibodies are specifically programmed to only target the foreign substance they were made to fight.
If youve ever had a hepatitis C infection, your body will make hepatitis C antibodies as part of its immune response.
Your body only makes these antibodies if you have hepatitis C or had it in the past. So the hepatitis C antibody test can confirm whether you have the virus by testing for these specific antibodies.
It may take 2 to 3 months after exposure for the test to detect antibodies. If needed, your healthcare professional may order an HCV RNA test, which can detect the virus after just 1 or 2 weeks.
If the antibody test is positive, an HCV RNA test can show whether the infection is current.
While people of any gender experience the same hepatitis C symptoms, 2014 research suggested some effects of the virus may differ, depending on the sex you were assigned at birth.
Researchers noted that:
- women have a higher chance of clearing the virus without treatment
- liver disease may progress more rapidly in men
- men have a higher chance of developing cirrhosis
E1 And E2 Glycoproteins
E1 and E2 are covalently bonded when embedded in the envelope of HCV and are stabilized by disulfide bonds. E2 is globular and seems to protrude 6 nm out from the envelope membrane according to electron microscope images.
These glycoproteins play an important role in the interactions hepatitis C has with the immune system. A hypervariable region, the hypervariable region 1 can be found on the E2 glycoprotein. HVR1 is flexible and quite accessible to surrounding molecules. HVR1 helps E2 shield the virus from the immune system. It prevents CD81 from latching onto its respective receptor on the virus. In addition, E2 can shield E1 from the immune system. Although HVR1 is quite variable in amino acid sequence, this region has similar chemical, physical, and conformational characteristics across many E2 glycoproteins.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Symptoms And Causes
What Drugs Treat And Cure Hepatitis C
The treatment of chronic hepatitis C has gone through several generations of medications. Not long ago, treatment was limited to interferon alpha-2b or pegylated interferon alpha-2b , and ribavirin . Interferon and pegylated interferon need to be injected under the skin , while ribavirin is taken by mouth. This combination therapy is infrequently used today, being recommended for only the least common genotypes of hepatitis C virus .
Since 2010, direct-acting antiviral drugs have been in use. The second generation of antivirals for HCV was the protease inhibitors telaprevir and boceprevir , both taken by mouth. These were used in combination with the earlier drugs to increase effectiveness . These drugs are also no longer in common use, and have been replaced by better options.
As more has been learned about how hepatitis C virus multiplies within the liver cells, new drugs continue to be developed to interfere with this multiplication at different stages. As such, we no longer think in terms of generations of drugs, but rather categories of action. Research and development of these direct-acting antivirals continue, with new agents coming to market every few months. Each category is improved and expanded by the addition of new drugs, which are safer and more effective.
Currently available and commonly used direct-acting antiviral drugs include:
- simeprevir
- Muscle aches
Selection Of Genomic Region
We constructed intergenotype similarity plots by means of the Simplot program using a window of 500 nt, which was moved along the HCV genome in steps of 50 nt . These plots show that E2P7NS2 is the most divergent large subgenomic region, followed by the 5 end of NS5B. We therefore focused on sequencing regions E2P7NS2 and NS5B, thus enabling us to directly compare their molecular evolution, in the context of the molecular-clock assumption. We designed genotype-free primers for NS5B spanning nucleotides 82008800 and genotype-specific primers for E2P7NS2 spanning nucleotides 25403290. Sequencing was performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions . Primer sequences are listed in Table S2 and reverse transcription-PCR protocols are available upon request.
You May Like: Can Hepatitis C Be Cured Totally
What If I Am Pregnant And I Have Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C can be passed from a mother to her child during pregnancy and during delivery. Per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , approximately 6 of every 100 infants born to HCV-infected mothers become infected with the virus. The risk is 2-3 times greater when the mother has HIV as well.
You and your doctor should discuss and decide if you should receive treatment for hepatitis C during your pregnancy.
How Can You Prevent The Spread Of Hepatitis C
Now that you know how you get hepatitis C, you can take steps to protect yourself from the virus. For instance:
- Avoid sharing needles or other paraphernalia related to intravenous drugs.
- Wear gloves if youre a health care worker or otherwise exposed to needles or potentially infected blood.
- Use barrier methodsaka condomsoutside of sexually monogamous relationships.
- Dont share toothbrushes or other dental equipment, nail clippers, or shaving tools.
- If youre getting a tattoo or piercing, make sure the artist or piercer uses sterile ink and needles.
If you have the hepatitis C virus, you can prevent passing it along to others by following those same steps, in addition to:
- Covering any open sores or wounds.
- Telling all your health and dental care providers you have the virus.
- Avoiding donating blood.
Also Check: Does Hepatitis C Lower Your Immune System
Encouraging Others To Get Tested For Hepatitis C
While the odds of passing on the hepatitis C virus are low, you should still tell anyone at risk that you have hepatitis C. You should tell sexual partners, spouses, and family members. Your infection may be difficult to discuss, but anyone at potential risk must know. That way, they can get tested and treated if needed. Read more on why you should get tested for hepatitis C.
Show Sources
Paul Berk, MD, professor of medicine and emeritus chief of the division of liver disease, Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New York City chairman of the board, American Liver Foundation.
Alan Franciscus, executive director, Hepatitis C Support Project and editor-in-chief of HCV Advocate, San Francisco.
Thelma King Thiel, chair and CEO, Hepatitis Foundation International.
David Thomas, MD, professor of medicine, Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore.
Howard J. Worman, MD, associate professor of medicine and anatomy and cell biology, College of Physicians and Surgeons, Columbia University, New York City.
The American Gastroenterological Association.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Most people infected with hepatitis C have no symptoms. Some people with an acute hepatitis C infection may have symptoms within 1 to 3 months after they are exposed to the virus. These symptoms may include
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you most likely will have no symptoms until complications develop, which could be decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.
You May Like: Hepatitis C Genotype 3 Treatment
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
- Do I need treatment?
- What treatment is best for me?
- What medicines should I take?
- Are there any medicines I should avoid?
- How can I cope with the side effects of treatment?
- Is there a therapist I can talk to?
- How long will my treatment last?
- Can hepatitis C be cured?
- Are organ transplants and blood transfusions safe?
- Is it safe for me to get pregnant?
Can Hepatitis C Be Prevented Or Avoided
The only way to prevent hepatitis C is to avoid coming in contact with an infected persons blood. Always have protected sex . Dont do intravenous drugs. Dont share personal care items with a person who has hepatitis C. If youre a health care worker, follow your workplaces standard safety practices.
You May Like: Can Hepatitis B Virus Be Cured
Evolutionary Analysis Provides Insight Into The Origin And Adaptation Of Hcv
- 1Bioinformatics Laboratory, Scientific Institute IRCCS E.Medea, Bosisio Parini, Italy
- 2Department of Biotechnology and Biosciences, University of Milan-Bicocca, Milan, Italy
- 3Department of Pathophysiology and Transplantation, University of Milan, Milan, Italy
- 4Don C. Gnocchi Foundation Onlus, IRCCS, Milan, Italy
Hcv Originated At Least 3000 Years Ago
Previous studies provided estimates of the time to the most recent common ancestor of HCV genotypes in a range between 200 and 1000 years ago, with one single study indicating that HCV origin may date 2000 years back . The tMRCA of equine/canine hepaciviruses was estimated to be recent, dating around 1800 CE .
It is well known that the temporal variation in rates of nucleotide substitutions often results in underestimation of the age of viral lineages . Purifying selection and substitution saturation are strongly associated with temporal rate variation .
Simulations experiments indicated that classic models tend to underestimate branch lengths in the presence of purifying selection and substitution saturation . Because both phenomena are more pronounced for internal branches, length underestimation is more severe for these branches and dating inferences are consequently affected . The use of models that allow site- and branch-specific variation in selective pressure can improve branch length estimates in the presence of both purifying selection and substitution saturation .
FIGURE 2. tMRCA estimation. Comparison of branch lengths obtained using the aBS-REL and the GTR models for the NS5B abd EHV phylogenies. Timescaled phylogenetic tree estimated for 67 HCV subtypes. The scale bar below the phylogeny represents years before present. The tMRCAs of analyzed nodes are reported in red with 95% confidence intervals. Geographic distribution of HCV endemic transmissions .
Recommended Reading: What Is Drug Induced Hepatitis
Can Hepatitis C Be Prevented
There is no vaccine for hepatitis C. But you can help protect yourself from hepatitis C infection by:
- Not sharing drug needles or other drug materials
- Wearing gloves if you have to touch another person’s blood or open sores
- Making sure your tattoo artist or body piercer uses sterile tools and unopened ink
- Not sharing personal items such toothbrushes, razors, or nail clippers
- Using a latex condom during sex. If your or your partner is allergic to latex, you can use polyurethane condoms.
NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
Evolutionary Analysis Of Hcv Receptors
Coding sequences for mammalian OCLN, CD81, CLDN1, and SCARB1 were retrieved from the NCBI1 database. A list of species is available in the Supplementary Table S1. DNA alignments were performed with the RevTrans 2.0 utility2, MAFFT v6.240 as an aligner) , which uses the protein sequence alignment as a scaffold for constructing the corresponding DNA multiple alignment. All alignments were screened for the presence of recombination using Genetic Algorithm Recombination Detection and two methods implemented in the RDP4 program . RDP and GENECONV were selected because they showed good power in previous simulation analyses and only breakpoints identified by both methods were accepted. The cutoff p-value was set to 0.01 in both GARD and RDP4. No method detected recombination in any alignment.
After running a codon model selection analysis in HYPHY , gene trees were generated by maximum-likelihood using phyML with the approximate likelihood-ratio test method .
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Ab With Reflex To Hcv Pcr
Hepatitis C Testing And Diagnosis
Doctors will start by checking your blood for:
Anti-HCV antibodies: These are proteins your body makes when it finds the hep C virus in your blood. They usually show up about 12 weeks after infection.
It usually takes a few days to a week to get results, though a rapid test is available in some places.
The results can be:
- Nonreactive, or negative:
- That may mean you donât have hep C.
- If youâve been exposed in the last 6 months, youâll need to be retested.
If your antibody test is positive, youâll get this test:
HCV RNA: It measures the number of viral RNA particles in your blood. They usually show up 1-2 weeks after youâre infected.
- The results can be:
- Negative: You donât have hep C.
- Positive: You currently have hep C.
You might also get:
Liver function tests: They measure proteins and enzyme levels, which usually rise 7 to 8 weeks after youâre infected. As your liver gets damaged, enzymes leak into your bloodstream. But you can have normal enzyme levels and still have hepatitis C. Learn the reasons why you should get tested for hepatitis C.
Hcv Binding Downregulates B72 And Inhibits Ig Production
As CD27+ memory B cells in HCV patients are anergic B cells,, the functions of memory B cells infected with HCV particles were examined accordingly. To determine if HCV-infected CD27+ B cells had attenuated signalling upon BCR ligation, Ca2+ mobilization was measured after immunoglobulin M stimulation with anti-human IgM. The HCV-infected CD27+ B cells had diminished Ca2+ mobilization , indicating that HCV-infected CD27+ B cells are anergic to BCR-mediated stimulation. To test if HCV-infected cells were prone to apoptosis, HCV-infected primary memory B cells isolated from patients were stimulated with CD40L+IL2+IL-10 or vehicle control ex vivo . Treated memory B cells were stained with annexin V and anti-CD27. After incubation with vehicle control or CD40L+IL2+IL-10 treatment, the percentage of annexin V+ cells was higher in the CD40L+IL4-stimulated HCV-infected B-cell subset than that of UV-irradiated supernatant-treated cells . As CD40L stimulation transactivates pro-apoptotic molecule Bax , Bax mRNA levels were also examined. The treatment was found to induce BAX after cross-linking B7.2 on HCV-infected memory B cells . These data suggested that, in the absence of survival signals, HCV-infected CD27+B cells were prone to apoptosis.
Figure 9: HCV infection impairs antigen recall responses in memory B cell.
Recommended Reading: What Do You Get Hepatitis C From
Questions For Your Doctor
When you visit the doctor, you may want to ask questions to get the information you need to manage your hepatitis C. If you can, have a family member or friend take notes. You might ask:
Can Hepatitis C Be Treated
Yes, since 2010 enormous progress has been made in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. New therapies called direct-acting antivirals are pills that act on the virus itself to eradicate it from the body, unlike older medicines like interferon injections which work by stimulating an immune response. These new treatments are very effective and can achieve cure rates of over 90%. In most situations now, there is no need for interferon, which was responsible for many of the side effects previously associated with HCV treatment. The new treatment combinations require shorter treatment durations , have reduced side effects and appear to be effective at all stages of the disease.
Because these new therapies are very new, they remain very expensive. As such, drug coverage from both government and private companies may require that your liver disease has progressed to a certain stage before they are willing to cover the cost of these drugs.
Your primary care physician may refer you to a specialist to determine whether you are eligible for treatment. A specialist will help you decide which drug therapy is best for you based on the severity of your liver disease, your virus genotype and whether or not you have been treated in the past.
Don’t Miss: Can Your Body Heal Itself From Hepatitis C
How Common Is Hepatitis C
There are approximately 30,000 new cases of acute hepatitis C every year in the United States as estimated by the CDC. In 2015, it was estimated that approximately 3.5 million Americans were infected with hepatitis C.
On a global scale, the prevalence of hepatitis C is greatest in Central and East Asia, North Africa, and the Middle East. In 2016, it was estimated that 177 million people worldwide had antibodies to hepatitis C virus.
- exposure to other people who do or might have hepatitis C.
What Is Hepatitis C

Hepatitis C is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis C virus . Hepatitis C is a blood-borne virus. Today, most people become infected with HCV by sharing needles or other equipment to inject drugs. For some people, HCV infection is a short-term or acute illness but for more than half of people who become infected with HCV, it becomes a long-term, chronic infection. Chronic HCV infection is a serious disease that can result in long-term health problems, even death. The majority of infected people might not be aware of their infection because they do not have any symptoms. There is no vaccine for hepatitis C. The best way to prevent HCV infection is by avoiding behaviors that can spread the disease, especially injecting drugs.
Don’t Miss: Physical Signs Of Hepatitis C
Zeroing In On The Hepatitis C Virus
The era of direct-acting antivirals that specifically target HCV began in 2011 with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approval of the first protease inhibitors. These drugstelaprevir and boceprevir, along with several similar drugs approved latertargeted the HCV protease that is critical for viral replication. When used in conjunction with peginterferon and ribavirin, protease inhibitors yielded SVR rates of up to 75 percent. However, this triple therapy was accompanied by additional side effects to those already present with peginterferon and ribavirin. Nevertheless, the success of HCV-specific protease inhibitors showed that the virus had vulnerabilities that could be exploited by a well-designed and properly administered drug.
More new anti-HCV drugs were developed and tested over the next several years. These new drugs included sofosbuvir and dasabuvir, which interfered with the activity of the HCV polymerase, an enzyme that is responsible for the viral replication. Members of a second class of drugs, ledipasvir and daclatasvir, targeted the NS5A region of the virus, which makes a structural protein critical for viral replication. Many of these drugs were initially tested in conjunction with peginterferon and ribavirin, or in combination with a protease inhibitor. Generally, the results were SVR rates of at least 80 percent.