What Is Viral Hepatitis
Viral hepatitis is an inflammation of your liver that’s caused by a virus. There are five types, but the most common ones in the U.S. are hepatitis A, B, and C. All of them affect your liver. Some of the symptoms are similar, but they have different treatments.
Hepatitis A. This type won’t lead to long-term infection and usually doesn’t cause any complications. Your liver heals in about 2 months. You can prevent it with a vaccine.
Hepatitis B. Most people recover from this type in 6 months. Sometimes, though, it causes a long-term infection that could lead to liver damage. Once you’ve got the disease, you can spread the virus even if you don’t feel sick. You won’t catch it if you get a vaccine.
Hepatitis C. Many people with this type don’t have symptoms. About 80% of those with the disease get a long-term infection. It can sometimes lead to cirrhosis, a scarring of the liver. There’s no vaccine to prevent it.
What Can Travelers Do To Prevent Disease
Getting vaccinated is the best way to protect against hepatitis B. Hepatitis B is a routine vaccination that infants in the United States receive at birth. The hepatitis B vaccine is over 90% effective at preventing infection and has been routinely recommended for infants since 1991. The vaccine is given in 2, 3, or 4 shots and the series of shots is usually completed by 6 months of age.
The hepatitis B vaccine is also recommended for unvaccinated travelers of all ages going to countries where hepatitis B infection is common. The vaccine is given in 2 or 3 doses. Check if Hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for your destination.
If you trip is soon, talk to your doctor about accelerated dosing and ask about getting the combination hepatitis A/hepatitis B vaccine.
If you traveled and feel sick, particularly if you have a fever, talk to a healthcare provider and tell them about your travel. Avoid contact with other people while you are sick.
Diagnosis Of Hepatitis B
Blood tests are available to determine if you are or have been infected with hepatitis B. It may take 6 months from the time of infection before a blood test can detect antibodies to hepatitis B, so follow-up testing may be required. During this 6-month period, until you know whether you are infected or not, take action to prevent potential infection of other people.
There are also tests that can assess liver damage from hepatitis B. The interpretation of these tests can be complicated and specialist advice is needed, so talk to your doctor.
All pregnant women are tested for hepatitis B. If you are found to have chronic hepatitis B, your doctor can help reduce the risk of transferring the infection to your newborn child.
Read Also: What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis A Virus
What Is The Outlook For People With Hepatitis B
The outlook for people with HBV is better now than ever before. You are certainly able to live a full life and help yourself stay healthy. You should make sure to have regular check-ups with a healthcare provider who is qualified to treat hepatitis B, possibly a liver doctor.
Make sure you are vaccinated against hepatitis A. Check with your healthcare provider or pharmacist before taking other medications or over-the-counter products, including supplements and natural products. These could interfere with your medication or damage your liver. For instance, taking acetaminophen in large doses may harm your liver.
Follow the usual guidelines for living a healthy life:
- Eat nutritious foods, choosing from a variety of vegetables, fruits and healthy proteins. It is said that cruciferous vegetables are especially good at protecting the liver.
- Exercise regularly.
- Dont smoke and dont drink. Both tobacco and alcohol are bad for your liver.
- Do things that help you cope with stress, like journaling, talking with others, meditating and doing yoga.
- Avoid inhaling toxic fumes.
About The Hepatitis B Virus
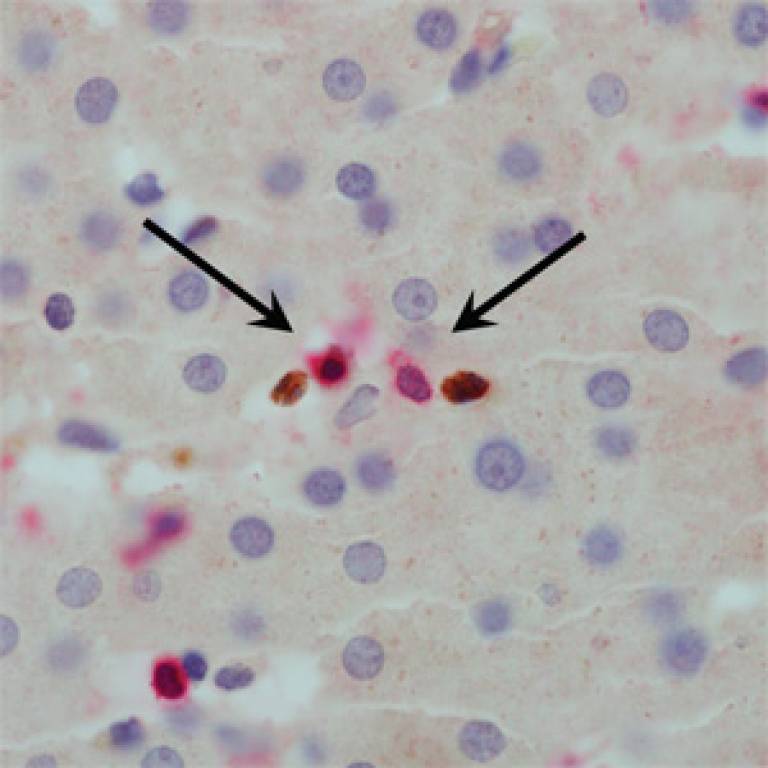
The hepatitis B virus is a small DNA virus that belongs to the Hepadnaviridae family. Related viruses in this family are also found in woodchucks, ground squirrels, tree squirrels, Peking ducks, and herons.
Structure of the Hepatitis B Virus The hepatitis B virus contains an outer envelope and an inner core.
- The outer envelope of the virus is composed of a surface protein called the hepatitis B surface antigen or “HBsAg”. The HBsAg can be detected by a simple blood test and a positive test result indicates a person is infected with the hepatitis B virus.
- The inner core of the virus is a protein shell referred to as the hepatitis B core antigen or “HBcAg,” which contains the hepatitis B virus DNA and enzymes used in viral replication.
Life Cycle of the Hepatitis B Virus
The hepatitis B virus has a complex life cycle. The virus enters the host liver cell and is transported into the nucleus of the liver cell. Once inside the nucleus, the viral DNA is transformed into a covalently closed circular DNA , which serves as a template for viral replication . New HBV virus is packaged and leaves the liver cell, with the stable viral cccDNA remaining in the nucleus where it can integrate into the DNA of the host liver cell, as well as continue to create new hepatitis B virus. Although the life cycle is not completely understood, parts of this replicative process are error prone, which accounts for different genotypes or genetic codes of the hepatitis B virus.
Also Check: Food To Cure Hepatitis B
How Do We Test For Hepatitis B
Testing for hepatitis B is done by blood tests, but the levels of bloods tests can change over time whether you have treatment or not. Blood tests detect whether a person has:
- the virus ,
- had the virus and/or
- protection against infection .
Anyone living with the virus ,will need to have further tests to see if they need to have treatment. The results of the tests can change over time, which can lead to misunderstanding about a persons status.
Further testing is done through more blood tests and scans. It can be very complex and confusing to patients, but they should continue to check in with their doctors as it can save their life. Even if someone does not need treatment now, they may need to have treatment at a later date. Most people who need treatment are asymptomatic and may feel that they are alright and do not need to have checkups. This can be very dangerous because, if someone leaves it until they feel sick, then it may be too late.
What’s The Difference: Hepatitis A Vs Hepatitis B
Chronic hepatitis B is the worldâs leading cause of liver cancer and can lead to serious liver diseases such as cirrhosis or liver cancer. Most adults who become infected with hepatitis B develop an acute infection and will make a full recovery in approximately six months. However, about 90% of infected newborns and up to 50% of young …
Also Check: How Common Is Hepatitis C
What Is The Best Way To Prevent Hepatitis B
The best way to prevent hepatitis B is by getting vaccinated. You must complete the series of shots for full protection. All infants should receive their first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth, followed by a second dose at 1 to 2 months, and a third dose at 6 to 18 months. Infants who did not receive a birth dose should begin the series as soon as possible.
All unvaccinated children and adolescents younger than 19 years of age should get vaccinated.
All adults 19 through 59 years of age are recommended to get vaccinated.
Adults 60 years and older with risk factors should get vaccinated.
A combination vaccine that provides protection against both hepatitis A and B is available for those age 18 years and older. This vaccine is a series of 3 shots over a period of 6 months.
Immune globulin gives short-term prevention of hepatitis B in people of all ages recently exposed to hepatitis B, but the vaccine is preferred for long-term prevention.
How Is Hepatitis B Spread
You can become infected with hepatitis B through exposure to blood, semen and other bodily fluids of an infected person. You can get the infection by:
- Having unprotected sex.
- Sharing or using dirty needles for drug use, tattoos or piercing.
- Sharing everyday items that may contain body fluids, including razors, toothbrushes, jewelry for piercings and nail clippers.
- Being treated medically by someone who does not use sterile instruments.
- Being bitten by someone with the infection.
- Being born to a pregnant woman with the infection.
Hepatitis B is not spread by:
- Kissing on the cheek or lips.
- Coughing or sneezing.
- Hugging, shaking hands or holding hands.
- Eating food that someone with the infection has prepared.
- Breastfeeding.
Also Check: Is There A Cure For Hepatitis
What Is Hepatitis B Virus
Hepatitis B virus attacks the liver. Hepatitis B virus infections are known as the “silent epidemic” because many infected people don’t experience symptoms until decades later when they develop hepatitis , cirrhosis , or cancer of the liver . Every year in the United States about 22,000 new hepatitis B infections occur and about 2,000 people die from their infections.
Hepatitis A: Questions And Answers
about 1% died. Can people become chronically in-fected with hepatitis A virus? No. Hepatitis A leads to a short-term infection, lim-ited to a few weeks or months, not a chronic infec-tion. Relapsing hepatitis A, as described above, goes away and is NOT a chronic infection. Both hepatitis B and hepatitis C viruses can cause chronic …
Read Also: The Cost Of Hepatitis C Treatment
Reduce Your Chance Of Infection
You can reduce your chance of hepatitis B infection by
- not sharing drug needles or other drug materials
- wearing gloves if you have to touch another persons blood or open sores
- making sure your tattoo artist or body piercer uses sterile tools
- not sharing personal items, such as toothbrushes, razors, or nail clippers
- using a latex or polyurethane condom during sex
Study Population And Follow

Each study site compares cohort patient records with the National Death Index, Social Security Death Index, or electronic state death registries annually for those patients known to have died or for those not seen in the health system for 2 years. Deaths are also ascertained from hospitals and clinics reporting through the EHR. EHR-reported deaths without a matching death certificate do not have MCOD data.
Follow-up was defined to begin on 1 January 2006, regardless of the date of first visit, and age was calculated from date of birth as of that date. The study population included patients receiving their first clinical services through 31 December 2013. Follow-up was truncated on 31 December 2014 or the date of death, whichever came first.
Recommended Reading: How Does A Person Get Hepatitis B
What Causes Hepatitis B
The hepatitis B virus causes hepatitis B. The hepatitis B virus spreads through contact with an infected persons blood, semen, or other body fluids. Contact can occur by
- being born to a mother with hepatitis B
- having unprotected sex with an infected person
- sharing drug needles or other drug materials with an infected person
- getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on an infected person
- being tattooed or pierced with tools that were used on an infected person and werent properly sterilized, or cleaned in a way that destroys all viruses and other microbes
- having contact with the blood or open sores of an infected person
- using an infected persons razor, toothbrush, or nail clippers
You cant get hepatitis B from
- being coughed on or sneezed on by an infected person
- drinking unclean water or untreated water that has not been boiled
- eating food that is unclean or has not been properly cooked
- hugging an infected person
- shaking hands or holding hands with an infected person
- sharing spoons, forks, and other eating utensils
- sitting next to an infected person
Mothers who have hepatitis B can safely breastfeed their babies. If a baby receives hepatitis B immune globulin and starts receiving the hepatitis B vaccine to prevent hepatitis B infection shortly after birth, hepatitis B is unlikely to spread from mother to child through breastfeeding.15
What Should You Know About Hepatitis B Before You Travel
Hepatitis B is quite common in China and other Asian countries, where as many as 1 in 12 people have the virus, though many dont know it. Before traveling to those places, you should make sure youve been vaccinated against the virus.
In addition to getting the vaccine, you can take these additional precautions to reduce your risk of contracting the virus:
- Refrain from taking illegal drugs.
- Always use latex or polyurethane condoms during sex.
- Make sure new, sterile needles are used during all piercings, tattoos and acupuncture sessions.
- Avoid direct contact with blood and bodily fluids.
- Know the HBV status of all your sexual partners.
- Ask your doctor about possible vaccination before you travel to a place where hepatitis B is common.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Hepatitis B is a liver disease that can cause serious damage to your health. One reason that is dangerous is that it can easily go undetected for years while damaging your liver. Talk with your healthcare provider about being tested for hepatitis B if you have any reason to believe that you were not vaccinated or if you have engaged in risky behavior. If you do test positive, follow the directions from your healthcare provider so that you can live a longer, healthier and happier life.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 07/09/2020.
References
Read Also: How Much Is Hepatitis A Vaccine
I Am A Healthcare Worker Who Did Not Develop Hepatitis B Antibodies After Immunization What Should I Do
Not everyone responds to the hepatitis B vaccine. In fact, in a group of adults younger than 40 years of age who have received two doses of the vaccine only 75 of 100 will be protected. Following the third dose, this number will increase to 90 of 100. However, people older than 40 years of age will be less likely to respond to the vaccine with increasing age.
Even if people do not respond to three doses, it does not mean that they are at high risk for hepatitis B. Because hepatitis B is transmitted primarily through blood and body fluids, using safety precautions while working will help decrease the chance of exposure to the disease. It is also possible that the immune response was not great enough to be measured by the laboratory test, but would still provide some level of protection upon exposure to hepatitis B. The CDC recommends getting the three-dose series again if an immune response is not generated following the first series.
About 5-10 of every 100 children and adults younger than 40 years of age do not respond to the third dose of the hepatitis B vaccine. Some of these people will be recommended to get the series of three doses again. About 5 of 100 people will still not respond after six doses. If these people are determined not to have chronic hepatitis B, they will be reliant on taking precautions to reduce the chance of exposure and relying on those around them for protection. In other words, these people will be reliant on herd immunity.
Mortality And Survival Plots
General population mortality data were provided for age groups in 5-year intervals. Liver cancer mortality was adjusted for the proportion with an HCC diagnosis, the percentage of HCC associated with hepatitis B, and the population prevalence of HbsAg. The same process was performed for CLD death. Mortality was also analyzed with respect to HbeAg status and adjusted by relative risk and age-specific HbeAg prevalence. The overall carrier mortality rate was obtained by summing the rates of non-liver, HCC, CLD, and non-HCC liver cancer. The values for noncarriers were calculated using the same methods. Survival plots and life expectancies were obtained by using an abridged life table, whereby a hypothetical cohort was subjected to age-specific mortality rates, with survivors proceeding to the subsequent age interval. Relative mortality risks were calculated and standardized to the 2006 Taiwan population distribution.
Read Also: How You Contract Hepatitis B
The Hepatitis B Vaccine
The hepatitis B vaccine sometimes known by the trade name Recombivax HB is used to prevent this infection. The vaccine is provided in three doses.
The first dose can be taken on a date you choose. The second dose must be taken one month later. The third and final dose must be taken six months after the first dose.
Adolescents 11 to 15 years old may follow a two-dose regimen.
Prevent Infection After Contact With The Virus
If you think you have been in contact with the hepatitis B virus, see your doctor right away. Doctors typically recommend a dose of the hepatitis B vaccine to prevent infection. In some cases, doctors may also recommend a medicine called hepatitis B immune globulin to help prevent infection. You must get the vaccine dose and, if needed, HBIG shortly after coming into contact with the virus, preferably within 24 hours.
Read Also: Home Remedies For Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B Causes And Risk Factors
Itâs caused by the hepatitis B virus, and it can spread from person to person in certain ways. You can spread the hepatitis B virus even if you donât feel sick.
The most common ways to get hepatitis B include:
- Sex. You can get it if you have unprotected sex with someone who has it and your partnerâs blood, saliva, semen, or vaginal secretions enter your body.
- Sharing needles. The virus spreads easily via needles and syringes contaminated with infected blood.
- Accidental needle sticks.Health care workers and anyone else who comes in contact with human blood can get it this way.
- Mother to child.Pregnant women with hepatitis B can pass it to their babies during childbirth. But thereâs a vaccine to prevent newborns from becoming infected.
Hepatitis B doesnât spread through kissing, food or water, shared utensils, coughing or sneezing, or through touch.