What Do You Need To Know About Hepatitis B And C Coinfection
Hepatitis B and hepatitis C share some common transmission routes, including through blood-to-blood contact, and so hepatitis B and hepatitis C coinfection is possible. Anyone who is diagnosed with hepatitis C should also be screened for hepatitis B and vice versa.
Both hepatitis B and C affect the liver. When people have two active infections of the liver, one virus dominates the other. In most cases, the hepatitis C virus is the dominant virus and the hepatitis B virus is suppressed.
There are highly effective and widely accessible treatments available to cure hepatitis C called direct-acting antivirals. Anyone with hepatitis C should discuss treatment options with their healthcare provider, including people with a hepatitis B and C coinfection. Owing to the relationship between the two viruses in the liver, when a person is cured of hepatitis C, hepatitis B virus can flare up. When people are treated for hepatitis C with direct-acting antivirals, hepatitis B treatment may be considered to stop the reactivation of hepatitis B.
Is There A Cure For Hepatitis
According to Zappas, there is no technical cure for viral hepatitis, and antibodies will always test positive in a patient who has experienced hepatitis A, B or C. The management of chronic hepatitis B is complex and based on a myriad of factors. Some patients manage their condition with long-term antiviral medications.
However, vaccinations for hepatitis A and B have proven highly effective. Hepatitis A and B vaccinations are recommended and routinely done in infancy, Zappas affirmed. Most people respond to these vaccinations, but post-vaccination testing may be indicated in high-risk patients.
The outlook is even brighter when it comes to hepatitis C: Over the last 10 years, the hepatitis C treatment regimens have evolved, Zappas said. Now, theres nearly a 90% cure rate with certain antiviral medications, which can eradicate the replication of the hepatitis C RNA and therefore abate the damage of the virus on the liver. It is important to note that patients are not immune to hepatitis C after treatment, and can be reinfected and/or contract another strain.
To measure the effects, providers look for a sustained virologic response indicating that the virus remains inactive, which is evaluated between 12 and 24 weeks after beginning the medication.
To reference the work of our faculty online, we ask that you directly quote their work where possible and attribute it to FACULTY NAME, a professor in the USC Suzanne Dworak-Peck School of Social Work
What Should You Know About Hepatitis B Before You Travel
Hepatitis B is quite common in China and other Asian countries, where as many as 1 in 12 people have the virus, though many dont know it. Before traveling to those places, you should make sure youve been vaccinated against the virus.
In addition to getting the vaccine, you can take these additional precautions to reduce your risk of contracting the virus:
- Refrain from taking illegal drugs.
- Always use latex or polyurethane condoms during sex.
- Make sure new, sterile needles are used during all piercings, tattoos and acupuncture sessions.
- Avoid direct contact with blood and bodily fluids.
- Know the HBV status of all your sexual partners.
- Ask your doctor about possible vaccination before you travel to a place where hepatitis B is common.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Hepatitis B is a liver disease that can cause serious damage to your health. One reason that is dangerous is that it can easily go undetected for years while damaging your liver. Talk with your healthcare provider about being tested for hepatitis B if you have any reason to believe that you were not vaccinated or if you have engaged in risky behavior. If you do test positive, follow the directions from your healthcare provider so that you can live a longer, healthier and happier life.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 07/09/2020.
References
Also Check: What Hepatitis Is Not Curable
Certified By The Joint Commission
We have received The Gold Seal of Approval® by The Joint Commission, the leading accreditor of healthcare organizations in America, reflecting a commitment to high-quality patient care. Our Comprehensive Stroke Center is certified by The Joint Commission as providing the most advanced stroke care, and Tisch Hospital is recognized for its excellence in perinatal, palliative, and ventricular assist device care.
Is There A Cure For Chronic Hepatitis B
Currently, there is no complete cure for hepatitis B. But when managed properly, those living with the virus can expect to live a normal life. Maintaining a healthy diet and avoiding alcoholic beverages and tobacco products are crucial components in managing the disease.
You should also visit a doctor familiar with hepatitis B at least annuallythough twice a year might be best to monitor your liver through blood tests and medical imaging. As with most diseases, detecting it early leads to a better outcome. If youre exposed to the virus, you should get an antibody injection within 12 hours of exposure.
Also Check: How Does One Contact Hepatitis C
What Makes Yale Medicine’s Approach To Treating Hepatitis B And C Unique
The Viral Hepatitis Program at Yale Medicine represents one of the leading viral hepatitis treatment programs in the country and is engaged in innovative research focused on advancing the care of patients with chronic hepatitis B, C and D infections.
A multidisciplinary team of faculty physicians and mid-level providers offer a coordinated approach to preparing patients for success. Services include structured hepatitis patient education classes, mindfulness-based stress reduction techniques , a formal physician-guided weight-loss program and access to clinical trials evaluating current and new therapies that are not available in routine clinical practice.
Our program is a core member of several national and international observational cohort studies which contributes to the advancement of science of hepatitis treatment around the world.
“Our team at Yale Medicine is uniquely equipped to serve patients with viral hepatitis from Connecticut and beyond and aims to offer outstanding, individualized, patient-centered care to help educate and guide patients through their treatment,” says Dr. Lim. We have specialists who have nationally recognized expertise in the management of viral hepatitis in special populations, including HCV-HIV coinfection, end-stage renal disease, cirrhosis/liver failure, post-liver transplant, and prior failure to respond to all-oral direct acting antivirals .
How To Reduce Your Risk
Dont share needles or other drug-use equipment. If you use intravenous drugs, take part in a needle exchange program.
Dont share personal care articles, such as razors, scissors, nail clippers or toothbrushes, with an infected person.
If you get a tattoo, body piercing or acupuncture, make sure all equipment is clean and sterile. Needles should always be new, not used, and never homemade.
Wear latex gloves whenever you might come into contact with someone elses blood or body fluids.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Genotype 2 Treatment Guidelines
What Makes Yale Medicines Approach To Treating Hepatitis B And C Unique
The Viral Hepatitis Program at Yale Medicine represents one of the leading viral hepatitis treatment programs in the country and is engaged in innovative research focused on advancing the care of patients with chronic hepatitis B, C and D infections.
A multidisciplinary team of faculty physicians and mid-level providers offer a coordinated approach to preparing patients for success. Services include structured hepatitis patient education classes, mindfulness-based stress reduction techniques , a formal physician-guided weight-loss program and access to clinical trials evaluating current and new therapies that are not available in routine clinical practice.
Our program is a core member of several national and international observational cohort studies which contributes to the advancement of science of hepatitis treatment around the world.
Our team at Yale Medicine is uniquely equipped to serve patients with viral hepatitis from Connecticut and beyond and aims to offer outstanding, individualized, patient-centered care to help educate and guide patients through their treatment, says Dr. Lim. We have specialists who have nationally recognized expertise in the management of viral hepatitis in special populations, including HCV-HIV coinfection, end-stage renal disease, cirrhosis/liver failure, post-liver transplant, and prior failure to respond to all-oral direct acting antivirals .
How Is It Treated
Hepatitis A is treated using supportive methods. These can include things like rest, fluids, and healthy foods. Medications can also help to ease some symptoms like fever, aches, and pains.
Theres a vaccine available to protect against infection with HAV. This is typically recommended for children as well as for people at an increased risk for contracting the virus.
Also, receiving a single dose of the hepatitis A vaccine may prevent you from becoming ill if youve been exposed to HAV. For it to be effective, the vaccine needs to be given of exposure.
You May Like: Where Can I Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine For Free
Treatment Of Hepatitis A B And C
There is no cure for hepatitis A. You have to get sick. But it is useful to discuss vaccination against hepatitis A and B with your doctor.
You actually feel sick for 2 to 3 weeks. After this, there is a recovery period. Sometimes it takes months to regain your strength.
- In 10% of cases, the hepatitis A infection lasts longer, with possible recurrence after a few weeks or months.
- In 1% of cases, the course is very severe, with acute liver failure and death .
- A hepatitis A infection never becomes chronic.
In hepatitis B, 90 percent of infections heal spontaneously. In the other 10 percent, you remain a carrier of the virus for life . You can also infect other people. In the longer term, this can also lead to liver cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Avoid straining your liver while recovering from hepatitis B:
- eat healthy food
- avoid drugs that burden your liver
If the doctor does not determine a cure, he can consider a number of treatment options.
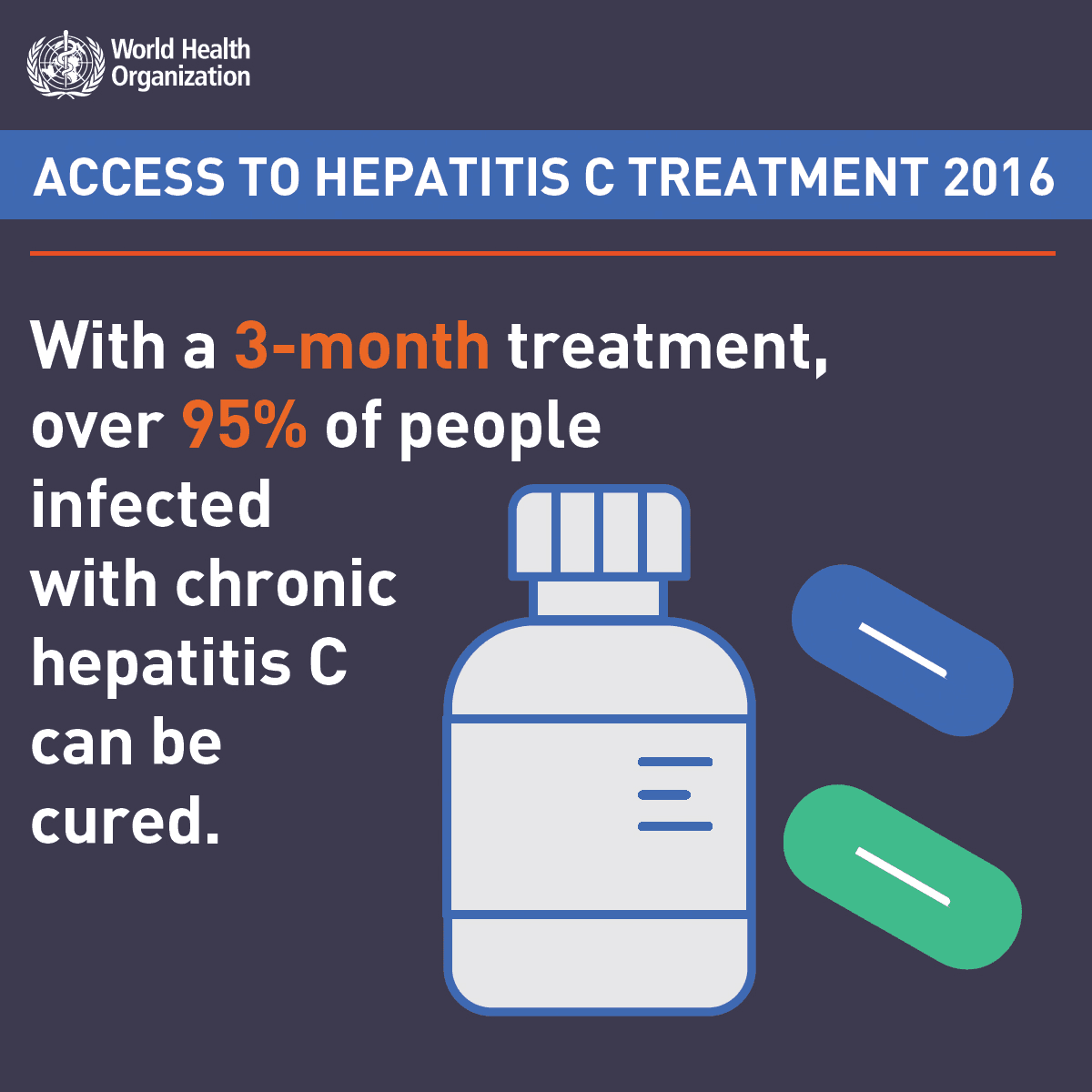
Hepatitis C is very treatable if you start treatment on time. A treatment gives more than a 95% chance of recovery. The treatment lasts 2 to 3 months.
In the absence of treatment, the disease becomes chronic in 3 out of 4 people. Early treatment prevents permanent liver damage.
What Is The Outlook
Most people with hepatitis A recover without any complications. Once youve had hepatitis A, you cant get it again. Antibodies to the virus will protect you for life.
Some people may be at an increased risk for serious illness from hepatitis A. These include:
acute hepatitis B infections in the United States in 2018.
Don’t Miss: Malignant Neoplasm Of Hepatic Flexure
Diabetes Obesity And Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Several studies have shown a strong link between type II diabetes and liver cancer. Build-up of fat in the liver is common among persons with type II diabetes and may increase the risk of cirrhosis and liver cancer. This risk is higher in patients who also have other risk factors, such as heavy alcohol consumption or chronic viral hepatitis infections.
Obesity, which can contribute to fatty liver disease and cirrhosis, is a major risk factor for the development of type II diabetes, which, in turn, can increase the chance of developing liver cancer. It is unclear whether obesity directly causes liver cancer. Chronic hepatitis B and C infections are most strongly associated with liver cancer, but diabetes and obesity are major health problems that are becoming increasingly important risk factors for liver cancer.
In nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, excess fat builds up in the liver of people who drink little or no alcohol. The most severe form of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is called nonalcoholic steatohepatitis . People with NASH have fat in their liver, along with inflammation and liver damage. They usually have no symptoms and do not know that they have a liver problem. NASH can be severe and can lead to cirrhosis. NASH is estimated to be the third most common liver disorder in North America and the most common in Australia and New Zealand.
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis C And How Do You Get It
Nyu Long Island School Of Medicine
NYU Long Island School of Medicine focuses on educating physicians and academic leaders in primary care, and preparing its students to deliver outstanding patient care and become authorities in local and national health systems. Its three-year curriculum combines medical education, research, and quality patient care, and reduces the traditional medical school curriculum by one full year. Full-Tuition Scholarships are offered to all matriculated students, making it more financially feasible for students to choose careers in the important fields of primary care, internal medicine, pediatrics, and obstetrics and gynecology.
Basic, translational, and clinical research are integrated with population health and health systems science to create a scientifically rigorous learning environment that is also diverse, inclusive, comprehensive, and compassionate. These innovations are paired with a structured career and academic advising program that involves academic coaching, specialty advising, and monthly learning community sessions to offer a truly personal approach to medical education.
You May Like: Signs Of Hepatitis C In Males
Are Hepatitis B And C Preventable
Hepatitis B is a vaccine-preventable disease.
There is a three-shot vaccination series that is very effective in protecting people against the virus if theyre exposed. In the United States, all newborns are vaccinated for hepatitis B and all pregnant women are screened for hepatitis B during pregnancy. This way, mothers infected with hepatitis B can take protective steps to decrease the risk of transmission of the virus to the child.
There is no vaccine for hepatitis C.
What If You Test Positive
If a test says you have viral hepatitis, you can take steps to protect the ones you love. For hepatitis A, wash hands frequently. For hepatitis B and C, avoid sharing nail clippers, razors, or toothbrushes. Hepatitis B, and sometimes hepatitis C, can be passed through sexual contact. Make sure everyone in your household gets the hepatitis B vaccine. An important step is to see a specialist to discuss treatment options.
Also Check: What Is Drug Induced Hepatitis
Overview Of Hepatitis B And C Management
Justin Hooper, PharmD, BCPS
Tyler, Texas
US Pharm. 2009 34:32-41.
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver that is often caused by one of five hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, or E. Hepatitis A and E are commonly contracted by ingestion of contaminated food or water, while transmission of hepatitis B and C occurs by parenteral contact with infected body fluids. No specific drug therapy is available for the treatment of hepatitis A or E. Hepatitis B and C infections are worldwide concerns because they often lead to chronic liver disease and even death. Much effort has been dedicated to global eradication of these diseases through education and vaccination. Still, viral hepatitis is a major public health concern. While both hepatitis B and C are associated with significant morbidity and mortality, the therapeutic approach to treatment varies by virus type, and each will be discussed separately.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis B And C
In most patients, hepatitis B develops slowly over the course of several decades, and thus most patients have no symptoms. People who have advanced liver disease such as cirrhosis of the liver may experience complications and symptoms that reflect liver failure. Other symptoms include:
- A buildup of fluid within the abdominal cavity
- Confusion and tremors , which are complications due to the inability of the liver to filter out toxins that are normally cleaned out by a healthy liver
- Vomiting of blood, or blood within the stool . This is a complication in which enlarged veins within the esophagus or stomach bleed as a consequence of increased pressure around the diseased liver.
Most patients with chronic hepatitis C infection report no symptoms. But some patients may have very nonspecific symptoms related to fatigue and discomfort on the right side of the abdomen. Often, symptoms that lead to a diagnosis of hepatitis C are noticeable only at the end stage of liver disease, when the patient has developed liver cirrhosis and liver failure.
Because hepatitis B and C typically have no specific symptoms, many people who have the viruses dont even know it.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Vaccine Dose Schedule
Acute Hepatitis B Infection
An acute infection begins immediately after exposure to the hepatitis B virus. In adults, this phase can last for two to six weeks. During the acute infection, the virus is highly active and can be passed to others. During this phase, there are few or no symptoms in most children and in many adults . Symptoms, when they do appear, may include fatigue, loss of appetite, jaundice, , nausea, vomiting, rash, dark urine, joint discomfort or pain, and abdominal discomfort or pain. About one percent of people in the acute phase can experience liver failure. When this occurs, symptoms of advanced liver disease, like bleeding or bruising more easily, brain fog or confusion, and jaundice, can be seen.
Most adults clear the virus on their own within six months and become immune to it. Blood tests can be done six months after diagnosis to determine whether a person is immune. Immune adults will have a not-detectable result on a hepatitis B surface antigen test, a detectable result on an anti-hepatitis B surface antibody test and a detectable result on an anti-hepatitis B core antibody test. If there is no hepatitis B virus present in the blood and the antibodies have formed, it means the person has cleared the infection and they cannot pass it on to someone else. However, the virus genetic materials still reside in their liver and can be reactivated in the future especially if the person takes medicines that profoundly suppress their immune system.
Notify Partners And The Environment
Encourage the people you live with and your sex partners to get vaccinated if you have hepatitis A or B.
Not only your regular partner but also everyone in your immediate environment must be informed if it turns out that you are infected with hepatitis A or B.
Also, inform your sex partners from the past six months. Would you rather not do that? Then discuss this with your doctor. They can inform them by means of a letter partner notification so that you remain anonymous.
Also Check: Hepatitis B And C Home Test Kit