Who Should Not Receive The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Talk to your healthcare provider before getting the hepatitis B vaccine if:
- You have had a severe allergic reaction to the hepatitis B vaccine or any of its ingredients in the past.
- You have had an allergic reaction to yeast in the past.
- You are moderately or severely ill.
- You are currently taking immunosuppressive medications.
In addition, pregnant people should not receive the Heplisav-B or PreHevbrio vaccines until more safety information is available.
Who Should Receive The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Vaccination is the most reliable way to prevent getting hepatitis B or developing serious related medical complications.
The CDCs Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommends that people in all age groups get the hepatitis B vaccine, including:
- All infants within 24 hours after birth
- Children and teens who have not previously been vaccinated against hepatitis B
- Adults ages 19 to 59
- Adults ages 60 and older with at least one risk factor for hepatitis B
Adults over 60 who are not at risk of developing hepatitis B can also receive the HepB vaccine if they choose.
Persons With Inadequate Immunization Records
Evidence of long term protection against HB has only been demonstrated in individuals who have been vaccinated according to a recommended immunization schedule. Independent of their anti-HBs titres, children and adults lacking adequate documentation of immunization should be considered susceptible and started on an immunization schedule appropriate for their age and risk factors. Refer to Immunization of Persons with Inadequate Immunization Records in Part 3 for additional information.
Don’t Miss: How Do I Know If I Have Hepatitis C
Who Should Receive Hepatitis B Vaccination
- All newborns before hospital discharge. Infants born to hepatitis B-positive women need hepatitis B vaccine and HBIG within 12 hours of birth.
- All children and adolescents not previously vaccinated.
- Children born in the U.S. to individuals born in a country with high hepatitis B endemicity.
- All individuals at risk of hepatitis B infection:
- Sex partners of hepatitis B-positive persons
- Sexually active persons who are not in a long-term, mutually monogamous relationship
- Persons seeking evaluation or treatment for a sexually-transmitted disease
- Men who have sex with men
- Persons who inject drugs
- Household contacts of hepatitis B-positive persons
- Persons born in countries where hepatitis B infection is endemic should be tested and vaccinated if susceptible
- International travelers to regions with high or intermediate rates of endemic hepatitis B infection
- Health care and public safety workers that may be exposed to blood or blood-contaminated body fluids
- Residents and staff of facilities for developmentally disabled persons, corrections facilities, and other facilities that serve adults at risk for hepatitis B infection
- Persons with end-stage renal disease, including pre-dialysis, hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, and home dialysis patients
- Persons with chronic liver disease
- Persons to age 60 years with diabetes
- Persons with HIV infection
- All other persons seeking protection from hepatitis B infection.
Others For Testing And Pregnancy And B Vaccine
If you must sign up to develop protective? The manufacturer recommends the standard adult dosage 20 g10 mL using a 2 dose schedule if it is unlikely that there will be compliance. Hepatitis b hepatitis b vaccine for schedule adults. For all adults age 19 with certain medical conditions.
Just For Fun InPrep Guide Act
Also Check: What Are The Side Effects Of Hepatitis C
Indications For Recombivax Hb Indications For Recombivax Hb
RECOMBIVAX HB® is indicated for prevention of infection caused by all known subtypes of hepatitis B virus.
RECOMBIVAX HB is approved for use in individuals of all ages.
RECOMBIVAX HB Dialysis Formulation is approved for use in adult predialysis and dialysis patients 18 years of age and older.
RECOMBIVAX HB is indicated for prevention of infection caused by all known
RECOMBIVAX HB is indicated for prevention of infection caused by all known subtypes of hepatitis B virus.
RECOMBIVAX HB is approved for use in individuals of all ages.
Global Burden Of Disease
Approximately two billion people worldwide had been exposed to HBV in 1995. In 2015, based on serological data, around 3.5 percent of the general population globally were infected with HBV and more than 250 million people were estimated to have chronic infection and these people remain at risk of developing cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. More than 90 percent of individuals with chronic HBV resided in the AsiaPacific region, where most countries have high prevalence rates of HBV infection and more than 99 percent of HBV-infected people in this region acquired infection through vertical transmission from their mother or in early childhood. As an example of this risk, 22.8 million out of 80 million people living in China with chronic HBV infection are women of child-bearing age. Acquisition of HBV during adulthood is associated with a high rate of symptomatic hepatitis but a low rate of chronic infection.
Read Also: What Are The Effects Of Hepatitis C
When To Delay Or Avoid Hepb Immunization
Doctors delay giving the vaccine to babies who weigh less than 4 pounds, 7 ounces at birth whose mothers do not have the virus in their blood. The baby will get the first dose at 1 month of age or when the baby is discharged from the hospital.
The vaccine is not recommended if your child:
- is currently sick, although simple colds or other minor illnesses should not prevent immunization
- had a serious allergic reaction after an earlier dose of the vaccine or is allergic to baker’s yeast
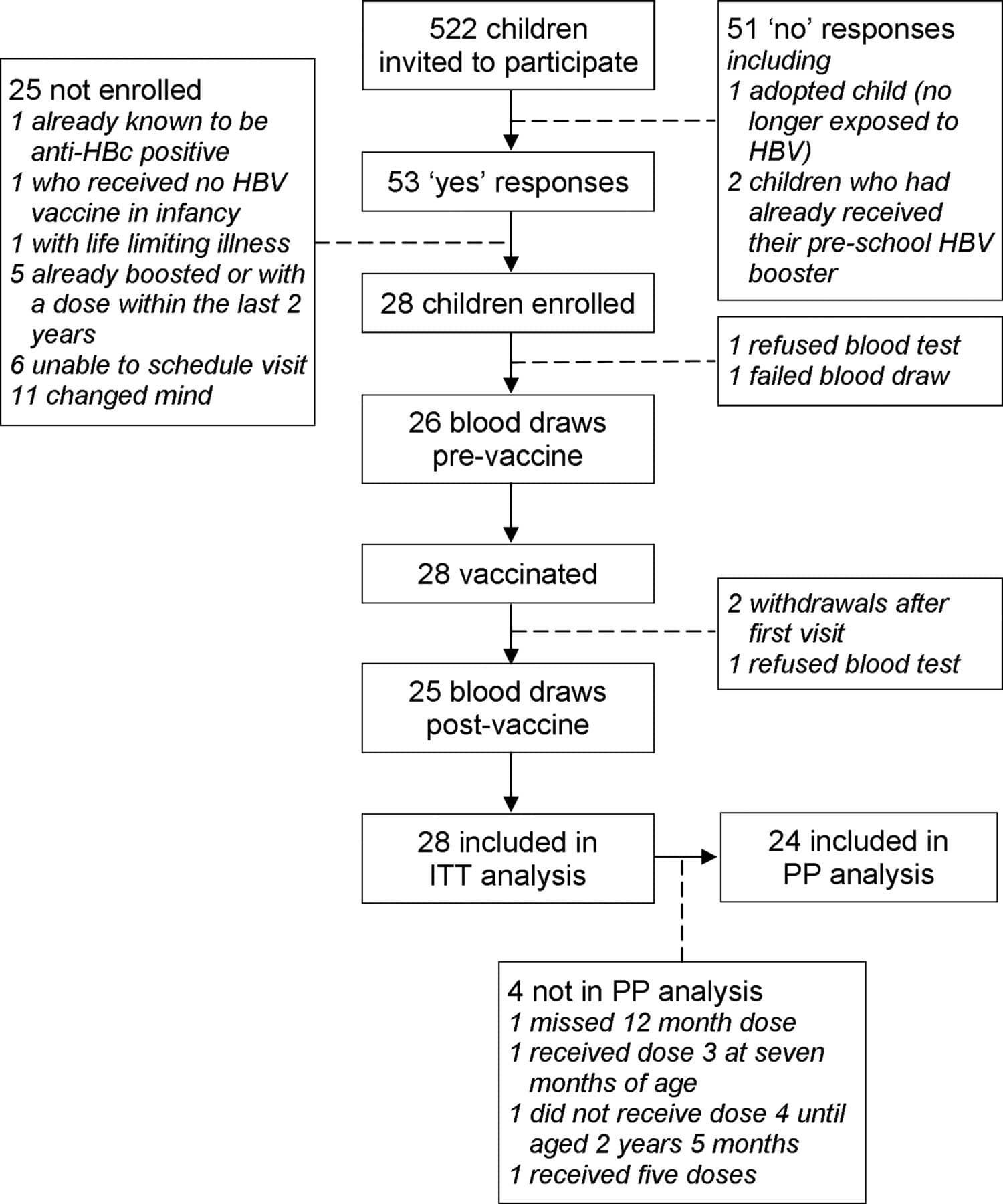
Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule: Standard Accelerated And Combination
Getting poked with a needle is never fun, but its an extremely important part of protecting yourself and others from infectious diseases! The hepatitis B vaccine is known to be one of the most effective vaccines in the world and very safe too! As a blood-borne disease that typically has no symptoms, hepatitis B can easily be spread by accident simply because people are unaware that they have it! Modes of transmission include mother-to-child during birth, unprotected sex, injection drug use, unsafe medical procedures, and the sharing of personal items that may contain blood remnants, such as body jewelry, razors, and toothbrushes. Although certain precautions can be taken to prevent transmission, the only way to completely protect yourself is to get vaccinated. Once you have been vaccinated, you are protected for life!
There are a few options for receiving the hepatitis B vaccination. In most countries, the vaccine is available through a doctors office or a health clinic. The most common option is the standard three-dose vaccine. This consists of three separate doses of the vaccine given through intramuscular injections. In order for the vaccine to be effective, there must be a minimum amount of time between doses. If the minimum amount of time is not followed, the vaccine will not provide full, long term protection from the infection.
3 Dose Schedule:
2-Dose Schedule :
- 1st shot At any given time
- 2nd shot At least 28 days after the first shot.
Read Also: Does Hepatitis C Make You Itch
Reducing Hbv Infections And Deaths By 2030
As part of their plan to address HBV, the CDCs Division of Viral Hepatitis announced a goal to reduce HBV infections by 90% and HBV-related deaths by 65% in 2030.
The Department of Health and Human Services also announced a goal to eliminate viral hepatitis as a public health threat in the United States by 2030.
To help meet these goals, the CDC has outlined new hepatitis B vaccination recommendations for 2022. Vaccines can help prevent the disease and have reduced the number of reported hepatitis B cases by 90% since being introduced in 1982.
A hepatitis B vaccine is now recommended for adults ages 19 to 59 years without risk factor screening and disclosure. This helps increase vaccination coverage and decrease cases.
The vaccine is also recommended for adults ages 60 years or older with risk factors for hepatitis B. Risk factors can include having sex without a condom or barrier method, sharing needles, and having a job that exposes you to human blood, among others.
Its also recommended that adults 60 years or older without known risk factors get a vaccine. New clinical guidance advises providers to offer vaccinations to this group. Previously, clinical guidance instructed providers to administer the hepatitis B vaccine only when it was requested by a patient.
The CDC also continues to recommend hepatitis B vaccination for all infants and unvaccinated children under the age of 19 years.
Persons New To Canada
Health care providers who see persons newly arrived in Canada should review the immunization status and update immunization for these individuals, as necessary. In many countries outside of Canada, HB vaccine is in limited use.
All persons from a country that is endemic for HB should be assessed and vaccinated against HB if not immune and not infected. Individuals born in developing countries are more likely to be carriers of HB, necessitating vaccination of their sexual and household contacts based on review of their serologic test results. HB vaccine is recommended for all household contacts whose families have immigrated to Canada from areas in which there is a high prevalence of HB and who may be exposed to HB carriers through their extended families or when visiting their country of origin.
Children adopted from countries in which there is a high prevalence of HB infection should be screened for HBsAg and, if positive, household or close contacts in the adopting family should be immunized before adoption or as soon as possible thereafter. Adults going to pick-up children from these countries should be vaccinated before departure. Refer to Immunization of Persons New to Canada in Part 3 for additional information.
Read Also: How Can Hepatitis C Be Transferred
Advisory Committee On Immunization Practices Recommendations
In February 2018, ACIP approved recommendations for Heplisav-B vaccine as an option for previously unvaccinated or incompletely vaccinated persons, including:
- Adults 18 years of age and older who have a specific risk, or lack a risk factor but want protection. See ACIP Recommended Immunization Schedule for Adults for risk factors.
How Is The Hepatitis B Vaccine Made
People are protected against hepatitis B virus infection by making an immune response to a protein that sits on the surface of the virus. When hepatitis B virus grows in the liver, an excess amount of this surface protein is made. The hepatitis B vaccine is made by taking the part of the virus that makes surface protein and putting it into yeast cells. The yeast cells then produce many copies of the protein that are subsequently used to make the vaccine. When the surface protein is given to children in the vaccine, their immune systems make an immune response that provides protection against infection with the hepatitis B virus.
The first hepatitis B vaccine was made in the 1980s by taking blood from people infected with hepatitis B virus and separating or purifying the surface protein from the infectious virus. Because blood was used, there was a risk of contaminating the vaccine with other viruses that might be found in blood, such as HIV. Although contamination with HIV was a theoretical risk of the early, blood-derived hepatitis B vaccine, no one ever got HIV from the hepatitis B vaccine. That is because the blood used to make vaccine was submitted to a series of chemical treatments that inactivated any possible contaminating viruses. Today, there is no risk of contaminating the vaccine with other viruses because the surface protein is manufactured in the laboratory.
Recommended Reading: How Can Someone Get Hepatitis B
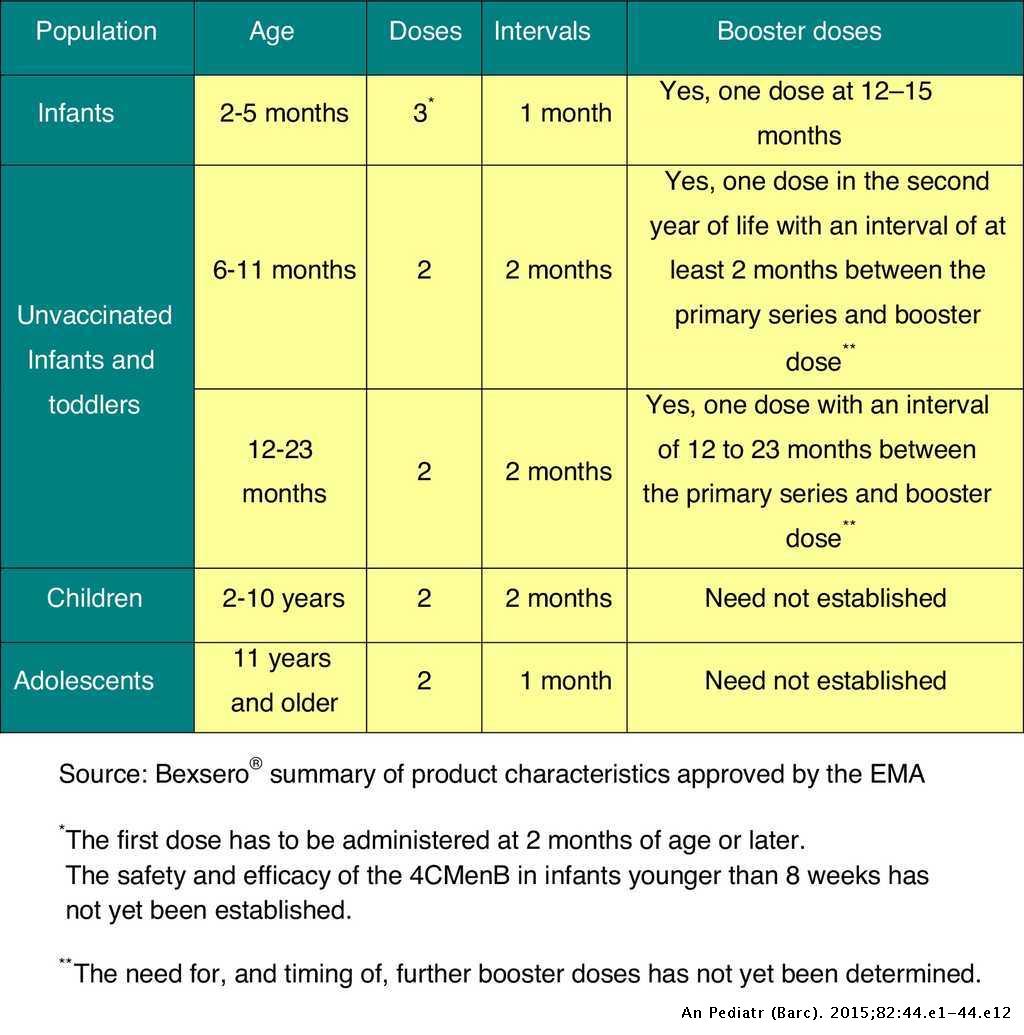
Hepatitis B Vaccination Schedule For Children And Infants
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that babies and children receive three 0.5 milliliter doses of either Engerix-B or Recombivax HB, starting just after birth.
The current recommended hepatitis B vaccine schedule for children and infants is as follows:
| Hepatitis B Vaccination Schedule for Infants and Children | |
|---|---|
| Hepatitis B Vaccine Dose | |
| 3 | 618 months old |
If your child is undergoing hemodialysis, your healthcare provider may recommend that they receive additional doses of the HBV vaccine.
Babies And Children Can Develop Chronic Hbv
You may be wondering why the recommendations for the HBV vaccine start on the first day of life.
Adults who contract HBV will likely not experience long-term complications from hepatitis B. But the same is not the case for babies. As many as of babies who contract an HBV infection at birth from their mothers become chronically infected with HBV.
Children between the ages of 1 and 5 who get an HBV infection have a 25 percent of people who become chronically infected during childhood will develop liver cancer or cirrhosis. Thats why pediatricians want children to have immunity from HBV from the earliest possible age. Many babies and children exposed to HBV receive post-exposure prophylaxis, which decreases chance of infection.
If youre pregnant, youll most likely have a blood test to see if youre positive for hepatitis B. This allows doctors to find out if theres a chance that you could pass on the virus. These tests are highly sensitive and have a good accuracy rate, but they arent perfect. Additionally, a pregnant person may become infected between the time of the test and giving birth. The first dose of the vaccine given at birth lowers the risk of a newborn baby contracting hepatitis B.
Don’t Miss: How Long Can Someone Live With Hepatitis B
How Is Hepatitis B Treated
Immunoglobulin, a passive immunisation, can be administered within 12 hours of an at-risk exposure to help prevent HBV infection. Treatment for chronic disease is through the use of antiviral medications and medications containing naturally-occurring proteins. A liver transplant may be necessary in the event of severe liver damage.
A Hepatitis B vaccination schedule is the best way to prevent infection.
Does The Hepatitis B Vaccine Have Side Effects
Some children will develop pain or soreness in the local area of the shot, and low-grade fever.
There is one extremely rare, but serious, side effect. About 1 out of every 600,000 doses of the hepatitis B vaccine will cause a severe allergic reaction, called anaphylaxis, with symptoms including swelling of the mouth, difficulty breathing, low blood pressure or shock. Anaphylaxis usually occurs within 15 minutes of receiving the vaccine. Although anaphylaxis can be treated, it is quite frightening. People should remain at the doctors office for about 15 minutes after getting the vaccine.
Although the hepatitis B vaccine is made in yeast cells, no one has ever been shown to be allergic to the yeast proteins contained in the hepatitis B vaccine .
Also Check: Blood Donation Hepatitis B Antibodies
Preparations Of Hepatitis B Vaccine
Hepatitis B vaccine is produced using recombinant DNA technology. A plasmid containing the gene for hepatitis B surface antigen is inserted into common bakers yeast, which then produces HBsAg. The HBsAg is harvested and purified. This vaccine cannot cause hepatitis B virus infection because no potentially infectious viral DNA or complete viral particles are produced during this process.
Single-antigen and a combination formulation that combines hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccines are available. Two single-antigen vaccines, Engerix-B® and Recombivax HB®, are conjugated with aluminum. A newer formulation, HepB-CpG , uses the immune-stimulating adjuvant, cytidine-phosphate-guanosine oligodeoxynucleotide .
What Hepatitis B Immunisation Involves
Full protection involves having 3 injections of the hepatitis B vaccine at the recommended intervals.
Babies born to mothers with hepatitis B infection will be given 6 doses of hepatitis B-containing vaccine to ensure long-lasting protection.
If you’re a healthcare worker or you have kidney failure, you’ll have a follow-up appointment to see if you have responded to the vaccine.
If you have been vaccinated by your employer’s occupational health service, you can request a blood test to see if you have responded to the vaccine.
You May Like: How Can You Contract Hepatitis
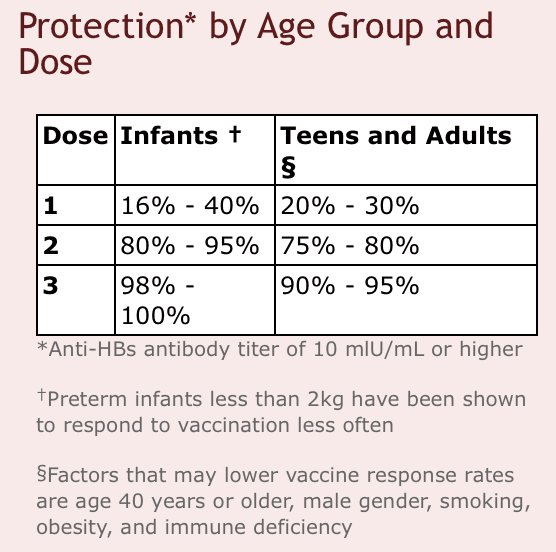
For Adults And Children
This vaccine schedule involves three doses within 2 months, followed by a booster dose at 1 year.
The initial accelerated doses provide immediate protection from HBV, and the booster dose helps provide long-term protection.
Below is the accelerated vaccination schedule approved for both adults and children:
| Vaccine series | |
|---|---|
| 2 months after the first dose | 1 year after the first dose |
Why Do You Need A Hepatitis B Shot
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that cant be transferred person-to-person unless you have contact with an infected persons bodily fluids. Annual infection rates of HBV are going down in the United States thanks to vaccines. So you might be wondering if you or your child needs a shot to protect against hepatitis B.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis B And C
Why Is The Hepb Vaccine Recommended
People who dont know they’re infected can spread the hepatitis B virus. So it cant be avoided just by being careful. That’s why health experts recommend that all babies get the vaccine right from birth.
The HepB injection usually creates long-term immunity. Most infants who get the HepB series are protected from hepatitis B infection beyond childhood, into their adult years.
Eliminating the risk of infection also decreases risk for cirrhosis of the liver, chronic liver disease, and liver cancer.
Babies And Hepatitis B Vaccination
Pregnant women have a routine blood test for hepatitis B as part of their antenatal care.
Babies born to mothers infected with hepatitis B need to be given a dose of the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of their birth, followed by further doses at 4, 8, 12 and 16 weeks of age, plus a final dose when they’re 1 year old.
Babies of mothers identified by the blood test as particularly infectious might also be given an injection of HBIG at birth on top of the hepatitis B vaccination to give them rapid protection against infection.
All babies born to mothers infected with hepatitis B should be tested at 1 year of age to check if they have become infected with the virus.
Also Check: Unspecified Viral Hepatitis C Without Hepatic Coma