Routine Administration Schedule For Hepatitis B Vaccine In Adults
- The dosing schedule is 0, 1 to 2 months, and 4 to 6 months.
- There is some flexibility in the schedule, but be sure to keep in mind the minimum intervals between doses:
- At least four weeks between doses #1 and #2
- At least eight weeks between doses #2 and #3
- At least 16 weeks between doses #1 and #3
- If your patient falls behind on the hepatitis B vaccination schedule , continue vaccinating from where your patient left off. The series does NOT need to be restarted.
What Are The Possible Side Effects Of Hepatitis B Immunisation
All medicines and vaccines can have side effects. Sometimes they are serious, most of the time theyre not.
Generally, the chance of having a serious side effect from a vaccine is much lower than the chance of serious harm if you caught the disease.
Talk to your doctor about possible side effects of hepatitis B vaccines, or if you or your child have possible side effects that worry you.
Common side effects of hepatitis B vaccines include:
- soreness where the needle went in
- low-grade fever
- body aches.
The Consumer Medicine Information links in How do you get immunised against hepatitis B? list the side effects of each vaccine.
Persons New To Canada
Health care providers who see persons newly arrived in Canada should review the immunization status and update immunization for these individuals, as necessary. In many countries outside of Canada, HB vaccine is in limited use.
All persons from a country that is endemic for HB should be assessed and vaccinated against HB if not immune and not infected. Individuals born in developing countries are more likely to be carriers of HB, necessitating vaccination of their sexual and household contacts based on review of their serologic test results. HB vaccine is recommended for all household contacts whose families have immigrated to Canada from areas in which there is a high prevalence of HB and who may be exposed to HB carriers through their extended families or when visiting their country of origin.
Children adopted from countries in which there is a high prevalence of HB infection should be screened for HBsAg and, if positive, household or close contacts in the adopting family should be immunized before adoption or as soon as possible thereafter. Adults going to pick-up children from these countries should be vaccinated before departure. Refer to Immunization of Persons New to Canada in Part 3 for additional information.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Home Test Kit
Costs Health Utilities And Mortality Rates
contains all cost values and utility values for health states. Direct program costs and direct medical costs are included. All final cost figures were converted to 2010 U.S. dollars using the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics Consumer Price Index . The Supplementary Data describes the calculation of other-cause mortality rates for people with diabetes.
Persons With Inadequate Immunization Records
Evidence of long term protection against HB has only been demonstrated in individuals who have been vaccinated according to a recommended immunization schedule. Independent of their anti-HBs titres, children and adults lacking adequate documentation of immunization should be considered susceptible and started on an immunization schedule appropriate for their age and risk factors. Refer to Immunization of Persons with Inadequate Immunization Records in Part 3 for additional information.
Recommended Reading: Where To Get Tested For Hepatitis
How And When Is Hepatitis B Vaccine Given
Depending on which vaccine is used, the Hepatitis B vaccine schedule and dose may vary. You may need three to four doses for longlasting immunity
For children, the hepatitis B vaccine schedule is as follows: Children are given their first shot at birth, and the course is completed by 6 months from then. The second dose is administered at the one month mark and the third at 6 months. Pregnant women with hepatitis B should give their babies a shot of HBV antibodies as well as the vaccine shot upon birth and conduct followup blood tests.
What Are The Hepatitis B Vaccine Ingredients
|
Ingredient |
|
|
Chemically inactivated Hepatitis B protein is among the main ingredients |
|
|
Aluminum Phosphate |
It’s used as an adjuvant. Adjuvant is a substance added to the vaccine to boost immune response |
|
Sodium Chloride, Sodium Borate and other salts |
Inactive ingredient. Used as acidity regulator |
Other components from include trace amounts of the following used in the manufacturing process:
-
yeast proteins
-
formaldehyde which kills the HBV in the vaccine
You May Like: Chronic Viral Hepatitis C Contagious
Recommended Adult Dosing Volume Of Monovalent Hepatitis B Vaccine
- Age 19 years and younger: Use 0.5 mL per dose .
- Age 20 years and older: 1.0 mL per dose .
For a one-page sheet reviewing the hepatitis B dosing schedule for children and adults, consult IACs Hepatitis A and B Vaccines: Be Sure Your Patients Get the Correct Dose. For complete dosing information, consult the ACIP hepatitis B vaccine recommendations for adults.
Hepatitis B Vaccine On The Nhs
A hepatitis B-containing vaccine is provided for all babies born in the UK on or after 1 August 2017. This is given as part of the 6-in-1 vaccine.
Hospitals, GP surgeries and sexual health or GUM clinics usually provide the hepatitis B vaccination free of charge for anyone at risk of infection.
GPs are not obliged to provide the hepatitis B vaccine on the NHS if you’re not thought to be at risk.
GPs may charge for the hepatitis B vaccine if you want it as a travel vaccine, or they may refer you to a travel clinic for a private vaccination. The current cost of the vaccine is around £50 a dose.
You May Like: Hepatitis A Vaccine Schedule For Adults
The National Vaccine Injury Compensation Program
The National Vaccine Injury Compensation Program is a federal program that was created to compensate people who may have been injured by certain vaccines. Claims regarding alleged injury or death due to vaccination have a time limit for filing, which may be as short as two years. Visit the VICP website at www.hrsa.gov/vaccinecompensation or call 1-800-338-2382 to learn about the program and about filing a claim.
When To Delay Or Avoid Hepb Immunization
Doctors delay giving the vaccine to babies who weigh less than 4 pounds, 7 ounces at birth whose mothers do not have the virus in their blood. The baby will get the first dose at 1 month of age or when the baby is discharged from the hospital.
The vaccine is not recommended if your child:
- is currently sick, although simple colds or other minor illnesses should not prevent immunization
- had a serious allergic reaction after an earlier dose of the vaccine or is allergic to baker’s yeast
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Antibody With Reflex
What Happens If I Miss A Dose
The first Hepatitis B Vaccine Dose is designed to trigger the immune response, the second is a booster to solidify it, and the third is to ensure that you have a longlasting immunization response. The timing is critical, as it helps in generating a durable response. The major risk in missing or delaying a dose is that you may not achieve the desired immunity. However, missing a dose does not require you to restart the whole process, just ensure that you complete the course Hepatitis B Vaccine schedule and check if you need followup tests or additional booster shots.
Who Should Get Immunised Against Hepatitis B
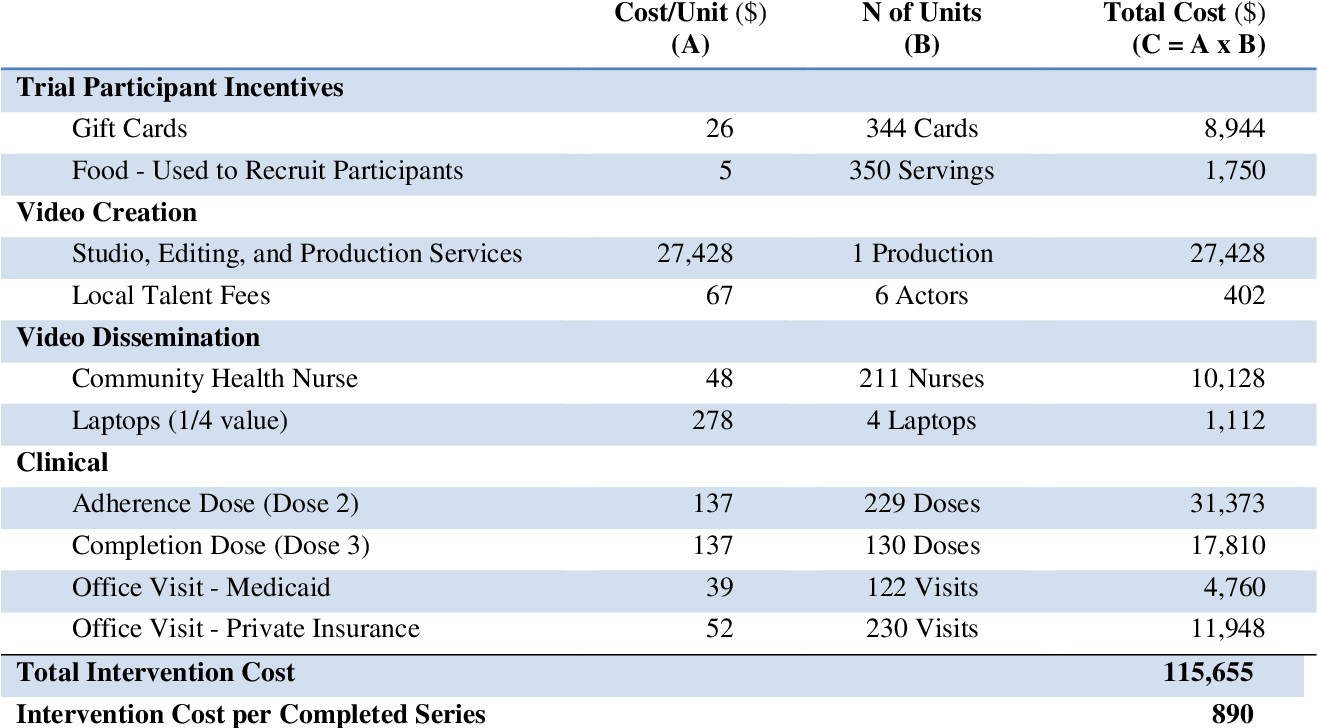
Anyone who wants to protect themselves against hepatitis B can talk to their doctor about getting immunised.
Hepatitis B immunisation is recommended for:
People under 20 years old, refugees and other humanitarian entrants of any age, can get hepatitis B vaccines for free under the NIP. This is if they did not receive the vaccines in childhood. This is called catch-up vaccination.
Don’t Miss: Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis
Risks Of A Vaccine Reaction
- Soreness where the shot is given or fever can happen after hepatitis B vaccination.
People sometimes faint after medical procedures, including vaccination. Tell your provider if you feel dizzy or have vision changes or ringing in the ears.
As with any medicine, there is a very remote chance of a vaccine causing a severe allergic reaction, other serious injury, or death.
How Much Does The Hepatitis Vaccine Cost
The Hepatitis A and B vaccination are designed for both travelers and anyone who wants to receive the vaccination on a voluntary basis.
It is highly recommended for those traveling to Central and South America, as well as Central and East Europe, receive the vaccination. The Hepatitis A vaccine protects against the virus for up to 10 years, while the Hepatitis B vaccination requires a course of three injections over the course of six months.
The cost of a Hepatitis vaccination is going to depend on the type of vaccination received and the location.
You May Like: How Do I Know If I Have Hepatitis B
Common And Local Adverse Events
HB vaccine
HB vaccine is well tolerated. Reactions are generally mild and transient, and include: irritability, headache, fatigue and injection site reactions in 10% or more of recipients.
HAHB vaccine
There is no increase in adverse events when HAHB vaccine is compared with HA vaccine given alone or concomitantly with HB vaccine at a different injection site. When the adult formulation of HAHB vaccine is given to children in the 2 dose schedule, there is no increase in adverse events compared with those occurring after administration of the pediatric formulation of HAHB vaccine.
DTaP-HB-IPV-Hib vaccine
Reactions are usually mild and transient, and include fever, irritability, restlessness and injection site reactions .
HBIg
Headache, diarrhea, fever, urticaria, angioedema and injection site reactions may occur.
Who Should Take The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Besides newborns, others who should take the vaccine are:
-
Unvaccinated people under the age of 19
-
Anyone with a sexual partner with hepatitis B
-
Sexually active people outside of a longterm monogamous relationship
-
People being examined for STDs
-
Men having sexual intercourse with other men
-
People who share druginjecting equipment
-
Anyone sharing living space with an infected person
-
Anyone whose job puts them in contact with infected persons, or blood and bodily fluids
-
People with endstage renal disease, or chronic liver disease
-
Workers at facilities for the developmentally disabled
-
Anyone who has travelled to a region with significant rates of the infection
-
People with HIV infections
Don’t Miss: Medications Used For Hepatitis C
Who Should Not Take The Hepatitis B Vaccine
It is important to note that there are certain exceptions when it comes to taking the vaccine. Do not take the vaccine if youve had a severe allergic reaction to a previous dose or are allergic to yeast, since yeast is used to make the hepatitis B vaccine.
Also, consult your healthcare provider about the vaccine components if you have any other lifethreatening allergies. If you are unwell with a mild illness like a cold, taking the vaccine is safe. However, if the illness is serious, it is advisable to consult your doctor and wait.
Persons With Chronic Diseases
Refer to Immunization of Persons with Chronic Diseases in Part 3 for additional general information about vaccination of people with chronic diseases.
Chronic renal disease and patients on dialysis
People with chronic renal disease may respond sub-optimally to HB vaccine and experience more rapid decline of anti-HBs titres, and are therefore recommended immunization with a higher vaccine dose. Individuals undergoing chronic dialysis are also at increased risk for HB infection. In people with chronic renal disease anti-HBs titre should be evaluated annually and booster doses using a higher vaccine dose should be given as necessary.
Neurologic disorders
People with conditions such as autism spectrum disorders or demyelinating disorders should receive all routinely recommended immunizations, including HB-containing vaccine.
Chronic liver disease
HB immunization is recommended for non-immune persons with chronic liver disease, including those infected with hepatitis C, because they are at risk of more severe disease if infection occurs. Vaccination should be completed early in the course of the disease, as the immune response to vaccine is suboptimal in advanced liver disease. Post-immunization serologic testing may be used to confirm vaccine response.
Non-malignant hematologic disorders
Persons with bleeding disorders and other people receiving repeated infusions of blood or blood products are considered to be at higher risk of contracting HB and should be offered HB vaccine.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Contagious Through Urine
If I Already Have Hepatitis B Can The Vaccine Treat It
No. The hepatitis vaccine prevents hepatitis, but doesnt cure it if you already have it. If you have hepatitis B, there are other treatment options.
However, if you recently got exposed to the hepatitis B virus and you havent had the vaccine yet, tell your doctor right away. The vaccine and possibly other treatment can reduce your chances of getting hepatitis B if you get it within 2 weeks after you came into contact with the virus. The sooner you seek care after being exposed to hepatitis B, the better, so try to get there right away.
How Does The Hepatitis B Vaccine Series Work
The vaccine protects you from the hepatitis B virus by getting your body’s immune system to make antibodies. Those antibodies protect you by fighting off the virus if it ever gets into your body.
Usually, the vaccine is spaced out into three different shots called a hepatitis B vaccine schedule. One month after your first shot, you get the second shot. Six months after your first shot, you get the third shot. If you miss your second or third dose, get it as soon as you remember.
The hepatitis vaccine is super effective. Its worked really well to lower the number of people who get hepatitis B every year.
You May Like: Hepatitis A Curable Or Not
Which Adults Should Be Vaccinated Against Hepatitis B
According to CDC recommendations, adults in the following groups are recommended to receive hepatitis B vaccine:
General
- All people age 18 years and younger.
- Anyone 19 years and older who wants to be protected from hepatitis B.
People at risk for infection by sexual exposure
- Sex partners of people who are hepatitis B surface antigen -positive.
- Sexually active people who are not in long-term, mutually monogamous relationships.
- People seeking evaluation or treatment for a sexually transmitted disease.
- Men who have sex with men.
People at risk for infection by percutaneous or permucosal exposure to blood or body fluids
- Current or recent illegal injection drug users.
- Household contacts of people who are HBsAg-positive.
- Residents and staff of facilities for developmentally challenged people.
- Healthcare and public safety workers with reasonably anticipated risk for exposure to blood or blood-contaminated body fluids.
- People with end-stage renal disease, including predialysis, hemo-, peritoneal- and home-dialysis patients.
Others
- International travelers to regions with intermediate or high levels of endemic HBV infection.
- People with chronic liver disease.
- People with HIV infection.
- People with diabetes who are age 19 through 59 years. For those age 60 and older, clinicians should make a determination of need for
- vaccination based on their patients’ situation.
In a future issue, we will review the various hepatitis B serologic tests, who needs testing, and when they need it .
Guidance On Reporting Adverse Events Following Immunization
Vaccine providers are asked to report, through local public health officials, any serious or unexpected adverse event temporally related to vaccination. An unexpected AEFI is an event that is not listed in available product information but may be due to the immunization, or a change in the frequency of a known AEFI.
Refer to Reporting Adverse Events Following Immunization in Canada and Adverse events following immunization in Part 2 for additional information about AEFI reporting.
Read Also: How To Treat Viral Hepatitis
Hepatitis A Immunisation Service
Hepatitis A vaccines are given as a needle, either on their own or as a combination vaccine. They can be provided by a variety of recognised immunisation providers. If you’re eligible, you can get the hepatitis A vaccine free under the National Immunisation Program .
- Listen
Find information that will help you deliver your service to your patients
Do I Need To Pay For Hepatitis A Immunisation
Vaccines covered by the NIP are free for people who are eligible. See the NIP Schedule to find out which vaccines you or your family are eligible to receive.
Eligible people get the vaccine for free, but your health care provider may charge a consultation fee for the visit. You can check this when you make your appointment.
If you are not eligible for free vaccine, you may need to pay for it. The cost depends on the type of vaccine, the formula and where you buy it from. Your immunisation provider can give you more information.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Home Test Kit
Who Can Help Me
If youre concerned about paying for HCV medications, remember that you arent alone as you seek treatment. There are people and organizations that can help you, including the following:
- Your doctor. They can help you by ordering and documenting the tests youll need so you can qualify to get your medications, especially if youre working with a liver or infection specialist.
- Most drug manufacturers. There are patient assistance programs that offer free or reduced-cost medications for people who meet their criteria.
- Patient advocacy groups. These groups provide assistance with all aspects of HCV treatment. For instance, if your insurer denies treatment, you can appeal the decision with help from one of these groups. Your doctor can also help in this situation.
Drug companies and patient advocacy groups are a great place to start when looking for help paying for HCV medications. Heres a list to get you started.
How Do Vaccinations Work
People often cite the benefits of having anatural immunity to diseases, which only happens if a person has the live disease at some point in their life.
But Dr Wood said while that was considered “ideal”, there was no way to ensure that person only experienced the mild form of a disease.
“Because the way each person’s body deals with the disease is different and we can’t predict what you will do if you get exposed to the disease,” he said.
“You might be lucky and get a mild disease. Or you might be unlucky and get the really nasty severe complications of the disease.”
Dr Wood said the vaccinations being used have been around for decades, and there was a long history of understanding how they worked and how safe they were.
“Adults should be reassured that we’re not experimenting, we’re giving them tried and tested vaccines and our aim is to prevent them from getting the nasty real-life diseases,” he said.
The way a vaccination works is by mimicking the disease without actually giving the person the disease.
“So the vaccine in a sense tricks the body into thinking that they’re seeing the real disease,” he said.
“It then makes the antibodies, and the cellular immune response.
“So if down the track you see the real disease, your body goes, ‘Ah I recognise this, I’ll know what to do’ so you don’t get the full blown disease.”
Read Also: Is Milk Thistle Good For Hepatitis C