Treatment For Chronic Hbv Infection
For chronic HBV infection, antiviral medications are available.
This is not a cure for chronic HBV. However, it can stop the virus from replicating and prevent its progression into advanced liver disease.
A person with a chronic HBV infection can develop cirrhosis or liver cancer rapidly and without warning. If a person does not have access to adequate treatment or facilities, liver cancer can be fatal within months of diagnosis.
People with a chronic HBV infection require ongoing medical evaluation and an ultrasound of the liver
Who Is More Likely To Get Hepatitis B
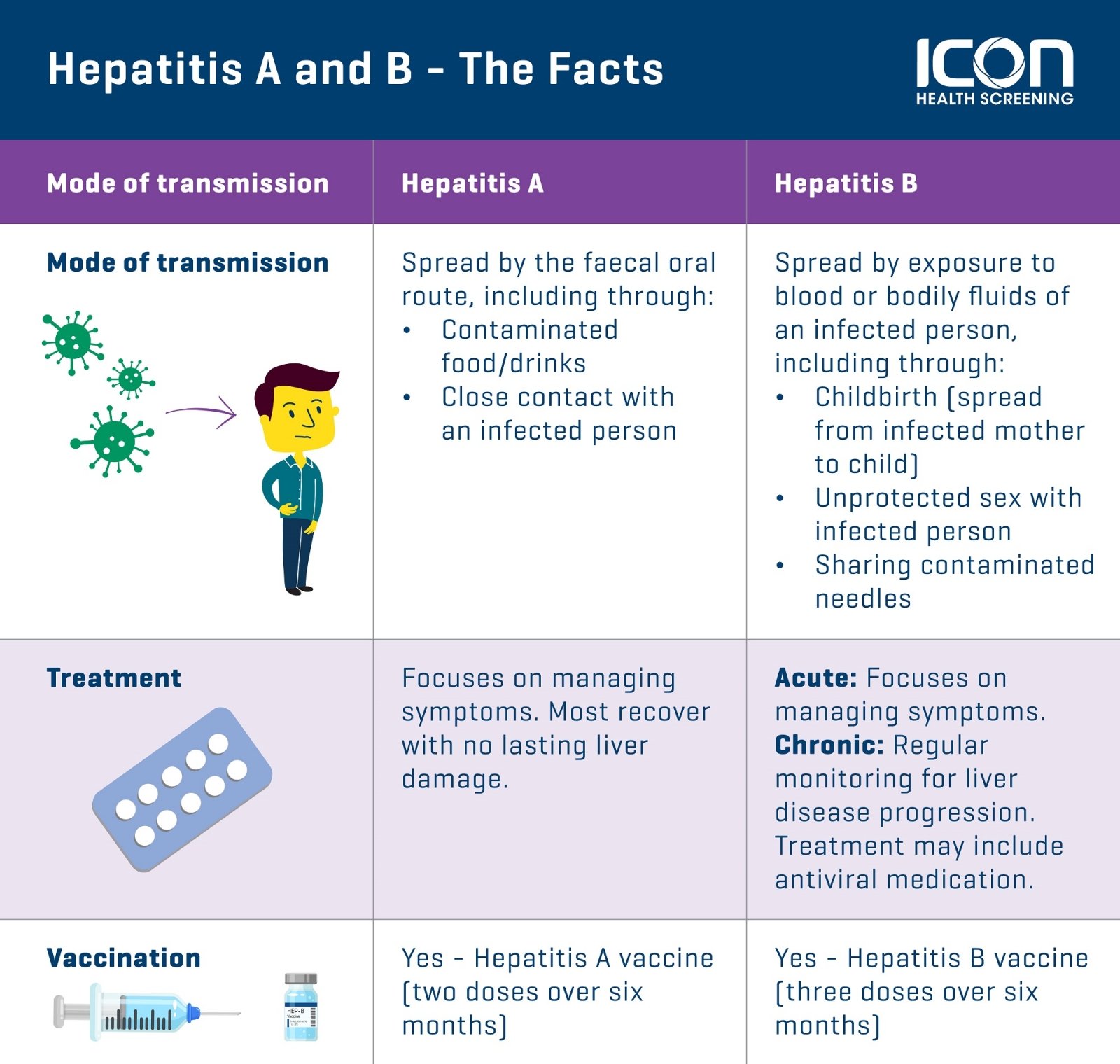
People are more likely to get hepatitis B if they are born to a mother who has hepatitis B. The virus can spread from mother to child during birth. For this reason, people are more likely to have hepatitis B if they
- were born in a part of the world where 2 percent or more of the population has hepatitis B infection
- were born in the United States, didnt receive the hepatitis B vaccine as an infant, and have parents who were born in an area where 8 percent or more of the population had hepatitis B infection
People are also more likely to have hepatitis B if they
- are infected with HIV, because hepatitis B and HIV spread in similar ways
- have lived with or had sex with someone who has hepatitis B
- have had more than one sex partner in the last 6 months or have a history of sexually transmitted disease
- are men who have sex with men
- are injection drug users
- work in a profession, such as health care, in which they have contact with blood, needles, or body fluids at work
- live or work in a care facility for people with developmental disabilities
- have been on kidney dialysis
- live or work in a prison
- had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before the mid-1980s
In the United States, hepatitis B spreads among adults mainly through contact with infected blood through the skin, such as during injection drug use, and through sexual contact.12
What Is Chronic Hepatitis B
Doctors refer to hepatitis B infections as either acute or chronic:
- An acute HBV infection is a short-term illness that clears within 6 months of when a person is exposed to the virus.
- A person who still has HBV after 6 months is said to have a chronic hepatitis B infection. This is a long-term illness, meaning the virus stays in the body and causes lifelong illness. An estimated 850,000 to more than 2 million people in the U.S. have chronic HBV.
The younger someone is when infected, the greater the chances for chronic hepatitis B.
Recommended Reading: Is Hepatitis A Sexually Transmitted
Whats The Outlook For People With Chronic Hep B
The majority of people who have hep B as adults fully recover within 1 to 3 months. Children under the age of 5 are at the highest risk of developing chronic hep B infection.
Medications can help manage chronic hep B, but about 15 to 25 percent of people die prematurely from liver cancer, cirrhosis, or liver failure.
More than half of liver cancers are caused by chronic hep B infection. Taking your medications as prescribed and following your healthcare professionals recommendations can help you minimize your chances of complications.
Is There A Cure For Hepatitis B
The long and short answer is that there is not yet a cure for hepatitis B. Understanding why requires insight into the virus itself and the challenges cure researchers face.
Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus . While most people exposed to hepatitis B will spontaneously clear the virus soon after infection, a proportion will go on to develop a chronic infection.
Of these, around one in four will develop severe liver complications, including cirrhosis and liver cancer, typically years after the initial infection.
Efforts to find a cure for hepatitis B have been underway since the virus was first identified by scientists at the National Institutes of Health in 1966. It soon became clear, however, that numerous hurdles would need to be overcome before an actual cure could be achieved. Chief among these are:
Read Also: What Kind Of Doctors Treat Hepatitis C
Symptoms Of Chronic Hepatitis B
Symptoms of chronic hepatitis B vary depending on how badly the liver is damaged.
Many people with chronic hepatitis B, particularly children, have no symptoms. People who have symptoms usually feel generally ill and tired and lose their appetite. Some people have a low-grade fever and vague discomfort in the upper abdomen.
Often, the first specific symptoms occur when the liver disease has progressed and there is evidence of cirrhosis. Symptoms can include
-
An enlarged spleen
-
Deterioration of brain function due to malfunction of the liver
Brain function deteriorates because toxic substances build up in the blood and reach the brain. The liver normally removes them from the blood, breaks them down, then excretes them as harmless by-products into the bile or blood. The badly damaged liver is less able to remove them.
People have a tendency to bleed because the damaged liver can no longer synthesize enough of the proteins that help blood clot.
What Are The Risk Factors For Hepatitis B And C
Hepatitis B: Although most commonly acquired early in life, adults can also contract it. Hepatitis B is largely transmitted through bodily fluids. It can be passed at birth from a hepatitis B-infected mother or through exposure in early childhood to body fluids, blood or contaminated medical instruments. Hepatitis B can also be transmitted through intranasal and injection drug use as well as infected tools used during tattooing and body piercing.
Hepatitis C: The key risk factors are also intranasal and injection drug use, tattoos and body piercings, high-risk sexual contact, blood transfusions before 1992 and organ transplantation.
Another key risk factor for hepatitis C is being born from 1945 to 1965, during the baby-boom years. Eighty percent of all people who currently have hepatitis C in the United States were born in that timeframe.
Although the reasons that baby boomers are more likely to have hepatitis C than others arent entirely understood, its believed that most were infected in the 1970s and 1980s, when rates of hepatitis C were at their peak.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommend that all U.S. adults born from 1945 to 1965 undergo a one-time screening test for hepatitis C. Connecticut is one of several states that has written this recommendation into law. In Connecticut ,the law requires that primary care clinicians screen all adults born within those years.
Also Check: What Is The Cure Of Hepatitis B
Unlikely Sources Of Infection
Trace levels of HBV can also be found in saliva, tears, urine, and feces but in amounts that are highly unlikely to cause infection.
While vaccination remains the cornerstone of HBV prevention, there are ways to further reduce the risk of transmission, especially if you or someone in your household has hepatitis B:
- Wash your hands with soap and water if exposed to blood.
- Avoid sharing razors or toothbrushes.
- Use condoms during sex.
What Do I Need To Know About Having Hepatitis B
If you have chronic hepatitis B, getting the right medical care can help you stay healthy. Taking good care of your liver is important. Talk with your doctor before you take any prescription medication, over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, or nutritional supplements to make sure they wont hurt your liver. You should also stay away from alcohol, because drinking can damage your liver.
Read Also: How Long Can Hepatitis C Live Outside The Body
Prevent Infection After Contact With The Virus
If you think you have been in contact with the hepatitis B virus, see your doctor right away. Doctors typically recommend a dose of the hepatitis B vaccine to prevent infection. In some cases, doctors may also recommend a medicine called hepatitis B immune globulin to help prevent infection. You must get the vaccine dose and, if needed, HBIG shortly after coming into contact with the virus, preferably within 24 hours.
Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk In Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B
Chronic hepatitis B is now recognized as one of the most important cause for the development of HCC, accounting for over 50% of the HCC cases worldwide. However, it was not until the mid-1970s that scientists recognized the causative role of chronic hepatitis B in HCC development. This was following the discovery of the hepatitis-associated antigen, now known as the HBsAg, which has been reported to persist in patients with chronic hepatitis B with or without cirrhosis, leading to HCC development in a significant proportion of patients.41 Various mechanisms have been proposed in the pathogenesis of HCC in patients with chronic HBV infection. Integration of the HBV DNA into the hepatocyte genome and the epigenetic regulation of the minichromosome cccDNA result in chromosomal instability and activation of cancer-related genes along with inactivation of cancer-suppressive genes through interference with various cellular transcription and signal transduction processes.42 In addition, chronic hepatitis B results in release of cytokines and growth factors as part of the adaptive immune response, leading to hepatocyte necrosis and fibroblast proliferation, resulting in liver fibrosis/cirrhosis.43
As such, patients with chronic hepatitis B, especially those at high risk, should be continuously screened for HCC, regardless of the virologic remission .27
James E. Balow, … Howard A. AustinIII, in, 2008
You May Like: How Can You Catch Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B Vs Hepatitis C
Hepatitis has many different types. HBV and the hepatitis C virus have both acute and chronic forms.
The main difference between HBV and HCV is how they spread from person to person. Although HCV is transmissible via sexual activity, this is rare. HCV usually spreads when blood that carries the virus comes into contact with blood that does not.
What Are Clinical Trials For Hepatitis B

Clinical trialsand other types of clinical studiesare part of medical research and involve people like you. When you volunteer to take part in a clinical study, you help doctors and researchers learn more about disease and improve health care for people in the future.
Researchers are studying many aspects of hepatitis B, such as
- progression of hepatitis B and long-term outcomes
- new treatments for hepatitis B
- prevention of reactivated or worsening hepatitis B in people receiving cancer treatment
Read Also: Duration Of Tenofovir Treatment For Hepatitis B
Is Hepatitis B Contagious
Hepatitis B is highly contagious. Its transmitted through contact with blood and certain other bodily fluids. Although the virus can be found in saliva, its not transmitted through sharing utensils or kissing. Its also not transmitted through sneezing, coughing, or breastfeeding.
Symptoms of hepatitis B may not appear for 3 months after exposure. Symptoms can last for several weeks.
But even without symptoms, you can still transmit the infection to others. The virus can live outside the body and remains infectious for at least
Hepatitis B is a highly contagious condition. Its associated with many serious complications, some of which can be life threatening.
But there are many treatment options available and multiple ways you can prevent infection, including getting vaccinated.
If you suspect you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a doctor to prevent infection and determine the best course of treatment for you.
Reduce Your Chance Of Infection
You can reduce your chance of hepatitis B infection by
- not sharing drug needles or other drug materials
- wearing gloves if you have to touch another persons blood or open sores
- making sure your tattoo artist or body piercer uses sterile tools
- not sharing personal items, such as toothbrushes, razors, or nail clippers
- using a latex or polyurethane condom during sex
You May Like: What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis C
Is There A Cure For Chronic Hepatitis B
Currently, there is no complete cure for hepatitis B. But when managed properly, those living with the virus can expect to live a normal life. Maintaining a healthy diet and avoiding alcoholic beverages and tobacco products are crucial components in managing the disease.
You should also visit a doctor familiar with hepatitis B at least annuallythough twice a year might be best to monitor your liver through blood tests and medical imaging. As with most diseases, detecting it early leads to a better outcome. If youre exposed to the virus, you should get an antibody injection within 12 hours of exposure.
What Are The Types Of Hepatitis B
There are two types of hepatitis B infection: acute and chronic.
Acute
An acute infection happens at the beginning, when you first get infected with hepatitis B. Many people are able to clear it from their bodies and recover. In fact, this is true of about 4 in 5 adults who are infected.
Chronic
If you are not able to clear the infection within six months or longer, you have chronic hepatitis B. It is chronic hepatitis B that leads to inflammation and the serious, and possibly fatal, illnesses of cirrhosis of the liver and liver cancer. Treatment can slow disease progress, reduce the chance of liver cancer and increase your chances of surviving.
Don’t Miss: How Does Hepatitis B And C Spread
What Problems Can Hepatitis B Cause
Hepatitis B is a serious infection. It can lead to cirrhosis of the liver, liver failure, or liver cancer, which can cause severe illness and even death.
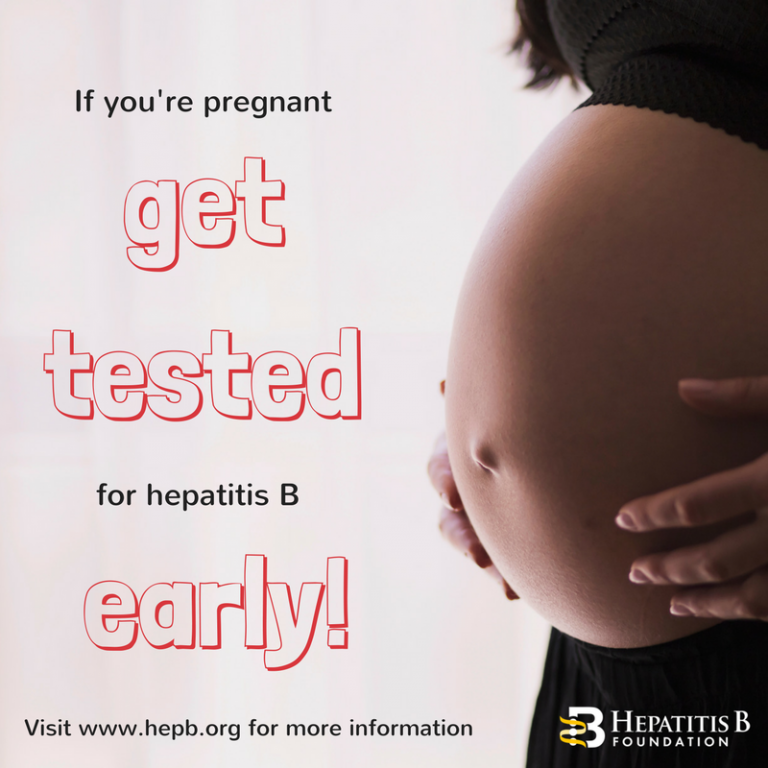
If a pregnant woman has the hepatitis B virus, her baby has a very high chance of having it unless the baby gets a special immune injection and the first dose of hepatitis B vaccine at birth.
Sometimes, HBV doesn’t cause symptoms until a person has had the infection for a while. At that stage, the person already might have more serious problems, such as liver damage.
Hepatitis B And Pregnancy
If youâre pregnant, you might pass the virus to your baby at birth. Itâs less likely to happen during your pregnancy.
If your baby gets the virus and isnât treated, they could have long-term liver problems. All newborns with infected mothers should get hepatitis B immune globulin and the vaccine for hepatitis at birth and during their first year of life.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Symptoms And Treatment
How Do Doctors Treat The Complications Of Hepatitis B
If chronic hepatitis B leads to cirrhosis, you should see a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. Doctors can treat the health problems related to cirrhosis with medicines, minor medical procedures, and surgery. If you have cirrhosis, you have an increased chance of liver cancer. Your doctor may order blood tests and an ultrasound or another type of imaging test to check for liver cancer.
If chronic hepatitis B leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
Clearing Acute Hepatitis B
Some studies suggest that up to 95% of adults with acute HBV infection will spontaneously clear the virus, usually within six months, with no lasting repercussions.
Chronic hepatitis B occurs when the immune system does not clear the virus. Around one of every 20 people acutely infected with HBV will progress to this persistent stage of infection.
Chronic hepatitis B is a slowly progressive disease in which ongoing inflammation causes the gradual scarring of the liver. This can lead to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma .
However, the course of chronic HBV infection is not set. Some people may progress faster than others, while others may never develop overt symptoms.
Statistically speaking:
- The risk of cirrhosis in people with chronic hepatitis B is approximately 10% to 20% over 20 years, increasing to 40% after 30 years.
- The risk of hepatocellular carcinoma increases by 2% and 3% per year in people with HBV and cirrhosis. People without cirrhosis can also get it, but the annual risk drops to around 0.02%.
Don’t Miss: Hepatic Porphyrias Diagnosis And Management
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test
A hepatitis B surface antigen test shows if you have an active infection. A positive result means you have hepatitis B and can transmit the virus to others. A negative result means you dont currently have hepatitis B.
This test doesnt distinguish between chronic and acute infection. This test is used together with other hepatitis B tests to determine the state of a hepatitis B infection.
Treatment Of Chronic Hepatitis B
-
Antiviral drugs
-
People with chronic hepatitis B have been taking antiviral drugs for a long time.
-
They are treated with hepatitis immune globulin before and often after transplantation.
Hepatitis B immune globulin is obtained from the blood of people who have high levels of antibodies to hepatitis B. It is given by injection into a muscle or into a vein. It helps the body fight infection.
You May Like: Hepatic Steatosis Versus Hepatocellular Disease
What Are The Treatment Options For Chronic Hep B
For people with acute hep B infection experiencing mild symptoms, doctors often recommend rest, a healthy diet, and fluids to speed up recovery. Severe symptoms may need to be treated in a hospital.
According to the Hepatitis B Foundation, there are currently seven drugs approved by the FDA to treat chronic hep B in the United States. Not everybody needs to take medication, but some people will need to take medication for the rest of their lives.
These drugs fall into one of two categories:
- Antiviral drugs. These drugs help reduce inflammation and liver damage. Theyre usually taken daily in pill form for at least a year.
- Immune modulator drugs. These drugs boost your immune system to help your body fight off the virus. Theyre administered as an injection over 6 to 12 months.
Theres no cure for hep B, acute or chronic, at the moment. However, clinical trials continue to investigate new treatment options.