Signs & Symptoms Of Autoimmune Hepatitis
Most cases of early autoimmune hepatitis have no symptoms and can only be detected by routine blood tests . The symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis differ depending on its severity and may include:
- Itchy skin, dark urine, pale stools, disorientation, abdominal swelling, and leg swelling if the disease gets worse
When Should We Refer An Aih Patient To A Specialist Centre
Timely consultation with an expert centre and/or transplant centre is recommended in case of diagnostic uncertainties, patients with features of variant syndromes, pregnant patients and issues regarding optimal disease management.15 For patients who fail to demonstrate a sufficient biochemical response after use of a second immunosuppressant or when the treating physician is unfamiliar with prescribing second-line therapy, expert advice should be sought. Finally, patients who present with acute liver failure and are eligible for liver transplantation should be transferred to a transplant centre .
Researching Autoimmune Liver Disease
The focus of our research at Mount Sinai has been to identify ways to slow the progression of autoimmune liver diseases. We evaluate the genetic and environmental influences of liver disease. We also research treatments with minimal side effects. Our studies have led to several clinical trials and global collaborations.
Our research teams dedication means you have access to comprehensive, groundbreaking care. We have made strides in diagnosis to post-transplantation care. Our team also supports patient-directed self-help groups for those with autoimmune diseases.
You May Like: Signs Of Hepatitis C In Males
Incomplete Or Failed Response To Treatment
Some people with autoimmune hepatitis have an incomplete response to treatment, meaning that treatment helps but does not lead to remission. If you have an incomplete response to treatment, you may need to take different medicines to help prevent liver damage.
Some people may fail to respond to treatment, meaning that the inflammation and liver damage of autoimmune hepatitis keep getting worse. Your doctor may recommend additional blood tests and higher doses of medicines. If liver damage leads to complications, you may need treatment for complications.
What Are The Risk Factors For Type Ii Autoimmune Hepatitis
The common risk factors of Type II Autoimmune Hepatitis include:
- Individuals, with autoimmune diseases, such as diabetes mellitus , celiac disease, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, inflammatory bowel disease including ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis , immune thrombocytopenia , and Gravess disease. More individuals with Type II AIH present autoimmune disorders
- Gender: AIH occurs at a much higher rate in females
- Genetic predisposition and family history: In vast majority of Type II AIH, there is no family history, and hence, the current recommendation is not to screen family members for the condition
- Hemolytic anemia
- Presence of bacterial or viral infections has been known to cause the development of the condition. The exact mechanism of how this happens is still being researched into
- Use of certain medications have been reported to be a risk factor for the development of AIH
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
Recommended Reading: What Food Is Good For Hepatitis C
What Causes Chronic Inflammation Of The Liver
The exact cause of the condition has not yet been identified however, research suggests that the condition is linked to certain white blood cells in combination with foreign substances in the body misreading liver cells and attacking them. This attack causes the characteristic inflammation and liver deterioration.
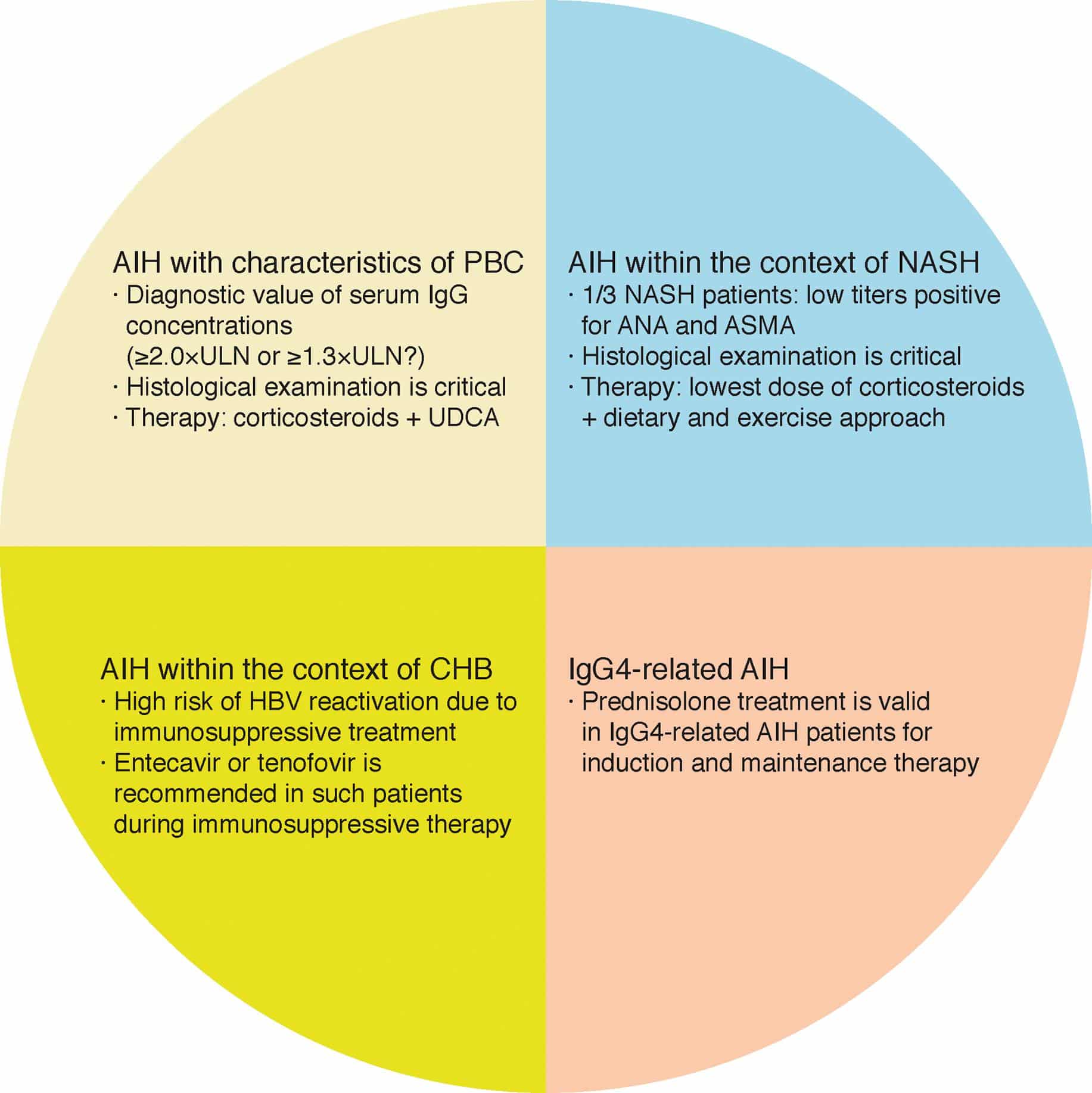
Overlap And Outlier Syndromes
A sizeable percentage of cases of autoimmune liver disease that generally fit into one diagnostic category will show clinical, serologic, or histologic features more characteristic of another type of autoimmune liver disease. When overlap in all three areas is present, the diagnosis of an overlap syndrome should be considered. However, it should be noted that it is controversial whether these overlap syndromes are distinct entities or variants of the major autoimmune hepatopathies, and standardization of diagnostic criteria and terminology is lacking.
The term overlap syndrome is used primarily to describe variant forms of autoimmune liver disease that present with both cholestatic and hepatitic features that do not fit readily into the usual diagnostic categories,, and which generally have overlapping characteristics of AIH+PBC or AIH+PSC .
Table 6 Variants of autoimmune liver disease
Evidence for a PSC-PBC overlap syndrome is limited and based upon case reports.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Prevent Hepatitis C
Are Other Treatments For Autoimmune Hepatitis Available
People who do not respond to standard immune therapy or who have severe side effects may benefit from other immunosuppressive agents such as mycophenylate mofetil, cyclosporine, or tacrolimus. People who progress to end-stage liver diseasealso called liver failureor cirrhosis may need a liver transplant. Transplantation has a 1-year survival rate of 90 percent and a 5-year survival rate of 70 to 80 percent.
What Are The Causes Of Autoimmune Hepatitis
Autoimmune hepatitis occurs when the white blood cells of the body produce an inappropriate immune response against the liver cells, thereby causing inflammation and damage. The exact cause of autoimmune hepatitis is not known. Affected people may have a genetic predisposition for the condition, which may be triggered by an environmental factor. Around 20% patients suffering from a genetic condition called autoimmune polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis-ectodermal dystrophy syndrome suffer from autoimmune hepatitis.
The environmental trigger could be:
- Drugs like infliximab, minocycline, atorvastatin, diclofenac, isoniazid, methyldopa, nitrofurantoin, and propylthiouracil, the hepatitis A vaccine, and herbal agents like black cohosh and dai-saiko-to. The autoimmune hepatitis may improve after stopping the medication
- Viruses such as hepatitis A, B, or C, or measles virus
Autoimmune hepatitis is of two main types, type 1 and type 2
- Type 1 autoimmune hepatitis usually first manifests in adolescence or young adults. Females are most commonly affected.
- Type 2 autoimmune hepatitis is less common than type 1 and usually first manifests in children. Its prognosis or outcome is often worse than type 1 disease.
Also Check: Lamivudine Dose In Hepatitis B
What Causes Autoimmune Hepatitis
Experts dont know what causes autoimmune hepatitis, but it is more likely to show up in people with other autoimmune conditions, including:
- Fluid buildup in the belly
- Rectal bleeding or vomiting blood
The symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis may look like other health problems. Always see your healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
Epidemiology: An Increasing Trend
AIH commonly affects middle-aged women, but occurrence in childhood or adolescence is observed.8,9 Worldwide, the peak incidence of AIH is around 50 to 60 years of age, and the highest incidence was observed around 60 to 70 years in both South Korea and Japan.9,10 Similarly to other autoimmune diseases, female preponderance is distinct in AIH, and the male-to-female ratio is around 1:4 to 1:6.
The burden of AIH appears to be increasing worldwide, and the point prevalence reported in the published literature after 2000 is shown in Fig. 1.8,11–18 The point prevalence of AIH is reported to be 10 to 25 per 100,000 population in European countries, and 5 to 25 in the Asia-Pacific region. Among these, epidemiological studies were serially conducted twice in Sweden and Japan.11,18,19 Although the study design, study area, and case findings were different, the point prevalence in Sweden was 10.7 and 17.3 in 2003 and 2009, respectively, indicating a 1.7-fold increase in 6 years.11,18 Likewise, in Japan, the prevalence of AIH was 8.7 and 23.9 in 2004 and 2016, respectively, and thus tripled over a 12-year period.19 It is also of note that although AIH was thought to be less frequent in Asia, the point prevalence recently reported is similar to that of the rest of the world .
The point prevalence of autoimmune hepatitis in Europe and the Asia-Pacific region, reported after 2000.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Ab Reactive Means
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Type Ii Autoimmune Hepatitis
The severity of signs and symptoms of Type II Autoimmune Hepatitis may vary from one individual to another. In some, it may be mild, resulting in a delayed diagnosis of the condition. Some individuals are diagnosed incidentally during wellness checkups. In other individuals, the signs and symptoms may be severe.
The signs and symptoms of Type II AIH are usually more severe and may include
- Loss of appetite
- Enlarged or swollen liver
- Amenorrhea in women
The signs and symptoms of the underlying condition , if any present, may be noted.
Why Should We Treat An Aih Patient

Typically, the first question of AIH patients after hearing their diagnosis is: Do I need treatment?. Untreated AIH leads to progression of fibrosis to cirrhosis and, eventually, end-stage liver disease. Older studies showed that immunosuppressive treatment with steroids in AIH patients not only improved liver function tests, but also improved symptoms and prolonged survival.46 More recent studies have shown that treatment also leads to regression of liver fibrosis, even at the cirrhotic stage of disease.7 This data indicates that treatment is warranted in patients with AIH.
You May Like: What Are The Causes Of Hepatitis D
What Are The Complications Of Autoimmune Hepatitis In A Child
Autoimmune hepatitis can cause scar tissue to start forming on the damaged liver . This makes it harder for the liver to work properly. Over time, lots of scar tissue can build up in the liver . This can block the blood flowing through the liver and may lead to problems such as bleeding in the esophagus or stomach, or water in the belly . Cirrhosis also can cause the liver to fail signs may be jaundice , bleeding/bruising, or confusion.
Side Effects Of Steroids And Azathioprine
Steroid side effects are dose and time dependent, and arise if a dose exceeding 7.5-10 mg/d is administered over several months. The most common side effect is the development of cushingoid features. In a retrospective monocentric study of 103 adult AIH patients, mostly treated according to a standard protocol with a steroid starting dose of 1 mg/kg per day and a mean follow-up period of 95 mo, 15.5% developed cushingoid features. Although not severe, these changes are often a great concern for the patients, and may lead to non-adherence, with the dangerous consequence of poor disease control. Almost half of AIH patients discontinue steroids because of cosmetic changes or obesity. Severe, but less frequent steroid side effects include osteoporosis, brittle diabetes, cataract, psychosis and hypertension. They are mainly related to the initial high dose, and are reversible. Monitoring of these complications is advisable, including ophthalmologic controls and bone density scans on a regular basis.
Measurement of the azathioprine metabolites 6-TGN and 6-methylmercaptopurine can be helpful in identifying drug toxicity and non-adherence, and in distinguishing azathioprine hepatotoxicity from disease non-response, as shown by a retrospective study in adults, and a small prospective study in children, but an ideal therapeutic level of the 6-thioguanine metabolites has not been established for AIH, unlike for inflammatory bowel diseases .
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis A Outbreak Michigan Restaurant
Search For A Clinical Trial
Clinical trials are research studies that test how well new medical approaches work in people. Before an experimental treatment can be tested on human subjects in a clinical trial, it must have shown benefit in laboratory testing or animal research studies. The most promising treatments are then moved into clinical trials, with the goal of identifying new ways to safely and effectively prevent, screen for, diagnose, or treat a disease.
Speak with your doctor about the ongoing progress and results of these trials to get the most up-to-date information on new treatments. Participating in a clinical trial is a great way to contribute to curing, preventing and treating liver disease and its complications.
Start your search here to find clinical trials that need people like you.
Goal And Indication Of Treatment For Aih
The aim of treatment in AIH is to achieve complete biochemical and histological remission, and prevent further progression of liver fibrosis. Complete biochemical remission is associated with the normalization of both serum alanine aminotransferase and IgG levels. Whereas increased mortality is observed in AIH patients with cirrhosis compared to those without cirrhosis,36 histological regression of fibrosis, as well as an improved long-term outcome will be attained by complete biochemical remission.37,38 Although the patients with AIH who should be treated are poorly defined, those with advanced or active AIH are expected to have a poor outcome and absolute indication for treatment. On the other hand, patients with mild disease may not require prompt treatment, and be closely monitored until elevation of ALT and/or IgG.5
You May Like: How Bad Is Hepatitis B
About Autoimmune Liver Disease
Autoimmune liver diseases are typically long-lasting and recurring conditions. This means that you may experience persistent immune system attacks that destroy liver cells. As cells die, scar tissue known as fibrosis forms. Autoimmune diseases tend to progress slowly, and you may have long periods without symptoms. When scarring becomes extreme, liver function weakens and eventually may result in a condition known as cirrhosis. Cirrhosis is also known as liver failure or end-stage liver disease. The only cure for this condition is organ transplantation. While the only cure for severe cirrhosis is transplantation, we can help you manage the symptoms of the disease with medication before or instead of transplantation.
Our liver specialists work closely with other experts at Mount Sinai to provide a comprehensive approach to treating you if you have multiple autoimmune conditions. Our goal is to keep your immune system active and related symptoms under control.
Mount Sinai liver specialists work with colleagues in rheumatology, endocrinology, gastroenterology, radiology, and pathology to manage autoimmune liver disease. We use state-of-the-art methods of diagnosis and treatment.
If end-stage liver disease develops and you need liver transplantation, we have the expertise to help you. We have extensive experience treating patients with autoimmune liver disease. After living with chronic liver disease, through treatment, we can help restore your quality of life.
Autoimmune Hepatitis Causes And Risk Factors
Doctors aren’t sure exactly what causes your immune system to turn against your liver. Your genes may have something to do with it, since AIH can run in families.
But genes aren’t the whole story. Something you come into contact with may trigger your genes to set autoimmune hepatitis in motion. This could include:
- Medicines such as statins and hydralazine or antibiotics like nitrofurantoin and minocycline
- Infections such as viral hepatitis, herpes, Epstein-Barr, and measles
You May Like: Which Hepatitis Has A Vaccine
What Is An Autoimmune Disease
An autoimmune disease causes your immune system to attack healthy cells in your body by mistake. It can affect different parts of your body. There are more than 80 types of autoimmune diseases.
Verywell / Danie Drankwalter
Fortunately, autoimmune hepatitis is treatable with corticosteroids and outcomes are good in patients who seek early treatment.
How To Use Prednisone And Azathioprine
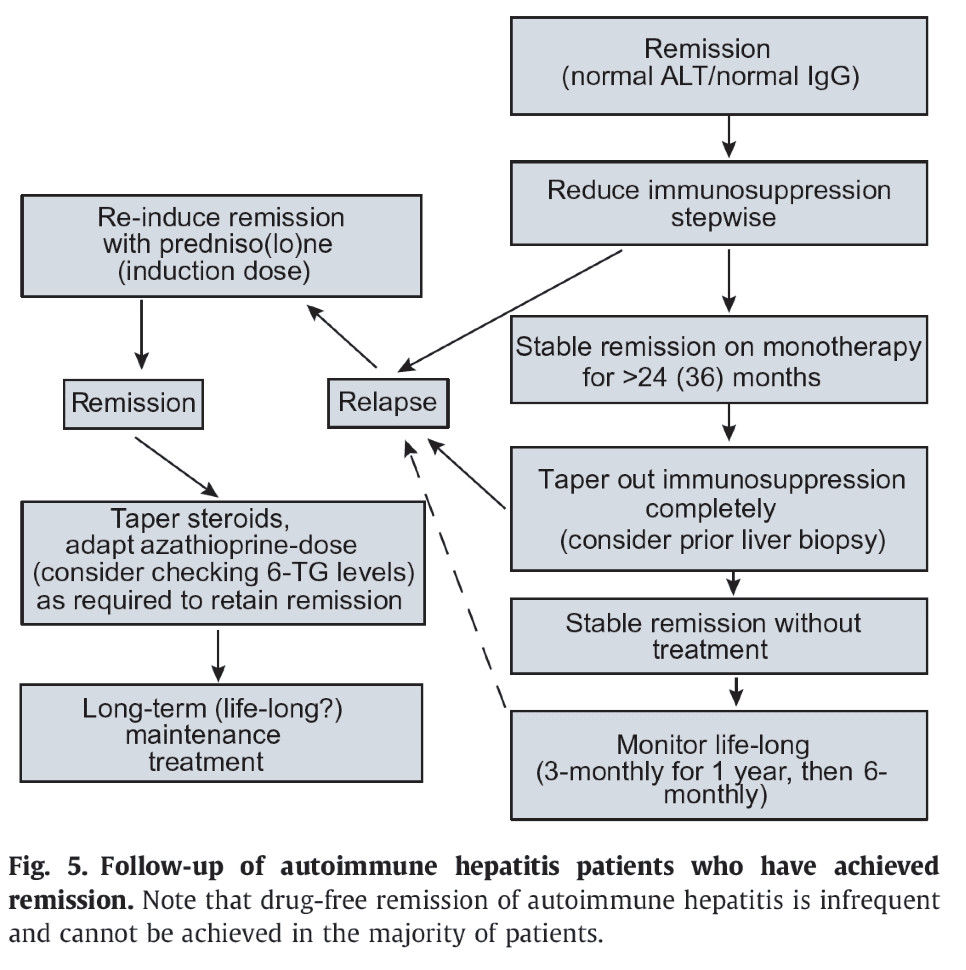
There is no treatment schedule applicable to all AIH patients. The suggested algorithms and treatment schedules must be tailored to the single patient, taking into account the severity of the disease, age and co-morbidities.
The AASLD guidelines published in 2010 recommend two alternative schedules: either prednisone alone at a dose of 60 mg/d or a combination of prednisone 30 mg/d and azathioprine 50 mg/d as initial treatment, favouring the latter because of fewer steroid side-effects. However, as azathioprine can be hepatotoxic, particularly in cirrhotic and jaundiced patients, the more recent guidelines by the European Association for the Study of the Liver recommend that it is added after two weeks of steroid monotherapy , when partial disease control has been achieved. In addition, this approach avoids the problem of distinguishing between azathioprine-induced hepatotoxicity and non-response, this distinction being an important issue in clinical practice. A retrospective series of 133 adult patients reports better results with a combination of steroids and another immunosuppressant from disease presentation compared to steroids alone or steroids followed by the addition of azathioprine/other immunosuppressants. Of note, only 2% of the patients included in this study were jaundiced at presentation, possibly explaining the high remission rate on azathioprine, without hepatotoxicity.
Read Also: What Are The Early Warning Signs Of Hepatitis C
What Are The Causes Of Type Ii Autoimmune Hepatitis
The exact cause of Type II Autoimmune Hepatitis is currently unknown. It is caused by a combination of environmental, genetic, and immunological factors. The immunological factors may constitute certain preexisting autoimmune disorders such as diabetes, inflammatory bowel diseases, rheumatoid arthritis, Gravess disease, among other conditions.
- Generally, AIH occurs when the immune system is compromised and begins to function abnormally. This causes the immune system to attack the liver, which is healthy, causing liver inflammation or hepatitis
- Some drugs and certain infections have been found to contribute to this abnormal response of the immune system. While, stoppage of the particular drug or treating the infection may alleviate the symptoms, attack on the liver and inflammation may continue to take place, even after such remedial measures are taken
- Some researchers have proposed that certain genetic factors may predispose an individual to AIH. This may be a reason why this condition has been observed to run in families, in some rare cases
How Is Type Ii Autoimmune Hepatitis Diagnosed
The diagnosis of Type II Autoimmune Hepatitis is based upon a combination of clinical findings and lab test abnormalities. It is important to rule out other causes of chronic hepatitis, such as alcohol-induced hepatitis, viral hepatitis, and drug-induced hepatitis, before arriving at a diagnosis of AIH.
The following tests and exams may be used in the diagnosis of Type II AIH:
- A complete medical history and a thorough physical examination. The physician may request for a list of all medications that are currently being taken
- Often times, the physician may recommend blood tests to assess the functioning of liver, in order to confirm a diagnosis. The liver contains a large number of enzymes. When the liver is injured, these enzymes are released into blood and they may be analyzed through various blood tests:
- Testing for common enzymes such as aspartate transaminase and alanine transaminase
- Patients with Type II AIH, typically have high levels of anti-LKM1 and/or anti-liver cytosol type 1 antibodies in their blood
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis A Causes Symptoms Treatment