Important Questions And Needs For Future Research
Treatment Of Acute Hepatitis B
-
Supportive care
-
For fulminant hepatitis B, antiviral drugs and liver transplantation
No treatments attenuate acute viral hepatitis, including hepatitis B. Alcohol should be avoided because it can increase liver damage. Restrictions on diet or activity, including commonly prescribed bed rest, have no scientific basis.
Viral hepatitis should be reported to the local or state health department.
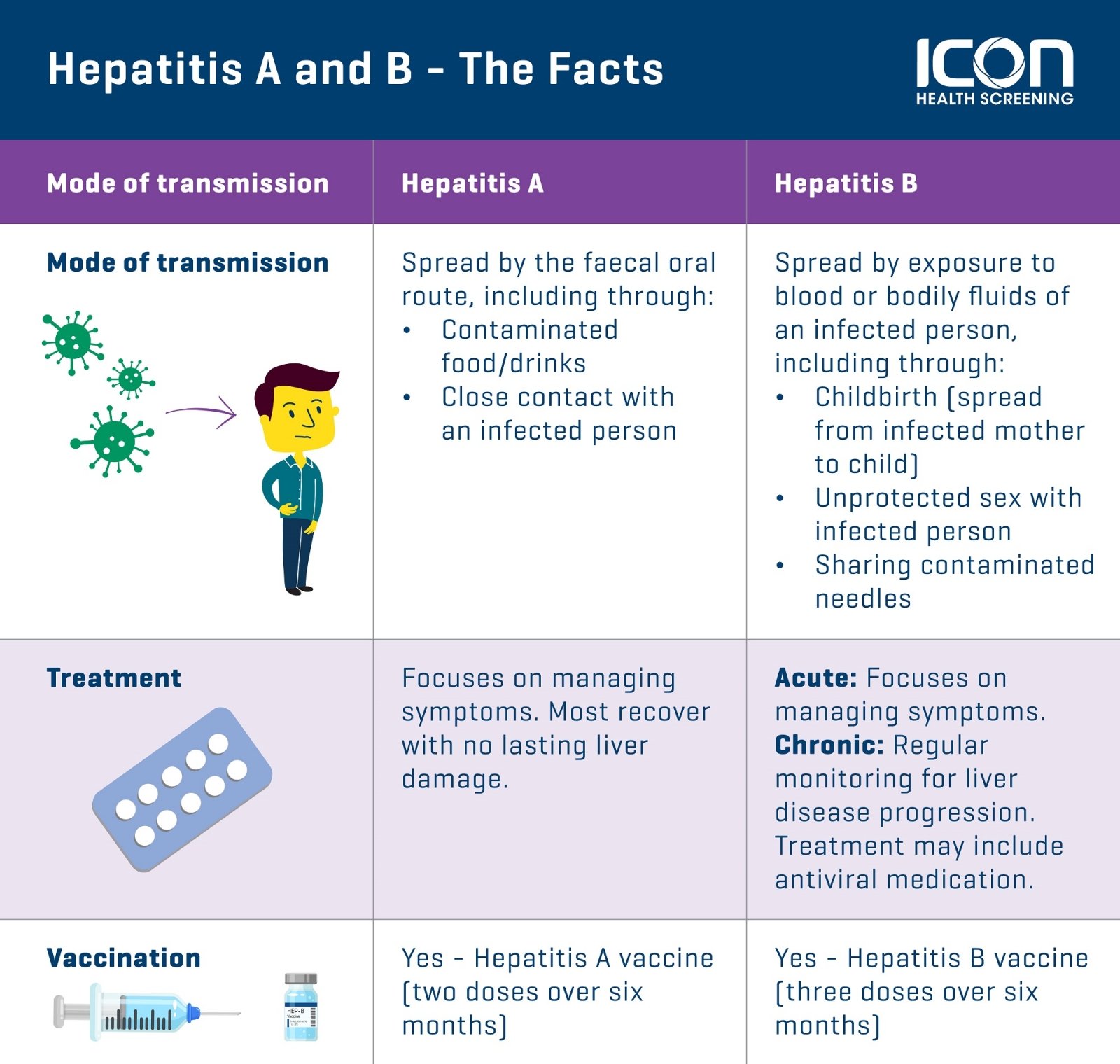
How Is Hepatitis B Spread
- Having unprotected sex.
- Sharing or using dirty needles for drug use, tattoos or piercing.
- Sharing everyday items that may contain body fluids, including razors, toothbrushes, jewelry for piercings and nail clippers.
- Being treated medically by someone who does not use sterile instruments.
- Being bitten by someone with the infection.
- Being born to a pregnant woman with the infection.
Hepatitis B is not spread by:
- Kissing on the cheek or lips.
- Coughing or sneezing.
- Hugging, shaking hands or holding hands.
- Eating food that someone with the infection has prepared.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Know If You Get Hepatitis
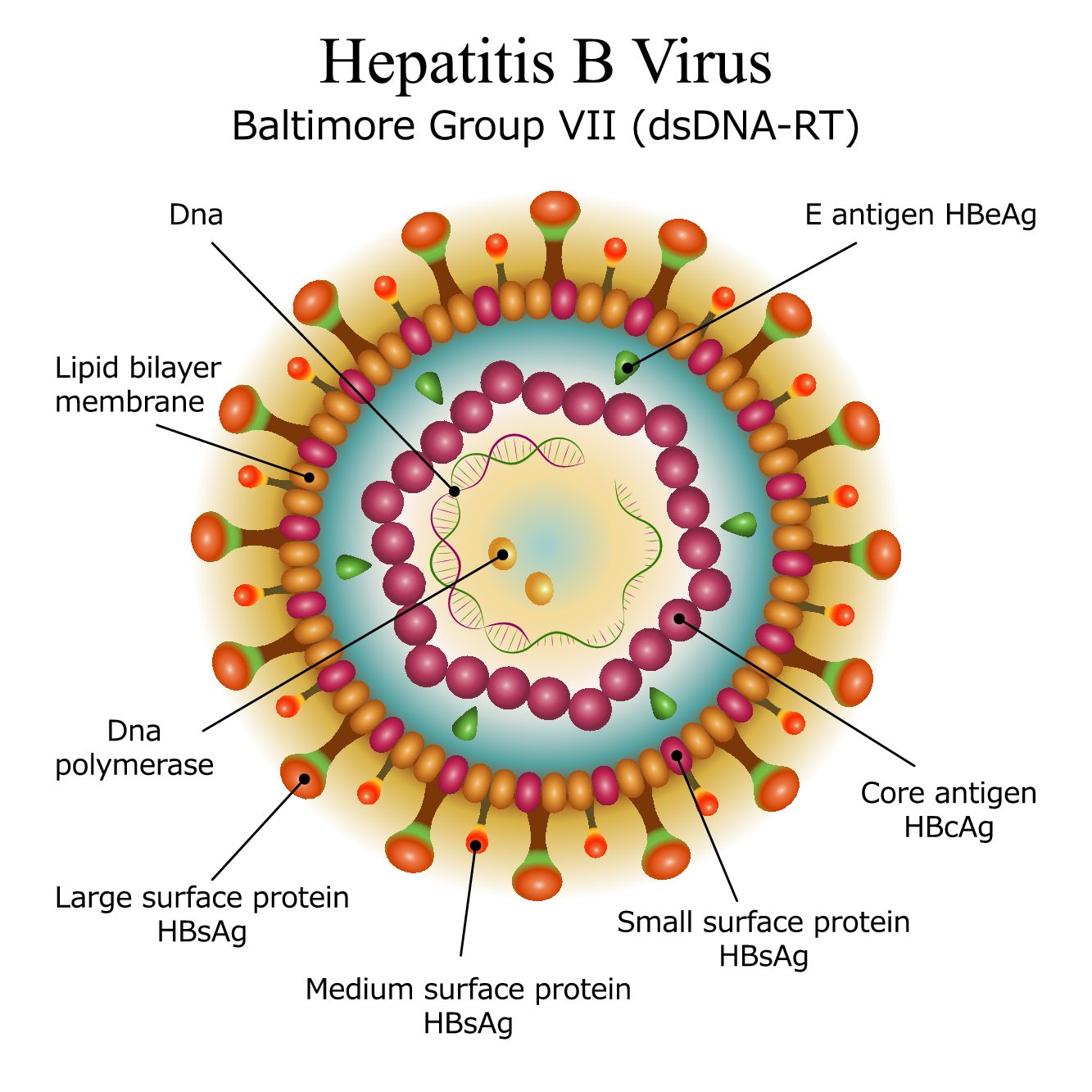
About The Hepatitis B Virus
The hepatitis B virus is a small DNA virus that belongs to the Hepadnaviridae family. Related viruses in this family are also found in woodchucks, ground squirrels, tree squirrels, Peking ducks, and herons.
Structure of the Hepatitis B Virus The hepatitis B virus contains an outer envelope and an inner core.
- The outer envelope of the virus is composed of a surface protein called the hepatitis B surface antigen or “HBsAg”. The HBsAg can be detected by a simple blood test and a positive test result indicates a person is infected with the hepatitis B virus.
- The inner core of the virus is a protein shell referred to as the hepatitis B core antigen or “HBcAg,” which contains the hepatitis B virus DNA and enzymes used in viral replication.
Life Cycle of the Hepatitis B Virus
The hepatitis B virus has a complex life cycle. The virus enters the host liver cell and is transported into the nucleus of the liver cell. Once inside the nucleus, the viral DNA is transformed into a covalently closed circular DNA , which serves as a template for viral replication . New HBV virus is packaged and leaves the liver cell, with the stable viral cccDNA remaining in the nucleus where it can integrate into the DNA of the host liver cell, as well as continue to create new hepatitis B virus. Although the life cycle is not completely understood, parts of this replicative process are error prone, which accounts for different genotypes or genetic codes of the hepatitis B virus.
Hiv And Hbv Coinfection

About 2% of people with HIV in the United States are coinfected with HBV both infections have similar routes of transmission. People with HIV are at greater risk for complications and death from HBV infection. All people with HIV are recommended to be tested for HBV, and if susceptible, are further recommended to receive the hepatitis B vaccination or, if chronically infected, evaluated for treatment to prevent liver disease and liver cancer. For more information about HIV and HBV coinfection, visit HIV.govâs pages about hepatitis B and HIV coinfection.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Treatment Side Effects
How Long Can You Live With Hepatitis B
Most people who contract hepatitis B during adulthood fully recover within 1 to 3 months.
People with chronic hepatitis B may have a higher risk of developing long-term liver problems, like cirrhosis or liver cancer, which require treatment and may be life threatening.
Keep in mind that the risk of developing chronic hepatitis B is higher for babies and children, especially if they have not been vaccinated against the virus.
How Can I Get Free Or Low
The hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccines are covered under most insurance plans.
- If you have insurance, check with your insurance provider to find out whats included in your plan.
- Medicare Part B covers hepatitis B vaccines for people at risk.
Find a clinic near you where you can get vaccines for hepatitis A and B.
Don’t Miss: How Contagious Is Hepatitis A
What Are The Risk Factors For Getting Hepatitis B
Due to the way that hepatitis B spreads, people most at risk for getting infected include:
- Children whose mothers have been infected with hepatitis B.
- Children who have been adopted from countries with high rates of hepatitis B infection.
- People who have unprotected sex and/or have been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection.
- People who live with or work in an institutional setting, such as prisons or group homes.
- Healthcare providers and first responders.
- People who share needles or syringes.
- People who live in close quarters with a person with chronic hepatitis B infection.
- People who are on dialysis.
Why A Liver Virus Would Damage The Kidney
Damage to the kidney from hepatitis B virus is not usually a result of direct infection. In fact, the immune system’s abnormal reaction to certain parts of the virus may play a larger role in disease causation.
These viral components will typically get attacked by your antibodies in an attempt to fight the infection. Once this happens, the antibodies will bind with the virus, and the resultant debris will get deposited in the kidney. It can then set off an inflammatory reaction, which could cause kidney damage. Hence, rather than the virus directly affecting the kidney, it is your body’s response to it that determines the nature and extent of kidney injury.
Don’t Miss: Can Hepatitis C Be Transmitted
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test
A hepatitis B surface antigen test shows if you have an active infection. A positive result means you have hepatitis B and can transmit the virus to others. A negative result means you dont currently have hepatitis B.
This test doesnt distinguish between chronic and acute infection. This test is used together with other hepatitis B tests to determine the state of a hepatitis B infection.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hbv
Hepatitis B virus can cause an acute illness with symptoms that last several weeks, including yellowing of the skin and eyes , dark urine, extreme fatigue, nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain. Most of the time HBV infection is ASYMPTOMATIC.
Joint pains, muscle aches, rash, and jaundice may occur in some people. People can take several months to a year to recover from the symptoms. These people may not know that they are infected, and may therefore not go and see a doctor. People with chronic hepatitis B infection may later develop serious problems like liver cancer and liver failure. These people may not know that they are infected, and may therefore not go and see a doctor. People with chronic hepatitis B infection may later develop serious problems like liver cancer and liver failure.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Symptoms Mayo Clinic
Read Also: How Can You Contract Hepatitis C
Hepatitis A B And C: What Is The Difference
A, B, C D and E.
Aside from the letters associated with it, how much do you know about hepatitis? Whats the difference between the types? And if you get a vaccination for hepatitis, which are you protected from?
We spoke with Moises Ilan Nevah, MD, a transplant hepatologist/gastroenterologist and medical director of the Liver Transplant Program at Banner University Medical Center Phoenix, to help better understand the similarities and differences between the various types of hepatitis, who is at risk and when to get vaccinated.
Can Hepatitis B Be Prevented
The hepatitis B vaccine is one of the best ways to control the disease. It is safe, effective and widely available. More than one billion doses of the vaccine have been administered globally since 1982. The World Health Organization says the vaccine is 98-100% effective in guarding against the virus. Newborns should be vaccinated.
The disease has also been more widely prevented thanks to:
- Widespread global adoption of safe blood-handling practices. WHO says 97% of the blood donated around the world is now screened for HBV and other diseases.
- Safer blood injection practices, using clean needles.
- Safe-sex practices.
You can help prevent hepatitis B infections by:
- Practicing safe sex .
- Never sharing personal care items like toothbrushes or razors.
- Getting tattoos or piercings only at shops that employ safe hygiene practices.
- Not sharing needles to use drugs.
- Asking your healthcare provider for blood tests to determine if you have HBV or if you are immune.
Also Check: How Do You Get Viral Hepatitis
Hepatitis B Can Be Prevented
Hepatitis B is a vaccine-preventable disease. The hepatitis B vaccine has been available since the 1980s and is safe and highly effective at preventing infection. At least 3 doses of hepatitis B vaccine are needed to prevent infection with the hepatitis B virus . The first dose should be given to babies within 24 hours of birth, followed by 2 to 3 additional doses for full protection.
Transmission Of Hepatitis B
HBV is often transmitted parenterally, typically via contaminated blood or blood products. Routine screening of donor blood for hepatitis B surface antigen has nearly eliminated the previously common posttransfusion transmission, but transmission through needles shared by drug users remains common. Risk of HBV is increased for patients on dialysis and in oncology units, and for hospital personnel in contact with blood.
Infants born to infected mothers have a 70 to 90% risk of acquiring hepatitis B during delivery Infection Neonatal hepatitis B virus infection is usually acquired during delivery. It is usually asymptomatic but can cause chronic subclinical disease in later childhood or adulthood. Symptomatic infection… read more ) unless they are treated with hepatitis B immune globulin and are vaccinated Prevention Neonatal hepatitis B virus infection is usually acquired during delivery. It is usually asymptomatic but can cause chronic subclinical disease in later childhood or adulthood. Symptomatic infection… read more immediately after delivery. Earlier transplacental transmission can occur but is rare. The risk of vertical transmission of HBV is also mitigated by treating actively infected pregnant women with high viral loads in their third trimester with tenofovir.
The virus may be spread through mucosal contact with other body fluids , but infectivity is far lower than that of hepatitis A virus, and the means of transmission is often unknown.
Read Also: What Is The Test For Hepatitis B
How Is Hepatitis B Prevented
Testing & Vaccination
- The hepatitis B vaccine offers excellent protection against HBV. The vaccine is safe and highly effective. Vaccination consists of 3 doses of vaccine over the course of 6 months. Protection lasts for 20 years to life.
- The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that all children should receive hepatitis B vaccine starting at birth. .
- The CDC recommends hepatitis B vaccine for persons traveling to countries where HBV is common .
- If you have one or more risk factors for hepatitis B infection, you should get a simple HBV blood test. The blood test will determine whether you are:
- immune to hepatitis B or
- susceptible to hepatitis B and need vaccination or
- infected with hepatitis B and need further evaluation by a physician
Perinatal Hepatitis
- California law requires testing of all pregnant women for hepatitis B infection
- If the mother is HBV-infected, she will pass the infection to the baby during the birth process, unless the baby gets immunized within hours of birth
- Giving the infant HBIG and HBV vaccine right away will reliably prevent infection of the infant
- Other family members should best tested for hepatitis B too, and given vaccine if they are not already infected or immune
Healthy Habits
After Exposure to Hepatitis B
How Common Is It
In 2006, the Public Health Agency of Canada reported the incidence of HBV as 2.0 cases for every 100,000 or about 650 cases reported annually in Canada. In the year 2013, the incident rate was 0.5 per 100,000 . Incidence of the disease varies from region to region but has been declining due to increasing use of the vaccine and universal immunization programs.
Don’t Miss: How To Contract Hepatitis B And C
If I Have No Symptoms How Would I Know If I Have Hepatitis B
To confirm whether or not you have hepatitis B, you will need blood tests.
If you have at least one risk factor , you should ask your health care provider to be tested for hepatitis B. Also, you should be tested for hepatitis B if:
- you were born in a region where hepatitis B is more common, including Asia, Africa, southern and eastern Europe, the Pacific Islands, the Middle East, and the Arctic
- one or both of your parents immigrated from a region where hepatitis B is more common
- you live or travel to regions where hepatitis B is more common
- you have a family history of liver disease or liver cancer
- you have been in prison
- you are pregnant
- you have ever used injection drugs, even just once
- you have unexplained abnormal liver enzymes or if
- you receive medicines that suppress the immune system.
Other Body Fluids And Tissues
Synovial fluid , amniotic fluid, cerebrospinal fluid, and peritoneal fluid can contain the hepatitis B virus, but the risk of transmission to workers is not known.
Feces, nasal secretions, sputum, sweat, tears, urine, and vomit have not been implicated in the spread of hepatitis B. Unless they are visibly contaminated with blood, the risk of contracting hepatitis B from these fluids in the workplace is very low.
Hepatitis B is not transmitted by casual contact. For example, hospital employees who have no contact with blood, blood products, or blood-contaminated fluids are at no greater risk than the general public. However, the virus can spread through intimate contact with carriers in a household setting, possibly because of frequent physical contact with small cuts or skin rashes. The virus can also spread through biting and possibly by the sharing of toothbrushes or razors. It is not spread through sneezing, coughing, hand holding, hugging, kissing, breastfeeding, sharing eating utensils, water or food.
Don’t Miss: Cost Of Hepatitis C Medications
How Common Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is fairly common in Africa and the western Pacific region. Throughout the world, there are about 292 million people who are infected with chronic hepatitis B. In the U.S., the figure exceeds 2 million people.
The number of infections had been falling in the U.S., but fewer vaccinations among adults combined with the onset of the opioid crisis and injected drug usage has resulted in the numbers rising again. Infected women can pass the infection on to their babies. Children who are infected before age 5 are more likely to have chronic infection than those infected later in life.
American Association For The Study Of Liver Diseases Recommendations
The 2016 AASLD guidelines for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B as well as select recommendations from the 2018 AASLD guidance update on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B are outlined below and in the Guidelines section.
Adults with immune-active chronic hepatitis B infection
Administer antiviral therapy to lower the risk of morbidity and mortality associated with chronic hepatitis B infection.
The recommended initial agent for adults is PEG-IFN, entecavir, or tenofovir.
Adults with immune-tolerant chronic hepatitis B infection
Antiviral therapy is not recommended.
The AASLD suggests obtaining ALT levels at least every 6 months to monitor for potential transition to immune-active or -inactive chronic hepatitis B.
For select patients older than 40 years, the AASLD suggests antiviral therapy in the setting of normal ALT levels, elevated HBV DNA , and significant necroinflammation or fibrosis on liver biopsy specimens.
Adults with HBeAg-positive immune-active chronic hepatitis B who seroconvert to anti-HBe on nucleoside analog therapy
After a period of treatment consolidation , consider discontinuing NA therapy in noncirrhotic HBeAg-positive adults who seroconvert to anti-HBe while on NA treatment. If antiviral therapy is stopped, monitor the patient every 3 months for a minimum of 1 year for recurrent viremia, ALT flares, seroreversion, and clinical decompensation.
Adults with HBeAg-negative immune-active chronic HBV infection
Inpatient care
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Test Kit Walgreens
Is There A Cure For Chronic Hepatitis B
Currently, there is no complete cure for hepatitis B. But when managed properly, those living with the virus can expect to live a normal life. Maintaining a healthy diet and avoiding alcoholic beverages and tobacco products are crucial components in managing the disease.
You should also visit a doctor familiar with hepatitis B at least annuallythough twice a year might be best to monitor your liver through blood tests and medical imaging. As with most diseases, detecting it early leads to a better outcome. If youre exposed to the virus, you should get an antibody injection within 12 hours of exposure.