What Are The Side Effects Of Hepatitis C Treatment
Overview
Hepatitis C virus is a stubborn but common virus that attacks the liver. About 3.5 million people in the United States have chronic, or long-term, hepatitis C.
It can be difficult for the human immune system to fight HCV. Fortunately, there are several drugs available to treat hepatitis C. Read on to learn more about hepatitis C treatments and their side effects.
The main types of HCV medications prescribed today are direct-acting antivirals and ribavirin. In rare cases where DAAs are not accessible, interferons may be prescribed.
What Can I Do To Manage Hepatitis B
- Do not drink alcohol. Alcohol can increase liver damage. Talk to your healthcare provider if you drink alcohol and need help to stop.
- Do not smoke. Nicotine can damage blood vessels and make it more difficult to manage hepatitis B. Smoking can also lead to more liver damage. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your healthcare provider before you use these products.
- Eat a variety of healthy foods. Healthy foods include fruits, vegetables, low-fat dairy products, beans, lean meats and fish, and whole-grain breads. Ask if you need to be on a special diet.
- Drink more liquids. Liquids help your liver function properly. Ask your healthcare provider how much liquid to drink each day and which liquids are best for you.
How Is Hepatitis B Immune Globulin Given
Hepatitis B immune globulin is injected into a muscle or into a vein through an infusion pump. A healthcare professional will give you this injection.
For prevention after exposure to contaminated blood: Hepatitis B immune globulin is usually given as soon as possible after exposure to an infected person, preferably within 7 days. A booster medication is then given 24 hours later. Your doctor may also recommend that you receive a hepatitis B vaccine when you start treatment with hepatitis B immune globulin.
For liver transplant: Hepatitis B immune globulin is given as part of the transplant procedure, and then for several weeks or months afterward. The medication is usually given to transplant patients every day for 7 days, then every 2 weeks for the next 11 weeks, followed by monthly injections from then on.
For prevention after sexual contact with an infected person: Hepatitis B immune globulin is given as a single dose within 14 days after the last contact. You should also receive a hepatitis B vaccine if you will continue to have contact with the infected person.
For prevention in people sharing the home of an infected person: hepatitis B immune globulin should be given to infants younger than 12 months old, caregivers who may come into contact with the infected person’s blood, and people who share razors, toothbrushes, or other personal items with the infected person. Household members may also need to receive hepatitis B vaccine.
You May Like: Diagnostic Test For Hepatitis B
Antiviral Drugs And Covid
The worldwide outbreak of COVID-19 virus infection is associated with theunavailability of specific drug to combat with this viral infection. To date,nearly 10million people are infected and about 500,000 people die worldwide dueto COVID-19 viral infection. To find the solutions for this viral infection,great efforts have been made and are continued to develop vaccines, smallmolecule drugs or monoclonal antibodies that can prevent the infection spread toavoid the expected human, social and economic devastation related to thisinfection. Several FDA approved drugs have been reported in the literature andin hospitals during clinical trials to treat or reduce the COVID-19severity.
Can Hepatitis C Be Treated
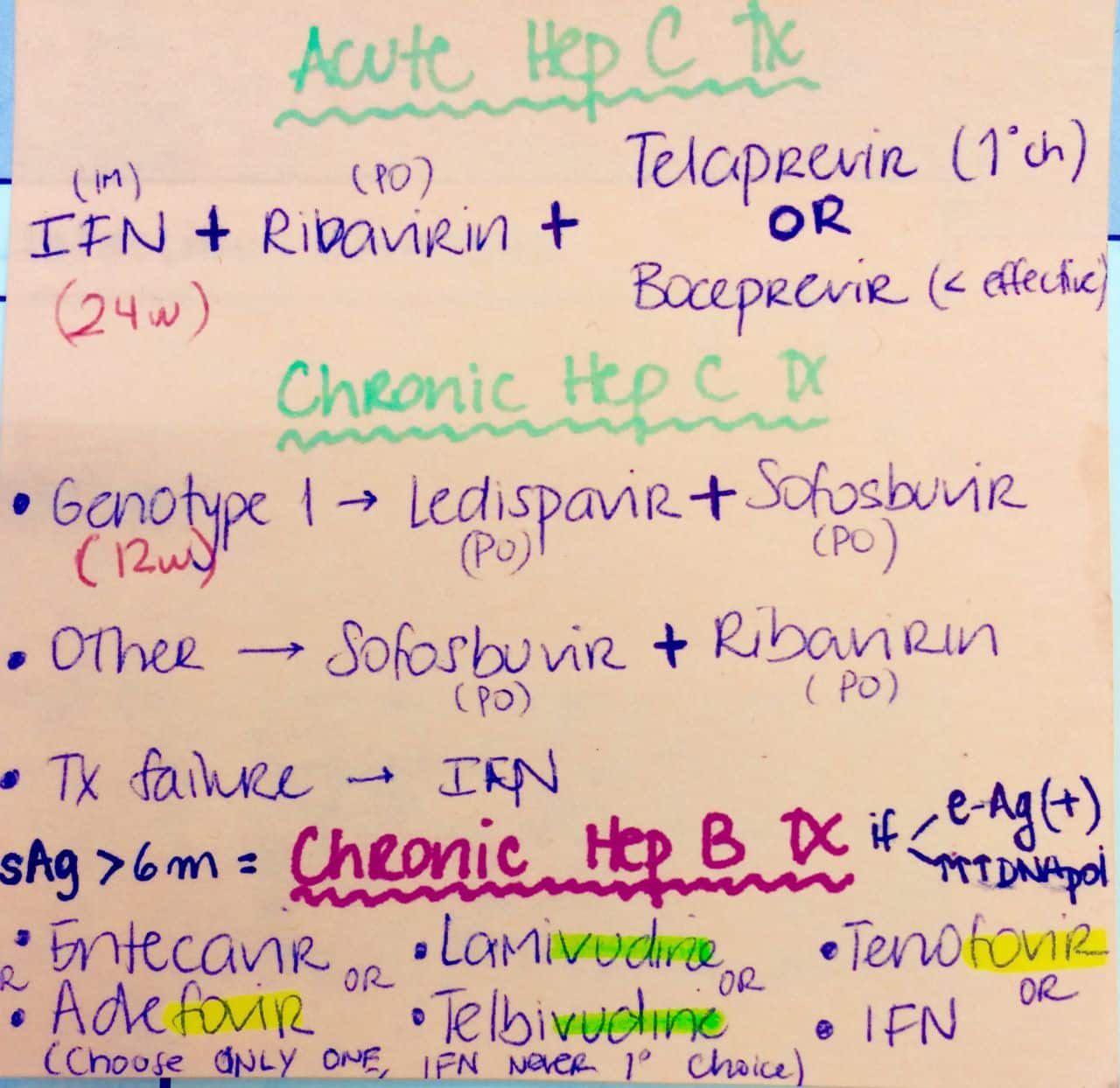
Yes, since 2010 enormous progress has been made in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. New therapies called direct-acting antivirals are pills that act on the virus itself to eradicate it from the body, unlike older medicines like interferon injections which work by stimulating an immune response. These new treatments are very effective and can achieve cure rates of over 90%. In most situations now, there is no need for interferon, which was responsible for many of the side effects previously associated with HCV treatment. The new treatment combinations require shorter treatment durations , have reduced side effects and appear to be effective at all stages of the disease.
Because these new therapies are very new, they remain very expensive. As such, drug coverage from both government and private companies may require that your liver disease has progressed to a certain stage before they are willing to cover the cost of these drugs.
Your primary care physician may refer you to a specialist to determine whether you are eligible for treatment. A specialist will help you decide which drug therapy is best for you based on the severity of your liver disease, your virus genotype and whether or not you have been treated in the past.
Read Also: What Is Acute Hepatic Porphyria
What Are Dosages Of Hepatitis B Vaccine
Dosages of Hepatitis B Vaccine:
Dosage Considerations Should be Given as Follows:
- Engerix B: 1 mL intramuscularly at 0, 1, and 6 months
- Recombivax HB: 1 mL intramuscularly at 0, 1, and 6 months
- Adults receiving dialysis or other immunocompromising conditions
- Recombivax HB : 40 mcg intramuscularly at 0, 1, and 6 months, OR
- Engerix-B : 40 mcg intramuscularly at 0, 1, and 6 months
Routine vaccination
Catch-up vaccination
- Unvaccinated children should complete a 3-dose series
- Children aged 11-15 years: 2-dose series of adult formulation Recombivax HB is licensed for use in children aged 11 through 15 years
Dosing Considerations
- Administer intramuscularly in the deltoid muscle
- Do not give IV/intradermal
Pediatric:
- low blood pressure
- pain when urinating
Suspected adverse events after administration of any vaccine may be reported to Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System , 1-800-822-7967
This document does not contain all possible side effects and others may occur. Check with your physician for additional information about side effects.
Dont Miss: Where Can I Get Hepatitis B Vaccine For Free
American Association For The Study Of Liver Diseases Recommendations
The 2016 AASLD guidelines for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B as well as select recommendations from the 2018 AASLD guidance update on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B are outlined below and in the Guidelines section.
Adults with immune-active chronic hepatitis B infection
Administer antiviral therapy to lower the risk of morbidity and mortality associated with chronic hepatitis B infection.
The recommended initial agent for adults is PEG-IFN, entecavir, or tenofovir.
Adults with immune-tolerant chronic hepatitis B infection
Antiviral therapy is not recommended.
The AASLD suggests obtaining ALT levels at least every 6 months to monitor for potential transition to immune-active or -inactive chronic hepatitis B.
For select patients older than 40 years, the AASLD suggests antiviral therapy in the setting of normal ALT levels, elevated HBV DNA , and significant necroinflammation or fibrosis on liver biopsy specimens.
Adults with HBeAg-positive immune-active chronic hepatitis B who seroconvert to anti-HBe on nucleoside analog therapy
After a period of treatment consolidation , consider discontinuing NA therapy in noncirrhotic HBeAg-positive adults who seroconvert to anti-HBe while on NA treatment. If antiviral therapy is stopped, monitor the patient every 3 months for a minimum of 1 year for recurrent viremia, ALT flares, seroreversion, and clinical decompensation.
Adults with HBeAg-negative immune-active chronic HBV infection
Inpatient care
Read Also: How Is Hepatitis C Spread
What Is Involved In A Liver Transplant
A liver transplant is considered necessary when the liver is damaged and cannot function or in some cases of liver cancer. Your liver is very important. It is responsible for many functions related to making sure that your body stays healthy and is able to digest foods.
You may be eligible for a transplant if you have chronic hepatitis B infection or some of the diseases that may result from it, including liver cancer and cirrhosis. You will have to complete testing and be evaluated before being approved for a transplant. It is likely that you will be placed on a waiting list while an appropriate organ is found.
Donated livers come from two types of donors: living and deceased. Because the liver can regenerate, it is possible to use part of a liver for transplant. The remaining sections in both the donor and the receiver will grow into livers of adequate size.
People who get liver transplants must take anti-rejection drugs for the rest of their lives. These drugs make you more susceptible to infection. However, liver transplants have become more successful over time and continue to improve.
Other Side Effects Of Heplisav
Some side effects of hepatitis b adult vaccine may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine. Also, your health care professional may be able to tell you about ways to prevent or reduce some of these side effects.
Check with your health care professional if any of the following side effects continue or are bothersome or if you have any questions about them:
Recommended Reading: How Do You Contact Hepatitis
What Do I Need To Know About Having Hepatitis B
If you have chronic hepatitis B, getting the right medical care can help you stay healthy. Taking good care of your liver is important. Talk with your doctor before you take any prescription medication, over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, or nutritional supplements to make sure they wont hurt your liver. You should also stay away from alcohol, because drinking can damage your liver.
Diagnoses And Causes Of Hepatitis
The first sign of hepatitis usually shows up on a generic liver function test or a complete blood panel, which tests the blood for compounds present. These are tests commonly done by your primary healthcare provider. If there are signs of liver damage, such as elevated liver enzymes, you may need to undergo further testing to determine whether your hepatitis is caused by a virus, an autoimmune disease, alcohol use or prescription drugs.
You May Like: Hepatitis B What Causes It
Immunisation Against Hepatitis A
Immunisation is the best protection against hepatitis A infection and is recommended for people in high-risk groups, and for unvaccinated people who have been in close contact with someone who has hepatitis A.
Immunisation against hepatitis A includes a course of injections over a 6 to 12-month period. Healthy people 12 months of age and over receive 2 doses of hepatitis A vaccine, or 3 doses if the hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccines are given as a combination.
You can complete any missed vaccine doses, even if the recommended time frame has passed. You do not need to start the vaccine course again.
If you are in close contact with someone who has hepatitis A be sure to have the hepatitis A vaccine if you have not already completed a vaccine course.
Babies under 12 months of age and people who have a weakened immune system who are also in close contact with a person with hepatitis A can have an injection of normal human immunoglobulin instead of the hepatitis A vaccine.
Protection against hepatitis A is available free of charge under the National Immunisation Program Schedule for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander children who live in high-risk areas .
How Is This Vaccine Given
The vaccine is injected into a muscle. Your child will receive this injection in a doctor’s office or other clinic setting.
The hepatitis B pediatric vaccine is given in a series of shots beginning shortly after birth. The booster shots are sometimes given 1 to 2 months and 6 to 18 months after the first shot. If your child does not receive a birth dose, the vaccine series should begin as early as possible.
Your child’s individual booster schedule may be different from these guidelines. Follow the doctor’s instructions or the schedule recommended by your local health department.
Don’t Miss: Physical Signs Of Hepatitis C
How Often To Use
You may be wondering how long you have to take Epclusa to treat hepatitis C. Youll likely use the drug once daily for 12 weeks. This is the amount of time it takes for Epclusa to clear the hepatitis C virus from your body.
Its extremely important to not miss or skip doses of Epclusa. Missed or skipped doses can lower the level of the drug in your blood, which may cause Epclusa to work less well than usual. As a result, the drug may not clear the hepatitis C virus from your system.
To avoid missing a dose, try setting a reminder on your phone. If you do miss a dose of Epclusa, its important that you call your doctor right away. Theyll advise you on the best action for you to take.
Hepatitis C is an infection caused by the hepatitis C virus. The virus is transmitted through blood or body fluids, which can occur in several ways, including:
- sharing needles with a person who has the virus
- getting pricked by a needle that has the virus, which can be common in a healthcare setting
- having sex with someone who has the virus without using a condom or other barrier method
Once inside your body, hepatitis C virus attacks cells in your liver, causing inflammation.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Antigens And Antibodies
How Are Hepatitis B And C Treated
Hepatitis B: Not all patients with chronic hepatitis B infection require treatment. At Yale Medicine, specialists decide on an individual basis whether a patient is an appropriate candidate for treatment. Generally, patients require treatment when their hepatitis B virus level is high, and when laboratory tests demonstrate significant inflammation or injury to the liver.
There are currently seven approved drugs for hepatitis B, two of which are considered to be first-line treatments. These drugs are oral pills taken once daily, and while theyâre very effective at suppressing the virus to very low or undetectable levels over the long term, they are not considered curative.
Therefore, the goal of treatment is to control the virus long-term and decrease the risk of hepatitis B related complications such as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Hepatitis C: For the greater part of the last 20 years, treatment of hepatitis C required the use of a chemotherapy-like injection drug called interferon, which has been associated with serious side effects and a low cure rate. Fortunately, advances in hepatitis C treatments within the last three years now allow for the use of oral medications that are significant improvements in terms of safety and effectiveness.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C
Starting Treatment Adjusting To Treatment
Many antiretroviral drugs that keep HIV under control have side effects, causing changes of various kinds. But not all people with HIV who take antiretroviral therapy or other medications for HIV-related conditions will experience side effects from their drugs. We are lucky to be living in an era in which many of the newer medications used to treat HIV cause far fewer side effects than were seen in the early years of the HIV epidemic.
Many people are able to stay on their medications for years with few, if any, side effects. When side effects do occur, they are often only temporary and will disappear after a few days or weeks. There can, however, be side effects that last as long as the drugs are continued in some cases, these side effects will remain even after the drugs are stopped.
People who are considering antiretroviral therapy are often concerned about side effects. Heres something to consider: If you talk to your doctor about possible side effects before starting treatment, you will be better prepared to deal with temporary, minor problems that can happen as you adjust to treatment. If there is a side effect that can be severe or life-threatening, you will know what to watch for.
Many people who start antiretroviral therapy find the side effects to be much more manageable than they expected. At the least, knowing the side effect will improve over time can make it easier to convince yourself to stick with a particular medication.
Treatment Of Patients With Decompensated Cirrhosis
Treatment of patients with decompensated cirrhosis ) is limited to regimens containing sofosbuvir and NS5A inhibitors. Protease inhibitors are not recommended due to the hepatic metabolization and subsequently significantly higher drug exposure in this group of patients. Thus, grazoprevir/elbasvir, glecaprevir/pibrentasvir or SOF/VEL/VOX should not be administered. To improve efficacy the remaining combination of sofosbuvir and NS5A inhibitor should be combined with RBV . Many studies and real-world data have shown that IFN-free antiviral therapy is safe in patients with advanced liver disease. However, patients are still at risk of hospitalization during therapy, mainly because of complications from liver disease . The efficacy of sofosbuvir/ledipasvir plus RBV was studied in the SOLAR-1 and -2 study. In GT 1 patients, SVR rates ranged between 87 and 96% and between 72 and 85% in CPS B and CPS C patients, respectively . The ASTRAL-4 study evaluated the use of sofosbuvir/velpatasvir in patients with CPS B, but not CPS C. Treatment duration of 12 weeks showed high rates of SVR for patients with GT 1, 2, 4 and 6 infection. SVR rates of GT 3 were low at 50% but could be increased to 85% by the addition of RBV . Even though the rate of treatment discontinuations is higher in patients treated with RBV, the additional antiviral substance significantly increases SVR rates .
Also Check: How Do You Test For Hepatitis
Side Effects Of Hepatitis C Treatment: What To Expect
Articles On Side Effects of Hep C Medications
Hepatitis C can be treated and even cured. And treatment is important. Hepatitis C, caused by a virus, can permanently damage your liver if you donât get treatment for it.
Treatment for hepatitis C keeps changing quickly. The standard treatment was typically interferon along with other drugs â usually ribavirin and either boceprevir or telaprevir .
But many people have a hard time with interferons side effects, which include fatigue, fever, chills, and depression. Treatment now involves direct-acting antiviral drugs . These medicines are highly effective for most people with hepatitis C and are interferon-free and often ribavirin-free. This means they typically have fewer side effects. The treatments are often simpler, using fewer pills for a shorter amount of time. DAAs are available as either single drugs or combined with other medicines in one pill.
ishonestNo.373 â Blackheads
Elbasvir-grazoprevir , ledipasvir-sofosbuvir , and sofosbuvir-velpatasvir are once daily combination pills. Depending on the type of hepatitis C infection, these can often cure the disease in 8 to 12 weeks. Other treatment options include: daclatasvir ombitasvir- paritaprevir-ritonavir or some combinations of simeprevir sofosbuvir peginterferon or ribavirin.
Ask your doctor whatâs best for you, based on your medical needs.
What Are the Some of the Most Common Side Effects of Hepatitis C Medications?
Elbasvir-grazoprevir