Im A Health Care Worker Who Was Recently Exposed To Hcv Is There Post
No. Immune globulin is not recommended for postexposure prophylaxis against HCV, and prophylactic antiviral therapy is also not recommended. However, following exposure, a health care worker should be tested for HCV antibody right away and at 6 months so that early HCV infection can be identified. Several studies suggest that interferon treatment begun early in the course of HCV infection is associated with a higher rate of cure however, further studies are needed to confirm this. There is no hepatitis C vaccine.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Symptoms Of Having Hepatitis C
Treatment To Prevent Hepatitis B Infection After Exposure
If you know youve been exposed to the hepatitis B virus and arent sure if youve been vaccinated, call your doctor immediately. An injection of immunoglobulin given within 12 hours of exposure to the virus may help protect you from getting sick with hepatitis B. Because this treatment only provides short-term protection, you also should get the hepatitis B vaccine at the same time, if you never received it.
Difference Between Acute And Chronic Hepatitis C
Hepatitis is a medical condition of the liver, characterized by inflammation of the liver which might possibly result in scarring, fibrosis, Cirrhosis and hepatic malignancies. There are 5 major entities of the virus, responsible for causing Hepatitis known as Hepatitis A, B, C, D and E. This article discusses,
1. What is Acute Hepatitis C Cause, Signs and Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
2. What is Chronic Hepatitis C Cause, Signs and Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
3. Difference Between Acute and Chronic Hepatitis C
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis C From
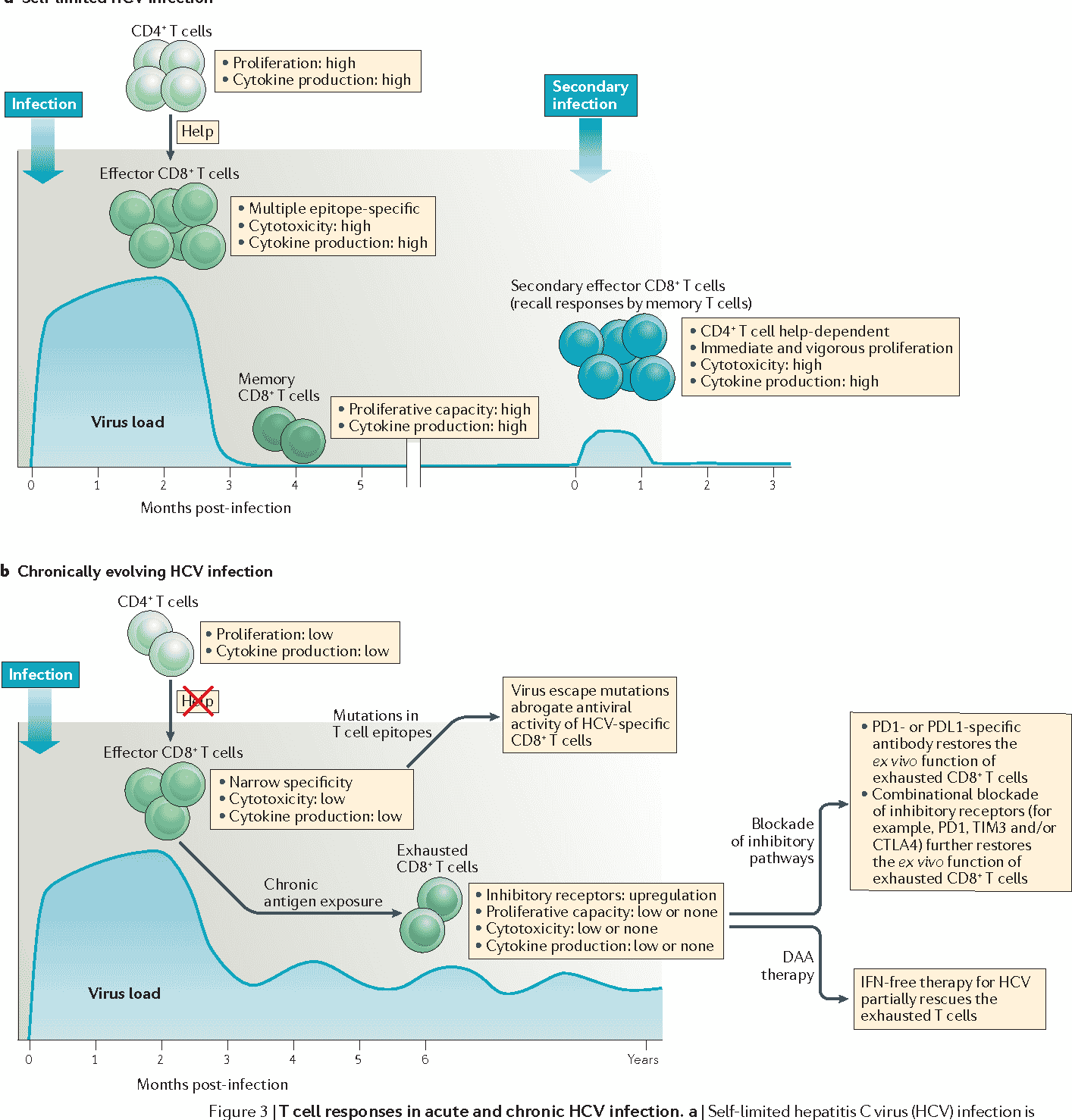
Laboratory Studies For Evaluation Of Initial Infection
The key laboratory studies utilized in the evaluation of possible acute hepatitis C are HCV RNA, anti-HCV, and alanine aminotransferase . Patients who become infected with hepatitis C virus typically develop abnormal laboratory findings in the following order: detectable HCV RNA, followed by elevation in ALT, and then anti-HCV . Patients who develop a clinical illness with acute HCV infection usually have onset of symptoms well after the onset of viremia, but soon after or concomitant with increases in ALT levels.
HCV RNA
Antibodies to HCV
Antibodies to HCV typically become detectable at about 50 to 60 days after infection the detection of HCV-specific antibodies significantly lags behind detectable HCV RNA levels. After 12 weeks, more than 90% of patients will have a positive HCV antibody test. The time period from initial infection until seroconversion is often referred to as the serologic window period . The use of only an HCV antibody test to diagnose acute HCV is not reliable, since only approximately 50 to 70% of patients have detectable HCV antibodies at the onset of symptoms. Further, a positive HCV antibody test does not differentiate acute from chronic HCV infection.
Hepatitis C Core Antigen
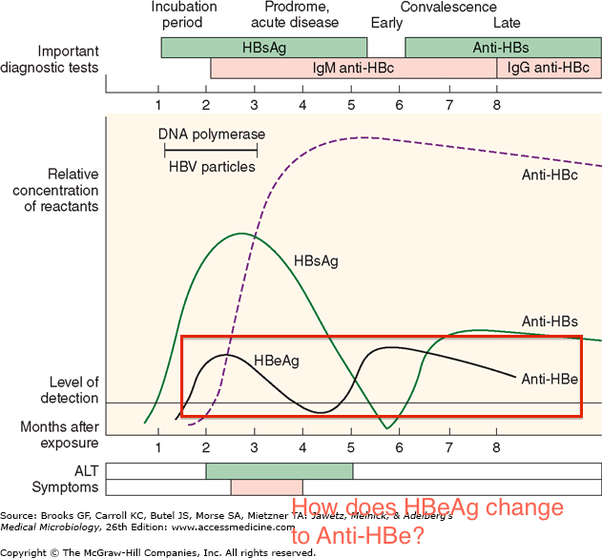
Chronic Hepatitis B Complications
Chronic hepatitis B can lead to
- cirrhosis, a condition in which scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue and prevents your liver from working normally. Scar tissue also partly blocks the flow of blood through the liver. As cirrhosis gets worse, the liver begins to fail.
- liver failure, in which your liver is badly damaged and stops working. Liver failure is also called end-stage liver disease. People with liver failure may require a liver transplant.
- liver cancer. Your doctor may suggest blood tests and an ultrasound or another type of imaging test to check for liver cancer. Finding cancer at an early stage improves the chance of curing the cancer.
Recommended Reading: Natural Remedies For Autoimmune Hepatitis
How Are Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C Spread From Person To Person
Like HIV, the hepatitis B and hepatitis C viruses spread:
- From mother to child: Pregnant women can pass these infections to their infants. HIV-HCV coinfection increases the risk of passing on hepatitis C to the baby.
- Sexually: Both viruses can also be transmitted sexually, but HBV is much more likely than HCV to be transmitted sexually. Sexual transmission of HCV is most likely to happen among gay and bisexual men who are living with HIV.
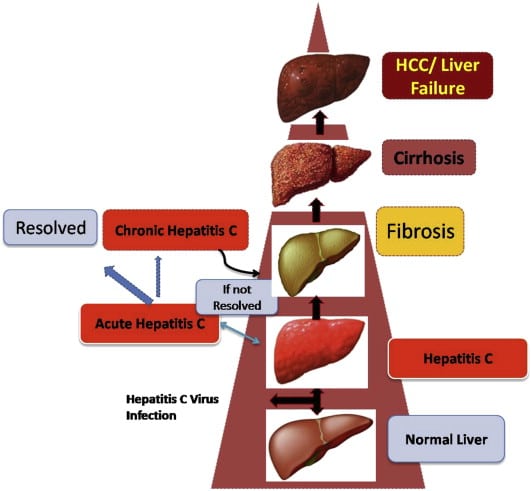
Acute Vs Chronic Hepatitis C: Whats The Difference
Without treatment, acute hepatitis C could become chronic.
Without treatment, chronic hepatitis C can cause damage to the liver over time. Scarring on the liver increases the risk of liver cancer and liver failure. Unfortunately, many people do not catch hepatitis C when its in the acute stage when its easier to treat.
Also Check: Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Interpreting Hcv Rna Test Results
It is essential that the provider understands how to interpret HCV RNA test results, especially during the course of HCV treatment.
| Result of HCV RNA Test | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| A quantified viral load — any exact number | Ongoing HCV infection |
| “Detected” | The HCV RNA is detectable but the number of international units is so low that it cannot be quantified accurately. This indicates extremely low level of virus is present. |
| “< 12 IU/mL” or “< 15 IU/mL” or “< 25 IU/mL” All of these are “less than the LLOQ” | HCV RNA is undetectable. No virus is detected at all in the patient’s serum specimen. |
Management Of Acute Hcv Infection
Acute hepatitis C infection is most often asymptomatic and frequently develops into chronic infection. Case reports of acute hepatitis C have increased in the US since 2010 and have most often been associated with parenteral exposures to blood or body fluids . Although HCV infection is primarily associated with injection drug use, certain behaviors primarily among men who have sex with menare risk factors for transmission . The syndemic of opioid use disorder and HCV and HIV transmission contributes to the burden of disease in certain populations .
Also Check: Natural Remedy For Hepatitis B
Definitions Of Acute Hcv Infection
Most commonly, acute hepatitis C virus infection is defined as the 6-month time period following acquisition of hepatitis C virus. The definition of acute hepatitis C is irrespective to whether the patient has clinical signs or symptoms of acute hepatitis. The rationale for choosing 6 months as the time period to define acute infection is based on evidence that most individuals who spontaneously clear HCV will do so by 6 months.
Treatment For Chronic Hbv Infection
For chronic HBV infection, antiviral medications are available.
This is not a cure for chronic HBV. However, it can stop the virus from replicating and prevent its progression into advanced liver disease.
A person with a chronic HBV infection can develop cirrhosis or liver cancer rapidly and without warning. If a person does not have access to adequate treatment or facilities, liver cancer can be fatal within months of diagnosis.
People with a chronic HBV infection require ongoing medical evaluation and an ultrasound of the liver
Also Check: How Can I Tell If I Have Hepatitis C
Don’t Miss: Does Planned Parenthood Test For Hepatitis
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis C
Treatment for hepatitis C is with antiviral medicines. They can cure the disease in most cases.
If you have acute hepatitis C, your health care provider may wait to see if your infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
If your hepatitis C causes cirrhosis, you should see a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. Treatments for health problems related to cirrhosis include medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If your hepatitis C leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
What Is Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a form of Hepatitis which is transmitted through the exposure to blood and blood products contaminated with the particular virus.
The most common methods of Hepatitis C transmission includes,
- Blood and blood product transfusion
- Contamination with infected injections during invasive medical procedures
- Unprotected sexual intercourse
- Intravenous drug users
Patients with Hepatitis C, in general, will suffer from fever, fatigability, weakness, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, joint pains and signs of jaundice .
Diagnosed as either acute or chronic Hepatitis C with relevant clinical signs and serological investigations, this condition is mainly treated with Antiviral medicines, which is known to be effective in 90% of affected individuals.
Donât Miss: What Can Hepatitis C Do To You
Recommended Reading: Causes Of Hepatitis C Transmission
Hiv And Hepatitis C Coinfection
HCV infection is common among people with HIV who also inject drugs. Nearly 75% of people living with HIV who report a history of injection drug use are co-infected with HCV. All people who are diagnosed with HIV are recommended to be tested for HCV at least once. People living with HIV are at greater risk for complications and death from HCV infection. Fortunately, direct acting antivirals that are used to treat HCV work equally well in people with and without HIV infection. For more information about HIV and HCV coinfection, visit the HIV.govs pages about hepatitis C and HIV coinfection.
Read Also: Is Hiv Transmitted More Easily Than Hepatitis
Recommended Testing For Diagnosing Acute Hcv Infection
RECOMMENDED RATING HCV antibody and HCV RNA testing are recommended when acute HCV infection is suspected due to exposure, clinical presentation, or elevated aminotransferase levels . I, C
Recommendations for HCV testing are also found in the Testing and Linkage to Care section.
Diagnosis of acute HCV infection enables estimation of annual incidence rates and transmission patterns, thereby facilitating implementation and assessment of prevention programs. At the individual level, a diagnosis of acute infection expedites linkage to care, counseling regarding high-risk behavior, and timely interventions to reduce virus transmission and liver disease progression . Some persons involved in high-risk behaviors practice serosorting, defined as using HCV antibody serostatus to determine whether to engage in high-risk behaviors with certain individuals . Thus, undiagnosed acutely infected persons may be at greater risk of transmitting HCV to their presumably seronegative contacts than would be expected by chance.
The best laboratory evidence to support a diagnosis of acute HCV infection is a positive HCV RNA test in the setting of a negative HCV antibody test , or a positive HCV antibody test after a prior negative HCV antibody test . There are rare instances in which these approaches may be misleading, such as in immunosuppressed individuals with impaired antibody production .
Discrete Exposure
Also Check:
Don’t Miss: Who Need Hepatitis B Vaccine
When To Seek Medical Advice
See your GP if you persistently have any of the later symptoms listed, or if they keep returning. They may recommend having a blood test that can check for hepatitis C.
Read more about diagnosing hepatitis C
None of these symptoms mean you definitely have hepatitis C, but itâs important to get them checked out.
You should also speak to your GP about getting tested if thereâs a risk youâre infected, even if you donât have any symptoms. This particularly includes people who inject drugs or have done so in the past.
Read about the causes of hepatitis C for more information about whoâs at risk of having the infection.
Page last reviewed: 27 October 2021 Next review due: 27 October 2024
Donât Miss: Hep Forte Hepatic Lipotropic Nutritional Support
I’m A Health Care Worker Who Was Recently Exposed To Hcv Is There Post
No. Immune globulin is not recommended for postexposure prophylaxis against HCV, and prophylactic antiviral therapy is also not recommended. However, following exposure, a health care worker should be tested for HCV antibody right away and at 6 months so that early HCV infection can be identified. Several studies suggest that interferon treatment begun early in the course of HCV infection is associated with a higher rate of cure however, further studies are needed to confirm this. There is no hepatitis C vaccine.
Also Check: What Do You Get Hepatitis From
What Makes Yale Medicines Approach To Treating Hepatitis B And C Unique
The Viral Hepatitis Program at Yale Medicine represents one of the leading viral hepatitis treatment programs in the country and is engaged in innovative research focused on advancing the care of patients with chronic hepatitis B, C and D infections.
A multidisciplinary team of faculty physicians and mid-level providers offer a coordinated approach to preparing patients for success. Services include structured hepatitis patient education classes, mindfulness-based stress reduction techniques , a formal physician-guided weight-loss program and access to clinical trials evaluating current and new therapies that are not available in routine clinical practice.
Our program is a core member of several national and international observational cohort studies which contributes to the advancement of science of hepatitis treatment around the world.
Our team at Yale Medicine is uniquely equipped to serve patients with viral hepatitis from Connecticut and beyond and aims to offer outstanding, individualized, patient-centered care to help educate and guide patients through their treatment, says Dr. Lim. We have specialists who have nationally recognized expertise in the management of viral hepatitis in special populations, including HCV-HIV coinfection, end-stage renal disease, cirrhosis/liver failure, post-liver transplant, and prior failure to respond to all-oral direct acting antivirals .
Dont Miss: Hepatitis C Antibody With Reflex To Hcv Rna
How Common Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is fairly common in Africa and the western Pacific region. Throughout the world, there are about 292 million people who are infected with chronic hepatitis B. In the U.S., the figure exceeds 2 million people.
The number of infections had been falling in the U.S., but fewer vaccinations among adults combined with the onset of the opioid crisis and injected drug usage has resulted in the numbers rising again. Infected women can pass the infection on to their babies. Children who are infected before age 5 are more likely to have chronic infection than those infected later in life.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Early Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
How Is Hepatitis C Transmitted
Because HCV is primarily spread through contact with infected blood, people who inject drugs are at increased risk for HCV infection. HCV can also be transmitted from an infected mother to child at the time of birth, from unregulated tattoos or body piercings, and from sharing personal items that may be contaminated with infected blood, even in amounts too small to see. Much less often, HCV transmission occurs through sexual contact with an HCV-infected partner, especially among people with multiple sex partners and men who have sex with men. Currently in the United States, health care related transmission of HCV is rare, but people can become infected from accidental needle sticks and from breaches in infection control practices in health care facilities.
Can Hepatitis C Be Prevented
There is no vaccine for hepatitis C. But you can help protect yourself from hepatitis C infection by:
- Not sharing drug needles or other drug materials
- Wearing gloves if you have to touch another personâs blood or open sores
- Making sure your tattoo artist or body piercer uses sterile tools and unopened ink
- Not sharing personal items such toothbrushes, razors, or nail clippers
- Using a latex condom during sex. If your or your partner is allergic to latex, you can use polyurethane condoms.
NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis A Is It Curable
Causes And Risk Factors
HCV causes hepatitis C. People contract the virus through blood-to-blood contact with contaminated blood. For transmission to occur, blood containing HCV must enter the body of a person without HCV.
A speck of blood, invisible to the naked eye, can carry hundreds of hepatitis C virus particles, and the virus is not easy to kill.
The report the following risk factors for developing hepatitis C:
- using or having used injectable drugs, which is currently the most common route in the U.S.
- receiving transfusions or organ transplants before 1992, which is before blood screening became available
- having exposure to a needle stick, which is most common in people who work in healthcare
- being born to a mother who has hepatitis C
The CDC offer advice on cleaning syringes if it is not possible to use clean and sterile ones. Although bleach can kill the HCV in syringes, it may not have the same effect on other equipment. Boiling, burning and using alcohol, peroxide, or other common cleaning fluids to wash equipment can reduce the amount of HCV but might not stop a person from contracting the infection.
It is extremely dangerous to inject bleach, disinfectant, or other cleaning products, so people should make sure they rinse the syringe thoroughly. A person should only ever use bleach to clean equipment if new, sterile syringes and equipment are not available.
People who are at risk due to these factors can have screening to rule out HCV.
- peginterferon alfa-2a
Who Should Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
All newborn babies should get vaccinated. You should also get the shot if you:
- Come in contact with infected blood or body fluids of friends or family members
- Use needles to take recreational drugs
- Have sex with more than one person
- Are a health care worker
- Work in a day-care center, school, or jail
You May Like: How You Contract Hepatitis B
Can Hepatitis Be Prevented
There are different ways to prevent or lower your risk for hepatitis, depending on the type of hepatitis. For example, not drinking too much alcohol can prevent alcoholic hepatitis. There are vaccines to prevent hepatitis A and B. Autoimmune hepatitis cannot be prevented.
NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Antibody With Reflex To Hcv Rna