The Sample Can Be Collected By A Range Of Healthcare And Lay Providers
Point-of care tests can be administered by a range of healthcare providers including family doctors, nurse practitioners and nurses as well as lay providers such as frontline workers and people with lived and living experience.12,21,22 Benefits of this task-shifting include expanding the availability of testing22 and allowing people with connections to a community to administer the test. Lay providers who have regular personal contact with clients may see greater uptake in testing from clients because they have well-established relationships.12 Some, but not all, provinces and territories permit lay providers to conduct point-of-care testing.
Taking A Hepatitis C Test
Hepatitis C testing is conducted on a sample of blood. Blood samples can be collected by a doctor, nurse, technician, or other health care provider from an adult patients vein using a small needle or a skin prick on a childs heel.
For an at-home hepatitis C test, patients collect a blood sample according to the manufacturers directions. Instructions provided in the test kit detail the steps to obtain a small sample of blood and mail it for testing.
Uspstf Hcv Screening Recommendations
In March 2020, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force issued updated recommendations regarding screening for HCV. The USPSTF now recommends routine screening for all adults in the United States 18-79 years of age, including pregnant women . The 2020 USPSTF recommendation for HCV screening was categorized as a grade B recommendation, which means that the USPSTF concludes with moderate certainty that screening for HCV in adults 18-79 years of age has substantial net benefit and that health care providers should offer this service . The USPSTF notes that most adults will require HCV screening only once, but those with ongoing risk of acquiring HCV will need periodic screening. For persons younger than 18 or older than 79 years of age, screening for HCV can be considered if the individual is considered at high risk for having acquired HCV. The 2020 USPSTF recommendations for HCV screening is clearly a major change from the prior 2013 USPSTF recommendations to screen adults born during 1945-1965 and those with known risk.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Genotype 2 Treatment Guidelines
Cdc Recommendations For Hepatitis C Screening Among Adults In The United States
- Universal hepatitis C screening:
- Hepatitis C screening at least once in a lifetime for all adults aged 18 years and older, except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection is less than 0.1%*
- Hepatitis C screening for all pregnant women during each pregnancy, except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection is less than 0.1%*
- Any person who requests hepatitis C testing should receive it, regardless of disclosure of risk, because many persons may be reluctant to disclose stigmatizing risks
Other Things To Know:
- After a successful course of treatment for hepatitis C, the hepatitis C antibody remains detectable, but the hepatitis C RNA will be undetectable.
- If you plan to donate blood, you will be tested for the hepatitis C antibody and will be turned away even if you do not have an active infection.
- Any patient with a positive test result for the hepatitis C antibody should have additional tests to determine whether or not the virus is still active.
Read Also: Hepatic Crisis In Sickle Cell Disease
What To Do If The Hcv Antibody Test Is Reactive
If the antibody test is reactive or positive, you need an additional test to see if you currently have hepatitis C. This test is called a nucleic acid test for HCV RNA. Another name used for this test is a PCR test.
If the NAT for HCV RNA is:
- Negative you were infected with hepatitis C virus, but the virus is no longer in your body because you were cured or cleared the virus naturally.
- Positive you now have the virus in your blood.
If you have a reactive antibody test and a positive NAT for HCV RNA, you will need to talk to a doctor about treatment. Treatments are available that can cure most people with hepatitis C in 8 to 12 weeks.
Finance & Getting Buy
Key stakeholders: Identify who in your organization needs to be on board to develop a point-of-care HCV RNA testing program.
Evidence: Write a list of reasons why they should support this initiative identify the benefits.
Partnerships: Consider partnerships with a range of stakeholders, would any of these stakeholders support your plan? In what way?
Elimination goals: Consider linking point-of-care HCV RNA testing to state, national or international strategic hepatitis elimination plans or goals
Risk management: Show management that you have thought about any possible risks. Identify any possible risks and demonstrate how you will manage them.
Budget: Put together a budget to show how much it will cost. Consider comparing the cost per point-of-care test and compare this to traditional testing methods.
Infrastructure: Identify what additional equipment you will need. Is there existing infrastructure you could use? Can you integrate this intervention into your existing services?
Staff, workflow and impact: Consider how you will staff the intervention. Can it work with your existing staff? Identify key staff who will be involved.
Training and protocols: Consider how you will train your staff, and who will run the training. Develop a relationship with a local laboratory or another quality assurance provider that can provide ongoing support for training.
Helpful resources:
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Liver Cancer Symptoms
Appropriate Uses Of The Hcv Rna Test
There are 4 major reasons that HCV RNA tests are used:
More rarely, HCV RNA is used when either very acute HCV infection is suspected or a false HCV Ab is suspected.
It would not be appropriate to repeatedly order HCV RNA viral load screening for a patient who is not on or was recently on HCV treatment, or to use the HCV viral load to determine the severity of the patient’s infection or the patient’s risk of developing significant liver disease.
Home Screening Tests For Hepatitis C
At-home screening tests provide privacy if you prefer not to go to a doctor or clinic for testing. These tests typically look for antibodies to hepatitis C, but they may not always test for active viral infection. Make sure you know what type of test youll be taking before you buy.
Many at-home tests have close to or the same reliability as blood tests received by a medical professional.
If youve recently been exposed to hepatitis C, wait several weeks before testing at home.
You May Like: Hepatitis A Ab Total Reactive
Articles On Reasons For Hep C Tests
As far as viruses go, hepatitis C is among the sneakiest. Once it’s in your blood, it travels to your liver, where it may settle in for a silent, long-term stay. This can lead to cancer or cause the organ to fail if you don’t treat it. In fact, hepatitis C is among the top reasons for liver transplants in the U.S.
If you think youâve been exposed, here are five reasons to get tested right away:
Test Results Are Available At The Same Appointment Which Can Reduce Loss To Follow
When clients are able to have a blood sample collected and learn their test result within the same encounter, it can be possible to obtain a swift diagnosis, and the emotional burden associated with having to wait for the results can be alleviated.17 This can also simplify the testing process and reduce the number of clinic visits or interactions with service providers related to hepatitis C care that a client will have to have.1,9,10,17,22,23
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Vaccine For Newborns Pros And Cons
Benefits Of Screening For Hepatitis C
If individuals with chronic hepatitis C are identified before they develop advanced fibrosis, cirrhosis, or hepatocellular carcinoma, 90%-100% can now be expected to respond to treatment, whereas previously only 66%-75% of individuals responded to treatment.8–13,24–27 Thus, detecting individuals with hepatitis C before they develop signs or symptoms of the disease can have an important impact on their subsequent clinical course. Sustained virologic clearance for more than 6 months after treatment of hepatitis C is also associated with a reduction in all-cause mortality.28
An Outline Of Recommended Testing For Screening And Diagnosis Of Hepatitis C
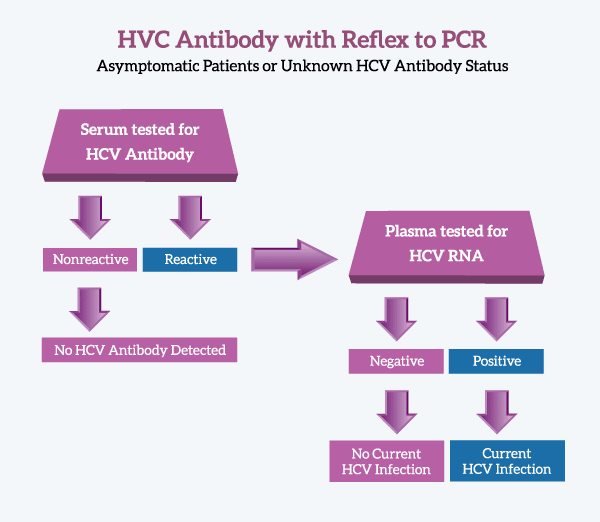
Step 1: Testing for HCV Antibody
- A positive antibody result indicates that a patient has been infected with hepatitis C at some point.
- A negative antibody result indicates that the patient has never been infected with hepatitis C.
- A positive antibody result alone does not distinguish between an active or previous hepatitis C infection.
Step 2: Testing for HCV RNA
- VA laboratories run an automatic “reflex” HCV RNA test for all hepatitis C antibody positive tests.
- From a single blood draw, the patient had 2 specimens collected in 2 tubes one for the HCV antibody test and, in case the antibody result was positive, a second for HCV RNA test.
- The clinician does not need to place an additional order and the patient does not need to return to the lab to have another blood draw.
Don’t Miss: Can You Have Hepatitis C And Not Know It
What Is A Hepatitis C Screening
Testing for hepatitis C involves a blood test called an HCV antibody test . This test determines if youve ever had a hepatitis C infection by checking your blood for HCV-specific antibodies.
If you test positive for HCV antibodies, youll need to undergo follow-up testing. Having antibodies does not mean you currently have an active infection. It may simply mean that you have had a prior exposure that your immune system cleared.
To check whether you have an active infection, a doctor will order a nucleic acid test . A positive result means the virus is currently active in your bloodstream. If you get a negative result, the virus was once in your body, but its not anymore.
- have ever had a needle-stick injury or potentially been exposed to HCV-positive blood
- have had a tattoo or piercing done outside of a professional sterile environment
According to the , HCV may be passed through sexual activity, though this is not common. The agency notes that your risk may be increased if you:
- have a sexually transmitted infection
- have sex with multiple partners
Managing Your Health While On Treatment
There are many things you can do to improve your health and feel better while on treatment for your Hepatitis C infection. And by taking good care of yourself, you will increase your chances of be able to take your medication as prescribed.
IMPORTANCE OF DIET AND NUTRITION
Contrary to some claims you might read on the Internet, there is no special Hepatitis C diet. However, a healthy diet can improve liver health in a person with Hepatitis C.
A well-balanced diet can lead to better liver functioning and lowered risk of cirrhosis of the liver. It can also help your immune system fight off illness. People with Hepatitis C tend to have higher rates of diabetes, but a good diet can help control blood sugar and reduce body fat, thereby lowering your risk for becoming diabetic.
Multiple studies have now demonstrated the benefit of drinking coffee to improve liver health in Hepatitis C. Studies suggest you need to drink more than two cups per day to gain this benefit. However, the research is not strong enough to make a recommendation to start drinking coffee and some people do not tolerate it well. But for those who currently do drink coffee enjoy!
General dietary recommendations include the following:
BE CAUTIOUS ABOUT DIETARY SUPPLEMENTS
Certain vitamins and minerals like vitamins A and D, iron and niacin can be harmful to your liver in high doses. Before taking a vitamin or supplement, its best to talk with your doctor, dietician or nutritionist.
ALCOHOL
Also Check: Hepatitis A And B Symptoms
Is Hepatitis C Treatable
Yes, and treatment has changed remarkably in the past four years. It used to be that the treatment generally lasted about 12 months and had many side effectsalmost like some types of cancer chemotherapyand cured only about 40 percent of those treated. Todays medicines are generally taken for three months, have few side effectsalmost like taking a cholesterol pilland cure about 95 percent of those treated. It has become an exciting time in terms of hepatitis C treatment.
Drawbacks To Screening For Hepatitis C
A patient’s worry or anxiety while waiting for test results, concerns about insurance coverage of evaluation and treatment, adverse effects of treatment, and complications associated with liver biopsy can limit screening for hepatitis C. However, the accuracy of HCV RNA testing, the availability of medication assistance programs for uninsured patients, and improved treatments with fewer side effects and shorter duration should allay some of the anxiety associated with the screening process.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Transfer Hepatitis C
What Does The Test Measure
Hepatitis C testing identifies antibodies to the hepatitis C virus, detects viral RNA, and/or determines the strain of hepatitis C. Hepatitis C testing may involve several different tests:
- Hepatitis C antibody test: Antibodies are a part of the bodys response to an infection. Testing for hepatitis C antibodies determines whether or not a patient has been exposed to the hepatitis C virus at some point in their life. If this test is positive, the next step is to test for hepatitis C RNA which can tell you if you have a current infection.
- Hepatitis C RNA test: RNA is a type of genetic material from the hepatitis C virus that can be detected in the blood. If test results are positive after a hepatitis C antibody test, doctors use a hepatitis C RNA test to look for and/or measure the amount of the virus in the blood. Qualitative HCV RNA tests can detect the presence of HCV RNA, while quantitative HCV RNA tests measure the amount of HCV RNA. Understanding the amount of HCV in the blood helps to monitor response to treatment.
- Genotype test: There are at least six types of hepatitis C, which are also called strains or genotypes. Treatment for hepatitis C depends on the strain, so genotype testing to guide treatment is performed in patients who are diagnosed with an HCV infection.
Who Should Get Tested For Hepatitis C
The CDC recommends that you get tested at least once no matter what. Definitely get screened if any of these things apply to you:
- You were born between 1945 and 1965.
- You use or inject drugs.
- You have ever injected drugs — even if it was just once or a long time ago.
- Youâre on kidney dialysis.
- You have abnormal alanine aminotransferase levels .
- You had a blood transfusion, blood components, or an organ transplant before July 1992.
- Youâve ever gotten clotting factor concentrates made before 1987.
- You received blood from a donor who later tested positive for hepatitis C virus.
- Youâre a health care worker, first responder, or have another job that exposes you to HCV-infected needles.
- You were born to a mother with HCV.
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis A Vaccine
Importance Of Adhering To Your Treatment Plan
Once you begin treatment for your Hepatitis C infection, youll want to do everything you can to make it a success. Adherence to your Hepatitis C medication regimen is an important predictor of successful treatment. When it comes to medications, this means that you want to adhere to taking them as prescribed meaning taking the right dose, the right way, at the right time, for as long as prescribed.
The goal of using medications to treat Hepatitis C is to:
- Clear the Hepatitis C virus from your body
- Prevent or slow down scarring of your liver
- Reduce your chance of developing cirrhosis and liver cancer
Proper adherence to Hepatitis C therapy will increase your chance of being cured and decrease the long-term complications of Hepatitis C.
Adhering to other aspects of your treatment plan is also important. Keeping your medical appointments and getting the necessary lab tests will help to maximize your chance of treatment success and minimize potential problems.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B E Antibody Reactive Means
Monitoring During Daa Treatment
Reviewed and updated: David E. Bernstein, MD, with the HCV Guideline Committee October 6, 2022
| RECOMMENDATIONS |
Monitoring of Patients Taking RBV
Monitoring for HBV Reactivation
Abbreviations: ALT, alanine transaminase AST, aspartate aminotransferase HBsAg, HBV surface antigen HBV, hepatitis B virus HCV, hepatitis C virus RBV, ribavirin. |
The adverse events associated with direct-acting antiviral treatment are listed in Table 8, below, and most are manageable. Patients who are taking RBV and experience insomnia may need to adjust the timing of the dose to earlier in the afternoon to avoid any sleep disruption.
| KEY POINT |
|
| Table 8: Adverse Events Associated with Direct-Acting Antivirals |
| Drug or Combination |
| Headache, fatigue, diarrhea, and nausea |
References
Recommended Reading: Is There A Vaccine For Hepatitis B And C