Hepatitis: 5 Ways You Can Contract This Disease
In 1990s hepatitis was considered as a widespread health problem. About 1.4 million people all over the world get hepatitis A annually. It has been estimated that in parts of Asia and Africa, approximately one in ten people suffers from chronic Hepatitis B. Hepatitis is a condition which involves inflammation of the liver, it is most commonly caused by the various strains of the hepatitis virus but could also be caused by infections, toxins, alcohol or autoimmune disorders. Hepatitis A, B, C, D, E are the five main types of hepatitis virus. Among this HAV is the most prevalent. And then HCV , it is the major cause of liver cancer and cirrhosis.
Have a question about
Risk Factors of Hepatitis A
Some risk factors of hepatitis A are,
- Household or unsafe sexual contact with an infected person.
- Sharing contaminated needles.
- Poor sanitation and personal hygiene.
- Use of street drug.
- Eating food that is prepared with an infected food handler.
- Contamination of food and water by feces of an infected person
Risk Factors of Hepatitis B
Some risk factors of hepatitis B are,
- Unprotected sex with several partners.
- Coming in contact with infected blood or the transfusion of infected blood
- Use of intravenous drug.
- Infants of hepatitis B positive mothers.
- Tattooing and body piercing.
Risk factors of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is also known as “an emerging public health threat” and the “silent epidemic”. Some risk factors of hepatitis C are,
Risk Factors of Hepatitis D
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Hbv Infection
HBV can cause a wide range of symptoms, from a mild illness and general feeling of being unwell to more serious chronic liver disease that can lead to liver cancer.
Someone with hepatitis B may have symptoms similar to those caused by other viral infections, like the flu. The person might:
- feel like throwing up or actually throw up
- not feel like eating
- have a mild fever
HBV also can cause darker than usual pee, jaundice , and belly pain.
People exposed to hepatitis B may start to have symptoms from 1 to 6 months later. Symptoms can last for weeks to months.
In some people, hepatitis B causes few or no symptoms. But even someone who doesn’t have any symptoms can still spread the disease to others.
Is Hepatitis Testing Recommended For People With Hiv
Yes. Everyone with HIV should be tested for HBV and HCV when they are first diagnosed with HIV and begin treatment. People with HIV who have ongoing risk factors for getting hepatitis B or hepatitis C should be tested annually.
In addition, HCV screening recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention call for:
- One-time screening for all adults 18 years and older
- Screening of all pregnant women during every pregnancy
- Testing for all persons with risk factors, with testing continued periodic testing those with ongoing risk.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C And Liver Transplantation
Hepatitis B And Your Liver
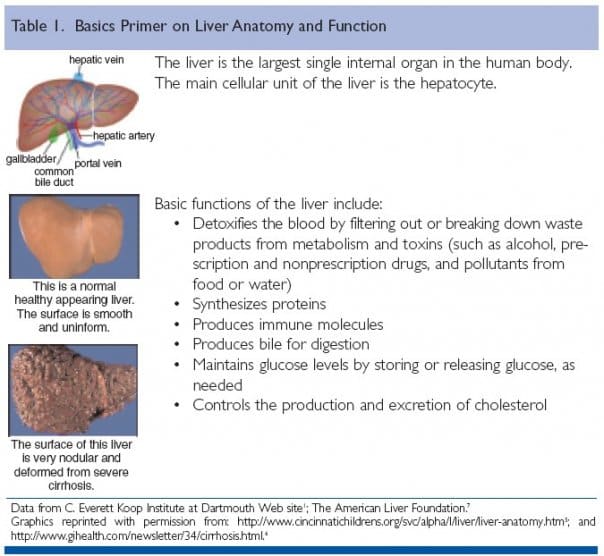
The liver is such an important organ that we can survive only one or two days if it completely shuts down – if the liver fails, your body will fail, too. Fortunately, the liver can function even when up to 80% of it is diseased or removed. This is because it has the amazing ability to regenerate – or create – itself from healthy liver cells that still exist.
If your body were an automobile, your liver would be considered the engine. It does hundreds of vital things to make sure everything runs smoothly:
- Stores vitamins, sugar and iron to help give your body energy
- Controls the production and removal of cholesterol
- Clears your blood of waste products, drugs and other poisonous substances
- Makes clotting factors to stop excessive bleeding after cuts or injuries
- Produces immune factors and removes bacteria from the bloodstream to combat infection
- Releases a substance called “bile” to help digest food and absorb important nutrients
The word hepatitis actually means inflammation of the liver. Thus, hepatitis B refers to inflammation of the liver caused by the hepatitis B virus. With early detection and appropriate follow-up medical care, people living with a chronic hepatitis B infection can expect to enjoy a long and healthy life.
Prevent Infection After Contact With The Virus

If you think you have been in contact with the hepatitis B virus, see your doctor right away. Doctors typically recommend a dose of the hepatitis B vaccine to prevent infection. In some cases, doctors may also recommend a medicine called hepatitis B immune globulin to help prevent infection. You must get the vaccine dose and, if needed, HBIG shortly after coming into contact with the virus, preferably within 24 hours.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Test For Hepatitis C
Also Check: What Hepatitis Vaccines Are There
Causes Of Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is spread through contact with blood that contains the hepatitis B virus. If infected blood or body fluids enter another persons bloodstream, that person may become infected.
The time from exposure to the hepatitis B virus to the appearance of the illness is 45 to 180 days.
Risky activities that can cause infection include:
- Sharing unsterile or unclean equipment for injecting drugs.
- Piercing the skin with equipment that is not properly cleaned, disinfected and sterilised.
- Sharing razor blades or toothbrushes.
- Coming into contact with infected blood through open cuts or the mucous membranes of another person.
- Having unprotected sex , especially if there is blood present.
Mothers who have hepatitis B can pass the virus to their babies or children at the time of birth or after birth. If the newborn baby is quickly immunised with 2 vaccines, they can be protected from getting hepatitis B.
All blood and blood products produced for medical purposes in Australia are carefully screened for hepatitis B and other blood-borne viruses. The risk of getting infected with hepatitis B from a blood transfusion is extremely low .
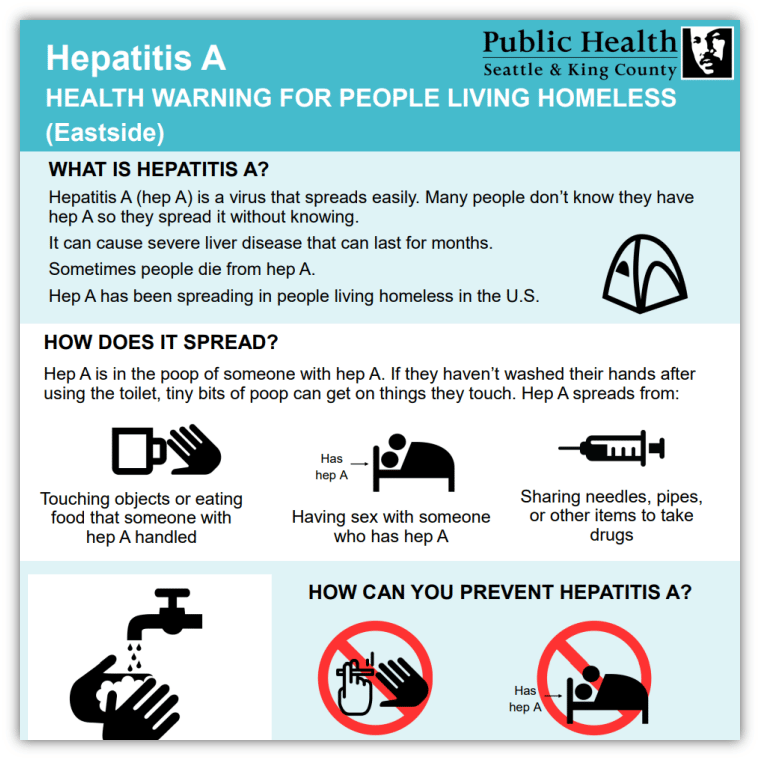
How Common Is Hepatitis A
In the United States, hepatitis A has become relatively uncommon. After the hepatitis A vaccine became available in 1995, the rate of hepatitis A infections declined by 95 percent in the United States. The number of reported cases of hepatitis A fell to 1,239 in 2014, the lowest yearly number of cases reported since the disease could be tracked.1 However, the number of reported cases increased to 3,366 in 2017, almost 3 times higher, mostly due to outbreaks among people who use drugs and people experiencing homelessness.1 Early reports suggest that the numbers of cases and outbreaks of hepatitis A increased further during 2018 and continue at these higher rates in 2019.2
Hepatitis A is more common in developing countries where sanitation is poor and access to clean water is limited. Hepatitis A is more common in parts of Africa, Asia, Central and South America, and Eastern Europe than it is in the United States.
Also Check: Immune To Hepatitis B Means
How Do You Get Hepatitis C
Just like hepatitis B, you can get this type by sharing needles or having contact with infected blood. You can also catch it by having sex with somebody whos infected, but thats less common.
If you had a blood transfusion before new screening rules were put in place in 1992, you are at risk for hepatitis C. If not, the blood used in transfusions today is safe. It gets checked beforehand to make sure its free of the virus that causes hepatitis B and C.
Its rare, but if youre pregnant and have the disease, its possible to pass it to your newborn.
There are some myths out there about how you get hepatitis C, so lets set the record straight. Its not spread by food and water . And you canât spread it by doing any of these things:
See your doctor as soon as possible if you have any of these symptoms.
Sometimes, people have no symptoms. To be sure you have hepatitis, youâll need to get tested.
Treatments For Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B usually clears up on its own without treatment. You may be offered medicine to help with the symptoms, such as painkillers or medicines to stop you feeling sick.
Your GP will refer you to see a liver specialist who will check how well your liver is working.
If hepatitis B lasts for over 6 months it is called long-term hepatitis B.
It is usually treated with antivirals and medicine to help relieve symptoms such as itchiness, pain, and sickness. You will also need to see a liver specialist for regular check-ups.
Read Also: What Is The New Drug For Hepatitis C
Good Nutrition And Rest
- All family members should eat a well-balanced diet that includes foods shown in the graphic MyPlate . You can find more information about balanced nutrition on the website ChooseMyPlate.gov .
- All family members should get at least 8 hours of sleep each night.
- Young children who are ill should rest during the day when possible.
Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis B
Anyone can get hepatitis B, but the risk is higher in:
- Infants born to mothers who have hepatitis B
- People who inject drugs or share needles, syringes, and other types of drug equipment
- Sex partners of people with hepatitis B, especially if they are not using latex or polyurethane condoms during sex
- Men who have sex with men
- People who live with someone who has hepatitis B, especially if they use the same razor, toothbrush, or nail clippers
- Health care and public-safety workers who are exposed to blood on the job
- Yellowish eyes and skin, called jaundice
If you have chronic hepatitis B, you may not have symptoms until complications develop. This could be decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis B screening is important, even if you have no symptoms. Screening means that you are tested for a disease even though you don’t have symptoms. If you are at high risk, your health care provider may suggest screening.
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis Be Antibody
Hepatitis B During Pregnancy
If a woman with HBV becomes pregnant, they may transmit the virus to their baby. Women should inform the doctor who delivers their baby that they have HBV.
The infant should receive an HBV vaccine and HBIG with 1224 hours of birth. This significantly reduces the risk that they will develop HBV.
The HBV vaccine is safe to receive while pregnant.
People with a high risk of HBV include:
- the infants of mothers with HBV
- the sexual partners of people with HBV
- people who engage in sexual intercourse without contraception and those who have multiple sexual partners
- men who have sex with men
- people who inject illicit drugs
- those who share a household with a person who has a chronic HBV infection
- healthcare and public safety workers who are at risk of occupational exposure to blood or contaminated bodily fluids
- people receiving hemodialysis, which is a type of kidney treatment
- people taking medications that suppress the immune system, such as chemotherapy for cancer
People can prevent HBV infection by:
- wearing appropriate protective equipment when working in healthcare settings or dealing with medical emergencies
- not sharing needles
- following safe sexual practices
- cleaning any blood spills or dried blood with gloved hands using a 1:10 dilution of one part household bleach to 10 parts water
A vaccine against HBV has been available since 1982.
People who should receive this vaccine include:
Where Is The Hepatitis B Virus Found And How Is It Transmitted
Blood is the major source of the hepatitis B virus in the workplace. It can also be found in other tissues and body fluids, but in much lower concentrations. The risk of transmission varies according to the specific source. The virus can survive outside the body for at least 7 days and still be able to cause infection.
Recommended Reading: Risk Factors Of Hepatitis B
Hepatitis A: Who Is At Risk
A prime risk factor for hepatitis A is traveling to or living in a country with high infection rates. You can check the CDCâs travel advisories to learn about recent outbreaks. Eating raw foods or drinking tap water can raise your risk while traveling. Children who attend daycare centers also have a higher risk of getting hepatitis A.
Can Hepatitis B And C Be Prevented
Today, all babies get vaccinated against the hepatitis B virus in a series of three shots over a 6-month period. Doctors also recommend catch-up vaccination for all kids and teens younger than 19 years old who didnt get the vaccine as babies or didnt get all three doses.
Unfortunately, theres no vaccine for hep C yet.
Also Check: How Hepatitis B And C Are Transmitted
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Viral Load Labcorp
How To Get Tested
Oftentimes, people with hepatitis B dont have symptoms. That’s why it’s important to get tested if you had unprotected sex or shared a needle with someone who may have been infected. Hepatitis B is detected by a blood test and is usually included in routine sexually transmitted infection screenings.
How Does A Person Get Hepatitis
A person can get hepatitis A through the following sources:
- Food or water contaminated with the fecal matter of an infected person
A person can get hepatitis B in many ways, which include:
- Having sexual contact with an infected person
- Sharing needles
- Being in direct contact with an infected persons blood
- Transferred from mother to the fetus
- Getting an infected needle prick
- Being in contact with an infected persons body fluid
A person can get hepatitis C through:
- Sharing infected needles
You May Like: Hepatitis B Vaccine Dose In Newborn
How Do Ticks Find Their Hosts
Ticks live in grasses and shrubs. They are not very mobile, and for this reason, they find their hosts by chance.
The tick must wait for potential hosts to brush past their location. If this occurs, the tick will attempt to climb onto them.
To climb onto their host, ticks use a technique that scientists call questing. When questing, the tick attaches itself to the tips of grasses or shrubs with its hind legs. It keeps its front legs outstretched. This readies it for grabbing onto potential hosts.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Hepatitis From Saliva
How Can A Person Contract Hepatitis From Contaminated Food
The Washington State Department of Health states that a person can come into contact with hepatitis A if they eat food or drink water that is contaminated with the feces of a person who has the virus.
The virus can, therefore, spread from a person who does not wash their hands after using the bathroom and then touches food.
The food itself can also be contaminated with hepatitis A. For example, people can contract hepatitis A if they eat oysters that farmers have harvested from sewage-contaminated water.
of hepatitis A transmission by:
- washing their hands for 20 seconds using warm soap and water before handling raw foods
- washing their hands after changing diapers
- washing their hands after using the bathroom
People should also sanitize their kitchen using the following steps:
You May Like: How Is Hepatitis B Diagnosed
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis A
Children who become infected with hepatitis A before age 6 usually have no symptoms or mild illness, and if they do become ill, they usually get better in under 2 months. Adults and older children who become infected with hepatitis A can have no symptoms or very mild illness , but most develop jaundice and other symptoms . Mild illness can resolve in 1-2 weeks, but more severe illness can last for months. Common symptoms of HAV infection include:
How Do You Know If You Have Hepatitis B
Signs and symptoms can vary, in particular by the age of the individual. Many individuals may not show symptoms . When symptoms develop, they include fever, joint pain, abdominal pain, fatigue, lack of appetite, nausea, vomiting, dark urine, clay-coloured bowel movements, or jaundice.
Most infections are asymptomatic or mild. Occasionally, people with serious cases of hepatitis B require hospitalization. A very small proportion of these patients develop a critical form of the disease called “fulminant” hepatitis B. This condition results from a sudden breakdown of liver function.
You May Like: What Doctor Treats Hepatitis C
What Laboratory Tests Are Available For Hepatitis B
Tests are available to detect the types of antigens used to identify the hepatitis B virus. The tests determine if the virus is present in the body tissue or blood. The amount of each type of antigen present indicates how advanced the disease is and how infective the individual has become.
Other tests are available to detect the bodys reaction to the viral infection or the bodys reaction to vaccination against the virus. These tests work by measuring the number of antibodies present in the blood.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Virus Antibody With Reflex To Pcr
Immunisation For Hepatitis B
Immunisation is the best protection against hepatitis B infection. A course of vaccination is recommended for all babies and people in high-risk groups.
Immunisation can be with a vaccine against hepatitis B alone or with a combination vaccine. To be immunised, contact your doctor or local council.
Protection against hepatitis B is available free of charge under the National Immunisation Program Schedule. In Victoria, immunisation against hepatitis B is free for:
- Babies at birth immunisation against hepatitis B alone as soon as possible after birth.
- Babies at 2, 4 and 6 months combination immunisation in the form of a diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, hepatitis B, polio and Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine .
- Premature babies at 12 months premature babies born under 32 weeks gestation or under 2,000g birth weight receive a single booster dose.
- Children up to and including 9 years of age.
- People aged less than 20 years having a catch-up immunisation.
- Refugees and humanitarian entrants aged 20 years and above.
In Victoria, free hepatitis B vaccine is provided for people who are at increased risk of infection, including:
Immunisation is also recommended, but not necessarily free, for people who are at increased risk of infection, including:
You May Like: Hepatitis B Vaccine Information Sheet
Read Also: Blood Work For Hepatitis B