Molecular Methods For Hbv Infection
HBV DNA is a direct measurement of the viral load, which reveals the replication activity of the virus. It is detectable at the early stage of infection and increases up to peak level approximately 3 months after the exposure to HBV and then gradually diminishes in chronic infection or disappears at the recovery from HBV infection.
As the prevalence of serologically negative HBV infection has increased, HBV-DNA detection has obtained more awareness in clinical medicine . The detection of HBV DNA is a reliable marker of replication activity, and higher titers of HBV DNA are related to the more rapid disease progression and higher incidence of HCC . Furthermore, HBV DNA testing is useful in routine clinical setting to determine patients who need antiviral therapy and monitor them for suitable treatment .
There are two principles of techniques to identify and quantify HBV DNA: signal amplification such as hybrid capture and branched DNA technology target amplification such as polymerase chain reaction . Real-time PCR can detect wide dynamic range of viral load . For this reason, it has come to be the standard method to detect and quantify HBV DNA in clinical setting. Furthermore, it can be fully automated and does not generate carry-over contamination . Table 1 displays the comparison of assays for quantitative measurement of HBV DNA.
Table 1
Read Also: All Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
American Association For The Study Of Liver Diseases Recommendations
The 2015 AASLD recommendations for the initial evaluation of HBsAg-positive patients is summarized below.
All patients
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Hepatitis B information for health professionals: hepatitis B FAQs for health professionals. http://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/HBV/index.htm. Available at . Updated May 31, 2015 Accessed: May 23, 2017.
Sorrell MF, Belongia EA, Costa J, et al. National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Conference Statement: management of hepatitis B. Ann Intern Med. 2009 Jan 20. 150:104-10. . .
Nguyen MH, Wong G, Gane E, Kao JH, Dusheiko G. Hepatitis B virus: advances in prevention, diagnosis, and therapy. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2020 Mar 18. 33:e2128652. . .
World Health Organization. Hepatitis B. July 27, 2021. Available at . Accessed: December 2, 2021.
McMahon BJ, Holck P, Bulkow L, Snowball M. Serologic and clinical outcomes of 1536 Alaska Natives chronically infected with hepatitis B virus. Ann Intern Med. 2001 Nov 6. 135:759-68. .
Chang MH, Chen CJ, Lai MS, et al. Universal hepatitis B vaccination in Taiwan and the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in children. Taiwan Childhood Hepatoma Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1997 Jun 26. 336:1855-9. .
Te HS, Jensen DM. Epidemiology of hepatitis B and C viruses: a global overview. Clin Liver Dis. 2010 Feb. 14:1-21, vii. .
Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
Some people with hepatitis B will be ill for only a few weeks. This is known as an acute infection. For others, the disease progresses to a lifelong illness, known as chronic hepatitis B.
Some people with acute hepatitis B have no symptoms at all or only mild illness. For others, it causes a more severe illness and they’ll need to go to hospital.
Often people are able to clear the virus from their bodies without treatment. This is especially the case if they get the infection as an adult. But in some cases, acute hepatitis B leads to chronic hepatitis B. Over time, chronic hepatitis B can cause serious health problems, including liver damage, cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Read Also: Why Screen For Hepatitis C
How Accurate Are The Sti Tests
Our simple home test kits are highly accurate when you:
-
wait the recommended window period before you test
-
follow the kit instructions carefully
-
complete additional tests in a clinic setting, if recommended by our clinicians.
Your samples are sent to our partner laboratory to be processed by specialist technicians. We use similar tests that are used by many NHS clinics.
If you are experiencing any STI symptoms, you should visit your local sexual health clinic for further testing and examination.
How Is Hepatitis B Spread
- Having unprotected sex.
- Sharing or using dirty needles for drug use, tattoos or piercing.
- Sharing everyday items that may contain body fluids, including razors, toothbrushes, jewelry for piercings and nail clippers.
- Being treated medically by someone who does not use sterile instruments.
- Being bitten by someone with the infection.
- Being born to a pregnant woman with the infection.
Hepatitis B is not spread by:
- Kissing on the cheek or lips.
- Coughing or sneezing.
- Hugging, shaking hands or holding hands.
- Eating food that someone with the infection has prepared.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Vaccine Booster For Healthcare Workers
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
You may not have any symptoms of Hepatitis B until several weeks or months after you are infected with the virus. Or you may never have any obvious symptoms.If you have symptoms, the illness usually begins with these flulike symptoms:
- Loss of appetite
- Foul breath and bitter taste in the mouth
- Dark brown urine
- Yellowish skin and eyes
- Pain just below the ribs on your right side, especially if you press on that part of your abdomen
- Bowel movements that are whitish or light yellow and may be looser than normal.
Some people develop a chronic form of the disease without having any obvious symptoms, even though damage to the liver may be occurring. The symptoms of chronic Hepatitis B may be persistent fatigue, weakness, and loss of appetite, as well as some of the other symptoms listed above.
What Blood Tests Are Important To Diagnose And Evaluate My Hepatitis B Infection
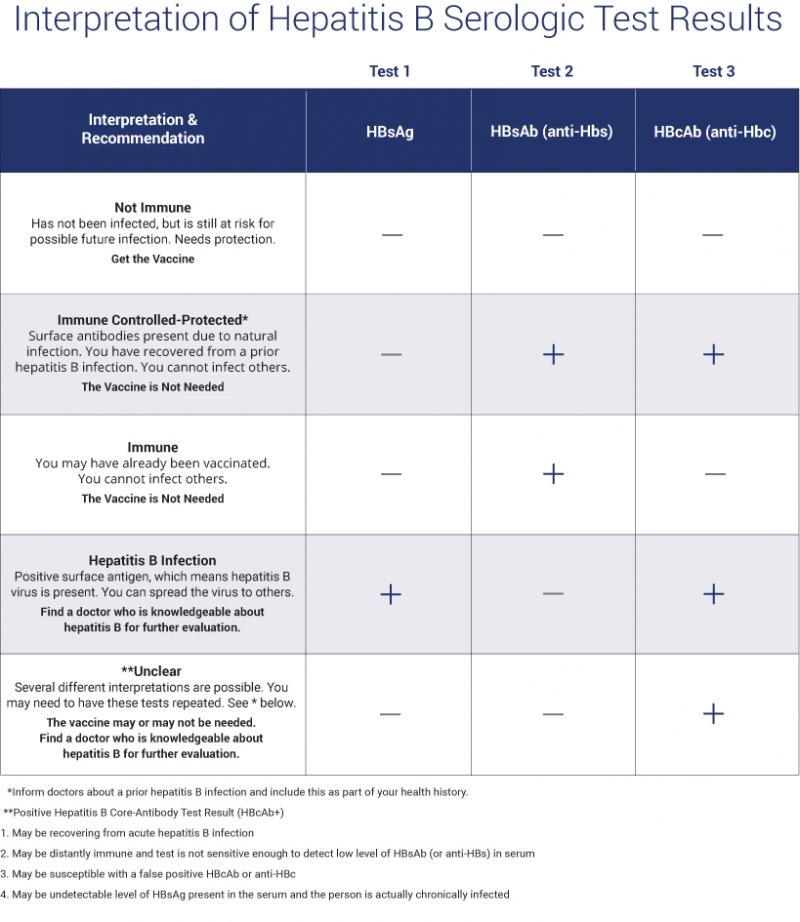
In order to understand your hepatitis B status, it is important that your doctor order the hepatitis B blood panel. This panel includes 3 basic biomarkers, but only one sample of blood is needed. Make sure you request a written copy of your blood test results so that you fully understand what tests were ordered and the actual results of each. Also, be sure to have your doctor clearly explain the results to you so that you fully understand your situation.
It is important to wait 6-8 weeks after a possible exposure before getting tested. If done before this time , the blood tests can have a false negative result. The window period is the time between exposure and the appearance of these markers in blood. The 3-part blood test includes the following:
1) Hepatitis B surface Antigen – This directly tests for the presence of the hepatitis B virus. It should be negative if there is NO virus present. 2) Hepatitis B surface Antibody – This tests for the production of protective antibodies against the hepatitis B virus. This blood test should be positive if the protective antibodies are produced in response to vaccination or recovery from a natural infection. 3) Hepatitis B core Antibody – This antibody does not provide any protection. A positive result may indicate that a person has been exposed to the hepatitis B virus. This test must be interpreted in relation to the above 2 test results.
Also Check: Hepatic Metastasis From Colorectal Cancer
Getting Treatment For Hepatitis B
If you’re in the early stages of the hepatitis B infection, you should be assessed by a doctor. You might need medication to help with the symptoms.
People with chronic hepatitis B , will need to see a specialist in liver disease. They may need medication to prevent liver damage and have regular tests. There are now very effective medications that can suppress the virus over many years.
Where Can I Find A Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test Near Me
Check our lab finder to locate a collection site in your area.
Note: Result turn around times are an estimate and are not guaranteed. Our reference lab may need additional time due to weather, holidays, confirmation/repeat testing, or equipment maintenance.
Detection Period:
For the majority of people, this test will have the highest level of accuracy at 12 weeks from an exposure or any time after. Some people may be detectable as early as 4 weeks from exposure.
Requirements:
It is recommended that someone taking Biotin stop consumption at least 72 hours prior to the collection of a sample.
Description:
You May Like: How To Catch Hepatitis B And C
Antibody To Hcv Antigens
- If negative, chronic HCV infection is ruled out in immunocompetent individuals. Because the antibody to HCV antigens response in immunocompromised persons can be blunted, a qualitative test for HCV-RNA may be required to rule out occult infection in such individuals. A new HCV core antigen test, which is currently under evaluation, can also be used to confirm active infection . However, the currently available HCV core antigen test is less sensitive, detecting less than 90% to 95% of HCV-RNA-positive specimens . Therefore, the current HCV core antigen should not be used for definitive exclusion of active infection.
- If found to be anti-HCV positive, the patient has been infected with HCV. Because most HCV infections are chronic , the presence of anti-HCV is correlated with active infection however, a qualitative test for HCV-RNA is currently required to confirm active HCV infection .
How Is Hepatitis B Diagnosed
Your health care provider will ask about your medical history and symptoms. Especially important is your history of Hepatitis B risk factors such as IV drug abuse.Your provider will examine your skin and eyes for signs of Hepatitis B. Your provider will check your abdomen to see if the liver is enlarged or tender.You will have blood tests. If blood tests show that your liver is not working normally, your provider will do tests to see if you are infected with the Hepatitis B virus.
Questions about online blood testing or how to order a lab test?
You May Like: Hepatitis A Causes Symptoms Treatment
How Long After Hepatitis B Exposure Should You Take A Test
People who think they may have come into contact with HBV and who are not vaccinated should contact a doctor within to get post-exposure prophylaxis treatment.
PEP treatment for hepatitis B can consist of the hepatitis B vaccine, an injection of hepatitis B immune globulin, which contains antibodies against HBV, or both.
The HBF states that it can take up to 9 weeks for HBV to show up in the bloodstream. The organization recommends that individuals who have never received PEP treatment get tested 9 weeks after exposure.
If the result is negative, a doctor may recommend the completion of the hepatitis B vaccine series.
Who Are Hepatitis B Carriers
Hepatitis B carriers are people who have the hepatitis B virus in their blood, even though they dont feel sick. Between 6% and 10% of those people whove been infected with the virus will become carriers and can infect others without knowing it. There are over 250 million people in the world who are carriers of HBV, with about 10% to 15% of the total located in India. Children are at the highest risk of becoming carriers. About 9 in 10 babies infected at birth become HBV carriers, and about half of children who are infected between birth and age 5 carry the virus. A blood test can tell you if you are a hepatitis B carrier.
Read Also: What Can Cause Hepatitis B
Who To Screen For Current Or Prior Infection
The following populations are considered at high risk of hepatitis B virus infection.
Which tests to use: Screen for current or prior infection with HBsAg, HBsAb, HBcAb Total
- Anyone born in or traveling to a region of intermediate to high HBV prevalence
- Asia: North Asia, Southeast Asia, and East Asia
- Malta and Spain
- Indigenous populations of Northern Canada
- Mexico, Guatemala, and Honduras
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis B
If you think you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a healthcare professional as soon as possible.
A doctor or other healthcare professional may administer the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine and a shot of hepatitis B immunoglobulin. This is a combination of antibodies that provide short-term protection against the virus.
Though both can be given up to a week after exposure, theyre most effective at preventing infection if administered within 48 hours.
If you receive a diagnosis of acute hepatitis B, a doctor may refer you to a specialist. They may advise you to get regular blood tests to ensure you dont develop chronic hepatitis.
Many people with acute hepatitis B dont experience serious symptoms. But if you do, it can help to:
- get plenty of rest
- take over-the-counter pain mediation, like naproxen, when needed
Other lifestyle changes may also be needed to manage your infection, such as:
- eating a nutritious, balanced diet
- avoiding substances that can harm your liver, such as:
- certain herbal supplements or medications, including acetaminophen
If blood tests show you still have an active infection after 6 months, your doctor may recommend further treatment, including medications to help control the virus and prevent liver damage.
Recommended Reading: Can You Recover From Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Test
This test checks whether a person is immune to HBV or whether the body has developed resistance to the virus.
Those who are immune to hepatitis B receive a positive result. A positive result may indicate that the person is vaccinated or is recovering from acute hepatitis B.
According to the Hepatitis B Foundation , people who are immune to HBV cannot contract the virus from other people or contaminated areas and therefore cannot spread HBV to others.
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Blood Test
This test is used to screen for infection with the Hepatitis B virus. The Surface Antigen test looks for a protein which is present on the surface of the virus. This protein will be present in the blood with an acute or chronic Hep B infection. Because it has a fairly early detection window, the Surface Antigen Test is often ordered by people who believe they have had a recent exposure. This test can detect the presence of Hepatitis B in chronic or long-term infections even if the person has no symptoms.
Hepatitis B is a viral liver infection which is spread through exposure to infected blood or bodily fluids. It is the most common cause of acute viral Hepatitis. Hepatitis B infections often show no symptoms but when symptoms do occur they are often described as flu-like. Common symptoms include abdominal pain, fever, loss of appetite, nausea, joint pain, fatigue, jaundice, and dark colored urine. Chronic Hep B infections can cause serious health complications like Cirrhosis and Liver Cancer.
Turnaround time for the Hepatitis B Surface Antigen test is typically 1 business day.
You May Like: Hepatitis C Vaccines For Adults
What Should You Know About Hepatitis B Before You Travel
Hepatitis B is quite common in China and other Asian countries, where as many as 1 in 12 people have the virus, though many dont know it. Before traveling to those places, you should make sure youve been vaccinated against the virus.
In addition to getting the vaccine, you can take these additional precautions to reduce your risk of contracting the virus:
- Refrain from taking illegal drugs.
- Always use latex or polyurethane condoms during sex.
- Make sure new, sterile needles are used during all piercings, tattoos and acupuncture sessions.
- Avoid direct contact with blood and bodily fluids.
- Know the HBV status of all your sexual partners.
- Ask your doctor about possible vaccination before you travel to a place where hepatitis B is common.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Hepatitis B is a liver disease that can cause serious damage to your health. One reason that is dangerous is that it can easily go undetected for years while damaging your liver. Talk with your healthcare provider about being tested for hepatitis B if you have any reason to believe that you were not vaccinated or if you have engaged in risky behavior. If you do test positive, follow the directions from your healthcare provider so that you can live a longer, healthier and happier life.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 07/09/2020.
References
Preparation Prior To Transport
Label the specimen container with the patients full name, date of collection and one other unique identifier such as the patients date of birth or Health Card Number. Failure to provide this information may result in rejection or testing delay.
Centrifuge if using SST. Place specimen in biohazard bag and seal. Specimens should be stored at 2-8°C following collection.
Specimens more than the following number of days post collection will not be tested:
- > 6 days for Hepatitis B surface antigen
- > 7 days for Hepatitis B e Antigen and Hepatitis B e Antibody
- > 10 days for Hepatitis B core Antigen and Hepatitis B surface Antibody
Don’t Miss: What Are The Signs Of Autoimmune Hepatitis